My Multiple Myeloma Cancer Log
--------------------------------------------
broken neck: 9/14/14 (sun)
hospital stay: 9/15/14 (mon) - 9/22/14 (mon)
cancer diagnosis: 9/15/14
neck (fusion) operation (Dr. Wh........): 9/18/14 (thur) Follow up:12/24/14,
3/18/15, 9/18/15
radiation (neck and back) (Dr. Hu....., Dr. Ni): 10/7/14 - 10/31/14,
11/17
hematological oncologist (Dr. .......): 10/14/14, 28/14, 11/17,
12/4, 1/2/15, 2/6, 3/9 - continuing (11/7/14 Dr. ........)
Lahey consulting hematological oncologist (Dr. W.........)
Dana Farber consulting MM specialist (Dr. L.........) (2/16)
Celgene Revlimid purchase (cycle #1) (10,167, no insurance) 11/24/2014
GP (Dr. An...) 10/9/14, 12/3/15
Dr. Ab...& Dr. He... (blood analysis): 10/14/14, 11/17, 12/24,
1/30, 3/2
zometa & carfilzomib infusions: (M.Y. infusion nurse) 10/31/14
(zometa continuing monthly, carfilzomib 3wk on/1wk off)
Dr. Ma..........: 12/9/14, 2/10/15 (bone man)
P.Su.... (physical therapy, neck)
Dr. Ta... and Dr At... 8/16/16 (eye team)
Dr V (4/24/17) (lung man)
created: 4/6/15
Go to homepage
My related essay 'Medicare Part D and Medigap: What cancer patients
on super expensive chemo need to know' is here
My related essay 'Drug Discount Cards Provide Big Savings for Drugs
not Covered by Insurance' -- Tutorial into the murky world of buying
erectile dysfunction drugs and other expensive drugs not covered by insurance
is here
MM drugs organized by class
Ninlaro
update (4/5/2016)
Drugs
to counter chemo 'side effects' (9/21/17)
Drugs
to increase hemoglobin and RBC (red blood count)
Tracking my cancer
** My key numbers in a
table
Introduction (update 7/27/15) (8/11/15)
(10/28/15)
Overview (May 2015)
MM tracking numbers
Overview of my
numbers (cycles 1 - 17.5)
My
numbers start to rise (10/26/15)
* Plot of my numbers
(1 - 9 months)
Plot
of my M-spike numbers for 12 months of 2016
Plot
of my M-spike and lambda free light chain for much of 2017
Equivalent
Freelite plot
Change in my numbers
(4/15/16)
Change in my numbers
(4/4/16)
Change in my numbers
(12/1/15)
Thresholds to trigger
chemo change
Cycle 9.5 confirms (9/4/15)
Cycle
8.5 results --- Too good to be true? (8/10/15)
Cycle 7.5
My cancer diagnosis story
Intro
Can't get my head
off pillow for 30 min!
Cancer diagnosis
and neck fusion operation
Treatments
-- Radiation of C2 (neck) and T12 (back)
Staging my multiple myeloma
Did I want a stem cell
replacement?
Did
I want to join a chemo clinical trial for new oral botzezomib added to
rev/dex?
Choosing a chemo regimen
Chemo
cost and insurance
500
dollar a day chemo pill!
Signing up for
medicare Part D drug plan
DNA variations -- cytogetics
My
cytogenetics test results (from Mayo clinic)
Free light chains
--- supplement to M-spike
Leading
indicator?
Free
light chains are a true leading indicator
Is
kappa or lambda free light chain a leading indicator?
Excess
free light chains damage the kidneys
Living with cancer
Run down (4/2/17)
Chemo transition
to maintenance (7/13/15)
An
advantage of cycled revlimid
Advantages of no streoids (11/20/15)
Daily pills (1/16/16)
(4/15/16)
Driving a car with
limited neck mobility
Key
neck trick
Bone pain
Kidney damage
Anemia -- Low blood
oxygen capacity
Really
bad anemia -- very low hemoglobin (9/20/17)
Hemoglobin
raising hormones ---Brand names: Epogen, Procrit and Aranesp
New
hospital schedule to address my anemia (9/26/17)
EPO
vs blood transfusions
Hypercalcemia
Vision issues
* How MM patients die
2nd look at stem
cell replacement option
Clinical trial time lag
Accessing my hospital records
Lahey new online
patient 'portal' (4/15)
Dana Farber portal (2/16)
End of 1st Remission -- switch to new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
(6/27/16)
4.5 month overview -- 2nd remission
(11/18/16)
** Plot of
my M-spike(s) numbers for 2016
Update
on new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
Relapsed
and refractory
New
agressive chemo for 2nd round -- pom/carfilzomib/dex (7/11/16)
Carfilzomib
risk breakdown
* Aspire
phase 3 clinical trial results for carfilzomib (2015)
Dana Farber update
on my cancer (jan 2017)
Two
cancers? -- surprising & discouraging new result(10/3/16) 10/17/16)
End of my
2nd remission -- New Test Results (mar 2017)
Pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo started off strongly with a big drop in free light chain in the first
cycle,
but after 8.5 months my lambda free light chain was rising strongly
as was M-spike and worse a little later
a pet scan showed my 9th rib plasmacytoma had also brightened substantially
in just the last 9 weeks,
so clearly the cancer has evolved around this chemo. My 2nd remission
has ended.
High
cost of carfilzomib and daratumumab infusions! (10/23/16) (10/14/17)
44.2k/yr
out of pocket cost of new chemo! (pom/carfilzomib/dex) (10/23/16)
Photos
from last day of carfilzomib infusion (3/21/17)
Begin pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo
(4/3/17)
Searching for a 3rd remission
Low
platelets --- known Ninlaro side effect
Begin pom/daratumumab/dex
chemo (8/1/17)
Searching for a 4th remission
-- failure
Castor
vs Pollux clinical trials
My
first dose infusion reactions
Infusion
times summary
* Blood type
baseline (prior to first daratumumab infusion)
End Game (10/8/17)
Health
update (10/8/17)
New
marrow needle biopsy
** MDS
a 2nd cancer --- "myelodysplastic syndrome" (10/4/17)
Health
update (10/14/17)
Health
update (10/21/17)
Repeated
blood transfusions
Health
update (11/28/17)
Super
low platelets (value 3)!
Pet scans
1st
PET scan results (5/19/16)
2nd
PET scan images (9/6/16)
3rd
PET scan images (1/11/17)
4th PET
scan images (3/22/17)
5th PET
scan images (7/10/17)
6th PET
scan images (10/20/17)
Big picture of MM treatment
options
Special topics in detail
My Pictures
Inventory of my
MM bone tumors (12/17/15)
Details
of cancer in my bones from MRI and CT scans during my hospital stay
(Aug 30, 2015)
One
year follow up cervical CT scan (9/16/15)
Failing
or failed C1,C2 fusion
Appendix
History
and info on the thalidomide class of drugs
Lahey Hospital and Medical
Center
Details of my
neck C1,C2 fusion operation
Lahey online patient 'portal'
About the
Lahey MM clinical trial I was offered
Protein Electrophoresis test
Nice
description of M-spike
Cytogenetics and deletion 13
My
cytogenetics test results (from Mayo clinic)
Variability
of patient response to chemo
Spectrum
of MM patients
What bones are affected by
MM?
Antibody proteins
More on 'Complete Response'
'Complete
response' discussion
Tom Brokaw perspective
Multiple Myeloma spectrum
'The
Role of CR (complete response) in MM' --- excellent 2009 French
paper
MM cure vs control debate
Criteria for my
MM progression (Aug 2015)
What
are the clinical implications of CR?
What
about 'Very Good Partial Response'?
** I achieve
CR (based on M-spike) (2/16)
'Understanding
Protein Electrophoresis' notes
M-spike to total protein
ratio (7/15)
Value
of kappa/lamda ratio in monotoring MM patients for relapse
MM
marker without a measurement of M-spike?
History of myeloma
Bone remodeling
Multiple myeloma drugs
Documentation
with little concern for patients
Clincial indicators
of disease progression
Clincial indecators
of disease relapse
Experiences of others
with MM chemo
Other blood cancers
Excerpts
from 'Multiple Myeloma Patient Handbook' Myeloma Canda
Blood test machines
Drugs used in Multiple Myeloma
MM
drugs organized by class
Ninlaro
update(4/5/2016)
Compassionate
Use (1/10/16)
MM treatment history
FDA
approval 'zoo'
Options for relapsed
muliple myeloma
Will Medicare pay?
Vertebrae terminology
and anatomy
Cervical
anatomy
Fracture
of dens
How
the C1,C2 dens joint really work
Reviewing my scans
Protein electrophoresis
equipment
New test results (aug 2016)
Heart tests (6/14/16)
Updated
view of the plasmacytoma behind my left eye (8/9/16)
Radiologist report
on my 8/9/16 brain MRI
Retinal tomography
-- 3d images of my retina
Arteries and veins of the
neck
What
to do if this (mini-stroke) happens again?
New test results (feb 2017)
Heart tests (2/14/17)
Heart
echocardiogram test
Lung tests
Pulmonary
function tests (2/22/17)
DLCO
test result
COPD
-- Pink Puffer and Blue Bloaters
Lung CT scan
My
strange collection of lung symptoms
Pulmonary
ventilation/perfusion scan (4/28/17)
Perfusion
images (4/28/17)
Spiriva
HandiHaler powder inhaler (4/24/17)
Incruse
Ellipta --- another once daily powder inhaler (5/4/17)
Red blood cell tutorial
Hemoglobin into the
normal range (3/6/17)
Iron blood tests (3/6/17)
Carfilzomib Reference
Appendix 2
plasmacytoma
Sphenoid bone
Proteasome and
'proteasome inhibitor' drugs
Daratumumab discussion
My key numbers in a table
Multiple myeloma (MM) being
a blood cancer a simple blood can reveal a lot about general level of cancer
in the body. Here is a table with all my key blood numbers since I was
diagnosed. The two most important blood cancer terms are on the left side
of the table: M-spike and (lambda) free light chain. M-spike is direct
measure of the quantity of clonal (cancer) anti-body cells in the blood
and is zero in a healthy person. Free light chain on the other hand has
a baseline value (0.57 to 2.63 mg/dL) in healthy individuals because it
is a by-product of how disease fighting immunoglobulin blood proteins are
made. The virtue of free light chain is that it is a 'leading indicator'.
It is the signal to watch when chemo is changed. Clinical trials use thresholds
of these two blood components as indicators of disease progression, [10
mg/dL for (lambda) free light chain and 0.5 g/dL for M-spike], so this
provides reference points to interpret the numbers.
rev/dex chemo
(21 of 28
day cycle)
(begun 11/24/14)
|
M-spike
IgG lambda
monoclonal peak
g/dL
|
M-spike
(fractional decrease
during cycle)
|
protein
cancer ratio
monoclonal proteins/total protein
|
lambda
free light
chain
(0.57 - 2.63)
(mg/dL)
|
kappa/lambda
free light
chain ratio
(0.26 - 1.65)
|
(involved - uninvolved)
free light
chain
(>10 mg/dL
indicates disease progression)
|
|
hemoglobin
(oxygen)
(13.8 - 17.4)
g/dL
|
WBC
(white blood
count)
(infection)
(4.4 - 11.3)
K/uL
|
granulo-
cytes
count
(1.4 - 6.6)
K/uL
|
platelet count
(clotting)
(150 - 450)
K/uL
|
IgG-blood
(0.75 - 1.4)
g/dL
|
albumin/(total
protein) ratio
(liver), (g/dL)
(0.52 - 0.58)
(nom)
|
creatinine
(kidney)
(0.6 - 1.3)
mg/dL
GFR
(calculated from creatinine)
|
calcium
(8.4 - 10.4)
mg/dL
|
baseline
11/17/14
|
5.31*
(very high)
|
|
50.1%
|
379
(super high)
|
<0.01
(0.58/379)
(super low)
|
378
|
|
9.9
|
4.65
(8.60 10/14/14)
|
3.55
76%
(5.96 10/14/14)
|
268
|
5.46
|
.23
(2.4/10.6 )
(very low)
|
1.2
(> 60)
(1.4 earlier)
(1.7 hospital)
|
7.8
(11.0 11/7/14)
|
cycle 1
12/24/14
|
1.82
(.05 IgG kappa)
|
x.66
|
23.9%
(0.7% kappa)
|
8.17
|
.21
(1.70/8.17)
(low)
|
6.47
|
|
12.4
|
5.91
|
3.07
52%
|
221
|
1.89
|
.42
(3.2/7.6)
(low)
|
1.2
(> 60)
|
8.4
|
cycle 2
1/30/15
|
.99
(.06 IgG kappa)
|
x.46
|
13.6%
(0.8% kappa)
|
2.74
(nearly normal)
|
.52
(1.42/2.74)
(normal)
|
1.32
|
|
13.9
|
5.51
|
3.25
59%
|
204
|
1.09
(normal)
|
.52
(3.8/7.3)
(normal)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.4
|
cycle 3
3/2/15
|
.67
(IgG kappa monoclonal band detected, but too small to quantitate)
|
x.32
|
8.93%
|
2.65
|
.60
(1.58/2.65)
|
1.07
|
|
15.5
|
5.87
|
5.40
92%
|
164
|
0.92
|
.53
(4.0/7.5)
|
1.2
(> 60)
|
9.5
|
cycle 4
4/3/15
|
.34
|
x.49
|
5.48%
(VGPR)
|
1.50
(minimum)
|
.93
(1.39/1.50)
|
0.11
|
|
13.7
|
4.89
|
3.67
75%
|
154
|
0.62
|
.56
(3.5/6.2)
|
1.2
(> 60)
|
9.3
|
cycle 5
5/1/15
|
.24
|
x.29
|
3.81%
|
1.84
|
.82
(1.51/1.84)
|
0.33
|
|
13.2
|
4.07
|
2.56
63%
|
156
|
0.67
|
.56
(3.5/6.3)
|
1.3
(55)
|
9.0
|
cycle 6.25
6/1/15
|
.23
|
x.04
|
3.83%
|
2.25
|
1.24
(2.79/2.25)
|
<0
|
|
12.3
|
3.37
|
2.57
76%
|
209
|
0.64
|
.55
(3.3/6.0)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.9
|
Chemo transition to maintenance (began 5/24/15):
revlimid: 25 mg/day => 10 mg/day (21 of 28 day cycle); dexamethasone:
40 mg/wk => 0
aspirin (blood thinner): 325 mg/day => 162 mg/day; zometa (biphosphate)
infusion (bone strengthening) monthly => unchanged |
cycle 7.5
7/6/15
|
.19
|
x.17
|
3.17%
|
2.37
|
1.09
(2.59/2.37)
|
<0
|
|
13.4
|
4.67
|
2.76
59%
|
122
|
0.77
|
.58
(3.5/6.0 )
|
1.1
(> 60)
|
8.7
|
cycle 8.5
8/3/15
|
"No monoclonal
immunoglobulin
detected"
(< 0.05)?
Immunofixation:
No bands detected
(< 0.015)?
|
x(.75)
|
< 1%?
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
|
14.0
|
4.23
|
2.46
58%
|
127
|
--
|
.58
(3.7/6.4 )
|
1.3
(55)
|
9.5
|
cycle 9.5
8/31/15
|
Weak oligoclonal IgG bands present
Immunofixation:
Band(s) present
|
small
increase,
but not quantifable
|
< 1%?
|
2.68
|
1.09
(2.91/2.38)
|
<0
|
|
14.6
|
5.30
|
3.15
66%
|
124
|
0.93
|
.56
(3.7/6.6 )
|
1.2
(> 60)
|
9.4
|
cycle 10.5
9/28/15
|
Weak monoclonal IgG lambda band detected, other weak oligoclonal
bands present.
Immunofixation:
Band(s) present
|
detectable,
but not quantifable
|
< 1%?
|
3.11
(little high)
|
1.17
(3.65/3.11)
|
<0
|
|
14.2
|
4.20
(little low)
|
2.49
59%
|
129
(little low)
|
0.97
|
.55
(3.6/6.6)
|
1.3
(55)
|
9.1
|
cycle
11.5
10/26/15
|
.07
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Immunofixation:
Band(s) present
|
x1.7?
|
1.04%
|
3.18
|
1.00
(3.18/3.18)
|
0
|
|
14.2
|
6.43
(bad cold)
|
4.96
77%
|
132
|
0.96
|
.52
(3.5/6.7)
|
1.1
(> 60)
|
9.1
|
cycle
12.75
12/1/15
|
.12
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
Immunofixation:
Band(s) present
|
x1.7
|
1.97%
|
4.08
|
0.95
(3.87/4.08)
|
0.21
|
|
14.0
|
3.76
|
2.25
60%
|
117
|
0.94
|
.56
(3.4/6.1)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.5
|
cycle
13.75
12/29/15
|
.16
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
Immunofixation:
no change from previous
|
x1.33
|
2.50%
|
6.41
|
0.65
(4.17/6.41)
|
2.24
|
|
14.5
|
3.20
|
1.61
50%
|
107
|
1.02
|
.58
(3.7/6.4)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.5
|
cycle 14.25
1/13/16
|
.18
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
Immunofixation:
no change from previous
|
x1.125
(two weeks)
|
2.65%
|
6.39
|
0.70
(4.46/6.39)
|
1.93
|
|
14.5
|
4.32
|
2.87
66%
|
144
|
1.13
|
.56
(3.8/6.8)
|
1.2
(> 60)
|
9.4
|
cycle 14.75
1/26/16
|
.16
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
Immunofixation:
no change from previous
|
x0.89
(two weeks)
(no change in last month)
|
2.58%
|
8.41
|
0.53
(4.48/8.41)
|
3.93
|
|
13.7
|
3.14
|
1.79
57%
|
99
|
1.00
|
.56
(3.5/6.2)
|
1.3
(55)
|
9.0
|
cycle 15.25
2/8/16
(Dana labs)
|
in the beta region, of insufficient quantity to be quantified.
<0.1 g/dL?
(.17 g/dL est from IgG)
|
--
(two weeks)
|
--
|
10.84
|
0.34
(3.66/10.84)
|
7.18
|
|
14.3
|
4.50
|
3.01
67%
|
137
|
1.06
|
.47
(3.19/6.8)
|
1.34
(52)
|
9.4
|
cycle 15.75
2/23/16
|
.22
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
|
x1.375
|
3.44%
|
12.00
|
0.38
(4.51/12.00)
|
7.49
|
|
14.2
|
3.02
|
1.54
51%
|
116
|
1.10
|
.55
(3.5/6.4)
|
1.4
(50)
|
8.8
|
|
Increase in maintenance dose (began 2/29/16): revlimid: 10 mg/day
=> 20 mg/day (28 of 28 day cycle initially), dexamethasone: none
(unchanged)
aspirin (blood thinner): 162 mg/day => unchanged; zometa (biphosphate)
infusion (bone strengthening) monthly => unchanged |
cycle 16.00
3/2/16
|
.22
Monoclonal IgG lambda. Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands.
|
x1.00
(one week)
|
3.44%
|
13.60
|
0.28
(3.77/13.60)
|
9.83
|
|
14.1
|
3.11
|
1.51
49%
|
147
|
1.12
|
.53
(3.4/6.4)
|
1.3
(55)
|
9.3
|
cycle 16.75
3/22/16
|
.31
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Monoclonal lambda light chains.
Additional weak oligoclonal IgG bands present
|
x1.41
(3 weeks)
|
4.92%
|
15.30
|
0.26
(3.96/15.30)
|
11.34
(> 10 mg/dL
diff limit)
|
|
13.6
|
3.08
|
1.66
54%
|
94
|
1.18
|
.54
(3.4/6.3)
|
1.2
( 60)
|
8.8
|
Revlimid maintenance ended, original rev/dex reestablished
(began 3/25/16): revlimid: 20 mg/day => 25 mg/day (cont Revlimd for first
7 wks, change to 21 of 28 days pending),
dexamethasone: 40 mg/wk, aspirin (blood thinner): 162 mg/day => unchanged;
zometa (biphosphate) infusion (bone strengthening) monthly => unchanged |
cycle 17.5
4/11/16
|
.25
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Weak Oligoclonal IgG bands present.
|
x0.81
(3 weeks)
|
4.24%
|
7.89
(3 wk Revlimid)
|
0.25
(1.96/7.89)
|
5.93
|
|
13.5
|
4.71
|
3.00
64%
|
88
|
0.858
|
.56
(3.3/5.9)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.9
|
cycle 18.25
5/2/16
|
.25
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobins decreased
|
x1.00
(3 weeks)
|
4.31%
|
10.20
(2 of 3 wk Revlimid)
|
0.16
(1.68/10.20)
|
8.52
|
|
13.4
|
6.13
|
4.59
75%
|
113
|
0.831
|
.59
(3.4/5.8)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.8
|
cycle 19
5/23/16
|
.24
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobins decreased
|
x0.96
(1st PET scan 5/19/16)
|
4.00%
|
9.57
|
0.15
(1.40/9.57)
|
8.17
|
|
13.2
|
4.46
|
2.88
65%
|
107
|
0.846
|
.58
(3.5/6.0)
|
1.2
(60)
|
8.7
|
cycle 19.75
6/13/16
(Dana labs)
|
(.46)
The beta M-spike concentration includes both the M-spike and physiologic
beta proteins,
and is thus an overestimate.
|
(3 weeks)
|
(7.93%)
overestimate
|
10.55
|
0.18
(1.86/10.55)
|
8.69
|
|
12.8
|
3.82
|
2.00
52%
|
79
|
0.767
|
.53
(3.09/5.8)
|
1.18
(60)
|
8.6
|
cycle 19.75
6/14/16
|
.24
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobins decreased
|
x1.00
|
4.36%
|
13.0
|
0.15
(1.92/13.0)
|
11.08
|
|
12.1
|
3.35
|
2.16
65%
|
88
|
0.843
|
.56
(3.1/5.5)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.3
|
cycle 20
6/20/16
|
.24
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobins decreased
|
x1.00
|
4.36%
|
9.02
|
0.18
(1.65/9.02)
|
7.37
|
|
11.7
|
4.22
|
2.48
59%
|
107
|
0.809
|
.56
(3.1/5.5)
|
1.1
(60)
|
8.5
|
cycle 20.25
6/27/16
|
.26
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x1.08
|
4.48%
|
10.80
|
0.21
(2.32/10.8)
|
8.48
|
|
12.3
|
3.34
|
2.24
(67%)
|
98
|
0.898
|
.55
(3.2/5.8)
|
1.1
(60)
|
9.0
|
| (5/16/16) With lambda free light chain
hovering for months near 10 mg/dL and M-spike at .25 g/dL an MRI found
a plasmacytoma growing behind left eye and a Pet scan (5/19/16) later found
other metabolically active bone lesions, indicating my cancer was outrunning
my rev/dex chemo. Clearly my first remission has ended and a new chemo
regimen is needed.
Chemo change (6/27/16)
Switched chemo rev/dex => pom/carfilzomib/dex (begun (6/27/16): pomalyst:
4 mg, 21 of 28 days, carfilzomib (infusion) six times/cycle with first
cycle 20mg x (body area index), dexamethasone 20 mg on days of carfilzomib
(continued during 4th week), aspirin (blood thinner): 162 mg/day => unchanged;
zometa (biphosphate) infusion (bone strengthening) monthly => unchanged.
(Carfilzomib for first cycle at 75% of its final strength.) |
|
28 day cyele
|
M-spike
IgG lambda
monoclonal peak
g/dL
|
M-spike
(fractional decrease
during cycle)
|
protein
cancer ratio
monoclonal proteins/total protein
|
lambda
free light
chain
(0.57 - 2.63)
mg/dL
|
kappa/lambda
free light
chain ratio
(0.26 - 1.65)
(kappa
free light chain
(0.33 -
1.94) mg/dL)
|
(involved - uninvolved)
free light
chain
(>10 mg/dL
indicates disease progression)
|
|
hemoglobin
(oxygen)
(13.8 - 17.4)
g/dL
|
WBC
(white blood
count)
(infection)
(4.4 - 11.3)
K/uL
|
granulo-
cytes
count
(1.4 - 6.6)
K/uL
|
platelet count
(clotting)
(150 - 450)
K/uL
|
IgG-blood
(0.75 - 1.4)
g/dL
|
albumin/(total
protein) ratio
(liver), (g/dL)
(0.52 - 0.58)
(nom)
|
creatinine
(kidney)
(0.6 - 1.3)
mg/dL
GFR
(calculated from creatinine)
|
calcium
(8.4 - 10.4)
mg/dL
|
cycle 20.75
7/11/16
|
.21
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x0.81
(2 weeks)
|
3.82%
|
3.25
|
0.55
(1.80/3.26)
|
1.46
|
|
12.9
|
2.50
|
1.29
(52%)
|
57
|
0.762
|
.58
(3.2/5.5)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.4
|
cycle 21.25
7/25/16
|
.18
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x0.86
(2 weeks)
|
3.40%
|
2.93
|
0.59
(1.72/2.93)
|
1.21
|
|
12.5
|
2.44
|
0.98
(40%)
|
84
|
0.664
|
.58
(3.1/5.3)
|
1.2
(60)
|
8.8
|
| (7/25/16) Carfilzomib dose increased 35% [20 mg x (body
area index)] => [27 mg x (body area index)] at beginning of 2nd pom/carfilzomib/dex
cycle (my body area index = 2.074) |
cycle 21.75
8/8/16
|
.20
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x1.11
(2 weeks)
|
3.77%
|
4.11
|
0.56
(2.29/4.11)
|
1.82
|
|
12.1
|
2.59
|
1.24
(48%)
|
61
|
0.546
|
.55
(2.9/5.3)
|
1.2
(60)
|
8.8
|
cycle 22.25
8/22/16
|
.16
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x0.80
(2 weeks)
|
2.67%
|
3.30
|
0.58
(1.92/3.30)
|
1.38
|
|
11.9
|
5.34
|
3.07
(58%)
|
131
|
0.627
|
.57
(3.4/6.0)
|
1.1
(>60)
|
9.3
|
(cycle 22.50
8/29/16)
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
|
10.9
(one week later)
|
4.57
|
3.32
(73%)
|
144
|
---
|
---
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.3
|
cycle 22.75
9/6/16
|
.17
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x1.06
(2 weeks)
(2nd PET scan 9/6/16)
|
2.98%
|
2.39
(normal)
|
0.74
(1.76/2.39)
|
0.63
|
|
11.5
|
4.30
|
2.58
(60%)
|
114
|
0.529
|
.56
(3.2/5.7)
|
1.3
(55)
|
8.7
|
cycle 23.00
9/12/16
(Dana Labs)
|
Monoclonal gammopathy with faint IgG Lambda paraprotein.
Immunofixation shows a faint M-spike that is not apparent on the
electropherogram and, therefore, cannot be quantitated
|
---
|
---
|
1.91
|
0.92
(1.75./1.91)
|
0.16
|
|
11.5
|
2.41
|
1.65
(68%)
|
83
|
0.505
|
.53
(2.94/5.6)
|
1.26
(56)
|
9.7
|
cycle 23.25
9/19/16
|
(.24 total)
.15
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
0.09
Monoclonal IgG kappa
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x0.88
or
x1.41
(2 weeks)
|
4.44% total
|
2.16
|
0.76
(1.64/2.16)
|
0.52
|
|
11.5
|
4.68
|
2.57
(55%)
|
165
|
0.574
|
.65
(3.5/5.4)
(high)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.0
|
cycle 23.50
9/26/16
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
|
11.3
|
4.37
|
3.05
(70%)
|
145
|
---
|
---
|
1.1
(>60)
|
8.6
|
cycle 24.00
10/3/16
|
(.26 total)
.15
Monoclonal IgG lambda
0.11
Monoclonal IgG kappa
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
IgG lambda unchanged
IgG kappa
x1.22
(2 weeks)
|
4.40%
total
|
2.23
|
1.66
(3.71/2.23)
|
(not applicable, both free light chains are involved)
|
|
12.4
|
4.96
|
3.20
(65%)
|
114
|
0.565
|
.58
(3.4/5.9)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.7
|
cycle 24.50
10/17/16
|
(.17 total)
.09
Monoclonal IgG lambda
.08
Monoclonal IgG kappa
Other weak oligoclonal IgG and IgM bands present
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
IgG lambda
x0.60
IgG kappa
x0.73
(2 weeks)
|
3.33%
total
|
2.18
|
0.89
(1.95/2.18)
|
(not applicable, both free light chains are involved)
|
|
11.6
|
2.84
|
1.58
(56%)
|
149
|
0.401
|
.63
(3.2/5.1)
|
1.2
(60)
|
7.8
(start 4 Tums/day)
|
cycle 24.75
10/24/16
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
---
|
|
12.5
|
5.54
|
3.56
|
125
|
---
|
---
|
1.4
(50)
|
9.4
|
cycle 25.00
10/31/16
|
(.18 total)
.10
Monoclonal IgG lambda
.08
Monoclonal IgG kappa
Other weak oligoclonal IgG and IgM bands
present
|
IgG lambda
x1.1
IgG kappa
x1.0
(2 weeks)
|
3.27%
total
|
1.84
|
0.86
(1.59/1.84)
|
(not applicable,
both free light chains are involved)
|
|
13.3
|
5.09
|
3.30
|
135
|
0.386
|
.58
(3.2/5.5)
|
1.4
(50)
|
9.5
|
cycle 25.25
11/7/16
|
.10
Monoclonal IgG lambda
A weak monoclonal IgG kappa band detected, but too small to quantitate
|
--
|
1.89%
|
2.03
|
0.73
(1.48/2.03)
|
--
|
|
11.7
|
4.00
|
2.96
|
122
|
0.381
|
.64
(3.4/5.3)
|
1.1
(>60)
|
8.9
|
cycle 25.50
11/14/16
|
.07
Monoclonal IgG lambda
A weak monoclonal IgG kappa band detected, but too small to quantitate.
|
--
|
1.35%
|
2.07
|
0.56
(1.15/2.07)
|
--
|
|
12.4
|
4.74
|
2.83
(60%)
|
177
|
0.398
|
.65
(3.4/5.2)
.62
(3.6/5.8)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.0
|
cycle 25.75
11/21/16
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
|
13.1
|
6.71
|
5.33
(79%)
|
141
|
--
|
--
.60
(3.8/6.3)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.6
|
cycle 26.00
11/28/16
|
.12
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Other faint oligoclonal IgG bands present..
|
IgG lambda
x1.7
|
2.35%
|
1.76
|
0.81
(1.42/1.76)
|
--
|
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
0.344
|
.63
(3.2/5.1)
.60
(3.4/5.7)
|
1.2
(60)
|
9.2
|
cycle
26.50
12/12/16
|
.12
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Other weak IgG bands also present
|
x1.0
|
1.97%
|
2.34
|
0.67
(1.56/2.34)
|
--
|
|
13.1
|
4.93
|
2.92
(59%)
|
172
|
0.449
|
.59
(3.6/6.1)
.60
(3.9/6.5)
|
1.1
(>60)
|
8.5
|
cycle 27.50
1/9/17
|
.12
Monoclonal IgG lambda
|
x1.0
(3rrd PET scan 1/11/17)
|
2.07%
|
2.51
|
0.48
(1.21/2.51)
|
1.30
|
|
12.8
|
6.33
|
3.99
(63%)
|
199
|
0.370
|
.59
(3.4/5.8)
.64
(3.9/6.1)
|
1.1
(>60)
|
9.4
|
cycle 27.75
1/18/17
(Dana Labs)
|
Immunofixation shows a faint M-spike that is not apparent on the
electropherogram and, therefore, cannot be quantitated.
:
Monoclonal gammopathy with IgG Lambda paraprotein.
Hypogammaglobulinemia
(antibodies low)
|
--
|
--
|
1.33
|
0.46
(0.61/1.33)
|
--
|
|
11.7
|
9.70
|
--
|
112
|
0.339
|
.--
|
1.49
(46)
|
9.4
|
cycle 28.50
2/6/17
|
.11
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Decreased gamma globulins
|
x0.9
(residual cold)
|
2.03%
|
2.83
(above
normal)
|
0.43
(1.22/2.83)
|
1.61
|
|
12.2
|
4.54
|
2.44
(54%)
|
175
|
0.348
|
.65
(3.5/5.4)
.59
(3.6/6.1)
|
1.1
(>60)
|
9.2
|
cycle 29.50
3/6/17
|
.17
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Additional oigoclonal IgG bands present
|
x1.54
(4th PET scan 3/22/17)
|
2.77%
|
4.55
|
0.46
(2.11/4/55)
|
2.44
|
|
14.1
(65 mg iron pill added 2/15/17
|
5.56
|
3.43
(62%)
|
170
|
0.472
|
.66
(4.0/6.1)
.57
(3.9/6.8)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.6
|
cycle 30.50
4/3/17
|
.17
Monoclonal IgG lambda
Additional oligoclonal IgG bands.
|
x1.00
(fatigued, run down)
|
2.98%
|
3.40
|
0.32
(1.09/3.40)
|
2.31
|
|
12.6
|
5.73
|
3.34
(58%)
|
187
|
0.459
|
.63
(3.6/5.7)
.58
(3.9/6.7)
|
1.3
(54)
|
9.0
|
Chemo change (4/3/17)
Swarped proteasome inhibitors today: pom/carfilzomib/dex => pom/Ninlaro/dex.
Began first cycle of new pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo on 4/3/17. For about
6-7 months (since 6/27/16) pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo has been effective,
but in the last 1-2 months that is no long the case with a rising free
light chain (4.55 mg/dL) and M-spike (.17 g/dL) plus importantly a recent
pet scan showing significant growth in my 9th rib plasmacytoma. Furthermore
carfilzomib appears to have done significant damage to my lungs in recent
months (DLCO = 13.98). As an experiment this change in chemo swaps out
the proteasome inhibitor in my current chemo for a different proteasome
inhibitor with a somewhat different target (carfilzomib => Ninlaro), Ninlaro
being the pill equivalent of Velcade, which has had a good ten year track
record and which my cancer has never seen. |
|
28 day cyele
|
M-spike
IgG lambda
monoclonal peak
g/dL
|
M-spike
(fractional decrease
during cycle)
|
protein
cancer ratio
monoclonal proteins/total protein
|
lambda
free light
chain
(0.57 - 2.63)
mg/dL
|
kappa/lambda
free light
chain ratio
(0.26 - 1.65)
(kappa
free light chain
(0.33 -
1.94) mg/dL)
|
(involved - uninvolved)
free light
chain
(>10 mg/dL
indicates disease progression)
|
|
hemoglobin
(oxygen)
(13.8 - 17.4)
g/dL
|
WBC
(white blood
count)
(infection)
(4.4 - 11.3)
K/uL
|
granulo-
cytes
count
(1.4 - 6.6)
K/uL
|
platelet count
(clotting)
(150 - 450)
K/uL
|
IgG-blood
(0.75 - 1.4)
g/dL
|
albumin/(total
protein) ratio
(liver), (g/dL)
(0.52 - 0.58)
(nom)
|
creatinine
(kidney)
(0.6 - 1.3)
mg/dL
GFR
(calculated from creatinine)
|
calcium
(8.4 - 10.4)
mg/dL
|
cycle 31.25
4/25/17
|
.16
Monoclonal IgG lambda
.
Weak monoclonal
IgG kappa band detected, but too small
to quantitate.
|
x0,94
(3 weeks)
|
2.91%
|
3.48
|
0.24
(0.84/3.48)
|
2.64
|
|
12.2
|
4.08
|
3.04
|
89
|
0.432
|
.71
(3.9/5.5)
.66
(4.1/6.2)
|
1.1
(65)
|
9.1
|
cycle 32.25
5/23/17
(5/30/17 recheck)
|
.16
Monoclonal IgG lambda
.
Weak monoclonal
IgG kappa band detected, but too small
to quantitate.
|
x1.00
|
2.81%
|
4.03
|
0.20
(0.81/4.03)
|
3.22
|
|
13.0
(14.1
5/30/17)
|
3.87
(4.61
5/30/17)
|
2.73
|
64
(early in off week)
(132
5/30/17)
(first week of Ninlaro cycle)
|
0.452
|
.61
(3.5/5.7)
.64
(3.8/5.9)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.0
|
6/7/2017
(at Dana
Farber)
|
|
--
|
--
|
4.37
|
0.25
(1.09/4.37)
|
3.28
|
|
13.8
|
4.44
|
3.15
|
98
|
0.476
|
.57
(3.7/6.5)
|
1.26
(56)
|
10.2
|
cycle 33.25
6/20/17
|
.15
Monoclonal IgG lambda
.
Weak monoclonal
IgG kappa band detected, but too small
to quantitate.
|
x.94
|
2.54%
|
8.42
(bad)
|
0.11
(0.92/8.42
|
7.50
|
|
13.7
(13.5
6/29/17)
|
2.04
(3.13
6/29/17)
|
1.03
(1.78
6/29/17)
|
52
(early in off week)
(107
6/29/17)
|
0.523
|
.56
(3.3/5.9)
.60
(3.6/6.0)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.5
|
cycle 34.25
7/18/17
|
.26
Monoclonal IgG lambda.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased
|
x1.73
|
4.26%
|
11.30
(above disease progression
threshold)
|
0.08
(0.94/11.30)
|
10.36
|
|
13.9
|
3.16
|
2.40
|
58
(early in off week)
|
0.679
|
.51
(3.1/6.1)
.59
(3.8/6.4)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.3
|
Ninlaro review (6/20/17)
About three months ago (4/3/17) a (new) pill proteasome inhibitor (Ninlaro)
was swapped in for my old infused proteasome inhibitor (carfilzomib). This
change was prompted because my lambda free light chain was beginning to
rise (4.55) and after 9 months on carfilzomib it was continuing to damage
my lungs. Unfortunately the new (pom/Ninlaro/dex) chemo was relatively
ineffective and in ten weeks (6/20/17) my lambda free light chain was up
strongly (8.42) indicating another change in chemo was needed. This was
confirmed by a 5th pet scan (7/10/17) showing substantial growth in two
existing plasmacytomas in my ribs. By 7/18/17 lambda free light chain was
up to 11.3 mg/dL and M-spike up to .26 g/dL.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chemo change (8/1/17)
Switched chemo (pom/Ninlaro/dex) => (pom/daratumumab/dex) with
first daratumumab infusion (8/1/17 and 8/2/17) coordinated with starting
a new cycle of Pomalyst (pills). This is my 5th change in chemo. If successful,
daratumumab infusions will be once a week for 9 weeks. Pomalyst will continue
on a four week cycle (21 of 28 days with a week off). The pairing of daratumumab
with Pomalyst was only approved by the FDA weeks earlier (6/17/17).
Due to the delay in scheduling daratumumab infusions, I essentially had
two weeks off with no chemo. Prior to every daratumumab infusion limited
blood parameters will be measured to assess whether each infusion can be
done. (update --- inclusion of the free light chain test initially has
allowed some weekly cancer monitoring.)
Daratumumab is very different from my previous chemo. This is a very
large molecule. It is fully formed 'Y' antibodies that are all the same.
The manufacturer says daratumumab is not chemotherapy, describing
it as a CD38 targeted monoclonal antibody. Daratumumab decreases WBC (white
blood count) and platelets. |
|
8/1/17
begin
(pom/
daratumumab/
dex)
chem
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
--
|
|
12.6
|
4.39
|
3.44
|
123
|
--
|
.52
(3.2/6.2)
|
1.1
(65)
|
8.9
|
|
8/8/17
|
.49 IgG lambda
.05 IgG kappa
Pattern also suggests inflammation.
|
x1.88
(three weeks)
|
9.15%
|
5.04
(11.30 => 5.04) nice drop in first week)
|
.04
(.22/5.04)
|
4.82
|
|
13.5
|
2.65
(residual cold)
|
2.19
|
67
|
.817
|
.54
(3.7/6.8)
.56
(3.3/5.9)
|
1.2
(59)
|
8.7
|
|
8/16/17
|
.49 IgG lambda
.05 IgG kappa
|
x 1,00
(one week)
|
9.31%
|
4.37
|
.15
(.66/4.37)
|
3.71
|
|
12.4
|
1.92
(residual cold)
|
1.23
|
42
|
.742
|
.44
(2.8/6.4)
.53
(3.1/5.8)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.2
|
|
8/22/17
|
.51 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
Small monoclonal IgG kappa band may be an interference
by the drug daatumumab.
|
x1.04
(one week)
|
9.19%
|
5.84
|
.11
(.65/5.84)
|
5.19
|
|
11.7
|
2.29
(2.80 two days later)
|
1.60
|
39
(50 two days later)
|
.778
|
.52
(3.4/6.5)
.53
(3.3/6.2)
|
1.2
(59)
|
9.4
|
|
8/29/17
end
1st cycle
(pom/
daratumumab/
dex)
|
.37 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
Small monoclonal IgG kappa may be an interference by the
drug daratumumab.
|
x.73
(one week)
|
7.82%
|
6.91
|
.032
(.22/6.91)
|
6.69
|
|
10.7
|
3.17
|
2.24
|
62
|
.784
|
.53
(3.2/6.0)
.53
(2.9/5.5)
|
1.1
(65)
|
9.0
|
|
9/6/17
begin
2nd cycle
(pom/
daratumumab/
dex)
|
.37 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
location of the small monoclonal IgG Kappa suggests that the band is
the drug daratumumab.
Normal immunoglobulins decreased.
|
x1.00
|
7.82%
|
9.89
|
,028
(.28/9.89)
|
9.61
|
|
10.9
|
5.10
|
4.39
|
37
|
.825
|
.55
(3.6/6.5)
.53
(3.1/5.9)
|
1.3
(54)
|
9.1
|
|
9/13/17
|
.36 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
The location of the small monoclonal IgG Kappa suggests that the band
is
daratumumab
Normal immunoglobulins decreased.
|
x.97
|
7.61%
|
11.1
|
,03
(.32/11.1)
|
10.78
|
|
8.4
|
2.36
|
1.68
|
11
(9/14/17
Pomalyst suspended due to low platelets)
|
.683
|
.58
(3.0/5.2)
.47
(2.6/5.7)
|
1.1
(65)
|
8.9
|
Chemo change (9/14/17)
Pomalyst (and 162 mg daily aspirin) suspended because platelets are
extremely low (11). In the interim daratumumab (with dex) is my only chemo
drug. Pomalyst may return at lower dose if (or when) platelets exceed 50. |
|
9/19/17
|
.35 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
The location of the small monoclonal IgG Kappa suggests that the band
is
daratumumab
|
x.97
|
6.36%
|
11.2
|
.02
(.23/11.2)
|
10.97
|
|
8.5
|
3.40
|
2.13
|
10
(22 after platelet infusion)
|
.767
|
.53
(2.9/5.5)
.46
(2.8/6.1)
|
1.2
(59)
|
8.8
|
|
9/26/17
|
.53 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
The location of the small monoclonal IgG Kappa suggests that the band
is
daratumumab
|
x1.8
|
9.6%
|
15.9
|
.01
(.21/15.9)
|
15.69
|
|
7.0
(hemocrit 20.7)
|
6.05
|
5.00
|
10
|
.798
|
.53
(2.9/5.5)
.56
(3.3/5.9)
|
1.5
(46)
|
8.9
|
|
10/3/17
|
.54 IgG lambda
.06 IgG kappa
The location of the small monoclonal IgG Kappa suggests that the band
is
daratumumab
.71 IgG lambda
(10/6/17)
|
x1.02
|
9.8%
|
16.7
15.8
(10/6/17)
|
.01
(.16/16.7)
|
16.54
|
|
8.8
(hemocrit 25.6)
(after two red blood cell transfusions)
9.5
(10/6/17)
|
6.87
6.01 (10/6/17)
|
5.73
(10/6/17)
|
5
15
(10/3/17) after two platelet transfusions
8
(10/6/17)
|
.864
|
.56
(3.1/5.5)
.55
(3.6/6.6)
|
1.3
(54)
(10/6/17)
|
9.0
|
Chemo change --- new cancer (10/10/17)
Chemo (pom/daratumumab/dex) has
been discontinued because a marrow biopsy (of pelvis) 10/4/17 showed NO
multiply myeloma, even though blood data shows an M-spike of .5 g/dL. The
proposed explanation is that the marrow in some (smaller) bones still has
MM cancer. The marrow biopsy shows a systematic failure of the marrow
to make red blood cells and platelets. My new diagnosis based on the 10/4/17
marrow biopsy is 'Myelodysplastic syndrome (bone marrow failure disorder),
refractory cytopenia (low blood cell counts) with multi-lineage dysplasia
(abnormal shape). It is only repeated transfusions of red blood cells and
platelets (2 and 3 times a week) that has been keeping me alive in recent
weeks. |
|
10/10/17
|
.71 IgG lambda
.05 IgG kappa
|
--
|
--
|
18.9
21.8
(10/13/17)
|
.01
(.16/18.9)
|
18.74
|
|
7.6
7.6
(10/13/17)
|
4.41
2.59
(10/13/17)
|
4.05
2.25
(10/13/17)
|
11
12
(10/13/17)
|
.916
.941
(10/13/17)
|
.53
(3.3/6.2)
|
1.3
(54)
1.3
(10/13/17)
|
8.9
8.9
(10/13/17)
|
|
10/17/18
|
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
|
8.5
8.6
(10/20/17)
|
4.83
5.36
(10/20/17)
|
3.87
3.93
(10/20/17)
|
11
16
(10/20/17)
|
|
.45
(3/6.6)
.53
(3.4/6.4)
|
1.3
(54)
1.4
(49)
(10/20/17)
|
9.4
9.0
(10/20/17)
|
| 10/24/17 |
.99 IgG lambda
.05 IgG kappa
(10/27/17)
|
|
|
42.10
(10/27/17)
|
|
|
|
7.3
7.8
(10/27/17)
|
5.44
5.20
(10/27/17)
|
3.69
3.73
(10/27/17)
|
13
18
(10/27/17)
|
1.130
(10/27/17)
|
.52
(3.3/6.4)
|
1.5
(46)
1.5
(46)
(10/27/17)
|
8.6
9.1
(10/27/17)
|
| 10/31/17 |
1.02 IgG lambda
.05 IgG kappa
|
|
|
42.50
|
|
|
|
8.2
7.8
(11/3/17)
|
5.80
7.64
(11/3/17)
|
4.27
5.54
(11/3/17)
|
14
16
(11/3/17)
|
1.270
|
.47
(2.8/5.9)
.54
(3.5/6.5)
|
1.3
(54)
|
8.3
|
| 11/7/17
(radiation on back, 8 gray, 11/8/17)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.6
7.8
(11/10/17)
|
7.17
4.02
(11/10/17)
|
5.49
3.16
(11/10/17)
|
10
7
(11/10/17)
|
|
.52
(3.5/6.7)
|
1.2
(59)
|
8.7
9.1
(11/10/17)
|
| 11/14/17 |
1.22 IgG lambda
Monoclonal lambda light chain
1.08 IgG lambda
(11/16/17)
|
|
|
18.80
12.50
(11/16/17)
|
|
|
|
7.8
7.9
(11/16/17)
|
4.23
3.45
(11/16/17)
|
2.79
2.27
(11/16/17)
|
6
18
(11/16/17)
|
1.370
1.230
(11/16/17)
|
.52
(3.6/6.9)
.50
(3.3/6.6)
(11/16/17)
|
1.1
(65)
1.1
(65)
(11/16/17)
|
9.1
8.6
(11/16/17)
|
| 11/20/17 |
1.08 IgG lambda
Monoclonal IgG lambda
|
|
|
6.17
|
|
|
|
8.5
8.7
(11/24/17)
|
2.33
3.26
(11/24/17)
|
1.67
2.29
(11/24/17)
|
6
7
(11/24/17)
|
1.410
|
.53
(3.7/7.0)
.46
(3.0/6.5)
(11/24/17)
|
1.1
(65)
1.0
(73)
(11/24/17)
|
8.6
8.4
(11/24/17)
|
| 11/28/17 |
|
|
|
3.51
(12/1/17)
(close to normal)
Wow!
|
|
|
|
9.2
7.4
(12/1/17)
|
2.36
2.00
(12/1/17)
|
1.73
1.28
(12/1/17)
|
3 (!)
11
(immediately after transfusion)
6 -13
(12/1/17)
|
1.210
|
.46
(3.0/6.5)
|
1.0
(73)
|
8.8
|
| 12/4/2017 |
.79 IgG lambda
(12/6/17)
|
|
|
3.38
(12/6/17)
3.89
(12/8/17)
|
|
|
|
7.9
8.4
(12/6/17)
8.1
(12/8/17)
|
2.61
2.30
(12/6/17)
2.27
(12/8/17)
|
1.70
1.53
(12/6/17)
1.63
(12/8/17)
|
8
6
(12/6/17)
6
(12/8/17)
|
1.100
(12/6/17
1.110
(12/8/17)
|
.56
(3.5/6.3)
.57
(3.7/6.5)
(12/6/17)
|
1.1
(65)
1.0
(73)
(12/6/17)
|
8.5
8.7
(12/6/17)
|
| 12/11/2017 |
.80 IgG lambda
.74 gG
(12/13/17)
|
|
|
4.45
(12/11/17)
4.49
(12/13/17)
|
|
|
|
8.8
7.9
(12/13/17)
8.4
(12/1517)
|
2.17
2.09
(12/13/17)
2.28
(12/15/17)
|
1.52
1.47
(12/13/17)
1.65
(12/15/17)
|
5
11
(12/13/17)
9
(12/15/17)
|
1.050
(12/11/17)
|
.58
(3.7/6/4)
.48
(3.1/6.5)
(12/13/17)
|
1.2
(59)
1.1
(65)
(12/13/17)
|
8.5
8.9
(12/13/17)
|
| 12/18/2017 |
.73 gG
(12/20/17)
.76 gG
(12/22/17)
|
|
|
7.97
(12/20/17)
|
|
|
|
7.7
8.1
(12/20/17)
8.6
(12/22/17)
|
2.79
3.23
(12/20/17)
2.70
(12/22/17)
|
2.01
2.55
(12/20/17)
1.99
(12/22/17)
|
9
21
(12/20/17)
7
(12/22/17)
|
1.090
(12/20/17)
|
.52
(3.2/6/1)
.56
(3.7/6.6)
(12/22/17)
|
1.1
(65)
1.2
(59)
(12/22/17)
|
8.6
8.9
(12/20/17)
8.7
(12/22/17)
|
| 12/26/2017
(10/27/17 start Promacta -- 30 days, daily)
|
.74 gG
|
|
|
9.66
|
|
|
|
7.9
8.7
(12/29/17)
|
2.92
2.93
(12/29/17)
|
2.13
2.12
(12/29/17)
|
8
(after 4 days)
13
(12/29/17)
|
1.090
|
.55
(3.6/6.6)
|
1.2
(59)
|
8.8
|
|
1/2/2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.9
9.8
(1/5/18)
|
3.12
2.33
(1/5/18)
|
2.36
1.70
(1/5/18)
|
6
10
(1/5/18)
|
|
.56
(4.0/7.2)
|
1.2
(59)
1.4
|
9.1
9.0
|
|
1//8/2018
|
.78 gG
|
|
|
21.4
|
|
|
|
8.6
7.5
(1/11/18)
|
2.31
2.44
(1/11/18)
|
1.77
1.77
(1/11/18)
|
13
11
(1/11/18)
|
1.030
|
.49
(3.4/7.0)
|
1.1
1.0
(1/11/18)
|
9.1
9.2
(1/11/18)
|
| 1/15/2018 |
.87 gG
(1/18/18)
|
|
|
38.2
(1/18/18)
|
|
|
|
8.1
6.9
(1/18/18)
|
3.17
2.23
(1/18/18)
|
2.39
1.68
(1/18/18)
|
7
9
(1/18/18)
|
1.38
(1/18/18)
|
.52
(3.7/7.1)
|
1.3
(1/18/18)
|
8.9
(1/18/18)
|
| 1/22/2018 |
.99 gG
(1/25/18)
|
|
|
52.9
(1/25/18)
|
|
|
|
6.9
8.5
(1/25/18)
|
1.88
1.77
(1/25/18)
|
1.37
1.29
(1/25/18)
|
7
8
(1/25/18)
|
1.38
(1/25/18)
|
.52
(3.4/6.5)
|
1.3
|
8.7
|
| 1/29/2018
(8 gray radiation, to back tumor 2/2/18)
|
1.04 gG
(2/1/18)
|
|
|
68.6
(2/1/18)
|
|
|
|
7.8
8.5
(2/1/18)
|
1.75
1.59
(2/1/18)
|
1.32
0.90
(2/1/18)
(yikes)
|
4
10
(2/1/18)
|
1.51
(2/1/18)
|
.49
(3.2/6.5)
|
1.1
1.1
(2/1/18)
|
8.9
9.2
(2/1/18)
|
| 2/5/2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.2
8.2
(2/8/18)
|
1.73
1.66
(2/8/18)
|
1.31
1.28
(2/8/18)
|
8
14
(2/8/18)
|
|
|
1.1
(2/8/18)
|
9.4
(2/8/18)
|
| 2/12/2018 |
1.25 gG
|
|
|
55.3
|
|
|
|
6.6
7.2
(2/15/18)
|
2.08
2.38
(2/15/18)
|
1.57
1.56
(2/15/18)
|
2
8
(2/15/18)
|
1.70
|
.49
(3.6/7.4)
.44
(2.9/6.6)
(2/15/18)
|
1.2
1.1
(2/15/18)
|
8.9
8.4
(2/15/18)
|
| 2/19/2018 |
1.24 gG
|
|
|
53.6
|
|
|
|
7.2
8.7
(2/22/18)
|
2.90
2.68
(2/22/18)
|
--
1.58
(2/22/18)
|
2
7
(2/22/18)
|
1.62
|
.42
(3.0/7.1)
(2/22/18)
|
1.0
1.2
(2/22/18)
|
8.8
9.0
(2/22/18)
|
| 2/26/2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.1
7.6
(3/1/18)
|
3.12
2.16
(3/1/18)
|
2.54
1.16
(3/1/18)
|
5
19
(3/1/18)
|
|
.43
(3.1/7.2)
|
1.2
|
8.8
|
| 3/5/2018 |
|
|
|
89.9
|
|
|
|
7.5
|
3.28
|
1.85
|
5
|
1.81
|
|
|
|
* A month after my diagnosis my monoclonal M-spike was first
measured at 5.17 g/dL (10/14/14),
and in the following month just before beginning chemo it increased
to 5.31 g/dL (11/17/14) becoming the baseline.
Beta2-Microglobulin (10/14/14) = 6.9 mg/L (1.1 - 2.4 normal),
(> 5.5 mg/L indicates stage 3 MM)
VGPR = Very Good Partial Response (> 90% reduction)
CR = Complete Response (no detectable M-spike, no detection on immunofixation,
< 5% clonal cells in marrow aspiration)
GFR - glomerular filtration rate is the best test to measure your
level of kidney function and determine your stage of kidney disease.
(light blue: Lahey lab; darker blue: Dana Farber lab)
M-spike plot number table,
my numbers, my response to rev/dex chemo, my numbers table in image format(base
- cycle 9.5)
M-spike plot number table,
my numbers, my response to rev/dex chemo, my numbers table in image format2
(cycle 10.5 - cycle 14.75)
Comments on white blood cells, platelets, red blood cells
The Celgene Revlimid web
site says, "Revlimid causes low white blood cells and low platelets in
most
people',
and my numbers (above) show this. Pomalyst side effects are basically similar
to Revlimid, low white blood cells (neutropenia), low platelets (thrombocytopenia),
and low red blood cells (anemia). The 6/27/16 transition from Revlimid
to Pomalyst (rev/dex=> pom/carfilzomib/dex) was initially correlated to
a substantial drop in my WBC (3-4 => 2.5), but after a couple of months
it recovered. Platlets too shows an initial drop, but soon recovered and
after six months are normal. Hemoglobin was relatively unchanged, running
a little below normal.
My breathless on
the new carfilzomib chemo maybe be related not so much to the hemoglobin/red
blood cell count, but that red blood cells do not look normal under a microscope
(morphology): variations in size and appearance (teardrops, oval, polychromasia
(abnormally high number of immature red blood cells)).
======================================================================================================================================
I have a fatal blood cancer,
multiple myeloma. I started this essay seven months after my diagnosis
to document my disease, so in this respect it's part blog, but it's also
a general essay on multiple myeloma, on my interactions with the medical
community, on available MM chemo options, on my cancer genetics, on my
broken neck, on how decisions about my treatment get made.
Introduction (update 7/27/15) (8/11/15)
(10/28/15) (4/30/16) (4/30/16) (5/9/16)
I am still doing pretty
well at 20 months into my diagnosis, but a little more jittery and sleep
deprived since now I'm again taking a corticosteroid paired with my chemo
drug and have somewhat less energy. My numbers started to rise about six
months ago (from a low level about 99% down) and for four months we just
watched. As my numbers began to get within striking distance of my target
of .5 g/dL (M-spike) that I did not want to exceed, plans were made to
change chemo, i.e. change from 10 mg Revlimid (only) maintenance. First
change was suggested by a Dana Farber consultant to just double Revlimid
dose to 20 mg. A three week test showed it didn't work, both M-spike and
free light chain continued to rise as before. Next change was to go back
to original rev/dex chemo that I was originally on for first six months
(25 mg Revlimid (21 of 28 days) + 40 mg/wk dexamethasone) and surprisingly
in a 6 week test both numbers stopped rising and turned down a little:
free light chain (a leading indicator) dropping about 33% and M-spike down
20%.
(update 5/7/16)
The 6 week test was actually
two 3 week tests of rev/dex. Obviously the best news for the second 3 weeks
would have been that both tracking numbers drifted lower, and the worst
news would have been they both drifted higher. What happened is that M-spike
was unchanged (.25 g/dL) and lambda free light chain drifted a little higher
(7.89 => 10.2 mg/dL). (A complication in comparing these two 3 week tests
is that in the first 3 weeks Revlimid was taken every day. In the second
3 weeks cycled Revlimid was started (to help platelets down to 88) so Revlimid
was only taken two of the three weeks.) I think the best way to look at
these two short (sub-cycle) tests is as the two combined, a cycle and half.
What this shows is that the
rising pattern has been stopped (or at least been interrupted). M-spike
dropped 20% (.31 => .25 g/dL) and lambda free light chain dropped 33% (15.3
=> 10.2 mg/dL). I think this says we should now continue to a full cycle
on rev/dex and take another look. Of course lower numbers would be welcome,
but I won't be unhappy if rev/dex is able to hold M-spike (.25 g/dL)
for a while at half of my .5 g/dL target and 5% of my cancer level at diagnosis
(5.31 g/dL).
(10/28/15)
When people ask me how I
am, the short answer is, I am in the 'sweet spot' getting back to normal.
Chemo (so far) has been effective at beating back my cancer. At 13 months
the story I tell people is that 12 months ago I was diagnosed with stage
3 of 3 fatal blood cancer and given 12 months to live, but I'm still here.
This is completely true, but also misleading since the numbers in the literature
are historical. Even today Wikipedia (beta2microglobin), which is used
to stage MM, says for values > 4 mg/L median survival is 12 months, and
my value at diagnosis was far above this at 6.9 mg/L. Indeed at 17 months
in my beta2microglobin is still high at 4.1 mg/L. A 2011 french reference
lists median suvivial time with beta2microglobin >5.5 mg/L as 29 months
(2.5 yrs).
Some cancer patients opt
for aggressive treatment, I did the opposite. At three critical decision
points I made the more conservative choice for treatment of my stage 3
of 3 cancer, saying no a stem cell transplant, no to a clinical trial,
and no to aggressive three drug chemo. Luckily I responded well to my conservative
regimen. In six months my pill based chemo reduced the high levels of cancer
in my body by 96%. Then I transitioned to maintenance dropping one of my
two chemo drugs and reducing the dose of the other by 60%. [(update) My
latest blood work two months into maintenance shows a further drop in cancer
levels to about 99% down, below the threshold of the test.] Many multiple
myeloma patients have all kinds of problems, but except for a few months
recovering from my cancer caused broken neck and neck fusion operation,
I have had no serious problems. The neck fusion operation did leave me
with a permanent loss of half of my head rotation and some occasional neck
pain, but all in all I feel pretty good, and once my neck healed up I was
able to resume driving.
4th conservative decision (nov 2015)
I recently had to make a
4th semi-critical decision. Again I made the more conservative choice,
putting quality of life first. My neck fusion to repair a pathological
fracture of C2 is failing or failed. At a one year review my surgeon was
hoping to see that bone had grown into my C1,C2 hardware and C1 and C2
were fusing, but bone has grown into only one of the four screws, and there
are gaps in the C1,C2 fusion. Unhappy with what he saw on a CT scan my
surgeon suggested I might want to try a bone growth stimulator. There is
one brand approved by the FDA for the neck and the manufacturer recommends
that it be worn 4 hours/day. Wearing this thing for six months (my next
scheduled appointment with surgeon) would be a real pain. I'm probably
not going to do it, knowing that it's a long shot it would help, and there
a chance that the bone growth will continue since my body is getting back
closer to normal after going on chemo maintenance (discontinuing dexamethasone,
a corticosteroid) and my bones have probably been strengthened by monthly
bisphosphonate (zometa) injections.
The question is how long this
will last? No one can say, patients differ a lot in how they respond to
treatment. My (cancer) genetics are pretty good (but not the best), which
is probably why I have responded well to chemo, so statistically there's
a reasonable chance I will have 2-3 years before my cancer comes back,
but if I'm unlucky maybe six months to a year. When the cancer comes back,
and with multiple myeloma it always comes back, I will then have
maybe another year or two, but this is a bad period as things begin to
fail and more aggressive chemo drugs are used.
Overview (May 2015)
In Sept 16, 2014 at age
72 I was diagnosed with multiple myeloma after my neck broke in my sleep,
so overnight I went from being active and healthy, or so I thought, to
having cancer and a broken neck. Multiple myeloma (MM) is a fairly rare
cancer (1% of all cancers) that doctors will tell you is incurable, but
treatable. It only been in the last decade or so that reasonably effective
chemo for this disease has become available, meaning chemo that can extend
the (average) lifetime by a few years and is fairly well tolerated. However,
how an individual MM patient will respond to the currently available chemo
varies widely, depending strongly on what DNA variations his cancer cells
display, so personalized medicine comes into play here. Survival times
can vary four to one depending on whether a patient has good or bad DNA
with half to two thirds of patients falling into the good category.
A week in the hospital for
a neck fusion operation and lots of tests was followed by two months of
wearing a neck collar, two weeks of radiation to kill the cancer cells
in the neck and in a large bone lesion in my mid-back. Initially my blood
numbers were bad and x-rays showed a lot of bone tumors, diagnosis was
multiple myeloma stage 3 of 3 with the literature showing a median survival
of 12 months (!), but then DNA analysis of my cancerous bone marrow came
in and was positive, not the very best but pretty good. I have the hyperdiploidy
variation (extra copies of chromosomes), and that lowered my risk from
'high' to 'standard'. I said no to a clinical trial, no to a stem cell
transplant (a horrendous procedure requiring weeks in the hospital), and
began targeted chemo for multiple myeloma taking the widely used, but super
expensive, patented revlimid (slightly modified thalidomide) plus
the inexpensive corticosteroid dexamethasone. In five months this conservative,
but commonly used, pill based rev/dex chemo lowered the cancer in my blood
by 95.5%, which is considered a 'very good partial response' and is correlated
with longer survival.
The chemo side effects were
small at first but have lately begun to give me some jittery days, affecting
my sleep, and giving me anemia making me tire easily, but hopefully these
side effects will subside when I transition to a lower dose maintenance
regimen. Even though I have three large bone lesions (holes) and many smaller
ones, I have no bone pain, probably because my holes (really hollows)
remain inside the bones where there are no pain sensors. My neck
fusion operation has left me with some occasional neck pain and a permanent
loss of of about half my head rotation, but by trial and error I have learned
I can compensate for this by changing my driving style, reorienting my
car at intersections to lower the angle through which I need to look to
see oncoming traffic and twisting my back. In short after a few bad months
I am now doing pretty well.
MM tracking numbers
Multiple myeloma is very
unusual cancer in that being a blood cancer the amount of cancer in the
body, specifically how many cancerous blood plasma cells exist in the bone
marrow, can be accurately measured with a simple blood test. Amazingly
there is not just one, but two components of the blood that are
useful for tracking the amount of cancer in multiple myeloma patients.
M-spike and free light chain MM cancer indicators
The reason MM has tracking
indicators in the blood is that MM is a cancer of the marrow cells (plasma
cells) that make disease fighting antibody proteins in the blood. Antibodies
in the blood are normally all different with different molecular weights
to fight a wide range of invaders, but the cancerous plasma cells in the
marrow are clones that are genetically identical, so they make identical
blood antibodies. Therefore the area under any spike of blood proteins
with identical weights is taken as a (linear) measure of the total amount
of cancerous marrow cells in the body that created them. This indicator
is called the monoclonal spike or (for short) M-spike.
Caveat -- delayed fall
There's a caveat to M-spike
as an good indicator of marrow cancer cells. When chemo is started or changed
and M-spike is falling it may read falsely high for months. The
argument of the people who make the free light chain measuring equipment
(Binding Site, UK) is that there is a recycling mechanism that reconstitutes
anti-bodies slowing their clearance from the blood. The result is M-spike
has a downside lag, it tends to fall more slowly than the actual fall in
marrow cancer cells. There would be no comparable lag on the upside.
The anti-body protein is Y shaped,
made of two joined double strands, each of which is composed of a longer
(heavy) chain bonded to a shorter (light) chain. With this shape it can't
be made in one go like a classic textbook protein, it has to be made in
four pieces, which are later joined to form the complete Y shaped antibody.
There can never be perfect balance between the amount of light and heavy
chains that are made and one reference says, "for unknown reasons, the
plasma cells typically produce more light chains (40% more says Wikipedia)
than are required to create the whole immuno-globulins or monoclonal proteins."
A sensitive test is able to measure these partial antibodies in the blood,
which are the excess light and heavy chains that never joined up to form
a complete Y shaped antibody. There is an established test for the light
chains, called 'free light chain', and this is the second MM cancer indicator
in the blood. (There is also a test for the heavy chains in the blood,
but it much less accepted and standardized.)
It's not at all clear how
linearly
the
amount of free light chains in the blood track the cancerous MM cells in
the marrow. The above reference says only, "the amount of free light chain
production is linked to the activity of myeloma or plasma cell growth."
Wikipedia (serum free light chain measurement) describes a process where
the kidneys rapidly (hours) and efficiently remove free light chains from
the blood, and the levels in the blood only rise when the kidneys get overwhelmed.
In my case when my M-spike was very high pre-chemo (5.31 g/dL) my lambda
free light chain was also very high (379 mg/dL).
Free light chains have an
advantage over the M-spike as a MM cancer indicator in that their survival
time in the blood is hours not weeks or months as with the M-spike, hence
they track the amount of marrow cancer with much less lag. In the parlance
of the control engineer it is a leading indicator. This is very useful
in patient care to to evaluate chemo for its effectiveness, to see more
quickly when existing chemo stops working or if a new chemo is working.
Doctors tend to focus on the
'M-spike', which is the amount (g/dL) of identical (monoclonal)
Y shaped antibody proteins in the blood. For a healthy person the amount
of this indicator is zero. The other indicator, 'free light chains', is
the amount (mg/dL) of pieces of the antibody Y proteins found in the blood
(in my case 'lambda free light chain'). This indicator is found at a concentration
orders of magnitude lower than the M-spike and has a non-zero residual
value in healthy people, so it is not useful when cancer levels are low.
The virtue of free light chain is that when cancer levels are high it responds
much more quickly (and accurately says a manufacturer of test instruments)
to chemo. My numbers, plotted up below, show I had a 98% decrease in my
lambda free light chain (from a very high value) in just my first
month of chemo, whereas it took 8-9 months for my M-spike to show the same
proportional decline.
M-spike in beta region (feb 2016)
When considering how much weight to
put on M-spike vs free light chain, another consideration recently came
to light. I have an IgG plasma cancer so my M-spike consists of identical
IgG antibody proteins. IgG antibodies are large so they don't diffuse far,
putting them at the end of a serum electrophoresis distribution in a region
known
as gamma. Normal IgG antibodies have a range of weights so form a smooth
broad lobe in the gamma region. An IgG M-spike is typically seen as a narrow
spike on top of this broad peak. This is considered fortunate from an M-spike
testing point of view because the M-spike is easily measured above the
smooth background.
When Dana Farber recently
did an electrophoresis of my serum proteins, they reported my M-spike is
not in the gamma region, but in the adjacent beta region. I think this
means my cancerous plasma clones are producing an IgG antibody that is
smaller than the average IgG antibody, so it diffuses better and makes
into the beta region. The consensus seems to be that it is more difficult
to get a quantitative reading of an M-spike when it is in the beta region.
I suspect this means the normal beta region proteins form a series of peaks
such that an M-spike does not stand out and can be partially obscured.
Dana lab was unable to assign
a numerical value to my beta region IgG M-spike (.1 g/dL threshold??),
yet in the preceding months Lahey lab had reported five smoothly varying
and slowly increasing M-spike values ranging from .07 to .18 g/dL, slightly
decreasing to .16 g/dL two weeks before the Dana collection. As I write,
this apparent disparity is not yet resolved, but it argues that maybe my
M-spike should be somewhat discounted because of testing difficulties.
M-spike in beta region (june 2016)
In june 2016 while Lahey
was reporting M-spike at .24 g/dL, Dana Labs at about the same time reported
.46 g/dL, but noted its value was an "overestimate" since my lambda M-spike
is in the (noisy) beta protein region and includes some other normal proteins
found in the this region.
Overview of my
numbers (cycles 1 - 17.5)
I began chemo with standard
rev/dex and responded well, transitioning to a lower maintenance dose of
Revlimid after six months. Rev/dex caused my M-spike to decline about 99%
to the point where after 8 months (10 months after diagnosis) no numerical
value could be assigned, and my M-spike stayed unmeasurable for the next
three months. This is a good response, a CR (complete response) based on
M-spike. I was told by my Dana specialist that only 10-15% of patients
on rev/dex respond this well.
My numbers start
to rise (10/26/15)
After about a year, my M-spike
became measurable again (10/28/15), and for the next several months both
it and my free light chain showed a steady upward creep. Although in absolute
terms they were still low, this steady rise caused me concern as I didn't
want to wait until my body started deteriorating before changing chemo,
so I planned a consultation with a MM specialist at Dana Farber to get
his opinion. At our meeting he said if the pending free light chain hit
a target (10 mg/dL), which it did, then regardless of the M-spike he thought
a tweak now in my Revlimid maintenance dose was called for [10 mg
=> 20 mg]. However, when a few days later when the Dana labs were unable
to get a numerical reading of my M-spike, he then suggested perhaps it
was better to wait another month or two before changing course. When two
weeks later Lahey reported yet another increase in M-spike (.22 g/dL) and
free light chain (12.00 mg/dL), my oncologist and I agreed this was the
time (2/29/16) to increase my maintenance dose of Revlimid to 20
mg. I am comfortable with this as this as I see it as the smallest possible
stepup in chemo possible.
I was hoping to get 2-3 years
out of my first remission and this change is happening 15 months into chemo
(17 months after diagnosis) and less than a year into maintenance. Of course,
I am hoping it will be effective in arresting the rise in the numbers.
If it does and if side effects don't noticably change, then I think it's
fair to say the first remission continues, that this was just a 'tweak'
to the maintenance dose. We will see in another couple of months.
Didn't work
** Well the data is in (3/22/16).
A three week test showed clearly that increasing the maintenance dose of
Revlimid [10 mg => 20 mg] didn't work at all, both free light chain and
M-spike continued to rise strongly just as before [.22 => .31 M-spike and
12 => 15.3 free light chain]. It looks like my cancer is no longer responding
to Revlimid. (bummer)
Before abandoning Revlimid my
oncologist is suggesting a we try a few weeks of the (original) rev/dex.
While this is probably the smallest step and ordinarily I would like it
because it fits with my philosophy of taking small steps, the problem is
that my M-spike is rapidly approaching my personal max target (.5 g/dL)
that I don't want to exceed, and my lambda free light chain at 15.3 is
well above the 10 mg/dL target. At the current rate of increase (x1.41/three
wks) my M-spike will hit .43 in one more month if it doesn't work, and
I'm betting it won't. We need to plan now for a bigger step up in chemo
(to 2nd line drugs) for use soon. Not good news.
Worked
** Well the data is in (4/11/16).
A pleasant surprise, adding back the corticosteroid 'booster' seems to
be making Revlimid work again. In a three week test back to the original
rev/dex both numbers stopped rising and began to drop [.31 => .25 M-spike
and 15.3 => 7.89 free light chain]), bringing the free light chain below
the 10 mg/dL target. This chemo change was mostly just adding back the
original dex (40 mg/wk of dexamethaone), which is considered a 'booster'
for Revlimid, plus a minor tweak in the Revlimid dose (20 mg => 25 mg)
(not cycled initially).
My particular monoclonal antibody
is of type: IgG lambda, which means it is composed of the G heavy chains
(most common of five heavy types) and lambda light chains (less common
of the two light types, about 1/3rd of light chains are lambda).
Plot of my numbers
(1 - 9 months)
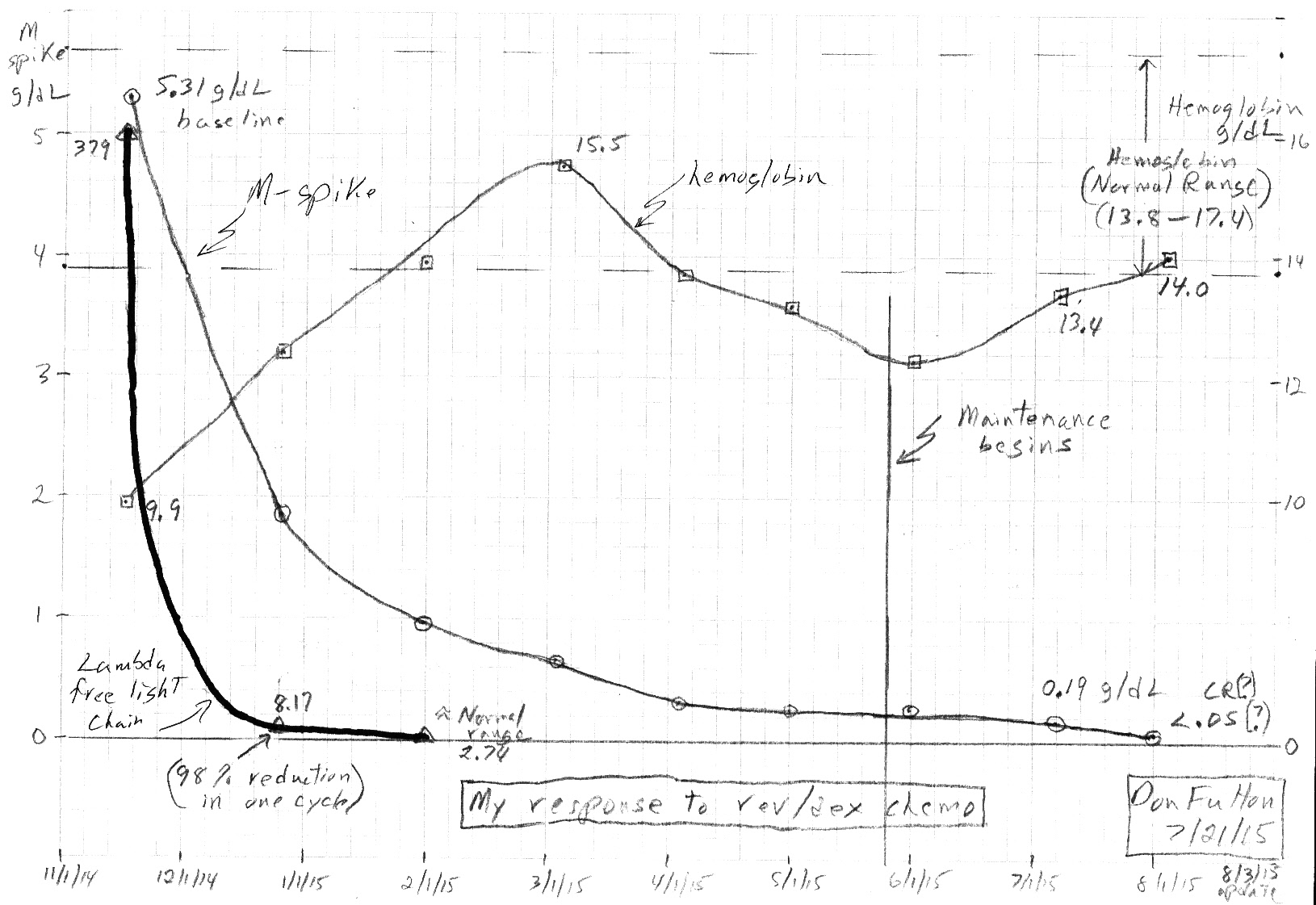
My first 9 months of (rev/dex) chemo.
Multiple myeloma is a very unusual cancer in that being a blood
cancer the level of cancer cells in the body
can be accurately measured with a simple blood test.
find this plot online: 'M-spike plot' (Google image search)
Plot
of my M-spike numbers for 12 months of 2016
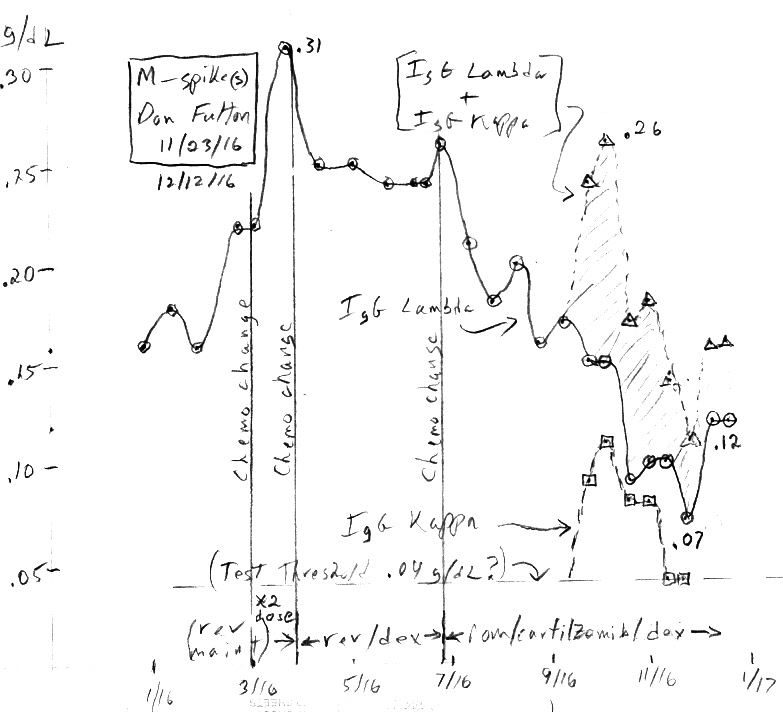
my M-spike numbers for all of 2016
Notice the big shift in this graph'a vertical scale from the plot
above
(5 g/dL vs 0.3 g/dL max)
On the left side of the table
are the two markers (proteins) in my blood that tracks the cancer. Free
light chain (with a lifetime in the blood of hours) responds rapidly to
changes in marrow cancer levels. The M-spike (with a lifetime in the blood
of weeks) responds more slowly. The doctors focus on the slow responding
M-spike, because it can go deeper and is a direct measure of amount of
cancerous (anti-body) proteins in the blood. Notice the fast responding
marker (free light chain) shows 98% of my cancerous marrow cells were (likely)
wiped out in the very first month of rev/dex chemo. [Well, maybe. How linearly
the free light chain marker correlates to the amount of cancer in the marrow
is murky.] My M-spike cancer levels in Aug 2015 (cycle 8.5) were reported
as undetectable, below the threshold of the test (probably .05 g/dL or
a little less).
The transition to maintenance
coincided with an increase in hemoglobin to the lower end of the normal
range where it has remainded ever since (10 months). The transistion to
maintanence, however, has caused platelets to drop below normal (minor
issue, which could be treated by adding back some dexamethasone).
---------------------------------------
Plot
of my M-spike and lambda free light chain for much of 2017
Includes three different
chemo regimes: pom/carfilzomib/dex, pom/Ninlaro/dex, and pom/daratumumab/dex,
which produced only a one month dip.
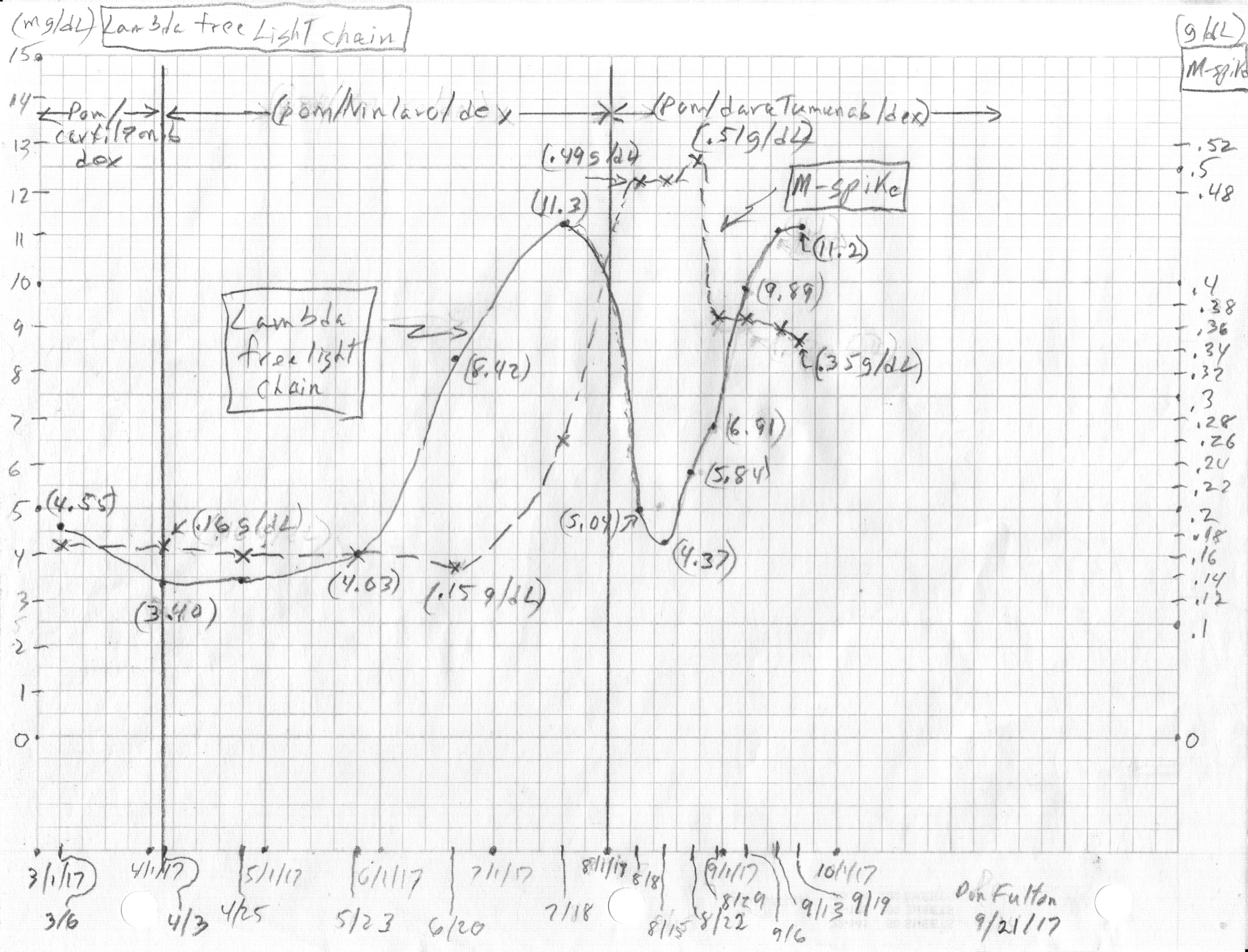
---------------------------------------
Equivalent Freelite plot
red: IgG production by cancerous plasma
blue: IgG serum concentration
SPE = serum protein electrophoresis
(source -- http://www.wikilite.com/wikilite/index.php?title=File:18.15.jpg)
Later I discovered a nearly
identical plot (above). This is from the Freelite (Wikilite) people (www.wikilite.com
and http://www.us.bindingsite.com/)
who advocate for use of free light chain to (rapidly) track MM cancer levels.
They explain that the long tail of IgG anti-bodies [= (M-spike + 0.1 g/dL
(nom) residual)] is due to a cellular recycling mechanism and argue that
it can give a false indication of residual disease for months. It's uncanny
how alike the two plots are, yet I never saw the Freelite plot until after
I done my plot!
The objective of chemo in
my case is to eliminate as much as possible of the cancer from my body,
which clinically means driving the amplitude of the M-spike (shorthand
for 'Monoclonal protein SPIKE') as low as possible, then switching to a
lower doses of chemo to attempt to hold the number low for as long as possible.
A reduction of greater than 90% (VGPR -- Very Good Partial Response), or
better still cancer levels below the threshold of the test (loosely speaking,
a CR -- Complete Response), is the target as these levels are associated
with longer survival (really longer disease free progression).
As the cancer cells in the
marrow decline, there is more room for the normal blood making marrow cells
to expand, hence this should allow blood number to tend toward the normal
range, but at the same time rev/dex can affect hemoglobin and WBC (white
blood count). A lower chemo dose in maintenance should hopefully reduce
the chemo side effects, important since my chemo (revlimid) has a record
of killing a few percent of patients with a 2nd cancer or a deep vein blood
clot. Thus entering maintenance I will be tracking so see if my blood numbers
improve.
Another criteria clinical
trials use for disease progression are new (or growing) bone lesions. This
is one of the black holes as cancer levels rise. My experience with my
femur tumor is (small) changes would be difficult to see on x-ray, and
my bone doctor seemed to focus on whether or not it hurt. Luckily so far,
except for my neck, I have been free of bone pain. The problem with relying
on bone pain as an indicator is that pain doesn't start until the lesion
has progressed significantly, penetrating to the surface of the bone. This
makes it a crappy indicator. I don't want my many bone lesions to begin
growing again, but I have no information as to what cancer level this begins.
In lieu of bone pain only a whole series of body x-rays (or spot x-rays
on my known large tumors) might be able to pick up changes in my bones
before pains begins, but I suspect this is a very insensitive test.
One problem is my x-ray baseline is old, the last series of full body x-rays
I had was more than a year ago. My doctor has had no serious discussion
with me about getting a new x-ray baseline. It might soon be useful
to seek out a 2nd (and 3rd) opinion at a major MM cancer center, to get
some perspective on these issues from an outside expert.
My numbers
Change in my numbers
(4/15/16)
At a meeting with my doctor
of 4/11/16 there was no new data to review because blood was taken that
day. We planned for the next step in chemo if the current test of original
rev/dex failed, which I, and I think my doctor, expected because the previous
three weeks of doubling the dose of Revlimid [10 mg => 20 mg] had done
nothing to arrest the rise in both numbers. The next chemo step planned
was to add a 3rd drug to rev/dex, a proteasome inhibitor either Ninlaro
(pill) or Velcade (injection). The plan was to try for Ninlaro and if blocked
by my Part D insurer, a fall back would be month on Velcade then try again
to get the Part D insurer to approve payment.
If rev/dex in the short three
week test appeared to be working, meaning it caused the numbers to fall
(or maybe just arrested the rise), then we would hold course and stay with
it. (If the two tracking number had split, one going up and one down, it
would have been a tough call, but that didn't happen.)
When the data came in a few
days later, a pleasant surprise, three wks on the old rev/dex arrested
the rise and caused both numbers to fall [.31 => .25 M-spike and 15.3 =>
7.89 free light chain]). I put more emphasis here on the free light chain
drop of 50%, because M-spike falling tends to lag and also
the lambda free light chain had fallen under its 10 mg/dL threshold, though
the kappa/lamda ratio showed no improvement coming in slightly below normal.
After seeing the free light
chain drop in half, I was less concerned about how much the M-spike would
drop, just that it would show a drop, and two days later the data came
in with a 20% drop, so both numbers had turned around. We would hold course
on rev/dex and would have another set of data in three more weeks (5/2/16)
from appointments previously set up. At this point I had been on Revlimid
7 wks straight, but my platlets were getting quite low (88), so my doctor
wanted to start cycling rev/dex. The first off week to start when my current
Revlimid pills ran out (first off day tues 4/19). Thus the 2nd three week
test of rev/dex I am just beginnng will be Revlimid (25 mg, one week off
and two weeks on) with (40 mg) dex continuing every fri. It will be interesting
to see if the decline continues and for how long it will hold.
Am I still in my first remission?
So an interesting question
now arises. Am I still in my first remission? I had declared my first remission
had ended, but now back at the original rev/dex after my M-spike had risen
to [.31 g/dL] or 6% of my pre-chemo (5.31 g/dL) and both numbers are falling.
No 3rd drug added or new drug swap in. If I taken the original clinical
trial offered me [(Ninlaro + rev/dex) vs rev/dex], I would have remained
on original rev/dex continuously, and this would clearly be treated as
still in first remission. Maybe the answer is yes.
Change in my numbers
(4/4/16)
For the last four months
(dec thru march) the upward trend in my numbers has continued: (M-spike
.16, .16, .22, .31 g/dL) (lambda free light chain 6.41,
8.41, 12.00, 15.30 mg/dL). When M-spike reached .22 and free light chain
12.00 (2/23/16), on the recommendation of a Dana Farber MM specialist the
dose of my maintenance Revlimid was increased from 10 mg to 20 mg. But
three weeks on the higher Revlimid dose gave no improvement at all. The
rise in both numbers continued just as before: (M-spike .22 to .31) and
(lambda free light chain 12.00 to 15.30).
The 20 mg Revlimid maintenance
dose was not working, so about ten days ago a quick decision was made to
put me me back on the original rev/dex. This is a small step up and chemo
and worth a couple of weeks or so to see if it is effective. The end of
my 1st remission can be dated to 3/25/16, the day I began to add back the
dexamethasone (at first paired with 20 mg Revlimid, in a few days was changed
to 25 mg) to the same rev/dex I took for 6 months when I first started
chemo in late 2014: (25 mg Revlimid (21 of 28 days) and dexamethasone (40
mg/wk)). The corticosteroid (dexamethasone), considered a 'booster' for
Revlimid, that I happily stopped ten months ago came back. (And two days/wk
of almost no sleep due to the corticosteroid came back too.)
This rev/dex test will be
a short one (about threeweeks) since I am closing in fast on my M-spike
target (.5 g/dL). Personally I will be surprised if going back on rev/dex
works, since my cancer just did not respond at all to a doubling of the
Revlimid dose. It acts like it has become resistant to Revlimid, but who
knows, maybe the 'booster' will help, the data will tell the tale. If it
doesn't work and the rise continues as before, my next blood sample (due
4/11/16) will probably show an M-spike above .4 g/dL. The next change
in chemo will be important and is not decided yet.
First remission ended (3/25/16)
My first remission 'officially'
ended with my recent chemo change back to rev/dex. (or did it? see
above) I only got ten months on Revlimid maintenance before my M-spike
numbers rising from a very low level (99% down) began to approach .5 g/dL,
which clinical trials usually use as the threshold (as applied to me) for
disease progression. And even more worrying (to me) my lambda free light
chain has continued to climb, up about 50% in the last two months. It passed
10 mg/dL, used as a threshold to join some clinical trials, around (2/1/16)
and as of (3/22/16) it reached 15.30 mg/dL.
I was hoping for 2-3 years
in my first remission, but I only got 1.5 yrs. My 2-3 yr expectation was
based on data showing the 50% point was about 2 yrs, and I had good cancer
genetics. Good genetics tend to 'predict' how well one responds to chemo,
and consistent with my genetics I did respond quite well, achieving a depth
of response that only about 10-15% of patients on rev/dex achieve. Rev/dex
dropped my M-spike levels about 99% (5.31 to <.05 g/dL) and my lambda
free light chain dropped from an initial 379 to 1.50, well centered in
the normal range. A good deep response tends to be correlated with a longer
time to disease progression, but in my case after three months of being
unreadable my M-spike began to climb. So bottom line 18 months after diagnosis,
a chemo change is needed to get into a 2nd remission.
Thresholds to trigger
chemo change
What should be the M-spike
and free light chain thresholds that trigger changes in chemo? I slowly
began to realize that clinical trials provide guidance here. The most common
end point used in MM clinical trials is disease progression. Every clinical
trial I have looked at uses a standard's committee guideline, which (applied
to me) is M-spike of .5 g/dL (technically it is an increase
of .5
g/dL from <0.05 g/dL). So this is a good hard number.
But there is additional threshold
guidance in clinical trials. Clinical trials for relapse MM patients have
both M-spike and free light chain thresholds, one of which must be exceeded
just to join the trial. In other words clinical trials on relapse
MM patients use these numbers verify you have a moderate level of cancer
in your body, that you are not in remission. Importantly the trial joining
requirement includes a free light chain threshold. This is useful, because
there is no free light chain threshold in the disease progression definition.
However, a (backup) free light chain threshold may be provided to define
disease progression for a class of MM patients who have no measurable M-spike
(or its urine equivalent).
I found the join criteria
for one trial (Ninlaro) to be thresholds M-spike >.5 g/dL and free light
chain >10 mg/dL (kappa/lambda ratio must also be abnormal). This M-spike
level is the same for disease progression, so at .5 g/dL you go from one
category to the other. Ninlaro's backup free light chain criteria for disease
progression was 10 mg /dL. Dana Farber doctor said to me his threshold
to trigger the doubling of Revlimid maintenance dose was lambda free light
chain exceeding 10 mg/dL. My latest free light chain reading is right on
the edge of meeting this first criteria. While my free light chain at 15.30
mg/dL is well above 10 mg/dL, my kappa to lambda ratio is still normal,
but just barely at .26 (0.26 - 1.65 normal). However, the backup progression
criteria (Ninlaro) defines the free light chain threshold differently as
follows: "Difference between involved and uninvolved free light
chain (FLC) levels (absolute increase > 10 mg/dl)". In other words it's
not the ratio, but the difference that is being used. I am now above this
theshold: [15.30 (lambda) - 3.96 (kappa) = 11.34 mg/dL > 10 mg/dL].
Another trial had M-spike
>1 g/dL and free light chain >?? mg/dL.
Thresholds bottom line: M-spike .5 g/dL, lambda free light
chain 10 mg/dL
Change in my numbers
(12/1/15)
The initial decline in my
cancer numbers has ended. For the last two months my numbers have begun
to tick upward [M-spike <.05, .07, .12], but since the beginning base
was low, my latest number is still low. The big question now is how long
to watch this trend without 'doing something', which realistically means
changing chemo. Of course, I am hoping it plateaus soon, but what if it
doesn't? A MM patient has few resources here. I asked my oncologist and
got only 'look for a trend'. One source of information is the definition
clinical trials use for MM disease 'progression', typically a major milestone
in the trials. The trials use as a threshold an M-spike
increaseof
.5 g/dL from minimum, which since my minimum was <.05 g/dL is is pretty
much an absolute level of .5 g/dL. Another source of information
is MM forums where MM patients detail their experiences, useful but numbers
here are all over the place.
On the one hand at .12 g/dL
I am now 25% of the way to the .5 g/dL clinical threshold with an increasing
trend. This is worrying. On the other hand .12 g/dL is still less than
at the end of my six months rev/dex chemo (.23 to .19 g/dL). Lambda free
light chain has crept up a little (4.08), but this is only about 1% of
my 379 pre-chemo. The kappa/lambda free light chain ratio has moved down
a little (1.17 > .95), but is still in the center of the normal range.
My albumin/(total protein) ratio is fine, my calcium level is fine, and
my IgG hasn't moved. My M-spike cancer level while up a little is still
nearly 98% down from my pre-chemo baseline (5.31 g/dL).
It's useful to extrapolate
the existing trend to make a prediction for my next number. There are only
two uptick intervals, but they both showed a x1.75 increase in the monoclonal
protein, a proxy for the plasma blood cancer in my marrow. This is a little
less than doubling in one cycle, so if this trend holds, my .12 g/dL in
early Dec would be expect to increase to .20 g/dL in early Jan 2016. I
could potentially be getting up into the .5 g/dL range by Feb/March so
I need to get busy with planning and research.
Cycle 9.5 confirms (9/4/15)
I'm a natural skeptic,
partly my engineering training, but I wasn't going to accept cycle 8.5
good tracking result at face value [no detection of M-spike or on immunofixation]
until I could see another reading the following month. Well the 2nd results
are in, and they basically confirms cycle 8.5 results. In cycle 9.5 cancer
is detected both in the M-spike and on immunofixation, but it was small
enough that it could not be quantified and that's the point. Taken together
it looks like my cancer levels are just about at the threshold of
the tests, probably a reduction of 98% to 99% in M-spike from my baseline
value. Now what exactly the test thresholds are remain to be determined.
Also two different doctors signed off of the results in the last two months
and that may make a difference.
Oligoclonal
The weak bands in cycle
9.5 are described as 'oligoclonal'. I can't find a good definition of this
term, but it seems to refer to several smaller spikes close together rather
a single large spike (monoclonal). What the clinical significance of this
is I don't know. The spikes are described as type IgG, which is the type
of cancer I have. I suppose oligoclonal might mean I have two spikes, one
with a lambda light chain and one with a kappa, which was reported in my
results many months ago.
Cycle
8.5 results --- Too good to be true? (8/10/15)
My latest M-spike (cycle 8.5)
looks a little too good to be true, which means it might not be. Previous
monthly values were 0.24, 0.23, 0.19 (g/dL), a slowly declining value that
appears to be approaching an assymptote a little below 0.20 g/dL, so what
is the probability that a month later that it has suddenly dropped to undetectable
levels (probably <0.05 g/dL)? I'd say there's a significant chance there's
a test error here. I did see that corticosteroids can affect the serum
protein phosphoresis test, so maybe going onto maintenance with the dropping
of dexamethasone is having an effect.
Notice the sloppy blood work reporting,
there are no M-spike numbers, it just says "No monoclonal immunoglobulin
detected" and the "immunofixation: no bands detected", which translated
means the monoclonal density is below the threshold of the tests. While
I believe this type of reporting is common, it begs the question: What
is the threshold of the tests? It should be reported as < xxx g/dL.
I read in one european paper the test threshold is normally around 0.03
to 0.05 g/dL, but this information is hard to come by. Multiple references
say the threshold of monoclonal protein detection by immunofixation is
lower still. One reference lists the thresholds as 0.05 g/dL for protein
electrophoresis and 0.015 g/dL for immunofixation.
When I asked my doctor about
the M-spike test threshold, she said she has seen levels as low as 0.1
(g/dL). Well I have seen levels as low as 0.05 (g/dL) in my own blood work
(small kappa monoclonal spike). I suspect the best way to really
understand this test would be to talk to the doctors at the hospital that
do the test and analysis, and I am pursuing this.
** I found (below) an interesting
tidbit on the excellent web site of Amerian
Association for Clinical Chemistry. Could this be the reason why after
entering maintenance and stopping dexamethasone a big change in M-spike
was found this cycle? (My doctor made a vague reference that sometimes
she has seen this happen.)
-- Aspirin, bicarbonates,
and corticosteroids can affect protein electrophoresis results.
---------------
Cycle 7.5
My numbers are in the table
above. The sketch shows my 96.4% reduction in M-spike over 7.5 month of
chemo, and hemoglobin, which improved for three months then rolled off
as chemo continued. My doctor appeared pleased with the first few months
of my M-spike reduction. In the first four 28 days cycles (about four months)
of rev/dex chemo my cancer levels dropped by a factor 15 (from 5.31 pre-chemo
to 0.34) into the VGPR range. One way to look at these numbers is to say
(on average) each 28 day cycle of rev/dex has cut the cancer level
about in half [geometric mean of the four fractional decreases is 0.47].
In later months the relative
declines have slowed, and there's some evidence I may be approaching a
plateau, but still each reading continues to be lower than the previous
reading. The first reading in maintenance showing an additional 17% decline.
========================================================================================================================================
Intro
As I begin to write this,
it has been about seven months since I was diagnosed with cancer (multiple
myeloma) and a broken neck caused by the cancer on the
same day.
Before my memories of those turbulent early months slip out of brain and
random notes get lost, I want to write them up in a personal cancer essay
that I plan to put online on my home page.
On Sept 15, 2014, age 72,
I was diagnosed with multiple myeloma, often called a 'blood' cancer, but
technically it is a cancer of the bone marrow plasma cells, considered
incurable but treatable. Marrow within bones make four types of blood cells:
red blood cells to carry oxygen, white blood cells to fight infection,
platelets to clot blood and plasma cells that produce a range of antibodies
that provide an immune response. An antibody is a large protein (string
of amino acids) made and exported by plasma cells at a rate of thousands/sec
for each cell. Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the bone marrow cells that
make blood plasma cells. A specific plasma cell can only turn out one type
of antibody, so when a marrow plasma making cell goes cancerous and makes
lots of clones of itself, the result is a huge excess of identical antibodies
in the blood. The concentration of identical antibodies in the blood, called
the M-spike (or monoclonal spike), is a marker for this cancer.
This is an usual feature for a cancer and useful as it allows the amount
of cancer in the body to be tracked using blood tests. My diagnosis that
day was triggered by multiple myeloma having so weakened some of my bones
that a bone near the top of my neck (C2) broke during sleep. This occurred
totally without warning, no previous symptoms or pain, all while I was
leading an active life and thinking I was in good health. But in reality
I probably had had multiple myeloma (or its precursor) for some time, possibly
years.
Multiple myeloma is a sneaky
disease that can, and often does, develop and metastasize throughout the
body without producing any symptoms. Multiple myeloma, screws up your blood
and can affect your kidneys, but primarily this cancer targets bones not
vital organs. And a key reason this cancer can fly under the radar is that
bones don't have pain sensors. Multiple myeloma can be hollowing out bones
from the inside without causing any pain. Often it is only when the 'holes'
the cancer is making in the bones reach the surface of the bone and disrupt
the membrane around the bone, called the periosteum which does have pain
sensors, or a bone breaks, is it that disease get discovered.
Can't get
my head off pillow for 30 min!
One Sun in Sept 2014 at age 72
I had gone to bed the previous night feeling fine. I thought I was in good
health, I was active, I had even taken a ballet class that day as I did
several times a week, only to find upon waking that I could not get my
head off the pillow! I live alone and after 30 min I was wondering if I
was ever going to be able to get out of bed. I finally was able to slide
out of the bed onto the floor holding my head and taking some pain. Having
no idea what was wrong and as a matter of principle avoiding doctors, I
wrapped a towel around my neck to support it, toughed out the pain and
hoped it was a neck spasm which I read about online, but when after 24
hours the pain began getting worse, I finally called 911. I visited two
emergency rooms that night. The first ambulance took me to my local hospital
(Winchester Hospital, Winchester MA), where I was told my x-ray showed
I had a broken neck and needed neck surgery. They said they couldn't do
that there I was to be transferred to their sister hospital, so in an hour
or two I was strapped into a full body carrier usually used for auto accident
victims and moved to Lahey Hospital (Burlington MA), where I was admitted
and was soon told that not only did I have a broken neck, but I also had
cancer, multiple myeloma.
Multiple myeloma, often called
a 'blood' cancer, is considered to be 100% fatal. According to the American
Society of Hematolgy blood cancers affect the "production and function
of your blood cells". The three main types of blood cancer affect different
types of white blood cells: Leukemia (abnormal white blood cells), Lymphoma
(abnormal lymphocytes which collect in the lymphatic system), Myeloma (abnormal
plasma cells that don't mature into disease fighting antibodies). In other
words 'blood' cancers are really bone marrow cancers. Blood cells don't
live long (3-4 days for white blood cells, 120 days for red blood cells),
so the bone marrow is continually cranking out new blood cells. Because
the volume inside bones for making blood cells is fixed, uncontrolled growth,
characteristic of all cancers, of one aspect of the blood making marrow
squeezes the normal marrow. More (abnormal) white blood cells being made
means fewer oxygen carrying red blood cells can be made. (Not sure how
accurate this is, but it's my tidy little picture.) A nice feature diagnostically
of this type of cancer is that analysis of your blood gives a good indication
of the extent of the cancer in your system.
Besides screwing up your
blood, multiple myeloma metastases widely to bone marrow throughout the
body, capable of softening bones to the point of breakage. It is not that
uncommon for people to first find out they have multiple myeloma only when
a bone breaks. However, my transition from seeming good health to finding
out I had both a (fatal) cancer and a broken neck all in one evening is
more extreme that any case I have come across. More commonly I find people
report they found out they have multiple myeloma from routine blood tests
or when they they go to the doctor complaining about persistent bone pain
(like Tom Brokaw). When lying flat on my back and being wheeled through
the corridor of the hospital a few days later, a resident leaned over to
me and simply said, you have to consider that you have cancer "from head
to toe". And that turned out to be right. X-rays showed bone lesions inside
my skull, down my neck and back and in my legs. Many were small, but I
had three big ones, 'holes' my doctor called them, in my neck (C2, which
broke), in my back (T12 with 30-40% bone loss), and discovered later in
my left femur (1.5" top-bot, spanning about 30% of the dia).
Cancer diagnosis
and neck fusion operation
To stabilize my broken neck
within days of entering the hospital I had a three hour C1,C2 neck fusion
operation. The bone that broke in my neck was C2, which is near the top
of the neck just below the skull. Much of the rotation of the neck comes
from the top vertebrae C1 sliding on C2. To keep the C2 vertebrae aligned
with C1 C2 has a vertical projection (called a dens or odontoid process),
shown below, that sticks up into the main donut hole of C1 where the spinal
column goes. What broke in my neck my surgeon explained to me, was that
the vertical projection of C2 had snapped off. (I remember him at a follow
up meeting pointing to white blob on an MRI saying see this bone is totally
separate.)
I was told by the same resident
who said I had cancer from head to toe, prior to my neck operation that
a C1,C2,C3,C4 fusion was being considered, which luckily was scaled back
to only two vertebrae (C1, C2) being fused instead of four. However much
of the rotation of the neck occurs between C1 and C2, so screwing C1 to
C2 with hardware has left me with a permanent loss of about half
my neck rotation. I can now rotate my head only about +/- 45 degrees, which
somewhat affects my ability to drive. For two months after the operation
my surgeon required me to wear a neck collar 24 hours a day for the first
month (sleeping in that thing was next to impossible) and during the day
for a second month. And the whole broken neck/fusion thing has left me
with a reoccuring semi-permanent pain in the neck. (See appendix for details
of the C1, C2 fusion operation.)
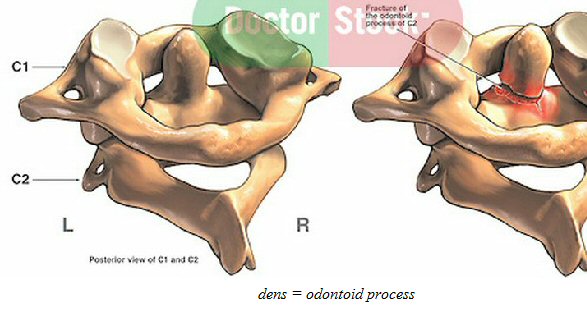 .
. 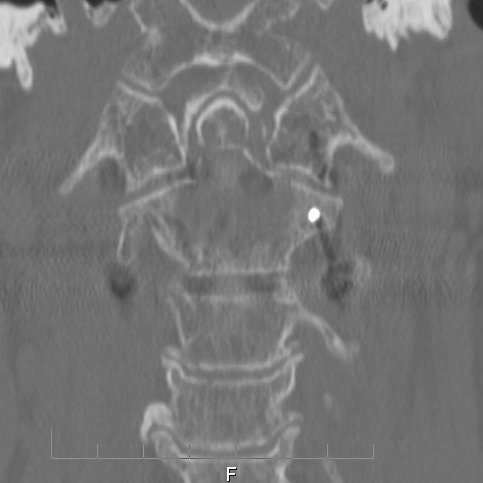
vertical projection of C2 vertebrae (dens or odontoid process) snapped
off while I was sleeping!
(right) C2 (dens) projection clearly shows in this x-ray of my neck
How does the neck provide lateral support to the head?
(update)
It has slowly dawned on me that
I don't really understand after my C2 vertebra broke what in my neck needed
to be stabilized. The reason for this is two fold: one I don't have a good
understanding of how the neck structurally supports the head, and two my
surgeon, who I have had very few minutes of face time with over 9 months,
has not explained it to me.
This much is clear to me.
When I awoke in bed that fateful day in Sept 14, I found my neck was suddenly
providing no lateral support, none, that's why I couldn't lift my
head off the pillow for 30 min. When I did manage to get out of bed, it
was by first sliding my lower body off the bed onto the floor such that
my neck & head were more like 45 degrees with respect to gravity. So
how does the cervical (neck) vertebral column transmit force from the thoracic
(chest) spine to hold the (heavy) head when the body is not vertical?
Frankly at this point I have no idea. In textbook sketches the spinal column
is nearly always shown vertical. This puts the spine in compression, and
it is easy to see how the spine works in compression, one vertebrae sitting
on top of another with disks in between to provide some movement and cushioning.
But what happens structurally when the body is not vertical? Do the spinal
and cervical vertebrae directly provide any lateral support, or must the
muscles hold the vertebrae column in compression to transmit lateral force?
If the dens on C2 did break,
why did I feel I had no lateral support for my head? Does the dens itself
provide lateral support, transmitting force from C2 to C1, or was it that
with no dens C1 was just free to slide around, so when the neck muscles
tightened the head + C1 slipped sideways causing pain? I am going to have
to research this.
Neck anatomy
There are some nice youtube
videos showing the anatomy of the neck. Below are some scn captures. There
are a LOT of muscles in the neck, including the big trapezius muscle in
the back, and nearly all these muscles run vertically. The center image
shows there are specific muscles that attach C2 to C7 to the rib cage.
Just from looking at the video you can see the muscles are arranged to
'pull down' on the vertebrae (and skull) allowing the cervical column to
be in compression. There are also ligaments between C1 and C2. I think
this is the answer to the lateral stability question.
The long (downward
pointing) projections of the neck verterbrae in the back are called the
'spinous process'. Wikipedia says they serve as an attachment point for
ligaments and muscles.
Notice there is no disk between
C1-C2. It is replaced by two sliding joints that allow C1 (and the skull)
to rotate 45 degrees or so with respect to C2. The right image is a top
down view (with the skull removed) showing C1 and the dens projecting upward
from C2. From this we can visualize how C1 rotates on C2. (The video lecturer
says the modelling is not entirely accurate here in that there is really
no space between the dens and the front rounded arch of C1. They actually
touch he says.) The purpose of the C2 dens is that it is a pivot
point around which the rounded (front) arch of C2 rotates. As I look at
the right figure, the C2 dens provides a hard stop preventing the C1/skull
from sliding backwards, but there doesn't seem to be any bone structure
to prevent C1/skull from sliding forwards and potentially compressng the
spinal column. It must be the muscles and legaments job to hold the head
centered or sliding forward, perhaps the big trapezius muscle which runs
up from the back to the back of the head is key. So is this the answer
to why I couldn't get my head off the pillow? Maybe.
Looking at the bone
structure of the neck it does seem to me that to lift the head off the
pillow (face up) some of the lifting force transmitted to C1/skull probably
comes via C2 dens pushing on the rounded front (anterior) arch of C1. It
might be that with the C2 dens broken off there was insufficient force
from the muscles and ligaments alone to lift the head. Or maybe with C2
dens gone my head tended to slide backward a little and that triggered
pain (by pushing on the spinal cord?).
.  .
. .
. 
(left) muscles attach C2 - C7 in neck to rib cage (front view)
(middle) more neck muscles (front view)
(right) top down view of C1 and C2 (top is front)
source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BrItOoELlZg
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ajL8D9JIja8
Crap neck video
There's crap about the neck
on Youtube too. Here's one by a doctor (Dr. Ross Hauser) pushing some sort
of injection to fix the ligaments between C1 and C2. His animation is absurd.
It shows as normal that C1 and C2 move as a unit when the head rotates.
C1 rotating more than C2 he calls that an instability saying it pulls on
the blood vessels going through C1 and C2 affecting the flow. I presume
there must be some slack in the blood vessels to allow C1 to C2 rotation,
which I hadn't thought about before. Of course he ignores the fact
that the anatomy of C1 and C2, with a sliding joint between them, shows
C1/skull are designed to rotate a lot with respect to C2, about 45 degrees
most references and my surgeon say. (If this guy isn't a quack, he is pretty
close to it. He's a shameless self promoter with books by him and his wife
on Amazon about curing back pain (Prolo Your Pain Away! Curing Chronic
Pain with Prolotherapy), cancer ('Treating Cancer with Insulin Potentiation
Therapy') and even a diet book.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YRBtisJhKlw
Treatments
-- Radiation of C2 (neck) and T12 (back)
I was in the hospital for
seven days, the first days filled with extensive diagnostic tests and waiting
for a cervical (neck) surgeon to become available. Two weeks after my release
from the hospital two weeks of daily radiation began in Oct 2014 to kill
then cancer cells in my two big bone lesions then known, in my neck (C2
that had broken) and T12 in my lower back. Radiation was pain free and
turned out to be nearly free of side effects as my radiation oncologist
explained to me that blood marrow cancer cells are more sensitive to radiation
than most cells, so a lower dose of radiation (about half) can be used.
The irradiation was done
with one of three multi-million dollar linear accelerators Lahey owns.
One semi-grusome aspect of the radiation procedure was since neck vertebrae
C2 high up near the skull was to be irradiated, my head could not move.
This was accomplished by making a form fitting mask of my face so my head
could be bolted to the table. A flat sheet with holes in a frame was softened
by wetting it, and then it was stretched (hard) over my face and the frame
bolted to the table. (You can see this mask below in the pictures.) I had
to stay bolted down quite a while (20-25 min) while it dried and hardened.
Then on each daily visit my mask would be pulled from the mask shelf, my
face again mashed down to the table as the frame was snapped down. Pretty
claustrophobic, stayed on for 10-15 min each day while the neck was irradiated,
during which time I have to breath through holes in the mask, but after
a day or so I got used to it and it was no big deal. In contrast the radiation
for the back, which immediately followed, was a breeze. The body was lined
up with tattoo marks that had been applied the first day, and I was just
told not to move for 10 min.
I was initially concerned
that radiation of C2, since it is near the top of the spinal column and
near the brain, would expose my brain to radiation. But my radiation oncologist
explained to me how the targeting is done (and the frequencies chosen)
giving sharp margins, and she assured me that my brain would be safe. I
think that was true as I noticed no mental effects at all from the radiation.
(update)
My C1,C2 neck fusion operation
failed, meaning the two vertebrae did not fuse. The bone only grew into
one of the four screws. My surgeon points to the neck radiation I got 18
months earlier to fight the cancer as the reason, saying that radiation
affects the ability of bone to grow. I haven't researched this, but that
is what he tells me.
Staging my multiple myeloma
After the neck operation
and radiation treatments, my cancer was worked up following a full body
set of x-rays and blood work specific for multiple myeloma to asses the
severity of my cancer and to plan for chemo. My numbers and prognosis were
not good. I was told I had stage 3 (of 3) multiple myeloma cancer. This
was based on extensive number of bone lesions found including my pathologic
neck fracture plus my high level of beta2microglobulin,
a key blood molecule used for staging MM. I did a literature search, and
it showed median survival for levels of beta2microglobin above 4.5
mg/L of only 12 months, and my number was 6.9! A sample of my bone marrow
(taken later) showed 70% of the cells were plasma cells, grossly high since
normally only 2-3% of marrow cells are plasma cells. One of my blood proteins,
lambda free light chain, had a density x150 higher than normal! I was consider
'high risk' and was being steered into an aggressive three drug regimen
of chemo drugs.
I told everyone
my goal at that time was to live long enough (about a year) to see Billy
Elliot again when it came to the Boston area in the fall (early Oct) of
2015. Responding to chemo pretty well, so I make it, so I have added a
new goal a little further out: To live long enough to see one of my favorite
shows again, the romantic musical 'She Loves Me', returning to Broadway
after 22 years. It's on the Roundabout Theater Company schedule for sometime
in early 2016 (no dates yet).
I now understand that the
very short survival times in the literature associated with high levels
of beta2microglobulin levels reflects (by necessity) historical data, and
this can be misleading where treatments options and survival rates have
improved a lot in the last 10-15 years as been the case with MM.
I resisted starting chemo until
I heard back on how my DNA tests, which take weeks because they are done
on my DNA sent to the Mayo Clinic came in, even though I was told by one
of the hospital's hematology oncologists one time to 'forget the DNA tests'.
Wrong!! I had done the right thing. When the DNA results came in, my doctor
was singing a different tune. Finally I had a little luck, I had the one
DNA mutation (of seven) that on average leads to a better response to chemo,
so overnight my risk dropped from 'high' to 'standard', and I was now being
steered to the most common multiple myeloma chemo combo of recent years
consisting of two drugs in pill form: revlimid and dexamethasone. The staging
process after the radiation took about a month so was not until the last
week of nov, about nine weeks after my diagnosis, that chemo began.
Chemo options
At this point in the narrative my memory
failed me a little. Reviewing my doctor(s) contemporaneous notes, I find
that before my DNA (cytogenic) results came in a substitute hematologist
(my regular oncologist was out sick that day) did indeed recommend I start
an aggressive chemo regimen called CyBorD: cyclophosphamide, bortezomib
(Velcade), and dexamethasone. But, but later when my favorable (hyperdiploidy)
DNA results came in dropping my risk to 'standard', my regular oncologist
notes show she gave me the the option of choosing between the three
drug CyBorD regimen (one of them injected) or the two drug dex/revlimid
(both pills) regimen. I asked for 48 hours to think about it. I opted for
quality of life over aggressive and chose dex/rev. I follow the philosophy
KISS (keep it simple stupid). Also I knew dex/rev had a good track record,
was the regimen that 50% of the patients would get in the clinical trial
I was offered, and at the time had been described by my doctor as 'standard'
chemo for multiple myeloma. With hindsite I am surprised that the option
of adding velcade to dex/rev wasn't mentioned, since I now find that RVD
(revlimid, velcade, dexamethasone) is the chomo regimen being used in a
phase 3 clinical trial for newly diagnosed MM patients.
FDA approval restrictions (update)
I may have discovered why
RVD was not recommended (or mentioned) to me as a chemo option. Reading
one of the ongoing phase 3 clinical trial description comparing RVD vs
[RVD + transplant] it says that while all three drugs are approved by the
FDA to treat MM, this particular combination has not approved for
treating newly diagnosed MM patients. The corollary being one of
the goals of the study is to obtain the FDA approval.
This drives home an issue
I have noticed, but probably not fully appreciated. The various treatment
drugs for MM that are approved by the FDA come with various restrictions.
They may be for MM patients who have had some prior other treatment, or
for MM patients whose disease has come back (refractory MM). For example
(according to a Celgene
press announcement) dex/rev was FDA approved in 2006 for MM patients
who have had at least one other therapy. Well that very likely included
me because I had radiation prior to beginning chemo. Only recently, in
Feb 2015 which is after I started chemo, was FDA dex/rev approval expanded
to cover newly diagnosed MM patients. It's a good bet that doctors, while
they don't say so, are in some way obligated or under pressure (fear?)
to recommend FDA approved chemo regimens. In fact the Celgene announcement
includes this quote:
"The approval of
REVLIMID as an option for use in all patients with multiple myeloma represents
a new paradigm in the management of this disease," said Kenneth Anderson,
M.D., Director, Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center, Dana-Farber/Brigham
and Women's Cancer Center. "We now have clinical evidence demonstrating
that starting and keeping newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients on
REVLIMID significantly improves progression-free survival."
Unlike other cancers where say
after a tumor is removed a person might have chemo for a month or two,
chemo for multiple myeloma (without a stem cell transplant) means essentially
staying on chemo forever, meaning I will likely be on chemo until
it stops working, which it invariably will. Thus side effects of the chemo,
as well of course as its effectiveness, are an important consideration,
it's a balancing act.
"The recommended
starting dose of REVLIMID is 25 mg orally once daily on Days 1-21 of repeated
28-day cycles in combination with
dexamethasone. Dexamethasone dosing is typically 40 mg (ten 4 mg pills
on single day!) taken on days 1,8,15,22 of the cycle. For patients > 75
years old, the starting dose of dexamethasone may be reduced. Treatment
should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity."
(Celgene revlimid proscribing sheet)
For historical reasons the
(obviously) high dose (10 x 4 mg/pill) of 40 mg/wk dexamethasone is referred
to as 'low dose'. The historical reason is that in years prior dexamethasone
as part of MM treatment was given in much higher doses! (The description
of 40 mg/wk (10 pills to be taken in a single day) as 'low dose' I found
to be absurd when I first came across it in the MM clinical trial I was
offered.)
Why revlimid or dexamethasone
works, or any of the chemo drugs for multiple myeloma, does not appear
to be well understood. These drugs mess around with the immune system changing
several pathways. Twenty-five years ago it was discovered clinically, and
essentially by accident, that thalidomide had anti-inflammatory properties
that was effective against some diseases, and later work showed it had
anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities properties too, so that prompted
work to develop variants like lenalidomide (revlimid) which would be better
tolerated and more effective. I know from reading some papers that the
reason that the chemo drugs stop working in multiple myeloma is also not
well understood and is an area of active research.
Revlimid risks
Revlimid (lenalidomide)
made by Celgene is a variant of an old drug, thalidomide. Celgene calls
revlimid a "thalidomide analogue" and as given for multiple myeloma has
real risks. The odds of it killing you are something like 3%-4%/year! There
are two big risk. One, it can cause a deep blood clot, which if it travels
to the heart is a heart attack or to the brain a stroke. To combat this
risk I am taking a full dose (375 mg) of aspirin every day a 'blood thinner'
meaning it makes platelets less likely to stick together. In one clincal
study 18 of 145 surviving patients (12.5%) got a secondary cancer in
four years on revlimid maintenance (10 mg).
"REVLIMID has demonstrated
a significantly increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary
embolism (PE), as well as
risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with multiple
myeloma who were treated with REVLIMID and dexamethasone
therapy." (Celgene revlimid proscribing sheet)
Two, revlimid can give you another
cancer! Some clinical trials involving revlimid have been stopped because
the data showed those getting revlimid had an excess of new cancers, which
was attributed to the revlimid. Presumably both of these risks are (to
some extent) dose and length dependent, but data on this is hard to come
by. I have been able to pry little about these risks from my doctors.
Decisions I had to make before chemo began
There were three clinical decisions
up front that I had to make. Decisions which due to the complexity of multiple
myeloma and all the various treatment options are difficult to get your
arms around in the short time in which you are asked to decide.
Did I want a stem
cell replacement?
One, was whether I might
at some point want a total stem cell replacement. I was told this was important
to decide up front because it affected the types of chemo that could be
used. At that point I had had enough of hospitals, and when I found out
a stem cell replacement meant a three week stay in the hospital, a long
recovery period and was fraught with risk, and was not a cure only a possible
life extension, I said no. Reinforcing that was I was told that until recently
people my age didn't qualify for a stem cell replacement, but people older
than me were now getting them. Keep it simple stupid is my motto. I preferred
a less aggressive treatment, perhaps not living as long, but hopefully
with a higher quality of life. If I was younger, I might have looked at
this differently, but at my age I found this an easy decision to make,
and have not wavered since, though I will reassess if facts change.
Revlimid does not exclude stem cell transplant
"The other reason it is important
to have a discussion at the beginning about the possibility an autologous
stem cell transplant is that it determines which chemotherapy drugs will
make up the initial treatment. Alkeran (melphalan) damages stem cells making
collection difficult or impossible. Thus, patients who elect to have stem
cells collected and stored are frequently treated with a Thalomid (thalidomide)-based
regimen that does not include Alkeran. "
Did
I want to join a chemo clinical trial for new oral botzezomib added to
rev/dex?
The second decision I had
to make up front was whether I wanted to join a multiple myeloma clinical
trial I qualified for that the hospital was offering. Lahey is a teaching
hospital for Tuft medical school. I read the multi-page paperwork on the
clinical trial I was given. This was a phase 3, double blind, placebo study
comparing a new triple multiple myeloma chemo combo against a standard
double multiple myeloma chemo treatment, which was in fact revlimid and
dexamethasone both in pill form taken daily at home. The study was evaluating
the effectiveness of adding a 3rd pill, a newly developed pill form of
an older injectable drug (velcade), generic name Ixazomib, by the manuf
of velcade, Millennium Pharmaceuticals. (update --- In Nov 2015 the proteasome
inhibitor pill that was the subject of this trial, now called Ninlaro,
was approved for sale by FDA.)
I really didn't like the
idea that I wouldn't know whether my side effects would be due to two or
three drugs, that the protocol was rigid (could be changed only by dropping
out of the trial) and various other restrictions. After some thought, I
found this also an easy decision to make, and I said no to the trial, even
though its expensive chemo drugs might have been provided free? Nope, I
rechecked the trial documents and only the new pill is provided free. The
cost of the revlimid "will be billed to you or your insurance carrier".
Yikes! Nice guys. Of course they omit that the cost of the revlimid is
10k/month! How do they ever get people to sign up for these clinical trials?
(I later found out that Lahey withdrew from the clinical trial I was offered.
What they couldn't get anyone to sign up?)
** I now see another issue,
which is finessed in the clinical trial paperwork. There's aparently no
maintanence. The dose of revlimid remains at 25 mg for years (7 years says
the paperwork), or until the discease progresses. This has got to increase
the risk of secondary cancers. My doctor never mentioned this issue to
me!
Choosing a chemo regimen
The 3rd decision, which I discussed
above, was choosing between an aggressive three drug chemo regimen that
included a general anti-cancer drug (cyclophosphamide) and an injectable
drug (velcade) or to opt for a two drug regimen in pill form (dex/rev --
dexamethasone and revlimid). I liked the idea of two drugs over three for
fewer side effects, and pills over hospital trips ever few days for injections,
so I chose dex/rev.
Chemo cost and insurance
The first shock about the
chemo was that Celgene's patented Revlimid is an extremely expensive tier
5 drug that costs about 500 dollars a pill! That's a 500 dollars a day
for 21 day of a 28 day cycle, or about 10k per month, about 120k/yr. In
contrast the other chemo pill, dexamethasone, a drug that mimics the function
of natural corticosteroid hormones regulated by the adrenal gland, was
cheap about 14 dollars bought 40 pills for the 28 day cycle. The weird
thing about dexamethasone is that largest dose made is 4 mg, but the usual
rev/dex multiple myeloma protocol is for 40 mg to taken on single day every
week, that's ten pills on that day. I read there were lots of options here,
so I asked my doctor if I could take five pills on two consecutive days
instead and she said OK.
500 dollar a day chemo
pill!
The huge cost of my chemo
immediately became an issue. Revlimid pills cost about 500 dollars each,
over 10k/month, over 120k/yr. I was a basic medicare patient with medicare
A (hospital) and B (physician and outpatient) coverage. Due to a quirk
in the law the standard form of chemo under consideration was not covered
by part A or B since it was available in pill only form. Injectable chemo,
because they occur in the hospital are covered under part B. The pills
would be covered under optional part D of medicare available only from
insurance companies, but I assumed that because I was already diagnosed
with cancer that buying part D coverage now would be impossible. This turned
out to be wrong, an insurance company has to accept you at standard rates,
regardless of your health status, but it took me a while to find this out.
I really fault my haematology
oncologist for no support here. In spite of several extended discussions
of the cost of revlimid with my doctor and her knowing that I only had
medicare part A and B coverage (no supplemental coverage), and my telling
her that my income was too high to qualify for any supplemental programs
to help pay for the cost of the drug, she refused to discuss cost insurance.
All she had to do was drop a hint, a single sentence like 'looking into
buying part D drug coverage, they have to accept you', but nothing. On
top of this by luck these these drug decisions were being made during the
end of the calendar year, which is the short open enrolment period of part
D.
Signing up
for medicare Part D drug plan
Doing online research I eventually
found out that if I applied for part D, the insurance company had to accept
me, and that the cost of the part D was for me negligible since I was facing
drug costs over a hundred thousands of dollars a year! (I don't think this
has anything to do with Obamacare, I think it was built into Part D when
it was established under Bush 2.) So I did my homework to pick an insurance
company and signed up with Cigna for part D drug coverage for 2015 (beginning
Jan 1, 2015). My chemo had began mid Nov 2014, about eight weeks after
my diagnosis (plus neck operation and radiation), and sure enough I found
it costs me out of pocket over ten thousand dollars for that first 28 day
cycle of revlimid. The insurance company's pharmacy (Cigna Speciality Pharmacy)
was a real bastard about payment (surprise!) demanding payment in full
before they would deliver the pills, even though as sole supplier they
had me totally over a barrel. I had the 10k in my checking account, but
(hidden) daily card limits got tripped, and it turned out to be a real
hassle trying to get the 10k delivered to them quickly so I could start
my chemo on schedule. After hours on the phone with the bank and Cigna,
Cigna eventually agreed to ship the pills after charging my debit card
8,999, just under its 9k daily limit, later adding a second charge to the
card for the balance. Nice guys....
You have got to be freaking kidding me
Some background, ever since
I started chemo in late 2014 I have been getting my 500/pill Revlimid chemo
pills home delivered from Cigna Speciality Pharmacy. I didn't actively
chose this pharmacy, like much in medicine the selection occurred by default.
I told my doctor and hospital that Cigna was my Part D insurer so every
month they forward my prescription there, and Cigna Speciality Pharmacy
calls me to arrange home delivery (I need to be home to sign for the pills)
and payment. I have been satisfied with this Cigna pharmacy as they reliably
deliver (by air) overnight, and with drugs like Revlimid that are patent
protected with a single supplier there's no incentive to dp price shopping.
It's a year later and I get
a letter from Cigna that says, "In 2016 Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy will
not
be a preferred network pharmacy". Say what!! The insurance company
Cigna has their own in-house pharmacy, yet as of 2016 when you buy Part
D coverage from Cigna their own pharmacy is not in the preferred network.
You have got to be kidding me. They advise switching to Walmart Home Delivery,
which they say is in the preferred network for my plan. (And note letter
about higher 2016 costs if you buy stick with them arrived Jan 22, 2016!)
Yikes, insurance companies... Luckily the letter has a caveat that applies
to me, saying if you take a tier 5 drug (Revlimid as a super expensive
cancer drug is a tier 5 drug), then you pay the same percentage of the
cost regardless of the pharmacy you chose.
(update --- What I didn't recognize
at the time was I had lucked out by starting (pill based) chemo during
the seven week Part D open enrollment period (oct 7 to dec 15). That's
why I was able to get in when I called.)
Delaying 2nd chemo cycle for Part D insurance to cut in
My second 28 day chemo cycle was
scheduled to start about ten days before Jan 1 when my part D drug coverage
would cut in, so my doctor suggested the start of cycle two be delayed
for a few days (turned out to be 10 days) until it cut in, thus saving
me from another 10k drug charge.
Part D coverage
Part D covers only a portion
of drugs costs and has a very complicated three part coverage formula with
a donut hole. My jan chemo out of pocket costs were about 4k, but because
revlimid is so freaking expensive, I was through the donut hole before
the month was over. For the next 11 months of 2015 I am in what is called
the 'catastrophic' phase of Part D where I pay only 5% of the retail cost,
or about 500/month, or 5.5k for the remaining 11 months of the year. Bottom
line by joining part D (drug coverage) I will cut my total out of pocket
drug costs in 2015 by something like a factor of twelve. My out of pocket
costs for the entire 2015 year, including that of plan D itself, will be
less than 10k I paid Cigna for revlimid in Nov 2014 without part D coverage.
DNA variations -- cytogetics
There are about eight known
variations in DNA that have an influence on the agressiveness of multiple
myeloma and the responsiveness to chemo. Only one is really positive (hyperdiploidy),
and here I had a little luck. I have the hyperdiploidy variation in my
DNA. I also have the negative factor Deletion 13, but my oncologist
says clinical practice shows the positive result overrides the negative
one. This test (FISH -- fluorescence in situ hybridization)) takes 2-3
weeks, and I think it was done by sending my marrow to the Mayo clinic.
The Mayo clinic has a cytogenetics laboratory, which (they say) is a 'leader
in the field of cytogenetics'. In the FISH analysis DNA probes are labeled
with different colored fluorescent tags to visualize one or more specific
regions of the genome.
From the table below I first
thought the hyperdiploid (not hypodiploid) variation was rare, but
the estimate is about half of multiple myeloma patients have this variation,
but of course nothing is ever simple. One paper I read says they see four
sub-populations in the hyperdiploid category with a 4:1 difference between
them in median survival (2.5 years to 10 years).
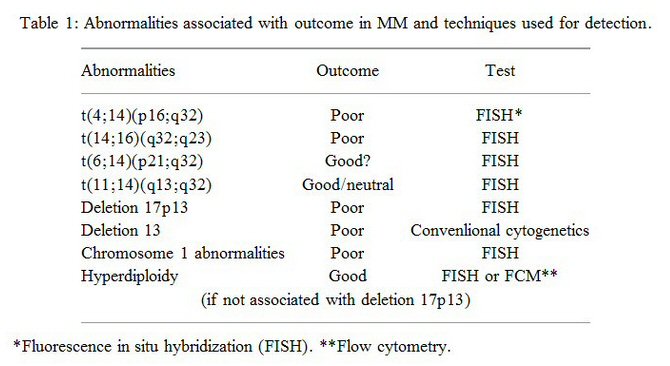
I have the hyperdiploidy variation (and deletion 13)
(Notice the 'poor' outcome for deletion 13 is when measured not
with Fish, but with the less sensitive conventional test.)
(my Mayo clinic cytogenetics results on my marrow are here)
Prior to my cytogenetics
test results becoming available (test takes several weeks) I was considered
'high risk' and in early Nov 2014 was being steered by my doctors toward
an agressive chemo regimen with standard anti-cancer drugs, but I resisted
starting chemo until the test results became available. When they did arrive
and I was found to be hyperdiploidy, there was a dramatic turn around.
My risk dropped to 'standard risk', and the recommended chemo was now the
standard mulitple myeloma targeted chemo of revlimid and dexamethasone.
I agreed and in late Nov 2014 I began by first cycle of dex/rev chemo.
(update, May 2015) I finally
pried the written report from the Mayo Clinic done on my extracted bone
from my doctor and have posted its key section in the Appendix. It details
which chromosones I have extra copies of (my good hyperdiploidy variation)
and maybe not so good chromosone 13 deletion where I have only one copy
instead of the usual two. The Mayo clinic used the Fish test.
M-spike blood test
To assess how well the dex/rev
chemo is working my doctors focus on one number in my blood, the mono-clonal
spike (or M-spike). Blood plasma cells turn into a wide range of antibody
cells, whose atomic weights that when plotted form a smooth curve. Because
one particular marrow cell that makes plasma cells has gone cancerous and
wildly clones itself, there is in my blood a huge excess of anti-bodies
(proteins) of one particular atomic weight, which shows up as a large spike
riding on top of the normal smooth curve of anti-body weights. A special
blood test is needed to spread out (spacially) the anti-bodies by atomic
weight. This test, called electrophoresis test, forces charged anti-bodies
to diffuse through an agarose gel by driving them with an E field (voltage).
The smaller the molecule the faster it can diffuse, so this test spreads
out the anti-bodies by atomic weight. [The force driving the diffusion
(F = qE) is also depends on the
charge of the anti-bodies, but the
net charge on biological molecules is affected by the surrounding medium's
ph
and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or
loss, respectively, of protons (H+) from the molecules' double H+/OH- charge.]
Free light
chains --- supplement to M-spike
When reading the postings
of other MM patients, I found some never mentioned an M-spike. This initially
confused me, but then I found out that about 20% (one reference) of MM
patients don't have a significant M-spike, so in these patients to track
the cancer doctors look to the free light chains. The difference between
them is the M-spike is the full monoclonal anti-body, whereas a monoclonal
light chain is only a portion of the anti-body.
Leading indicator?
I have included this marker (kappa/lambda
ratio) on the left side of my numbers table. One virtue it may have
over the M-spike is that it appears to respond more rapidly to cancer levels.
As such it might be a leading indicator for changes in cancer levels. Notice
in my numbers my lambda free light chain value dropped 98% [379 => 8] with
my first rev/dex chemo cycle vs a 66% reduction in M-spike! And the kappa/lamda
free light chain ratio dropped into the normal range at the end of two
cyles of rev/dex, while the M-spike was still high (0.99 g/dL).
My numbers shows the strength
and weakness of this free light chain marker. It moves fast, but it likely
loses it's usefullness when cancer levels are low because it doesn't go
to zero. It has a residual normal value with a wide range (0.26 - 1.65).
In contrast with a known time lag of months the M-spike will eventually
(maybe in 6 months or so) settle toward zero if all clonal cells are killed
off, so it looks to me that it should be much better than the free light
chains for measuring the depth of response to chemo. My guess is that this
is why it is the preferred MM tracker, not to mention that it has a much
longer track record, free light chain measurements, which use a new laser
scatter instrument, and only got approved within the last ten years.
I found a 2009
Mayo Clinic paper that says the recent introduction of quanitative
assays of free light chains has made it a useful cancer tracking indication,
saying "Surprisingly, free light chain quantification has also proved to
be prognostic ... for survival in MM". The paper also says that M-spike
is preferred over free light chain, and it cautions there are some (2009)
concerns that lambda coverage may not be complete. The paper says several
studies have shown that adding serum free light chain assays to M-spike
testing eliminates the need to screen urine for free light chains, which
because they are small pass through the kidneys readily. This point is
relevant to me because my monthly blood screening have routinely included
free light chain assays, but my doctors have never tested my urine.
-- Free light chain quantification
has also proved to be prognostic ... for survival in MM
-- Increased skewing of the ratio
between kappa and lambda light chains after a MM patient has been treated
is an indication of disease recurrence (Wikipedia
-- nephelometry)
-- FLCs (free light chains) are
thought to be associated with imbalances in heavy and light chain production
in monoclonal plasma cell populations
-- Although several disorders lead
to abnormal concentrations of kappa and lambda FLC, the FLC Kappa/Lambda
ratio appears to remain within the reference range except in the monoclonal
plasma cell proliferative disorders. (translation: only plama cancers appear
to affect the kappa/lambda ratio, so it is a good test to identify blood
plasma cancers)
-- The use of capillary electrophoresis
for SPEP (serum protein electrophoresis) and nephelometry for FLC (free
light chain) quantification would essentially automate screening for monoclonal
gammopathies. (In contrast "immunofixation electrophoresis" is described
as being costly because it must be done manually.)
** -- With treatment induced plasma cell kill, free
light chain concentrations (which have a lifetime measured in hours) decrease
rapidly and precipitously. In contrast the longer half live of intact immunoglobins
(measurable in weeks) leads to a long lag-time in the assessment of treatment
response. (From LabCorp
a manufacturer of blood test equipment)
-- In a 2005 report from
Sloan Kettering normalization of the free light chain ratio after one or
two cycle of chemo in MM patients was found to be significantly associated
with subsequent complete or near complete response as assessed many cycles
later using measurment of intact immunoglobins (M-spike). (This is consistent
with my response.)
**Free
light chains are a true leading indicator
Above is the key to why free light
chains are indeed a true leading indicator. It's due to the difference
in
the lifetimes in the blood of the light chains (hours) vs the intact monoclonal
proteins (weeks). This long lifetime of weeks for monoclonal protein explains
why even if the plasma cells are rapidly killed off by chemo, the concentrations
in the blood of intact clonal cells will fall slowly over several monthly
cycles. Whereas free light chains, with the caveat that they are clearly
abnormal, respond so quickly (hours) that they accurately track the concentrations
of clonal cells. So looking at my numbers rev/dex killed off most (98%)
of the marrow cancer cells in the 1st cycle and polished off most of the
remaining cancer cells by the end of cycle #2! (Well, this is if the response
is linear and it may not be.)
This allows the lifetime
of M-spike proteins in my blood to be estimated from the shape of my M-spike
curve and is probably 3-4 weeks, which is consistent with what I read.
At a 2015 Binding site MM
symposia a talk says, "Mark Drayson demonstrated that the half-life of
free light chains is measured in hours, whereas the half-life of
intact immunoglobulins is approximately 20-30 days. This means that free
light chain detection is able to give a much faster indication of response
to treatment than measurement of intact immunoglobulins." (video of the
15 min talk here)
A half-life of a month for M-spike would mean it would take 5 months for
a factor of x32 reduction and 7 months for a factor of x128 reduction.
These are times roughly comperable with what my data shows. However, viewing
the talk I think he said this M-spike lifetime is without dexamethasone.
With dexamethasone the M-spike time constant is reducted to 7 to 10 days,
which is totally inconsistent with my plotted data.
**Excess
free light chains damage the kidneys
Wikipedia has a page on
'serum free light chain measurement'. It discusses that discusses ''myeloma
kidney' (or Cast Nephropathy), where a component of urine binds to the
free light chains forming a precipitate that blocks the small tubes of
the kidneys. The referenced paper says, however, this is is a "potentially
reversible
cause of chronic renal failure." This condition is also discussed on the
Binding
site, which makes instruments to measure free light chains. They show
that levels of 'clonal' free light chains > 50 mg/dL (500 mg/L) are
potentially dangerous to the kidneys and require treatment. (My pre-chemo
free light chain was far in excess of this threshold at 379 mg/dL.)
My rising kidney numbers (update 2/24/16) (10/24/16)
My cretinine bounces around between 1.1 to 1.3. Excluding the time just
after diagnosis it had hit 1.4 only once in feb, but today (10/24/16) eight
months ago, but today (10/24/16) it hit 1.4 again.
---------------
As I see my pattern of rising
(but still low) numbers of the last few months, I am beginning to be concerned
about my kidneys. About two weeks ago my Dana Farber doctor said my kidneys
were not too bad, but not the best, and yesterday my infusion nurse looking
at my latest numbers said pretty much the same thing. Over the past 16
months of chemo my creatinine has bounced around, but alway remaining in
the normal range (.6 to 1.3 mg/dL). Two weeks ago (at Dana labs) for the
first time it was (barely) out of the normal range at 1.34 mg/dL. My latest
value from Lahey labs this week is 1.4. mg/dL. The last time I was 1.4
mg/dL was before I started chemo, and my GP referred to this level as 'renal
insufficiency'. Wikipedia (kidney disease), says "The process of most kidney
diseases is renal Insufficiency, renal failure, and then uremia." My highest
creatinine was when I was first diagnosed in the hospital at 1.7 mg/dL.
Another blood monitor of
kidney function the doctors call creatine clearance, but it appears in
blood work as GFR (see below), and it has gone from normal (> 60) to 55
a month ago, to 52 two weeks ago to 50 this week.
Creatinine clearance vs GFR
With regard to the to blood
parameters that track the health of the kidney I'm (or was) a little confused.
There are two kidney related parameters, 'creatinine' and 'creatinine clearance'.
Creatinine is a density in the blood of a waste product from the muscles
that the kidneys clear. 'Creatinine clearance' (CrCl) is defined as a measure
of the rate that the kidneys are able to clear creatinine. (How this is
measured I don't have a clue.) Both my Dana doctor and nurse mentioned
"creatinine" and "creatinine clearance" while talking about the health
of my kidneys. Creatinine in included in my blood work, but there is no
parameter in blood work given to patients called 'creatinine clearance',
or ''CrCl' (I see 'ClCr' used in literature), which is the abbreviation
I saw looking over a nurse shoulder at her screen.
I am now beginning to suspect
that 'creatinine clearance' is in my blood work (or a related value), but
under a different name. In Lahey blood work it's called GFR (EGFR on Dana
blood work). Wikipedia (renal function) says "Glomerular filtration rate
(GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid (blood) through the kidneys.
Creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that
is cleared of creatinine per unit time (mL/min) and is a useful measure
for approximating the GFR." According to Wikipedia 'eGFR', which
Dana uses, is a an estimated (or calculated) value, but what's actually
being measured is not clear. How can a single blood test measure a rate?
(It
can't, see below.) Lahey's GFR must be the same as Dana's eGFR because
it has got the same normal range.
GFR is 'calulated' from creatinine
OK, got it. 'GFR' (mL/min) in blood
work is not a real measured value. It is just measured 'creatinine'
scaled (engineers would say 'normalized') for race, sex, age, and weight.
The higher the measured creatinine, then the lower will be the calculated
creatinine clearance. (There is a precise test for creatinine clearance
which requires urinating into a jug for 24 hours, and then testing the
urine for creatinine. This works because almost no creatinine is broken
down and recycled by the kidneys, all the creatinine it extracts from the
blood is excreted into the urine. )
The time I waste with trying
to understand confusion like this, which is due to a lack of standards
and because doctors use different names from those used on blood work,
is a testament to the medical community basically not giving a shit about
informing patients.
Stages of chronic kidney disease
The National
Kidney Foundation gives the following interpretation of GFR, which
they describe as "best test to measure your level of kidney function and
determine your stage of kidney disease". (But of course it's not a test.
When determined from blood work, GFR is just creatinine normalized for
age, race, etc.) In my case for creatinine 1.2 and lower Lahey labs
just reports GFR >60. When after 15 months of chemo, my creatinine broke
out of the range of 1.1 to 1.3 hitting 1.4, the reported GFR was 50 (mild
to moderate loss of kidney function).
Diagnostic criteria for chronic
kidney disease is GFR < 60 for three months or (if GFR > 60) high levels
of albumin in urine. A urine test for kidney disease is standard. They
give another table showing that with GFR between 30 to 60 risk can be moderate,
high or very high depending on the level of albumin in urine. I have
never had my urine tested. (ask about this test)
|
stage of chronic kidney disease
|
description
|
GFR
mL/min
(ClCr)
|
|
1
|
Kidney damage with normal kidney function
|
>90
|
|
2
|
Kidney damage with mild loss of kidney function
|
89 to 60
|
|
3a
|
Mild to moderate loss of kidney function
|
59 to 44
|
|
3b
|
Moderate to severe loss of kidney functionModerate to severe loss
of kidney function
|
44 to 30
|
|
4
|
Severe loss of kidney function
|
29 to 15
|
|
5
|
Kidney failure
|
<15
|
pretty sure 'renal function' (mL/min) in literature is same
as GFR
Their site has the formula
for converting from creatinine to GFR. Playing with it I can see the big
variables are race and gender, with age secondary. They give several standards,
and I see that of of late feb 2016 Lahey has just changed their standard
from CKD-EPI to MDRD. When I plug in my numbers, here the what their (MDRD)
formula translates creatinine to GFR:
1.0 creatinine GFR = 73
1.1 creatinine GFR = 65
1.2 creatinine GFR = 59
1.3 creatinine GFR = 54
1.4 creatinine GFR = 50
(agrees with Lahey)
1.5 creatinine GFR = 46
1.6 creatinine GFR = 43
1.7 creatinine GFR = 40
1.8 creatinine GFR = 37
1.9 creatinine GFR = 35
2.0 creatinine GFR = 33
2.1 creatinine GFR = 31
2.2 creatinine GFR = 29
Nephelometry
Almost everyone has seen how a
shaft of sunlight in a dark room can show tiny dust particles suspended
in the air. Nephelometry is an automated version of this. It allows the
density of small suspended particles in a fluid to be measured by shining
a laser though the fluid and looking for reflected light to the side. The
brightness of the reflected light is a measure of the particle density.
This is a relatively new technique and is now widely used to measure pollutants
in air. It can be considered a measure of turbidity of a fluid. (Nephel
is derived from greek and means cloud.)
In blood analysis nephelometry
is used to measure of the concentration of proteins in blood plasma. Plasma
is blood with all the cells removed. This technique is exquisitely sensitive.
Whereas full immuglobins, like the M-spike, are given in units of g/dL,
free light chains are given in units of mg/dL. I read the threshold is
around 0.3 mg/dL. Calibration is used to compensate for shape, color and
reflectivity of various particles. The type of protein (M, G, or A) seem
to be detected by adding various anti-bodies as reagents. (Don't know the
details, but even large protein molecules are tiny, so prior to the test
some reactant may be added to react with the proteins.)
Protein electrophoresis
Most MM patients show a
tight high concentration (bar) in an abnormal location when proteins are
spread out by diffusion in a protein serum electrophoresis test The amount
material in this bar is measured (my guess is by measuring its brightness
in reflected ultraviolet light) is taken as a proxy for the amount of cancer
cells in the body's bone marrow. The total material of this bar is the
'monoclonal peak quant' (or M-spike) value in blood work. Here's a picture
I found online showing a multiple myeloma patient's anti-bodies spread
out, and the monoclonal M-spike is clearly visible. There's a bar (at the
other end) to which consists of albumin that makes up a little more than
half of normal blood protein.
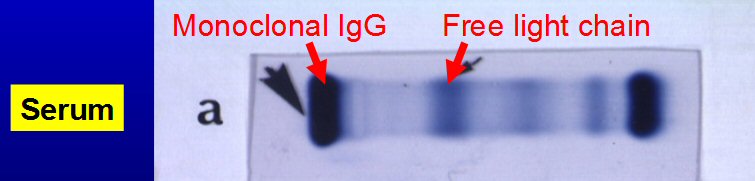
Multiple myeloma monoclomal peak quant band (left)
in output of protein electrophoresis test done on blood serum.
(protein migration here is right to left,
so the spike on right is probably albumin, yup)
Protein electrophoresis
-- "Protein electrophoresis
separates proteins based on their size and electrical charge. This forms
a characteristic pattern of bands of different widths and intensities on
a test media and reflects the mixture of proteins present in the body fluid
evaluated. The pattern is divided into five fractions, called albumin,
alpha 1, alpha 2, beta, and gamma. When a health practitioner is investigating
symptoms that suggest multiple myeloma, such as bone pain, anemia, fatigue,
unexplained fractures, or recurrent infections, to look for the presence
of a characteristic band (monoclonal immunoglobulin) in the beta or gamma
region; if a sharp band is seen, its identity as a monoclonal immunoglobulin
is typically confirmed by immunofixation electrophoresis, which by use
of anti-bodies determines which type of antibody (immunoglobulin) is present."
A review of my blood work (Monoclonal
profile serum panel) for the last seven months shows 'immunofixation' as
a follow up to protein electrophoresis was done only one time (end of 1st
cycle). Most monthly blood tests note "Immunofixation not performed" and
"No change in electrophoretic pattern since previous". This test uses antigens
to identify which anti-bodies make up the M-spike.
Dual M-spikes
When I reviewed my blood
work, I was surprised to find that in the early months of chemo I had two
measurable M-spikes: IgG lamda (initially 5.31 g/dL) and IgG kappa (0.05
g/dL). The meaning of this I don't know, because my doctors never mentioned
it, and I haven't researched it. It probably means nothing but who knows.
The IgG kapp spike is tiny, only about 1% of the IgG lamda spike. Curiously
there is no mention of a kappa M-spike in my baseline blood work, but after
the first cycle it is identified with a reading of 0.05 g/dL, 0.06 g/dL
after second cycle, and after third cycle it is identifed but marked 'too
small to quantitate'. It doesn't show up in subsequent cycles.
M-spike test threshold
One useful thing this small
M-spike does is show the threshold of the M-spike test (as done at Lahey)
is at least 0.05 g/dL. This is pretty consistent with what I have read
is the limit of the test. 0.05 g/dl is about four times less than my current
0.19 g/dL of my lamda IgG M-spike. All my oncologist had to say about the
M-spike test threshold is she has seen levels as low as 0.1 g/dl, but of
course my own blood record shows (kappa) monocloonal readings at one half
of this level.
How much increase in M-spike would be a problem?
Now I am in the decreasing
phase of my monoclonal M-spike, but as time goes on the cancer is going
to come back and it's going to rise. The obvious question is, how much
increase in M-spike would signify that the cancer is returning and
how much variation should be considered noise? A reference point is what
MM clinical trial use to define 'progression' of the cancer. That number
is an increase of 0.5 g/dl in the M-spike from the minimum level
achieved (see appendix for details). Say 0.24 is as low as my M-spike gets,
then an M-spike 0.5 g/dl higher, which is 0.74 g/dl, would trip a threshold
in a clinical trial and signal an end to TTP (time to progression) of the
disease.
To put this in perspective
my blood cancer level at the end of the fifth cycle has been driven down
by the chemo to 95.5% from my initial baseline (5.31 g/dl), but if, or
when, the level rises to (just) 14% (0.74/5.31 = 0.14) of my baseline that
is a clinical indication that the cancer is "progressing", i.e. coming
back. Or from another point of view if my blood cancer levels increase
from 96.5% down to (still) 86% down below pre-chemo that is a clinical
indication that my cancer is 'progressing', it is becoming immune to the
maintenance chemo.
Is
kappa or lambda free light chain a leading indicator?
The table of my numbers
above shows something interesting. Prior to chemo there were
two
markers
in my blood for my cancer: M-spike and lambda (or kappa) free light chain
blood. The M-spike a clonal immunoglobulin, a large Y shaped protein with
dual heavy and light chains. Normally it is not present at all, so its
''normal range' is effectively zero. Lambda and kappa free light chains
in blood are just fragments of immuglobins and both are always present
in small quantities with a normal range of [0.33 - 1.94 mg/dL (kappa)]
and [0.57 - 2.63 mg/dL (lambda)], and their ratio, which being a ratio
is less sensitive to test errors and variability, has a normal range of
[kappa/lamda 0.26 - 1.65]. A MM patient at diagnosis will typically
have both a large M-spike and one highly elevated free light chain. Since
the elevated free light chain can be either kappa or lambda type, a marker
for MM is a kappa/lamda free light chain ratio that is either sky high
(kappa clones) or nearly zero (lambda clones). I have a lambda cancer,
so my ratio prior to chemo was super low, nearly zero.
My baseline numbers were
M-spike = 5.31 g/dL and lambda 379 mg/dL. The sky high lambda free light
chain making my kappa/lamda ratio < 0.01. (The lambda blood free light
value of 379 value is so off the charts that I doubled checked that its
units are mg/dL in the lab reports.)
Here's what's interesting.
After just two cycles, while my M-spike had dropped about a factor
of five (5.31 => 0.99), my lambda free light chain had dropped by more
than a factor of 100 (379 => 2.74)! This brought my lambda free light chain
to very close to its normal range (0.57 - 2.63 mg/dL), and my kappa/lamda
ratio of 0.52 after two cycles was well within the normal range (0.26 -
1.65). In fact after just one rev/dex cycle my lambda free light
chain had declined 98% (379 => 8.17) giving me a kappa/lamda ratio
of 0.21 pretty close to the normal range [0.26 - 1.65].
This is a very fast and deep
response to rev/dex chemo (at least in my case), so free light chains might
be a good leading indicator going forward looking for signs of relapse.
In fact I saw one poster on the Myeloma Beacon forum recommending just
that.
(update -- I later learned
that the reason for rapid response of free light chains is well understood.
Free light chains have a lifetime in the blood of hours vs weeks for the
M-spike, so a measured 98% reduction in free light chains in the first
cycle probably means about a 98% reduction in clonal cells during the cycle,
because it is the clonal cells that are outputting the free light chains.
The rapid response of free light chains is touted as a clinical advantage
for assessing the effectiveness of chemo by the companies that make insturments
for measuring free light chains.)
This may not true
for everyone. A MM patient (K_Shash),
whose chemo is almost concurrent with mine, has been posting frequently
on Myeloma Beacon forum during his 8 months of RVD chemo. He has a kappa
cancer and began with a kappa free light chain value of 853 mg/dL. (I suspect
he messed up his units, it's more likely 85.3 mg/dL, because he had a kappa/lamda
ratio of 127 (0.26 - 1.65 normal). He had a reduction in his kappa free
light chain of a factor of 98% in three cycles, whereas I had the same
98% reduction in my first cycle. It took him 8 months for his kappa free
light chain to get into the normal range, and his kappa/lamda ratio of
1.74, while close, was still not quite normal (0.26 - 1.65).
Curiously he never mentions
his M-spike and calls the kappa free light chain value his 'main marker'.
In other words instead of focusing on this M-spike value, as my oncologist
does, it appears his oncologist is focusing on the kappa free light chain
value! (research this) One likely explanation may be that some MM patients
don't have an M-spike, so their cancer marker becomes the high free light
chain value. (Other MM patients have the reverse, an abnormal M-spike,
but normal free light chain values. It all depends on the nature of the
chomasoidal damage.)
A company that makes protein
measuring equipment (Freelite)
says 82% of MM patients have a (measurable) M-spike and 96% of MM patients
have abnormal free light chain value.
Another poster reports these
numbers: M-spike 2.16 g/dL, lambda 21 mg/dL, kappa 0.78 mg/dL, kappa/lamda
ratio 0.04. When my M-spike was in the 2 g/dL range (after one cycle),
my kappa/lamda ratio was 0.21, pretty close to the lower end of the normal
range.
Oxygen blood numbers and white blood cells
Prior to chemo my red and
white blood counts were quite a bit below normal. For the first three cycles
of chemo as the cancer decreased my red and white blood counts improved.
Heoglobin went from 30% below normal to well centered in the normal range.
This made sense to me because normal marrow cells should have room to expand
as the number of cancerous marrow cells decreased. But in the 4th cycle
and continuing in the 5th cycle the improvments of my red and white counts
reversed, dropping to the low end of normal at the 4th cycle and 5% below
normal at the 5th cycle. This disturbs me, and I can feel a low red blood
count, my blood has less oxygen carrying capacity. It doesn't take much
of a walk to get me breating hard. My doctors suggests that it's probably
a side effect of the chemo, and a well known side effect of revimid is
anemia, which is a low red blood count.
My initial dose of revlimid
(25 mg) has been maintained through the 5th cycle, and there is a good
chance it will be maintained for a 6th cycle (yup). I now have the OK from
my doctor to experiment with the dose of dexamethasone. If I want, I can
cut its dose from 40 mg/week to 20 mg/week to see if it will take the edge
off its well known side effects that are bothering me, loss of sleep and
a jittery feeling for 2-3 days. Beginning midway through the 5th cycle
I experimented with cutting the dose of dexamethasone in half, 20 mg/wk
(on a single day), and I did feel better, sleeping better and less jittery,
so I plan to continue at 20 mg/wk though the remaining half of the 5th
cycle and (probably) through the 6th cycle. My doctor is suggesting that
dexamethasone will probably not be part of maintenance (just revlimid),
so tapering off the dose now makes sense as the transition to maintenance
is coming up fast, probably
beginning with the 7th cycle.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Living with cancer
Run down (4/2/17)
My quality of life has degraded
a lot in the last couple of months. Nothing hurts, but I am getting completely
run down with episodes of diarrhea and vague belly pain, and most critically
a complete lack of energy and fatigue. Some days I feel OK, but had a run
of bad days. Some days I can hardly keep my eyes open. It's hard to say
what the cause is, but the likely prospect is the pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
I have been on for the last 8 months which appears to have (or may have,
assessment of my lungs continues) damaged my lungs. This chemo has just
ended and begging next week carfilzomib will be swapped out for another
proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro (Velcade in pill form).
I changed chemo three times
in 2016. Pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo begun at the end of June 2016 worked
well for six months, but in early months of 2017 I began to be more and
more limited in my activity by shortness of breath, and the last couple
of months I have felt quiet run down. How I feel varies from day to day.
Some days I feel pretty chipper, but just a few days ago after going out
to lunch I was so exhausted I pretty much napped for the entire day. Diarrhea
and vague admominal distresss comes and goes, which must be handledd with
Immodium and is a pain in the neck. A recent lung functional test (DLCO)
showed my oxygen intake was is half what it should be. A recent pet scan
picked up indicates some unexplained opacities in my right lung. A CT scan
of the lungs next week will hopefully clarify the situation.
For perspective I have an
aggressive cancer. Newly diagnosed MM patients are told you can reasonably
be expected to live 5-6 years. This doesn't apply to me. I am only 2.5
years into my MM treatment (diagnosed in Sept 2014) yet I have been racing
through the chemo options. I get plasmacytomas, soft tumors composed of
plasma cells, that only 5% to 10% of MM get, an indication of the aggressive
nature of my disease. My remissions tend to be less than the median. A
long standing on in my 9th rib and another one behind my left eye that
which has been beaten back with radiation and gives some residual double
vision.
My 1st remission (rev/dex)
is over and lasted about 18 months, My 2nd remission (pom/carfilzomib/dex)
is over and lasted 8 months. My free light chain values are rising (4.55
mg/dL), my M-spike is rising (0.17 g/dL) and a new pet scan should my rib
plasmacytoma has grown 50% (2 cm => 3 cm) in the last 11 weeks. With an
upcoming chemo change next week (pom/Ninlaro/dex) I will be looking for
a 3rd remission. If this doesn't work, and it's sort of a short term experiment
swapping out the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib for the proteasome inhibitor
Ninlaro, chemo will probably be changed to (pom/daratumumab/dex).
This chemo is built around a new humanized monoclonal antibody drug.
--------------------------------------------
Chemo transition
to maintenance (7/13/15)
About two months ago there
was a key change in my treatment. My chemo transitioned to what is called
'maintenance', meaning (some combination of) fewer cancer drugs and/or
lower doses. In my case the change was from [25 mg revlimid (21 of 28 day
cycle) + 40 mg/wk dexamethasone], which I have been on for six cycles (about
six months), to revlimid only at a lower dose [10 mg revlimid (21 of 28
day cycle)].
At the end of six cycles
of 'standard' chemo the key indicator of cancer in my body, monoclonal
spike, which is a measure of the amount of cancerous identical IgG clone
cells in my blood plasma, measured 0.23 g/dl, or about x20 times lower
than the value prior to beginning rev/dex chemo (5.31 g/dl). My chemo induced
95.7% decline is classified as a VGPR (very good partial response), the
threshold of which is > 90% decline. However, my monoclonal spike of 0.23
g/dl was still measurable with the standard electrophoresis test, which
has a threshold somewhere in the range of [0.05 to 0.1 g/dl], so
I did not qualify as having a CR (complete response).
This chemo transition raises
several important questions. One, does continuing to stay on a lower dose
of revlimid chemo indefinitely (maybe years) make sense? Two, what form
should maintenance take? Three, was the transition done at the right time?
In 2015 the first question
is easy to answer. Enough clinical trials have been held over the last
decade to make it relatively clear that continuing to take (some) revlimid,
which is fairly well tolerated, leads to a substantial improvement in 'time
to progression', though the evidence is less clear that it leads to longer
survival time. The clinical trials (as far as I know) provide less than
clear guidelines on the details of the maintenance, so I think there is
clinical judgement (guesswork) here. 10 mg of revlimid appears to be the
preferred maintenance does, though I think at least one clinical trials
from a decade ago may have kept the dose at 25 mg. (I need to spring for
$35 dollars to read this paper and find the details), because they reported
80 of 100 patients on revlimid for several years had a serious reaction.
It is certainly my expectation that a lower dose of revlimid would lead
to a (much) lower probability of its nasty, potentially fatal, 'side effects
(stroke, heart attacks and 2nd cancers!) which at 25 mg affect a few percent
of patients (per year).
My primary hemotological
oncologist originally suggested that maintenance should be 10 mg of revlimid
taken
every day (not 21 out of 28 days). She seemed to say that
when she discussed this with colleague(s) they recommended the revlimid
be 'cycled', meaning given 21 days out of 28. To get a 2nd opinion (prior
to the transition) I had a meeting with another hemotological oncologist
at Lahey and his (firm) suggestion was take it cycled (21 days out of 28).
So this is what I I told my primary oncologist this is what I preferred,
and she gave me no argument. There was no discussion at all (from either
oncologist) as to the rationale for their recommendation, and I (foolishly)
asked few questions. For example, why drop dexamethasone?
Does dexamethasone increase platelet count?
My Zemeta (biphosphate)
infusion nurse recently told me something interesting about dexamethasone.
With my recent transition to maintenance (lowering revlimid dose from 25
mg to 10 mg and dropping dexamethasone) the oxygen carrying components
of my blood (hemoglobin, red blood cell count, etc) which lately have been
quite a bit below normal have started to improve. However, the tranistion
to maintenance seems to have made one blood component, platelets, which
are responsible for blood clotting, worse. During my six months of regular
chemo platelets drifted lower but remained within the normal range (150
- 450). But one month into maintenance and platelets are only 122, quite
a bit below the normal range. I had no idea why this one blood components
seems to have gong into reverse, so it has been bothering me (have had
no chance to discuss this yet with my oncologist).
My infusion nurse today suggested
a possible reason why my platelet count might have gone lower and that
is with the transition to maintenance dexamethasone has been discontinued.
The nurse said some patients with platelet disease take only dexamethasone
as treatment. Very interesting. (I need to research this. Find out if dexamethasone
is sometimes used with 10 mg of revlimid.) If research confirms this, then
perhaps
adding a little dexamethasone (5 to 10 mg/wk) to 10 mg of revlimid for
maintenance might be worth a test. The tradeoff being (at least in my mind)
improved platelet count vs loss of sleep, a well known side effect of dexamethasone
that at 40 mg/wk (and 20 mg/wk) bothered me. I was never given any reason
for it to be discontinued by my doctor. In fact I have never been given
any explanation by my doctor of the role dexamethaone serverd, nor have
I found any good explanation online.
update (4/29/16) (5/2/16) --- My recent experience doesn't bear this
out. On 3/22/16 I returned to rev/dex, at this time my platelets were down
to 94. After three weeks taking dexamethasone (40 mg/wk as before), platelets
did not rise, but drifted still lower to 88. At that point my oncologist
suggested that because platelets were pretty low (88), it was better to
cycle Revlimid. Maybe this was right, because three weeks later, with one
of them being the Revlimid off week, platelets rose to 113.
What would have been helpful,
and both doctors know I am interested in the papers and details, would
have been a brief summary of the clinical trials on maintenance. I have
yet to come across a good summary, though I am aware that the New England
Journal of Medicine, a couple of years ago reported in one issue on three
clinical trials on revlimid maintenance, all of which showed it very beneficial,
and there was an editorial in that issue reinforcing this conclusion.
An advantage
of cycled revlimid
Now nearly two months into maintenance
I see an advantage of cycled revlimid that I had not anticipated. I always
try and start my cycles on Mon, so that means I should have run out of
revlimid on a Sun, which was yesterday, but I still had three pills left
in the bottle. That means I missed taking my revlimid on three days in
the last month, two of which I am pretty sure was when I was rushing around
in a ME hotel trying to make checkout time after a late breakfast. Since
it was originally proposed that I take 10 mg of revlimid continuously,
there can be little harm in just continuing to take the three, reducing
my 'off time' from 7 days to 4 days, so that is what I am doing. If the
prescriptions were written for continuous usage, forgotten days would result
in a pile up of $500/day pills.
Advantages of no steroids
(11/20/15)
I'm now six months off steroids
after having taken 40mg/wk of dexamethasone for six months while my M-spike
was being driven down. Here the improvements I have seen in my body since
stopping steroids.
* Vision --- My eye doctor
was amazed at the improvement in my left eye in the eight months since
my last exam. In Mar 2015 on steroids for four months for the first time
no vision correction worked for my left eye, and a scan of its retina shows
some macular degeneration in the center. Eight months later, six months
after stopping steroids, the vision in my left eye is greatly improved,
pretty close to my sharp right eye.
* Gums --- My dentist was
amazed at the improvement in my gums after stopping steroids. Comparison
photos shows my lower front gum went from raw and rough while on steroids
to pink and firm after being off steroids for about four months.
* Fingernails --- While on
steroids my fingernails were weak and always breaking. Off steroids for
a few months they began to strengthen and grow normally.
* Dark growths on the skin ---
During my induction chemo various raised dark crusted 'things' grew on
my skin. One that particularly annoyed me was on my forehead. After being
off steroids for a while, I found I could peal some of these dark crusty
surface layers off. Now six months off steroids the raised dark crusted
things are gone and the dark thing on my forehead has faded to nothing
but a slight discoloration on flat skin.
* Bone growth? ---- The jury is still
out on this one, but I am hoping my bone will improve and grow, in particular
that the fusion of C1,C2 vertebrae in my neck will be substantially better
with no steroids. At the one year review of my neck fusion operation (Sept
2015) bone growth into the hardware and between C1 and C2 was relatively
poor. But of that 12 months I didn't start chemo for two months, which
included two weeks of neck radiation, and then six months of steroids.
So that's 8 of 12 months where bone weakening cancer, radiation, and steroids
could very well have impeded the bone growth/fusion process. I am hoping
that with six months of no steroids between my one year review (sept 15)
and my 18 month review (march 16) will show improvements in bone health
comparable to other improvements in my body I have seen since stopping
steroids.
There are other changes that
may have influenced the outcome, but I suspect the steroids are the key
change. On my gums I switched to an automatic rotary toothbrush from a
manual one at my dentist suggestion. On the eye I began to take a dietary
supplement at my eye doctors suggestion which provides two quasi-vitamines
known to be present in the eye and for which this is some clinical evidence
that they may help macular degeneration. In the case of my bones I have
been getting a bone strengthening injection (zometa, monthly) since the
beginning of the year. This drug is given to elderly women with osteoporosis
(annually), and there is good clinical evidence that it strengthens bones
by altering balance between bone growth and bone disolving enzymes.
Less side effects (8/26/15)
About three months
into maintenance I see three changes in my body that indicates it's getting
back to normal. One is minor just cosmetic, some long existing 'things'
on my skin grew black crusts during chemo. On my forehead there has always
been a spot that was a little weird, but since it was always the same color
as the forehead skin it was not noticeable, but during my six months of
rev/dex chemo it became quite noticeable growing a raised black crust,
and the same thing happened on lots of spots on my neck and upper chest.
But now about three months into maintenance some of the crusts have come
off and the forehead thing is noticeably lighter in color. Is this due
to lots of sunlight and saltwater swimming this summer or going into maintenance?
Another improvement is my
fingernails now can grow long. This is a big change from my time on rev/dex
chemo where my fingernails easily splintered.
More importantly four months
ago (april 15) my dentist was upset with the look of my gums and a closeup
picture of my two lower front teeth and gums scared even me. The gum was
red and raw looking and the boundary to the teeth was ragged. The dentist
suggested I change to a automatic rotary toothbrush, which I did, but also
three months ago I went into maintenance dropping the corticosteroid dexamethasone
and reducing the dose of revlimid by 60%. Now four months later at my most
recent dental appointment the look of my gums is hugely improved. Side-by-side
pictures of the two lower front teeth area show a dramatic improvement.
The dentist describes the gums now as firm and pink like they should be,
and boundary to the teeth is smooth and clean looking. Is this due to the
rotary toothbrush, which I ran over the gums for four months, or the dropping
of dexamethasone three months ago?
I'm betting all of these
external issues were more likely than not a side effect of the chemo. Steroids
are very powerful. A few micrograms of dexamethasone on the skin will heal
breakouts overnight, and for six months I was ingesting 40 mg of the stuff
weekly! With the transition to maintenance and the dropping of the corticosteroid
my body is getting back (closer) to normal.
Was six months the right time to transition chemo to maintenance?
With a more recent perspective
that I gained from reading about free light chains, yes, six months was
not too soon to transition to maintenance, and maybe a quicker transition
could have been justified. The Freelite people, who make instruments that
measure free light chains, argue free light chains give a much truer indication
of cancer levels in the body than M-spike, at least for abnormal values
or big moves where the free light chain is outside its normal baseline.
The reason is M-spike has an inherent lag of months since once created
the monoclonal anti-bodies in the blood are cleared so slowly. My lambda
free light chain dropped 98% in my first chemo cycle and in 2-3 cycles
free light chain values were in (or close to) the normal range. The last
three months of the six months of the chemo was probably just waiting for
the M-spike to catch up.
---------------------------
There was little discussion
by my doctor as to why six months was the right time to make the transition,
and I didn't press the point. A major reason I didn't ask questions was
I was all for switching to maintenance soon since the side effects (particularly
loss of sleep from the dexamethasone) were beginning to get to me in the
last couple of months. I got the impression from reading multiple myeloma
blogs that six months was sort of a 'formula' that was widely used, though
some in the blog said you should flee an oncologist who does this without
taking your status into account. My primary haematological oncologist a
few months earlier had mumbled that some clinicians don't use a rigid time
table, but keep the revlimid dose at 25 mg until the monoclonal spike plateaus
and then go one more cycle. But when the time came to do the transition
nothing more was said of this option. However, after five months I had
achieved more than a 95% reduction in cancer levels, and my monoclonal
spike was close to plateauing since it barely dropped from cycle 5 to 6
(0.24 => 0.23 g/dl), though my doctor didn't know this because the decision
was made before the cycle 6 results were in. So all this seemed to add
up to making the transition in six months reasonable. Also my prreference
is always to opt for the most conservative treatment option that is reasonable,
and it qualified on this score.
Additional details: Besides
the 10 mg revlimid (21 days out of 28) I am taking daily aspirin as an
anti-coagulent (to counter the possibility of a blod clot since the disease
and revlimid thicken the blood). I was taking a full aspirin dose of 325
mg/daily, but (on my own) going into maintenance I decided to scale down
the aspirin dose. (I was aware that 1/4 aspirin dose is used in some countries
and clinical trials.) Only full and 1/4 doses are sold (even on Amazon!),
so I have gone over to taking two 81 mg (coated) aspirin/day for a half
(full) dose of 162 mg. My engineering judgement is that scaling down the
aspirin dose to (roughly) match the dose reduction of revlimid makes sense.
These 1/4 dose pills are tiny pill, so I can easily take the two with one
swallow. Also I am continuing to get a biphosphate (Zometa) infusion every
month, which strengthens bone, but is not technically a chemo drug.
One discordant note is Tom
Brokaw's treatment and his chemo transition. He's two years older than
me, but was diagnosed with multiple myeloma a year earlier than me. Within
days of his diagnosis he had a bone break (in his back). He's being treated
by one of the big guns in the field (Ken Anderson at Dana Farber in Boston)
and was put on rev/dex, and as he tells it they didn't recommend a stem
cell transplant. This is all pretty close to me, except in my case I made
the decision not to have a stem cell transplant not my doctors. However,
as best as I can tell (from the tidbits he drops) his transition to maintenance
was something like 16 months after his diagnosis, far longer than my six
months. Just prior to his transition to maintenance he announced his cancer
was in "remission", whatever the hell that means. So did his doctors treat
him to achieve a CR before going to maintenance? Probably. What I
am missing is all his details, his monoclonal spike, tumor load, etc. Whether
or not it is in his book I don't know, the reviews say the book has little
medical detail and is mostly stories about his life. This is an open issue
I am still working.
While I have
read elsewhere Brokaw was on rev/dex, the authoritive sounding posting
below from a MM forum says he was on RVD: Revlimid, Velcade and dex. [However,
a more recent posting on a MM forum splits the difference, saying it "looks
like" Brokaw started off on rev/dex and then graduated to RVD.] The addition
of Velcade (in infusion) is another standard option. [I am wondering if
Brokaw with his big name doctors got access to the pill form of Velcade
which was the option being tested in th clinical trial offered to me.]
The author assumes Brokaw means by remission is that he achieved
a CR (complete response) after 15 months or so of treatment. However, even
he doesn't know the details of Brokaw"s CR or his maintenance regime. [Brokaw
after 12 months of treatment said his cancer was undetectable (probably
meaning his monoclonal spike was below the test threshold), but that he
had one other marker to get down.]
And according to this posting
I am in much better shape than Brokaw. Brokaw has had several vertebrae
in his back collapse. He has had kyphoplasty to help repair them. He admits
to being in constant pain. He has been plagued by infections. He went out
hunting, but reports he got very tired and couldn't really function. (Kyphoplasty
surgery is done through a small incision where a balloon is inflated to
make a cavity in a collapsed vertebrae, then the cavity is filled with
a quick drying cement.)
http://multiplemyelomablog.com/2015/05/tom-brokaws-program-about-his-multiple-myeloma-a-pleasant-surprise.html
Rev without dex in maintenance
From www.myelomabeacon.comforum,
by Dr. Adam Cohen on Thu Apr 18, 2013 11:07 pm
Yes, Revlimid maintenance
(without dex) would be considered standard, and has been tested in 3 large
randomized trials, 2 done after stem cell transplant and 1 after non-transplant
induction. In all 3 trials, the use of Revlimid prolonged the time in remission
compared to no maintenance, though only 1 of the 3 has shown an improvement
in overall survival with maintenance. In these trials, Revlimid was given
continuously at a dose of 10-15 mg per day, though in practice, many oncologists
use the 3 weeks on/1 week off schedule to reduce the side effects such
as low blood counts.
Daily pills
(1/16/16)
(4/15/16)
One sign of being old and
sick is how many pills you take. Below is the pile of pills I take every
morning. I am not a big believer in (food) supplements. I take only two,
each recommended to me by my doctors.
My daily pills on revlimd maintenance (Jan 16, 2016)
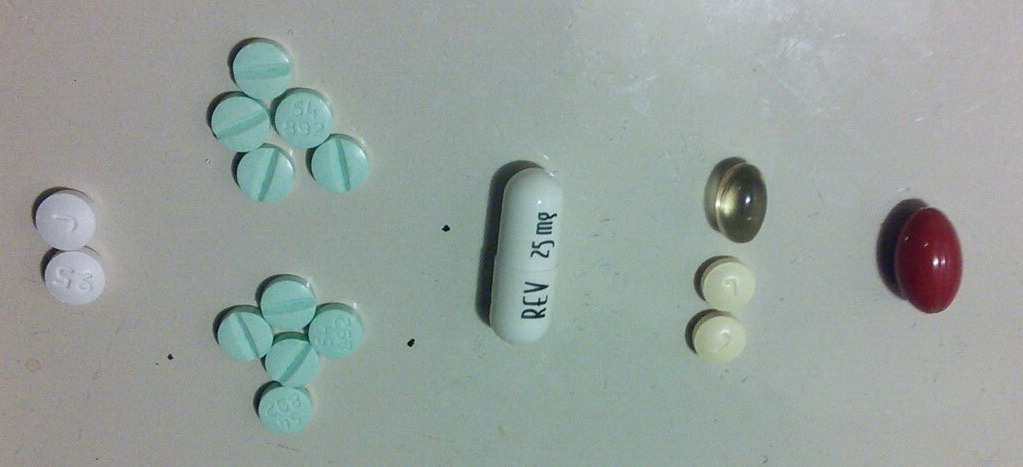
My friday pills back on rev/dex (April 15, 2016)
Once a week I add 40 mg of a corticosteroid in the form of ten 4
mg dexamethasone (green) pills on a single day.
Doctors refer to this as 'pulse' and a 'booster' for my chemo pill
Revlimid.
Top (left to right): two
sildenafil (Revatio generic used off label), Revlimid (10 mg, 500/pill)
chemo, two 81 mg aspirin (blood thinning to counter side effect of Revlimd),
vitamin D pill (important for bones in MM , my vitamin D is at the bottom
of the normal range), lutein & zeaxanthin pill (for vision, I have
the beginnings of macular degeneration in left eye). I can do each row
in one swallow. The while pills and the transparent vitamin D pill are
quite small.
Bot: I am back on rev/dex
by April 2016. Revlimid dose incrased 25 mg. Once a week (shown) ten 4
mg dexamethasone pills. The total weekly dose of 40 mg is taken on one
day (or spread over two) of a week, referred to as a 'pulse'. It is ten
pills because the largest dexamethasone pill made is 4 mg. Doctor's laughingly
refer to these ten pills as 'low dose" dexamethasone.
Neck pain
One of my biggest issues
since the C1,C2 fusion neck operation is a reoccurring stiff neck. It comes
and goes, but it's not unusual for me to need to adjust the angle of an
easy chair to find an angle that doesn't hurt, and sometimes this is hard.
Affects the positions I can comfortable sleep in too. Head left is reliably
OK, head right more problematic since it sometimes starts to hurt after
a while. I have no feelings in the back of my skull, because I assume the
nerves were cut during the operation, and it make sleeping on my back a
little weird, but the nerve issue is really just a minor issue. This 'stiff
neck' issue has been about the same since the collar came off and my neck
strengthened over the next month or two, hence I expect this issue to remain,
maybe forever.
Driving a
car with limited neck mobility
The biggest issue (by far)
with my fused neck has been learning how to safely drive a car. Normally
about half the rotation of the head uses the two large sliding joints between
C1 and C2, but I have lost this rotation term since hardware (and pending
bone fusion) holds C2 fixed to C1. The rotation of my head now is about
+/- 45 degrees (vs 90 degrees normally). I didn't drive my car for two
and half months after my neck operation. It was simply impossible to drive
with the neck collar as I could not turn my head at all, and it took a
month or two for my neck to strengthen when the collar came off after two
months. When I went to start my car after it sat for that long time, of
course the battery went dead, but AAA came and for a very reasonable price
tested the old battery and installed a new one. While I had been fearful
to drive again, that afternoon after the AAA guy left I took a little trip
a few hundred yards just driving around my local parking lots and it felt
OK.
My main worry was seeing
far enough leftward to safely cut into busy traffic. The problem occurs
right where I live. My apartment complex driveway angles rightward joining
a busy downhill, divided two lane road (rt 28) at an angle of 135 degrees.
I soon found that I could see 90 degrees left by adding a 45 degree back
twist to my 45 degree head twist. I couldn't hold the back twist for more
than a second or two, but that was OK leaving home as the car normally
needs to stop at the bottom of the driveway to wait for a break in the
traffic. At the beginning I thought leaving at night would be safer because
I could more easily see headlights, but I soon learned a trick to do it
safely during the day.
Key neck trick
The trick, the key trick I have
found to driving safely with limited neck rotation, is to avoid (whenever
possible) 135 degree lane mergers by angling the car leftward by 45 degrees.
In other words use the car to reduce the angle of lane merger, change a
merger which may be lined at 135 degrees to 90 degrees, which my back/head
rotation can manage. Leaving my apartment complex this is easy as the road
down the hill to rt 28 is very wide and normally the car needs to stop
anyway to wait for an opening in traffic. It may look to an observer a
little strange as the car cuts perpendicularly into traffic and then quickly
makes a sharp 90 degree turn into the right lane of a two lane road. But
this is a safe manuver. I can see the oncoming traffic and if the opening
is reasonable making the right hand turn is no problem.
For several months I drove
locally, first just a mile or two around town and then more and more, but
still all local, I stayed off the highway for quite a few weeks. My main
concern with the highways was the sharply angled entrances and exits (some
of them probably more than 135 degrees). They scared me and the problem
was made worse (much worse) at the time because it was winter and we had
record snowfall this year, so after a while the snow banks were so high
that coming down a highway off ramp you could not see the traffic on the
merge road at all. You had to go to the actual merge, stop and peer around
the snow banks.
For months I took taxis back
and forth to the hospital. I watched carefully how the (many different)
taxi drivers did highway entrances and exits. I then got on Google Earth
and looked closely at local entrances and exits near where I live. I found
some highway exits are no problem. These are exits that join the local
road at 90 degrees and/or a light. This is my local 128 exit (from north)
and also the 128 exit to the Lehay hospital.
Entrances are generally not
too bad. Entering onto busy 128 in rush hour can be tough. Many a time
I heard my taxi drivers curse as tightly packed cars and trucks would not
let them merge, but still I never saw them look back, they did it all with
the outside mirror. While there is going to be the odd merge which is risky,
I have come to believe that entering a highway is generally going to be
low risk, because it is normally done with using the outside mirror, and
I can see rearward using the outside mirror perfectly fine as it only takes
a a 45 degree (or less) twist. As a further twist at a clover leaf of two
crossing roads the entrace ramps before the overpass are to be preferred
as they will tend to be cleaner and longer, mainly because they don't have
exiting traffic crossing over in front of you. I went on Google Earth and
using its ruler feature took a real close look at my local highway (128)
cloverleaf entrances and exits, which look pretty typical. My local highway
entrance going north, which is before the overpass, has a long acceleration
lane, should be no problem here using only the outside mirror.
update (May 2015)
On the ride home from the
hospital I had often observed my taxi drivers having problem with the merge
into highway traffic. They used the normal ramp to go north on 128, which
approaching from the hospital is the ramp after the overpass. This is a
ramp with tougher, shorter merge lane and crossing traffic. So when I drive
to the hospital I avoid this potentially tough merge by simply making a
left turn (after the going under the same overpass) into a little mall
where I can easily reverse direction. At the expense of an extra minute
or two of travel time, I am able to enter the highway north using a ramp
before the highway giving me a safer merge, because it is longer and without
crossing traffic.
More worrying was my local exit
off the highway (128) close to where I live. This is the typical 135 degree
('yield') merge that is often taken at high speed when traffic is light,
and requires a stop if traffic was busy. But Google Earth shows, and I
confirmed this on a walk, that while its lined for a 135 degree merge,
near the end it flares open enough so that a car can stop (or nearly stop)
and angle left to make it a 90 merge just like with my driveway. I have
only taken this exit a couple of times, so I have not yet had the opportunity
to try this out. Sometime in middling traffic I worry it it going to be
a little tricky, because if I slow down quickly and unexpected and angle
the car strangely, I worry I could surprise the driver behind me and be
rear ended. It's all in the technique, probably the right approach is to
come in slow so I have the option to stop (and the driver behind me has
time to stop too). In general route planning is important. Circles are
tricky. I have only done one to date. In a parking lot if possible I always
take a spot I can drive forward out of, but realistically about half the
time backing out is required, and here I pull out my towing mirror to take
a look (from inside the car).
For a little added safely
I added (glued) a two inch 'blind spot' mirror to my built-in outside mirror,
but realistically this little mirror is so convex, that cars can't be seen
until they are about up to my bumper. It really is nothing more than a
blind spot mirror, so it doesn't provide any real help when merging. I
spent a lot of time looking for mirror on Amazon at my local auto parts
store. I bought a universal towing mirror ($25 bucks or so) that seems
to have some promise. It's quite large, adjustable as it is on a ball swivel,
but the universal mount, wrapping rubber bands around my outside mirror
so it sits outside my main outside mirror, I can see are just not going
to be reliable. With some added (cludgy) spacers top and bottom I can get
it on, but there is no way to properly tighten the rubber straps, and I
bet on my first trip to ME its going to fall off on the highway within
a few miles. Not only will it be gone, but its big enough to be a serious
road hazard, so I will need to stop an retrieve it, which will be dangerous.
There are (much) more expensive
towing mirrors. I saw a video of one with ratchets to tighten the straps,
and that's a step forward. Maybe I can find one with adjustment in the
hooks to the outside mirror frame, so the (unreliable) spacers can be eliminated.
A trip to my local auto body shop might solve the spacer problem by having
them weld in spacers. Maybe they could come up with another full mount
under the outside mirror. I have serious doubt an outside mirror can be
reliably added to my car, but have not given up yet. For now I keep the
large towing mirror in my inside door pocket. If I have time, I can pull
it out and use it to look around. I doubt this will ever prove practical
when entering or exiting the highway, but it does help when I am about
to back out of a parking space.
I know I am not obsessing
about a non-existent problem, because as I began began pushing envelope
and driving more, including some trips on the highway, and even into Boston,
I have had a few entrances that for one reason or other I did not handle
well and felt I could not see clearly and was not safe. One mistake I find
I make is (on the fly) misjudging the available spacing in the oncoming
traffic. A few times as I approached the street at the end of my driveway
the traffic was backed up and stopped from a traffic light I angled in
at 135 degrees, where I can poke my nose in so stopped cars generally allow
a merge after the light changes, but a couple of times before I could get
into position the cars started to move, and I was trapped at a 135 angle
and unable to see the on coming traffic. Solution, don't do this again,
adjust my driving technique, when traffic is stopped even then angle in
at 90 degrees. It will look weird and maybe make it more difficult to enter,
but I will be able to see so it should be safe. Technique, technique...
(Traffic circles remain a worry and I think I will just have to fudge this
by slowing down enough (stopping is not expected) so I can angle.)
Bone pain
Bond pain is common problem
with multiple myeloma, but (so far) I have not had any pain from any of
the 'holes' in my bones. The question is why not? This is an important
quality of life issue. It took me months to understand that what the doctors
were calling a 'hole' (in my femur) was really a hollowing out of the bone
from the inside beginning at the marrow/bone interface. On an x-ray
you can't tell if a hole is inside or outside, all you see is a contrast
change.
My understanding now is a
multiple myeloma 'hole' (probably) doesn't hurt until it penetrates (or
disturbs) the surface of the bone. For the most part bones don't have pain
sensors, but bones are surrounded by a membrane that nourishes them called
the periosteum, and it has pain sensors. (Sketches of the periosteum show
little blood vessels from it going into the compact bone under it. The
periosteum membrane is extremely thin, only about 100 microns, or 1/10th
of a mm.) When you break a bone, the reason it hurts is that the bone break
tears open the periosteum. Ok, maybe that explains my femur 'hole', but
this explanation only goes so far. X-rays show I have lost 30% or so of
the bone in one vertebrae of my mid back (T12), and it doesn't hurt either.
How could its periosteum not be disturbed? Does it even have a periosteum?
(Wikipedia says the outer surface of all bones (except for joints
like the knee) is covered have by a periosteum, and some tiny bones like
in the wrist.) When I asked the bone doctors how come T12 with its large
bone loss doesn't hurt? The answer I got was, 'I was lucky'. What kind
of an answer is this? How about some medical detail. Now this T12 back
tumor was irradiated, but it didn't hurt before it was irradiated. Maybe
the periosteum has reformed around my now reduced T12, after all when a
broken bone heals the periosteum around it must heal too. So bone pain
remains an open issue.
The hope is that the radiation
and chemo will halt the growth of these three large tumors (and many small
ones).
Kidney damage
Another common problem with
multiple myeloma is kidney damage. The simplified explanation is that the
kidneys filter various waste products and crap out of blood by running
it through using a network of fine blood vessels, but since blood in multiple
myeloma is not normal and can have too high a viscosity it slowly clogs
up the filters in the kidney. (I am sure this is vastly oversimplified.)
The usual marker here is creatinine, a muscle waste product. If the level
of creatinine is high in the blood, it means the kidneys are not doing
a good job removing it. My creatinine started off at 1.4 (slightly outside
the normal range) and has come down to 1.2 (just inside the normal range).
The Celgene sheet says revlimid is excreted (unchanged) by the kidneys.
Wikipedia gives the half-life of revlimid in the body as 3 hours, so in
24 hours the kidneys have cleaned the daily dose.
-- There are five
types of heavy chains: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE, and two types of light
chains: lambda and kappa. Each type of heavy chain can have either lambda
or kappa light chains there are thus ten possible types of immunoglobins.
* -- Plasma calls produce light chains and
heavy chains separately, which later assemble into the full immunoglobins.
"For some reason" more light chains than heavy chains are usually produced
with the excess light chains entering the blood steam (now called free
light chains). The kidneys extract the free light chains from the blood
and recyle the amino acids. (This explains why there is a baseline value
for both lambda and kappa free light chains in normal people (in the same
range of about 1 mg/dL +/- factor of 2). It's the excess light chains from
normal (disease fighting) immunoglobins.)
-- "Myeloma is classified
into different types depending on their immunoglobulin heavy chain and
light chain as follows: IgG (52%), IgA (21%), light chain (16%), Bi-clonal
(2%), and IgM (0.5%), while IgD and IgE are rare. Patients with light chain
myeloma are more prone to develop renal failure." (This begs the question,
What is 'light chain myeloma' anyway?)
Light chain myeloma
What is 'light chain myeloma'?
Ans: Occasionally, the malignant plasma cells make only the light chain
component of the antibody. These patients are said to have “light chain
myeloma.” (I have the IgG lamda band, so good news here.)
Immune system weakened
Another common problem with
multiple myeloma is reduced immunity. Since the cancer is in the plasma
making cells which turn into anti-bodies, the anti-bodies as a whole are
not normal. I may see this. It took me more than two weeks this spring
to shake off a cold, instead of the usual week. I read at the end a lot
of multiple myeloma patients die of pneumonia. But to date I have not been
able to really get my arms around this issue. It's all very vague and theoretical.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anemia
-- Low blood oxygen capacity
Notes on anemia from my early days on chemo
(2014-2015)
Anemia is
defined as 'low blood oxygen capacity due to not enough health red blood
cells'. In my case my blood oxygen terms (RBC, hematocrit, hemoglobin,
etc) started off prior to chemo up to 30% below the normal range. During
my first three chemo cycles as the cancer cells in my blood steadly declined
(by about a factor of ten) the oxygen terms in my blood steadily improved
to well centered in the normal range. The 'picture' painted for this is
that there is only so much room inside bones for blood producing marrow,
and the expansion of the cancerous blood plasma cells reduces the room
available for normal marrow that makes oxygen and white blood cells, so
a decrease in cancerous marrow cells allows normal blood marrow cells to
expand.
However, my
4th cycle blood numbers, while showing a nice continuing decrease in my
M-spike, showed the red and white blood terms going into reverse, loosing
the gain of the 3rd cycle, dropping to the lower end of the normal range
or in one case (hemoglobin) slightly below the normal range. My doctor
suggested this could be due to the chemo. In reading over the detailed
Celgene revlimid proscribing sheet I see it shows revlimid caused anemia
in about 1/3rd of those in a trial with 350 patients. (What their definition
of amemia is I don't know.) I sense my oxygen numbers are important to
how I feel. When they are low, I get tired easily, a few hours outside
can wipe me out for the rest of the day. (I also see a big decrease
in IgG blood (920 => 622) and IgM (93 => 46) taking them both below the
normal range. I don't really understand these terms.)
When I look
up references for anemia, I have seen it defined as homglobin levels
below 13-14 g/dl. In my blood work the normal range for hemoglobin is marked
at [13.8 - 17.4 g/dl], so this amounts to saying that pretty much any hemoglobin
level below normal constitutes anemia. A pencil note in one of my blood
works, I think recording what my GP told me, says anemia is hemoglobin
< 11 g/dL. My hemoglobin numbers in Nov 2014 were in the 10-11
g/dL range, so clearly I was anemic prior to beginning chemo. At the end
of my 3rd rev/dex cycle my hemoglobin was up to 15.5 g/dl, well centered
in the normal range, but after steady increases for the first three cycles
of chemo at the end of the 4th cycle there was a moderate decline to 13.7
(just barely below the normal range). This decline could very well be due
to (the cumulative effect of) revlimid, since anemia is one of its common
side effects, and my oncologist seems to think so.
Really
bad anemia -- very low hemoglobin (9/20/17)
In the last
few weeks my quality of life has been badly impacted by extreme shortness
of breath. I am Ok sitting or driving a car, but when I have to get up
to walk just a little, it is a struggle. I feel exhausted. This has come
on fairly suddenly. I read this extreme fatigue is perhaps the most common
symptom of cancer as the cancer begins to take over from the chemo.
From my reading
extreme fatigue is often caused by low oxygen carrying capacity of the
blood, and my hemoglobin value has recently dropped to a new low 8.4 g/dL.
This is only 60% of low edge of normal (13.8 g/dL) and far lower than it
has ever been in my three years of chemo. Even lower than when I was first
diagnosed (9.9 g/dL)! I recently changed my inhaler from the powder based
Incruse Ellipta to the mist based Spriva Respirmat and that didn't help.
Many tests in 2017 of my lungs and heart have not found a problem. It makes
sense to me that the most likely cause of my recent extreme fatigue is
reduced oxygen carry capacity of my blood as indicated by the very low
values of hemoglobin and RBC that my blood tests are showing.
The question
in terms of quality of life is what (if anything) can be done about it.
I read a quick fix is a blood transfusion. Outside of my neck surgery,
I have never had a blood transfusion. It comes with its own risks. I was
half expecting that with my hemoglobin at 8.4 g/dL (9/19/17) my doctor
might order one, but she didn't. Doing research I found that while this
level was the trigger for blood infusions, the trigger has dropped to 7
g/dL.
5 g/dL risks
Perspective
on the risks of low hemoglobin come from jehovah witness patients
who refuse transfusions. At 5 g/dL half of them die from this because the
heart cannot get enough oxygen to vital organs!
Hemoglobin
raising hormones ---Brand names: Epogen, Procrit and Aranesp
I had not
yet begun to research treatment for anemia, when in late summer of 2017
I heard an interview on PBS radio with the authors of a new book, 'Living
with Cancer', by David Ryan, chief of hematology/oncology at Mass General
Hospital and Vicki Jackson, chief of palliative care at the same hospital.
Mass General Hospital has a very good reputation for high quality care,
and this book was clearly relevant to my condition, so I immediately ordered
the book on Amazon. Here is Dr. Ryan in the book talking about severe anemia
with shortness of breath and the use of erythropoietin as an alternative
to blood transfusion to treat it. (pages 178 and 221).
--
"When patients are severely anemic, they can feel shortness of breath,
particularly when they move around", and he relates this to not having
enough red blood cells. (Yup, that is exactly how I feel.)
-- "Typically
your hematocrit needs to fall under 30 (30%) before you will feel shortness
of breath, normally our hematocrit runs about 40." (I meet this test,
my latest hemocrit value is 25.8% .)
-- "If your
red blood count is low, you might benefit from a transfusion or the administration
of a subcutaneous injection of erythropoietin, the body's natural hormone
that boost red blood cell production."
-- "Patients
who could benefit from a transfusion might elect to take erythropoietin
(epo) instead. ... A few years ago a couple of studies tied this drug to
an increase rate of blood clots which meant doctors stopped using it for
a while. Further studies have disputed these findings, and the use of epo
now appears to be safe. There are still a number of doctors who
are cautious about using it."
Erythropoietin(short
hand 'epo') is a hormone the body produces mostly in the kidneys (10% in
the liver) to encourage more red blood cell production. It is given can
be given as a subcutaneous injection. (It was used by Lance Armstrong as
an (illegal) way to improve his performance), but for cancer patients it
can be given intravenously weekly.
--
Erythropoietin is a protein with an attached sugar (a glycoprotein). It
is one of a number of similar glycoproteins that serve as stimulants for
the growth of specific types of blood cells in the bone marrow. There is
a blood test for this hormone called the 'epo test'. It requires an overnight
fast.
Erythropoietin
is sold under brand names: Epogen (Amben) and Procrit (Janessen).
There is also a closely related, longer lasting hormone called Aranesp
(Amgen). The first two appear to be the exactly the same drug. It has been
on the market for 28 years sold by two different manufacturers. The Epgoen
and Procrit prescribing documents say it can be given intravenously weekly
to cancer patients: 40,000 Units weekly. This would fit nicely with my
weekly dearatumumab infusion chemo. From the prescribing document
I see the threshold for use: hemoglobin <10 g/dL. At 8.5 g/dL I meet
this threshold easily. Increases of 2 g/dL can be achieved. This manufacture
of a body's hormone for use in clinical treatment was considered to be
one of the big early sucesses of recombinant DNA technology. The response
time is relatively slow, something like 0.5 g/dL in a week. Aranesp has
been on the market since 2001 and differs just sligthly in its amino acid
sequence.
Epogen and
Procrit
-- Epogen® & Procrit® (epoetin alfa) Injection, for intravenous
or subcutaneous use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
Aranesp®
(darbepoetin alfa) (a long acting version of Procrit). Approval 2001
There appears to be less emphasis in the Aranesp prescribing document for
cancer patients.
For cancer patients it is given weekly subcutaneously, or at a higher dose
subcutaneously every three weeks.
-----------------------------------------
New
hospital schedule to address my anemia (9/26/17)
After two
units of red blood cell transfusions over the last two days, I still have
shortness of breath, but it is less. I was able to shop at the market
today without it nearly killing me as it did just a few days ago. According
to one estimate two units of blood can increase your hemoglobin by 2 g/dL
so my hemoglobin might now be [7 g/dL => 9 g/dL]. Since the livetime of
red blood cells is about four months, this should hold for a while. We
will see in a week, when my hemoglobin will next be measured.
I now come
to hospital weekly (tues) for labs, and a chair is also reserved in the
infusion room. What happen in infusion room varies and is below:
1) Every week
I get a subcutaneous skin jab (upper arm) of hormone Aranesp (darbepoetin
alfa). This is prefilled syringe with a dose 200 mcg (calculated from 2.25
mcg/kg). (If it works for me, the prescribing document say it will take
a month or two for my (potentially chemo damaged) marrow to start to pump
out more red blood cells.)
2) Every
other
week a daratumumab infusion. This week was my 9th = (8 +1) daratumumab
infusion. According to the daratumumab prescribing document, daratumumab
for next two months is to be given every other week. Next week is my week
off.
3) If hemoglobin
is low (< 8 g/dL), then a red blood cell infusion (one unit)
4) If platelets
are low (< 20 K/uL), then a platelet infusion. My second
chemo drug imid (Pomalyst) remains suspended (along with 162 mg aspirin)
until platelets recover (> 50 or >30? K/uL).
------------------------------
Notes on Erythropoietin
From a book
on Blood I find the following comments about Erythropoietin therapy for
anemia.

-- Erythropoietin
therapy is very well tolerated provided that the patient's hematocrit is
kept in the mid to high 30s. Properly treated patients enjoy significant
improvment in quality of life including less fatique and enhanced appetite.
The majority of MM patients treated with rhEPO achieve a significant improvement
in red cell mass (> 2 g/dL hemoglobin). The response to treatment is prompt
and sustained provided that adequate iron stores are maintained.
There's a blood
test for erythropoietin too. The normal level is 10-15 mcg/L (homeostatic
conditions). This can give a window on how the kidneys are working. However,
the erythropoietin doses given for therapy are far, far higher than normal
body levels (10,000 mcg/L). Monitoring for the effectiveness of EPO administration
is usualy done watching serum hemoglobin levels rather than EPO levels.
EPO vs blood
transfusions (9/24/17)
Researching
this topic I find there is extensive literature going back more than 20
years as to whether it is better to use EPO (either thrice weekly subcutaneous
injections or weekly IV), the recombinant DNA drug erythropoietin (Procrit)
vs a blood transfusion to combat low hemoglobin (low oxygen carrying capacity)
levels. This debate is not only in the context of cancer patients, but
also kidney failure patients, patients undergoing surgery and even premature
babies who often need blood transfusions.
Early 1990s EPO clinical trials
I read the
early phase 3 clinical trials in the early 1990s of erythropoietin were
a spectacular success, close to a 100% effective response. Futhermore patients
did not get refractive to erythropoietin, it continued to work with apparently
little risk. However, these phase 3 clinical trials of EPO were done on
patients with anemia due to renal (kidney) failure. In other words in these
patients the marrow response to the hormone was Ok, the failure was in
the oxygen sensing and/or hormone generation in their kidneys.
The situation
in MM patients is very different. The issue here is much more likely to
be chemo damaged marrow not responding well to the hormone secreted by
kidneys. Since the situation is so different with MM patients, the relevant
literature on EPO for me should focus on the effectiveness of EPO in MM
patients.
EPO treatment in MM patients
From Multiple
Myeloma Research Foundation
-- If anemia
is severe and requires immediate treatment, patients should receive a blood
transfusion.
-- Erythropoietic
agents are generally well tolerated. However, recent studies have shown
that these drugs have been associated with an increased risk of blood clots.
Factors that can increase the risk of developing blood clots include: Treatment
with some common myeloma drugs including Revlimid, Thalomid, dexamethasone,
Adriamycin and Doxil.
-- Preventive
treatment with a blood thinner (such as heparin) may be considered for
high-risk patients.
-- Procrit/Epogen:
150 units/kg three times a week or 40,000 units once weekly
Aranesp: 2.25mcg/kg once a week or 500mcg every three 3 weeks
-- Supplemental
iron may be given in addition to erythropoietin therapy.
-- The effectiveness
of therapy is measured by the increase in hemoglobin and hematocrit ( number
and size of red blood cells). It takes some time for the body to produce
new blood cells, so the effect of erythropoietic agents may not be seen
for 2 to 6 weeks.
** -- Overall,
about 60% to 70% of cancer patients receiving cancer treatment respond
to erythropoietic agents.
-- An early
hemoglobin response to therapy (>1 g/dL rise after 4 weeks of therapy)
in patients with treatment-related anemia is often associated with reduced
transfusion requirements, higher hemoglobin response rates, and improved
quality of life. Having adequate iron levels may also improve responses
to erythropoietin therapy.
https://www.themmrf.org/multiple-myeloma-knowledge-center/myeloma-treatments-guide/growth-factors/erythropeietin/
Blood transfusions
-- Average
adult has between 8-12 pints of blood. One unit of blood is ~525 mL, roughly
the equivalent of one pint.
-- ** The average
patient requires around 4.6 units of blood (Canadian Blood Services website)
-- The procedure
usually takes 1 to 4 hours. (My infusion time for one unit of red
blood cells 1.5 to 2 hours)
--
Red blood cell (RBC) transfusions in most hospitalized patients should
be performed based on "restrictive," (7.1 g/dL ?) rather than "liberal,"
hemoglobin levels (7 - 8 g/dL), according to new clinical guidelines from
the American Association of Blood Banks. Mar 26, 2012
** -- Each
unit of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) is expected to raise circulating
hemoglobin (HGB) by approximately 1 g/dL.
(details of a what is in the bag of red blood cells from
a posting by an an obstetrician, Jeff Menegas)
--
The (transfused) unit of blood looks like this. Originally 530 grams of
blood is taken from donors. This is about 500 ml (blood), since blood is
about 6% heavier than water. According to the Mayo Clinic, if it is from
a normal female, it has a hematocrit of 34.9 to 44.5%, and so contains
between 174.5 and 222.5 ml of packed cells. If it is from a normal male,
it has a hematocrit of 38.8 to 50%, and so contains between 194 and 250
ml of packed (red) cells.
-- It is then
centrifuged, and most of the plasma is removed. The final product has a
hematocrit of between 70 and 75%. If it is from the female, and her hematocrit
is at the lower limit of the normal range, it has a final volume of between
233 and 249 ml (174.5/0.75 and 174.5/0.7), and if from a male at the upper
limit of the normal range, it will have a final volume of between 333 and
357 ml (250/0.75 and 250/0.7).
-- Typically the bag of packed
red blood cells will say on the label "From 500 ml CPD (or CPDA) whole
blood." CPD stands for citrate/phosphate/dextrose, an anticoagulant and
preservative, and the extra A is for adenine, which extends the shelf life.
Whole blood is not what is transfused, though. The original 500 ml is centrifuged,
and the cells are removed. The cell portion, which is what most people
think of when they see a transfusion, has a hematocrit of about 70 to 75%,
meaning it is 70% red cells and 30% liquid, mostly plasma.
-- Given that
a typical hematocrit in an adult is about 40%, the original bag of blood
will have something like 200 ml of packed red blood cells (40% of 500).
If the unit has a final hematocrit, after processing, of 70%, then the
total volume in the unit is 285 ml (200/0.7), but this is an average.
-- As I said
above, the only constant is the starting volume of 500 ml, and even this
is not exact, since it is actually measured by weight, not volume, and
takes the average blood density as 6% greater than water. So the starting
point is not really 500 ml, but about 530 grams.
-- All of this
is due to the normal variations between individuals. The ONLY constant
is what is written on the bag, "From 500 ml of CPD whole blood." This is
visible on the above label all the way to the left, between the two messages
in red.
Low platelet imid dose adjustment (9/25/17)
In recent
weeks my platelets have fallen very low with readings of 10, 11, 37 (month
earlier 39, 42 K/uL). (150 K/uL is the low edge of normal)
At 10 and 11 I have had platelet transfusions, which at 10 raised the immediate
level to 22. From the prescribing documents for the imids Pomalyst and
Revlimid (both from Celegene), platelets this low should trigger a suspension
of the drug until platelets recover, and following platelet recovery a
permanent dose reduction. The thresholds are a little different for the
two drugs:
Pomalyst
<25 stop, wait for >50, resume at next
lower dose (4 mg, 3 mg, 2 mg, 1 mg)
Revlimid
<30 stop, wait for >30, resume at next
lower dose (25 mg, 20 mg, 15 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5
mg)
=================================================================================================================================
Zometa --- bone strengthening
(update) I have been getting
Zometa infusions monthly for six or seven months now. I find it gives me
three 'bad' days (jittery, lot of time on toilet). Since in summer I like
to go to Maine midweek, I schedule the zometa infusions on Fri.
I learned something new from
the infusion nurse today, which is that a patient must have blood work
sometime within a month prior to the infusion. The reason she said (confirmed
in a paper) is that Zometa can affect the kidneys, so kidney numbers (presumably
creatine) need to be monitored.
-------------
Beside chemo I am getting
another regular treatment intended to strengthen my bones. This is an infusion
of a bisphosphonate, in my case Zometa (zoledronic acid). My understanding
is this treatment is given annually to elderly people with osteoporosis,
but MM patients get it once a month. It is not chemo, because it doesn't
target cancer cells, it just shifts the bone growth/absorption balance
in the body more toward bone growth. It's painless and relatively quick,
but it does required a trip to the hospital. My zometa infusion time now
about 10-15 min, but my first zometa infusion took much longer (over 2
hours).
The reason that my first
zometa infusion took so much longer time I later learned is it that it
also included 'hydration', an infusion of a large volume of saline solution
equal to about 11% of the volume of my blood. My doctor's notes say
prior to chemo I was developing hypercalcemia, which is high calcium in
the blood (from dissolving bones) and renal (kidney) insufficiency. The
doctors seemed to be particularly concerned advising me to drink plenty
of water. Increasing the volume of the blood is a standard treatment for
hypercalcemia, and maybe helps with renal issues too. My highest calcium
and creatinine blood numbers were calcium 11.0 mg/dl (8.4 to 10.4 normal)
and 1.4 mg/dl (.6 to 1.3 normal). Obviously a 11% increase in blood volume
instantly brought both concentrations down 10% and into the normal range.
Zometa as a hospital infusion
it is covered under medicare part B. It does have a serious risk which
affects a small fraction of those taking it, death of part of the jaw.
Other than this risk there are no side effects that I notice. Since for
the first six months of chemo I have been meeting with my oncologist monthly,
we soon shifted the monthly zometa infusions to an hour after to doctor's
appointment, thus saving a trip to the hospital. The cost of a single Zometa
infusion is [2,400 (drug) + 220 (injection) = 2,620]. My Medicare show
unlike almost all other Medicare charges, Medicareapproves 100%
of the amount billed, but it only
pays about 10% of this amount.
(I don't understand this.)
(update, Sept 2015)
The monthly zometa infusion
billings in summer 2015 run about 515 = [290 for the zometa + 220 for the
'injection into a vein']. Again the medicare billing is not too clear.
In the lower detail section it shows medicare approves 100% of the billed
amount and the amount I may be billed as zero, but at the top in what appears
to be a summary it says the amont paid to provider is 252 and I may be
billed 64. This looks like medicare is approving 315 for the procedure
with my 64 being 20% of the approved amount. (Some months there an extra
patient assessment charge of 85 thrown in which increased my payment to
80.)
Bottom line: my out of pocket
charges for monthly zometa infusions run 64 to 80. Below shows my out of
pocket monthly costs for blood work is only about 8, so that means my annual
out of pocket costs for routine [blood + infusion] comes to about 1k/yr.
I began monthly bisphosphonate
(zometa) infusions Oct 31,14, which is prior to beginning chemo. My docotor
told me recently (aug 15) that the usual course of bisphosphonate treatment
for MM is monthly for two years.
Cost of monthly blood work
To track my cancer my blood
is monitored monthly. The tests done have varied a little from month to
month. My M-spike comes from a protein electrophoresis serum test which
takes four days and is interpreted by doctor, who bills separately
Medicare billing records
show my monthly blood work (non including the doctor charge) runs about
350-400. All the tests are approved by medicare, but the amount that medicare
pays the hospital is sometimes less than 20% of the billed amount. For
example in june 2015 the hospital billed 401 and medicare paid the provider
70. In july 2015 the billing was 354 with medicare paying 85. In
both months the amount that I may be billed is shown as zero. The doctor
charges for the electrophoresis test are billed at 142 and medicare approves
39 with my share about 8.
Bottom line: my out of pocket
charges for monthly blood monitoring (including the clinical doctor's interpretation
of the electrophoresis test) is about 8 dollars. This is 20% of the doctors
charge, the hospital charges fully paid my medicare.
Hypercalcemia
"Many multiple myeloma patients
develop hypercalcemia, which is an increased level of calcium in the bloodstream.
Hypercalcemia results from the destruction of bone from osteolytic lesions
or sometimes from the development of generalized osteoporosis, in which
all the bones are soft and porous and have lost calcium. Hypercalcemia
in patients with multiple myeloma causes fatigue, lethargy and other symptoms.
Severe hypercalcemia is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
Typically, hypercalcemia is treated with bisphosphonates and hydration."
CRAB
Hallmark features of MM
according to the Mayo clinic are highlighted by the acronym 'CRAB -- Calcium
elevation, Renal insufficiency, Anemia, and Bone disease'.
Vision issues
When I had my annual eye
exam, about six months after my diagnosis, for the first time in my life
vision in my left eye could not be corrected. A (manual) scan of the retina
of the left eye showed (dry) macula degeneration. Is this related to multiple
myeloma or chemo or is it age/family related? It's true that my mother
had her vision badly affected by macular degeneration, but that was she
was in her 80s, much older than I am.
Turns out that dogs get multiple
myeloma too. Interestingly a lot of dogs with multiple myeloma end up with
vision problems, they are going blind. Is this a hint that multiple myeloma
in people can cause eye problems? My doctor tells me yes, it can happen
but it's quite rare. Nothing can be done about age or family, but it is
important to know if my vision issues are related to my cancer or to my
chemo. Dogs don't get (much) chemo, so if my vision problem is related
at all to my cancer the dog data would tend to (weakly) indicate it is
more likely to be the cancer than the chemo that is the cause. (I wrote
weakly because the one article I found about dogs vision problems said
it was due to bleeding in the eye and retina detachment.)
Looking at the published
revlimid side effects paperwork I find it can degrade vision, affecting
10% of patients after two years, but differently than macular degeneration.
** "The frequency
of onset of cataracts increased over time with 0.7% during the first 6
months and up to 9.6% by the 2nd year of treatment with rev/dex. (Celgene
revlimid proscribing sheet)
'Eye' food supplement
My eye doctor recommended taking
a (food) supplement with carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, saying there
is some clinical evidence this may help. I have not researched this, and
I am generally skeptical of food supplements, but I started taking a pill
for this. Why am I am not surprised that after taking this eye food supplement
daily for six weeks I can sense no improvement, if anything my eyes are
getting worse.
(Nov 2015)
While my eyes continue to
be variable, my impression is that they have been better in recent weeks
and months than they were when last tested. I am going to have my eyes
retested tomorrow, so we will see. I have been taking a food supplement
pill daily with lutein (25 mg) and zeaxanthin (5 mg) since my last eye
test. And perhaps more important for about the last six months, since my
chemo transitioned to maintenance, I have not been taking the corticostereoid
dexamethasone, and a lot of things in my body have improved (like my fingernails,
and skin growths), so I am hoping my eyes have improved too, or at least
not further deteriorated.
So another daily pill I need
to take. Now every day I take at least two pills: full dose aspirin and
a lutein/zeaxanthin pill. On days 1-21 I add the (large) revlimid capsule,
and at the beginning of each week the 'pulse' of dexamethasone requires
taking five (tiny) 4 mg pills (20 mg/dose). So during a chemo cycle the
number of pills I need to take daily is either 2, 3, or 8. I'm not a great
pill swallower and the 25 mg revlimid capsule is quite large, but
I find it goes down easily. The 4 mg dexamethasone pills are tiny, so I
do the five of these in two swallows. My oncologist gave me no specific
instruction on when to take them. The clinical trial paperwork wanted the
revlimid and dexamethasone taken an hour apart on an empty stomach. Too
much BS for me, I take all my pills together after eating breakfast or
lunch..
Overview -- How MM
patients die (5/3/17)
How MM patients die
My hematological oncologist
at our last meeting was talking freely about how MM patients die. This
is a change, as usually she don't talk about this. (Is this a hint?) MM
patients can die in a lot of ways, but she was telling me two common ways.
One is that they get an infection (like pneumonia) that they can't shake,
and another is that become dependent of blood product transfusion (like
platelets) and eventually they say enough is enough and just stop the tranfusion
letting nature take its course.
When I think about this,
they are both explained by the nature of where MM cancer cells are located.
MM is unusual in that the cancerous plasma cells that create antibodies,
one of the four blood cells types, are located in the marrow of bone, typically
in the large long bones, the ribs and vertebrae, though I already know
of an exception to this in that the narrow in the small sphenoid bone behind
my left appears to have a lot of cancer cells that have exploded out to
form quite a quite large plasmacytoma (soft tumor composed of plasma cells)
that affected my vision. I got (and still have) double visiion when looking
right because the sphenoid bone plasmacytoma was pushing on the muscles
that move the left eyeball reducing its range of motion.
Thus MM cancer cells are
effectively trapped growing in a fixed volume (assuming other bones
are pressed into survive, which they might be). This is very different
from cancers that form solid tumors in vital organs where the tumors can
just grow and grow. As the cancerous plasma cells grow in number (which
is what cancer cells do!) in this fixed volume, the space available inside
the marrow for the cells that create the other three types of blood cells
is reduced, so the number of white blood cells, red blood cells, plateltes,
etc in the blood slowly goes down. In addition the antibody cells created
by the cancerous plasma cells, since they are all clones (hence the 'M-spike',
one of the MM blood cancer markers), don't work effectively either.
Hence once the cancer evolves immunity to all the chemo drugs and begins
to grow, your blood gets all screwed up, the number of all four blood cell
types begins to decrease. This I think explains a lot about how cancer
patients are clinically affected, and how eventually they die.
For example, low levels of
white blood cells and anti-body cells, allow infections to take and not
be shaken, because your immune is compromised. Low levels of platelets,
which control clotting, leads to platelet transfusions, so essentially
you don't bleed to death internally. To pursue this further requires some
more knowledge of the nature of blood
Nature of blood
Diagrams on Wikipedia show
blood cell creation involves a long complex series of steps. There is a
whole chain of events in the marrow to create the four basic types of blood
cells. What really counts is the nature of the blood cells and plasma components
that comes out and form your blood.
Introduction
Here's an introduction from the
National Center for Biotechnology Information with a nice image of how
blood in a test tube naturally separates into three layers due to density
differences. Starting with the three separation levels they identify three
basic types, but these further divide into many, many others (as a look
at you own blood work will show). For example, as noted below, there are
many types of what are collectively called 'white blood cells' that individually
are tracked in blood work.
Antibodies are a small but
complex Y shaped protein, normally are all slightly different to fight
a wide range of infections. The wide range of anti-body proteins are created
by a similarly wide range of plasma cells. MM is a cancer of one
(or two) of the plasma cells that make antibodies. Antibodies are proteins,
a sequence of amino acids, and like all proteins they are small molecules,
so they are found floating around (effectively dissolved) in the watery
plasma of the blood.

(source -- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2263)
M-spike
The particular plasma cell that
has gone cancerous pumps out a huge amount of a single type of antibody.
This forms one of the diagnostic blood markers of MM. In the lab when antibody
proteins are spread out by weight and diffusion constant, in health people
they form a smooth curve since they are slightly different, but in most
MM patients a spike will be found riding on the curve. The area
under this spike is called the 'M-spike'. It is a measure of identical
(hence monoclonal) antibody proteins in the blood, so in a sense it tracks
the body average of how many cancerous plasma cells are in the bones. All
proteins in blood work are measured in units of g/dL, so in my tracking
table (above) I calculate the {M-spike/total protein] ratio}. This ratio
was at 50.1% before I started chemo in Nov 2014, but within about six months
my chemo had driven this ratio down to 3% to 4% (or less) where it has
remained for the last two years. So M-spike (and this ratio) works for
me, which is not true of all MM patients!
Marrow biopsy
An early bone marrow biopsy
(technically a bone marrow aspiration) into my hip bone, done with a long
needle to extract a sample of its marrow, showed that cancerous plasma
cells made up 70% of the sample, whereas normally it would be at less than
10%, meaning 70% of the available volume has been taken over by the expanding
cancerous plasma cells leaving only the remaining 30% for the cells that
create the other cells of the blood (check these numbers). This is a reduction
in space by a factor of three (90% =>30%). No wonder the blood is all screwed
up.
2nd look at
stem cell replacement option
From my research I find
that interest in stem cell transplants, which just a few years ago was
the gold standard for multiple myeloma, now seems to be lessening. My doctor
while saying she supported my decision to not have a stem cell transplant
and did not not think it unreasonable, still nevertheless occasionally
brings it up, like at our last appointment. In the intervening months I
leaned two new things about stem cell transplants. One is a guess I have
that it may be a driver as to how long doctors push to stay on high dose
chemo, because for bone marrow to be harvested and successfully reinserted
the number of cancer cells it contains must be small. The harvest goal
as I understand it is a CR (complete response), which in practical terms
means a 95% or more reduction in cancer cells from the original baseline.
Two, I have discovered from reading multiple myeloma patent postings
that there is an intermediate step that can be taken. After chemo drives
down the cancer cells to low levels, even though some don't plan on having
a stem cell transplant they go ahead and have marrow extracted from their
bones, which is then frozen and can remain for years. This is insurance,
it could provide an option in later years to do a stem cell replacement
when chemo stops working. Based on the small mount of marrow that was extracted
from my hip bone for my DNA assessment, I expect the more extensive marrow
extraction is likely an unpleasant and moderately painful outpatient procedure,
but since I haven't asked about this or researched it, I don't really know.
Chemo maintenance
As I write, an important
clinical decision in my chemo is coming up pretty soon, a transition from
high dose dex/rev to a maintanence regimen. On MM forums I find that patients
who have had stem cell transplants frequenty go long periods taking no
drugs at all. Several recently completed clinical trials summarized in
the New England Jouranl of Medine make a strong case for continuing to
take revlimid, but at a lower dose. I see the same pattern of revlimid
maintence in the ongoing phase 3 MM clinical trials. There the revlimid
maintanence dose is given as 10/15 mg. What this means is 10 mg, but pushed
to 15 mg if toxity can be handled and probably for younger patients. My
doctor is dropping hints that her recommendation for maintenance chemo
will likely be 10 mg revimid (no dexamethasone).
Clinical trial time lag
Reading about the clinical
trials and thinking about them, I begin to realize the huge time lag in
this process. Sure the clinical trial is the 'gold standard', and for the
medical community the lag is tolerable, progress slowly gets made and treatment
improves. But to a patient with limited lifetime the situation looks somewhat
different.
Clinical trials for MM chemo
are slow, really SLOW.... A phase 3 clinical trial needs to enroll 600-700
patients. This is 3% of all the patients diagnosed with MM in USA in a
year! It takes a long time to recruit so many patients. As treatment options
get more successful, the follow up time required to determine if a new
treatment works better than the old treatment takes longer and longer.
I see follow up times going out to six years. A MM clinical trial started
in 2010 is scheduled to run to 2018 or 2020. And this doesn't include the
time for phase 1 and phase 2 trials a new drug needs to reach the phase
3 stage. Bottom line when clinicians see (in limited testing) that a new
drug or drug combination is working well and might be preferred over the
current baseline treatment, it will take about a decade to confirm
if this is right. Hence treatments for MM based on clinical trial are really
based on thinking more that ten years old!
One way to cut the lag is
to play the odds. How successful have new MM drugs and drug combo been
when tested? In some fields clinical trials fail all the time, but my seat
of the pants guess is that for the last decade MM clinical trials have
been remarkably successful (need to research this). If this is right, it
means the drug companies are doing a great job, and the intuition of clinicians
has been good.
Seems to me what
clinicians do is fairly stright forward. If three drugs with different
mechanism are available, the obvious test is check if three different drugs
work better than two with acceptable side effects.
The drug companies make incremental
improvements to reduce side effects, improve response, and/or make drugs
easier to take. Millennium has a unique FDA approved drug, a proteasome
inhibitor, for MM (velcade), but it must be admnistered by injection, so
they develop a a proteasome inhibitor in pill form. How many years is it
going to take to check out this new form of a a proteasome inhibitor? A
lot. I see a 2012 announcement from Millennium that its new oral a proteasome
inhibitor (MLN9708) has shown a high response in phase 1/2 testing, but
in 2015 it's still an experimental drug, and the clinical trial I was offered
was a phase 3 test of it.
Accessing my hospital records
My experience has been accessing
my Lahey patients records is a black hole. In all my early multiple meetings
with doctors to stage my cancer and work up a chemo plan the subject never
came up. At these meetings I got print outs of my blood work, an occasional
copy of a paper, and oral descriptions of my DNA results. I first leaned
that I could get a print out of my 'history' from a nurse in the zometa
infusion room, who asked if I wanted it. Yes! It turned out to be many
pages consisting of contemporaneous notes my doctors had written up after
our meetings (who knew!) plus several sets of blood numbers. Until this
was handed to me I no inkling this data existed. When I later told my doctor
I had obtained my history, she didn't seem to know what I was talking about
and asked me to bring it in to show her on my next visit, which I did.
(I have found these doctor notes very useful in writing up this log. You
can't remember everything you are told, and I find the notes contain a
lot of information I was never told.) Later inquires about accessing my
history to nurses in the injection room would yield only the platitude
that 'your history is your history' and you have access to it.
In a separate building from
the hospital Lahey has patient document building. It's web site talks about
obtaining records or a relatively steep fee, so I didn't pursue this. Someone
told me (forget who, probably a nurse) that images (x-rays, etc) could
be obtained free. So I telephoned and it was confirmed that images were
free, and very quickly (day or two) I was able to pick up four DVDs full
of images (some of which are below). However, the image I was most interested
in, T12 bone loss, is not there (at least unable to find it in two complete
passed the DVDs.)
Come April 2015 and hospital
is converting to a new electronic record system from Epic and a patient
portal, called MyLaheyChart, is part of that conversion. The bs from Epic
is that this Lahey portal provides patients access to their medical data
and history. There is one link in the portal where they say copy this info
to a thumb drive which you can give to another doctor so he will know your
history. Oh, yea! My history is blank, no record of my cancer or
my neck operation. Not only that, but my latest blood work, the only data
available in the portal, is missing the most important number, the monoclonal
M-spike, which tracks the amount of cancer in my blood. Some service to
the patients this is.
Lahey new
online patient 'portal' (4/15)
In April 2015 finally added
a patient 'portal'. Turns out this is part of big, very expensive conversion
of the hospital to electronic records being subsidized by the government.
The EHR (Electronic Health Records) vendor they chose is Epic who pretty
much has a lock on most of the big medical centers in the US. This is a
privately held EHR company with 8,000 employees! The 'mychart' patient
portal is part of the EHR system. One aspect I immediately liked is that
it provides a convenient way to email your doctor with questions, and twice
I got replies in two days as advertised, but most of the portal is a bust.
Here's a quick rundown of
the problems (see appendix for details):
a) No history --- Doctors are told that the system supports patient care,
they can easily look up the patient's records. Whether history is
visible to doctors I don't know, but it's not available to me. There is
no history in the portal prior to the go live date in April 2015,
which mean no information that I have cancer or had an operation at the
hospital seven months ago.
b) Most important cancer number in my blood work ('Monoclonal peak quant')
is missing. I first thought this was a simple error, but I now
suspect that this important data might have been deliberately withheld
(supposedly so the doctor can go over it first). Ironic since
my doctor already showed me the number prior to my even signing up for
the portal.
(update) 'Monoclonal peak quant' showed up in my 5th cycle results (now
it's called MONOCLNPK!), but my 4th cycle test results
have never been updated, there it remains blank.
c) Data format stinks: every blood panel is a separate click, out of range
blood values are not marked (H/L), a compact blood work summary
is available, but well hidden (you need to click 'Download my record' and
then 'Preview your Lucy record'). Well that's sure clear...
From my reading what
the Epic mychart portal provides is not so much due to its capability (it
can do a lot), but on what features the sponsoring organization, i.e. Lahey,
has chosen to implement.
MyLaheyChart (update 9/2/15)
I just discovered a lot
of detailed information about me in Lahey records. I've been very critical
of their online portal (MyLaheyChart.org) because it didn't contain any
historical information. My earliest records only went back a few months
to April 2015 when the new (Epic) medical records system began at Lahey.
However, I just discovered this week that older records have been added
(no announcement!) and now go back to my time in the hospital (Sept 2014).
I had a lot tests in my week in the hospital multiple MRI's, CT scans and
x-rays. Turns out that the doctors that read the results type up (or dictate)
detail reports on what they find.
I found some interesting stuff. The x-ray
guy finds I have a broken 9th rib ["likely pathologic fracture right 9th
rib"]. NOBODY ever told me I had a broken rib! Another guy finds cysts
in my liver. If your a hypochondriac, this makes good reading. Even more
interesting I found during the neck operation that when they put the screws
into my neck bones one of them didn't go in right, straying out of the
bone into the spinal canal area, but they later fixed this. This is stuff
the doctors won't tell you.
On my broken rib
It might seem with the MM
diagnosis, and multiple bone lesions, and broken neck all in the span of
a few days that a broken rib is small potatoes, and in a sense it was.
Was that the reason nobody told me about it? I don't think so.
I think the issue here is
the specialization of doctors. In the hospital my (chief) doctor is cervical
surgeon and his team, he's a neck specialist. When I get out of the hospital,
I am handed off to the radiation doctor who has negotiated (so she told
me)
to irradiate two areas: my neck lesion and a big T12 spine lesion, so that's
her focus. Next in line in the doctor parade is my hematological oncologist
who specializes in blood cancers. Her job is to assess the severity of
my cancer and set up a chemo regimen. She doesn't do ribs either.
At one point I asked for
a consultation with a bone man because I was concerned about the stability
of my left femur with its large 'hole' clearly visible on x-rays. He only
looked at my femurs.
None of them do ribs. The
result is an x-ray finding of a broken bone, probably broken by the cancer,
was never forwarded to me.
Simplistic Lehay portal info
Below gives a hint about the quality
of the portal. In the test results area most of the tests have an info
link: "About this Test". I just clicked a few. Here's what the link of
the "PROTEIN ELECTROPHERESIS, SERUM" test says: (for starters 'Electrophoresis''
in the name of the test is spelled wrong!)
"The test (protein electrophoresis test) separates proteins in the blood
based on their electrical charge." (Not really. Yes, the charge
determines the (electrical) force pushing on a protein. But for a given
charge what distance a protein moves depends on its diffusion constant,
and that in turn depends on the size, weight and shape of the protein.
Small, light protein molecules are able to diffuse (move) in a gel more
easily than large, heavy proteins molecules. It is the combination of the
charge and diffusion constant differences that cause the various proteins
in blood serum to spread out in a gel strip so they can be identified.)
Dana Farber portal
(2/16)
Dana Farber cancer center
in Boston is one of the teaching hospitals of Harvard medical school and
is world famous as a treatment and research center for multiple myeloma.
They have more than a dozen doctors and researchers who are full time specialists
in the disease. I have recently begun seeing a doctor at Dana Farber in
Boston, so I have access to its online portal where I can see my test results.
I was hoping it would be better, meaning more patient friendly, than Lahey,
but it's not, in fact it is worse.
Background on Boston hospitals
For years now the bigger
hospitals in the Boston area have been buying up the smaller independent
hospitals, so that now in greater Boston there are essentially two groups
of hospitals with common ownership. The suburban group, owned by Lahey,
and the downtown group, owned by Partners Healthcare, which includes Dana
Farber and Mass General. The electronic medical records and portals of
both use Epic software.
Here's a sample of my blood
work as posted. Yikes! No concern for the patient at all. All the
blood components shown in the first panel excerpts (every one of them!)
are identified only by a cryptic three or four letter shorthand. Would
it kill them to write, say, after WBC (White blood cell count). I mean
the page is mostly blank. But either they can't be bothered, or more insidiously
it is done deliberately to keep patients from asking questions of their
doctors. I don't think I am being paranoid. Look at my PLT (platelets).
It is outside the normal range (Revlimid decreases platelets), but notice
there is no 'H' or 'L' marked to indicate an out of range value.
Yet the same print out at the hospital, which looks nearly identical, has
out of range values so marked. It was suggested to me by one of the blood
technicians at Lahey, which also omits 'H' and 'L' online, that 'H' and
'L' might be omitted to keep down questions.
Dana Farber online portal blood results (CBC and Differential panel,
partial, Feb 2016)
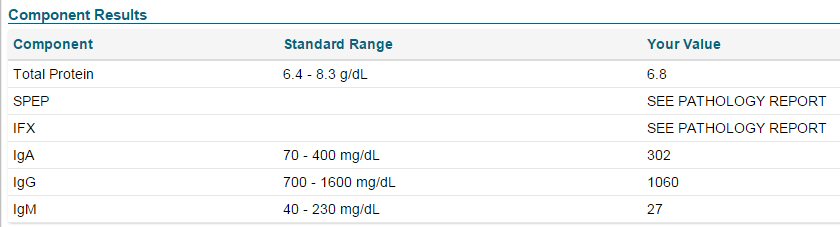
Dana Farber online portal blood results (SPEP panel, Feb 2016)
Blood collection issue
The cryptic SPEP caused
a problem when I had my blood taken at Dana. I always inquire if the blood
panels include (and here I describe it several ways to the blood technicians)
protein electrophoreses, M-spike, monoclonal spike. These are the terms
I use at Lahey. The Dana Farber blood technicians didn't know what I was
talking about. I was taken aside while they consulted someone who told
them yes the test was included. They then told me "SPEP panel" included
what I wanted, but SPEP meant nothing to me. This is a serious problem
of communication. Not only do the printed blood results use the cryptic
SPEP, but this is apparently the only way the blood technicians know to
describe the test.
Where's the M-spike?
I am more disappointed by the
results shown in the second panel. This blood panel and its key test are
identified only as 'SPEP'. I have been at this 16 months, and I didn't
know what this meant without looking it up. SPEP is shorthand for 'Serum
Protein Electrophoresis'. Lahey blood results call this panel 'Protein
Electrophoresis, Serum', you know, actual (medical) english. It's the protein
diffusion test that measures the primary marker of MM the M-spike (or monoclonal
spike). And here's the second problem and it is a big one. The M-spike
value is in the 'pathology report', but the pathology report is not
online. That's right a world class MM research center doesn't make the
primary marker for the disease available to its patients online! Lahey
routinely puts M-spike results online.
It is not a question
of prior approval. My doctor already gave me my M-spike results on the
phone. He confirmed the pathology report is not on the portal. I found
I can get the results in writing by calling the office and request they
mail it to me, so I did, but this is just so stupid... I expected better
of Dana Farber.
M-spike arrives online (after 10 days) (update 2/18/16)
Ten days after my blood
collection and a full week after my doctor called me to discuss the labs,
the Dana pathology report appeared online with the M-spike data. Why the
huge delay? Who knows. By the time it showed up online the hard copy I
had requested had arrived in the mail.
How many multiple myeloma patients might my hospital be treating?
A useful piece of information
I would like to have as a patient is how many other multiple myeloma patients
might my hospital be treating, but I find information like this very hard
to extract, certainly I can't get my doctors to talk about it.
Here's a back of the envelope
calculation: 22,000 new patients are diagnosed with multiple myeloma each
year in USA. Greater Boston has a population of about 4 million, let's
call it 1% of US population, so that's 220 new multiple myeloma patients
in greater Boston per year. Now how many hospital do they divided into.
I really have no idea how many large (cancer) hospitals there are in greater
Boston, but there must be at least ten in Boston alone, so a seat of the
pants guess is 20, so that's 11 new patients per hospital per year or roughly
one new patient per month per hospital. If the average patient survives,
what five years (?), then the typical large hospital is treating 60 patients.
If there are say 4 hematological oncologists on staff who handle multiple
myeloma, then each oncologist gets (on average) 3 new multiple myeloma
patients each year. But how are patients assigned since some staff members
may be new to the hospital while longer serving staff may already have
their quota of multiple myeloma patents? Let's say the 12 new multiple
myeloma patients per hospital per year are assigned to two newer younger
staff members, then each of them acquries a new multiple myeloma patient
every other month.
Thinking about it for a minute
I see a couple of other approaches to getting a number. MM in the literature
is described as being 1% of all cancers and 10% of blood cancers, so if
the hospital would state how many cancer patients it manages, or even better
how many blood cancers the that would give a number.
How much experience do new staff doctors have with MM?
A corollary of my patient
calculation just struck me. If new hematological oncologist on staff are
only acquiring newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients, then they probably
have had little experience in treating end of life conditions. Their multiple
myeloma patients have just not had enough time to get sick and die. (I
am particularly interested in this because I see my oncologist only joined
the hospital staff two years ago.)
I asked this of a consulting
oncologist doctor at Lahey and was told that new staff members who are
likely to be replacing staff members who have "retired" (or departed) will
typically take over their MM patients. (Sort of a boilerplate answer, but
probably is partly true.)
'Happy talk' from doctors
My regular oncologist goes
lite on the 'happy talk', but in my one meeting with another oncologist
(to get a 2nd opinion) I heard some things from him that I am skeptical
of and would classify as 'happy talk'.
One of these was a mention
that MM bone 'holes' (hollowed out areas of the bone from the inside) were
able to grow back. Directly contradicting this, or more specifically showing
how unlikely this is, I found a paper that focused on a single patient
where the dimension of 'hole' in his left femur was reduced in size by
a factor of two. In other words the (partial) growing back of bone to reduce
the size of a MM lesion is so unusual, and this was made clear in the abstract
of the paper, that it justified a whole paper being published to discuss
this happening in a single patient! So it can happen, but the consulting
doctor implied (without actually saying so) that this was possible or likely
to happen. Hence my characterization of it as 'happy talk'. [The status
of a large 'holes' is of particular interest to me, because I too have
a hole in my left femur (bigger than the one in the paper) and also substantial
bone loss in my T12 vertebra.]
Second comment I would classify
as happy talk was the comment that patients diagnosed with MM in 2015 will
survive 7 (or 8) years. Not only did this number seem high, but it was
this was thrown out at the end of the meeting with no qualifications about
staging, age, genetics or stem cell replacement, so for these reasons I
am skeptical of this and consider it happy talk. I do occasionally see
high numbers, but survival numbers in MM clinical trials, which admittedly
reflect older treatments, are much less than this. However, Mayo Clinic
does claim a median survival time is now about 8 years, so maybe the comment
is reasonable.
Cancer.org gives median survival
time of less than four years for stage II and 2.5 years for state III (I
am stage III), but cautions this is for people treated 5 to 25 years ago.
This is probably hard data found in completed clinical trials, which would
have begun at least a decade ago.
-- "The average
newly diagnosed myeloma patient 15 years ago, for example, was about one-third
as likely as someone without myeloma to live another five years. By the
end of the 2000s, in contrast, that same myeloma patient would be 45 percent
as likely as someone without myeloma to live another five years." (http://www.myelomabeacon.com)
I don't see this a big improvement, and is saying as of a few years ago
less than half MM patients were surviving five years.
Mayo clinic, a leader in MM
treatment, reports high numbers: close to 90% 3 years survival.
-- "Although the
disease remains incurable, with the introduction of autologous stem cell
transplant (ASCT) and newer agents, such as thalidomide, bortezomib, lenalidomide,
and carfilzomib, median overall survival (OS) has increased from 2 to 3
years a decade ago to greater than 8 years currently." (Mayo
clinic, 2013). The reference given for this is survival time is this
paper: Kumar, S.K., Rajkumar, S.V., Dispenzieri, A. et al. Improved survival
in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood.
2008; 111: 2516–2520), but a look at this paper shows 50% survival
time of less than four years! And as I scan the full text, I don't see
any support in this 2008 paper for an 8 year survival claim. (As a footnote,
the paper shows the median time to relapse after stem cell transplant was
only 13 months. Yikes!)
Why multiple myeloma relapses
Why multiple myeloma invariably
comes back after chemo is an area of active research. Different teams have
different theories. Research from Mayo clinic identifies the cause as immature
cells are not touched be chemo and later they mature and reboot the cancer.
http://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/files/2013/09/News-Release-Multiple-Myeloma-Sept.-18.pdf
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
My Pictures
Yup, this is me...
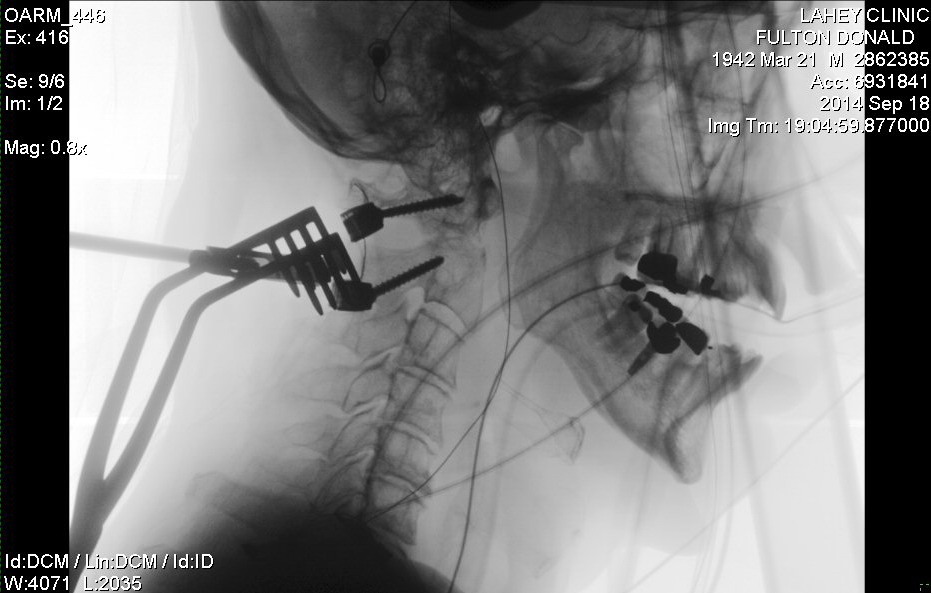
positioning hardware during neck fusion operation (9/18/14)
Forked clamp holds the incision open, some of the screws into C1,
C2 vertebra are in.
(jaw clearly shows my dental implant and various caps)
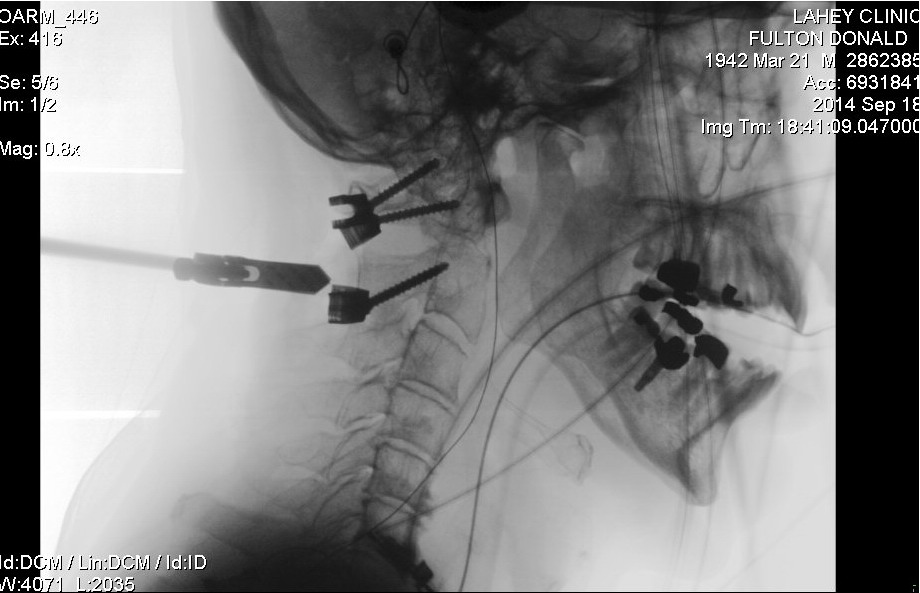 .
.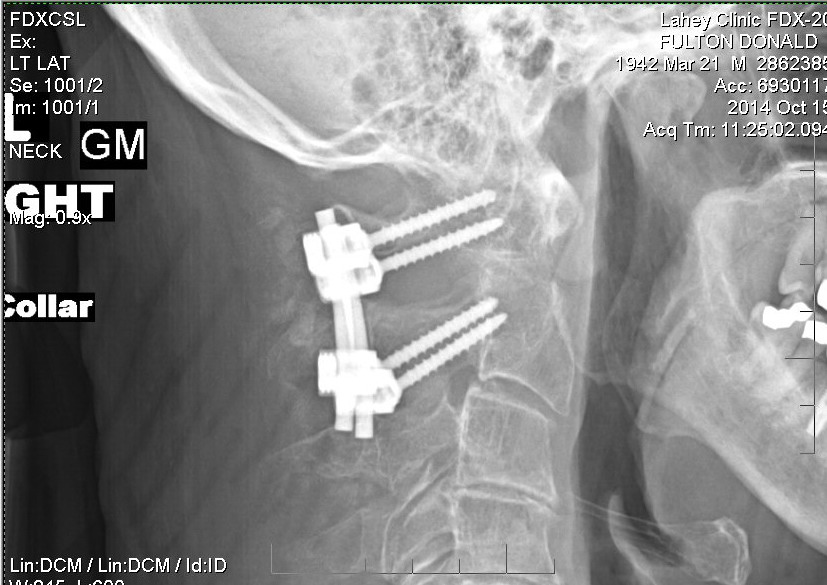
left: x-ray taken during operation
right: x-ray check of c1,c2 hardware alignment a month after operation.
(The rods are clamped
to the screw heads with sort of an inside-out nut and bolt
configuration.).
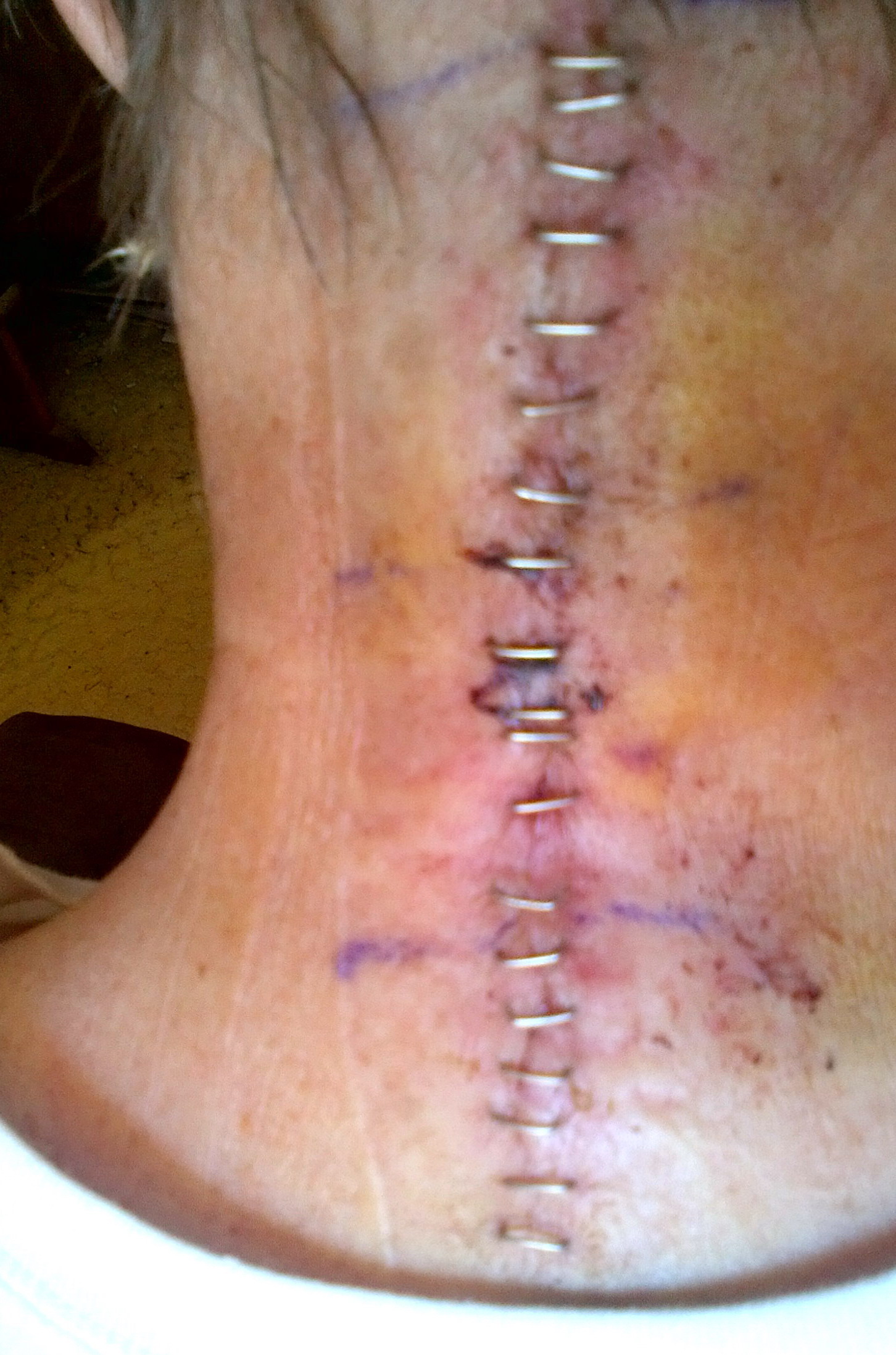 .
.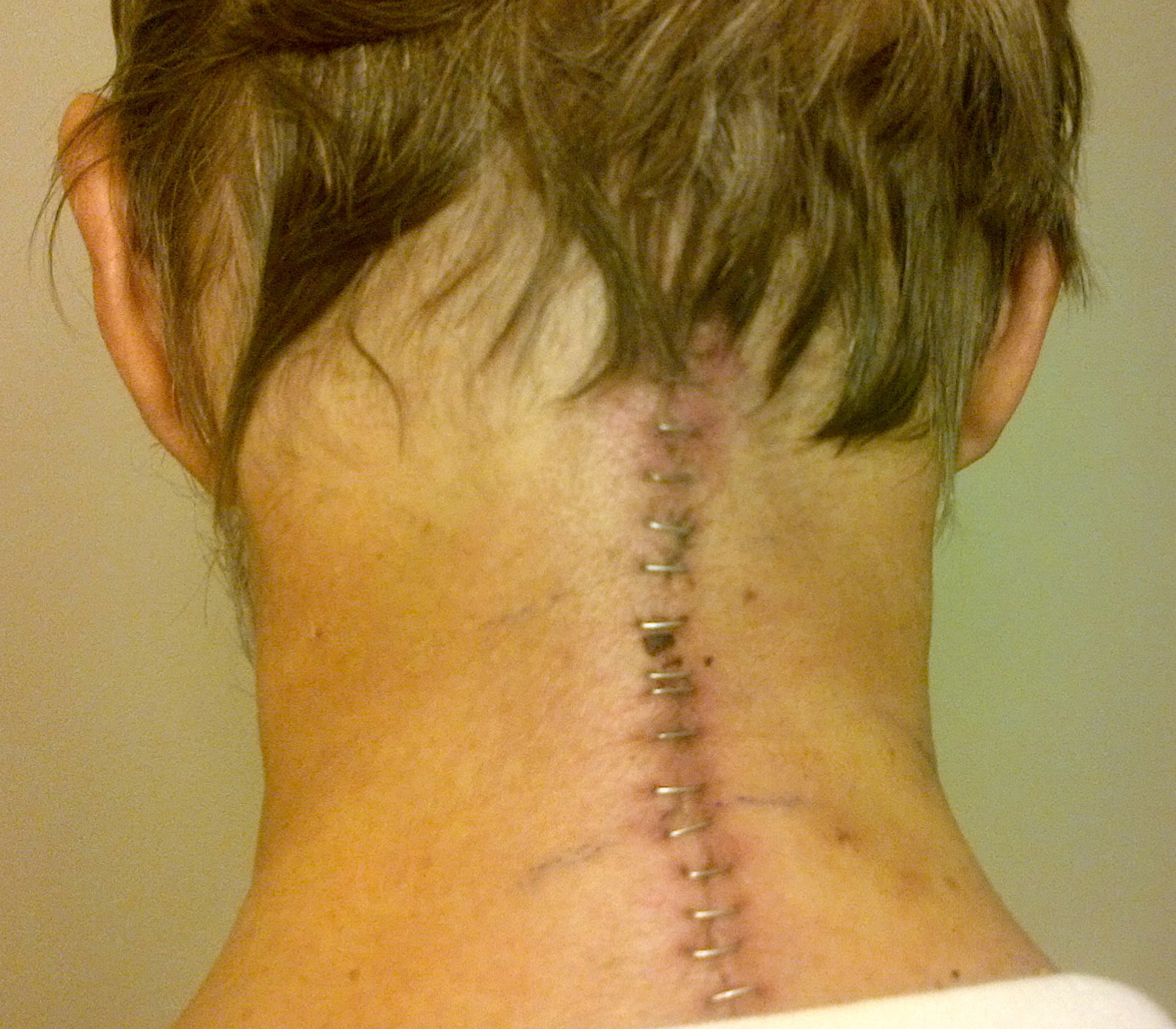
left: neck staples at home five days after operation
right: neck staples a week later (note the healing).
(The staples were removed a day later (10/1/14) by a nurse practioner
at Lahey
who said the healing looked good, no sign of infection.)
 .
.  .
. 
freaking stiff neck collar worn high (left) and really high (right)
right: Miami J c-spine immobilizer by Ossur (my collar was adjustable
Miami J)
24 hours/day for a month after operation and during day for 2nd
month
(It was supposed to be worn under the chin and tight where it gave
the best support,
but that was very uncomforable and impossible to eat, so I usually
loosened it a little and let it ride up.)
 .
. 
my custom made radiation mask
used to bolt my head to the table during neck radiation
two x-ray views of large (1.5" top to bottom) 'hole' on outside
surface of my left femur (contrast enhanced).
This bone tumor was not irradiated because it was not discovered
until later, when my MM was staged.
It took me a long time to understand that what the doctors were calling
a 'hole' was really INSIDE the bone.
It is a hollowing out of the bone beginning at the marrow/bone interface.
This 'hole' doesn't hurt, and the reason for that is probably that
the 'hole' has not penetrated to the surface,
hence the pain sensor filled membrane around the bone (periosteum)
is undisturbed.
 .
. .
. 
left: summer 2014 before cancer diagnosis
center: selfie taken in early Jan 2015 (on chemo, 3.5 months after
diagnosis and neck operation)
right: selfie in radiation mask (who says cancer can't be fun)

my hospital room at Lahey (room 38 in Central 7th floor) first morning
in hospital (Tues 9/16/14)
(only picture I have taken during 7 day hospital stay)
My radiation oncologist showed
me beautifully clear images of my back, and went over in great detail my
loss of bone in T12 vertebrae. My hospital documentaion dept has supposedly
given me all my images (4 DVDs!), but I cannot find those T12 images. The
closest images I can find are below and from comparison to an MRI I found
online with T12 labeled, it does look like the verterbrae near the bottom
with the weirdness is probably T12. I can't make any sense of the weirdness
of T12 in these images. In the top images it appears to overhang the adjacent
disks, but in the lower images the right side of the disks adjacent to
T12 looked thinned.
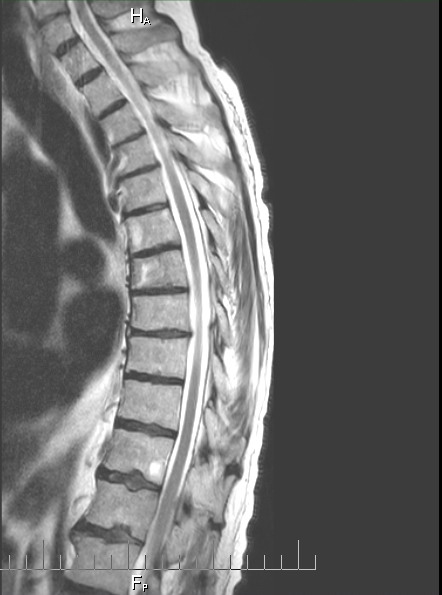 .
.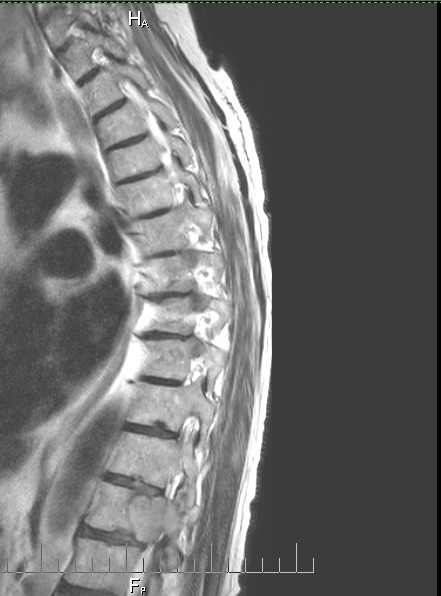 .
. 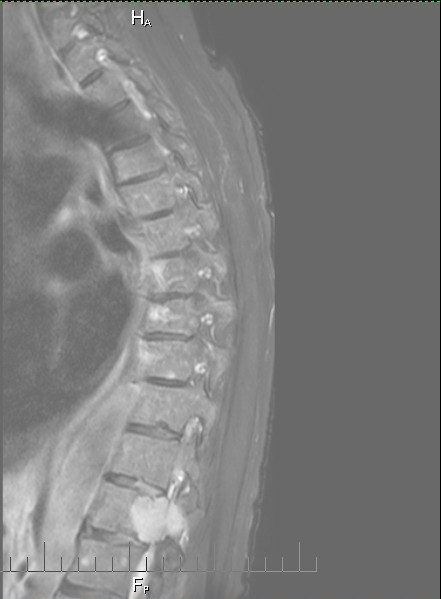
Vertebra T12 lesion (I assume) in various MRI views (9/18/14)
(left -- normal appearance)
(center, right -- T12 lesion visible near bottom)
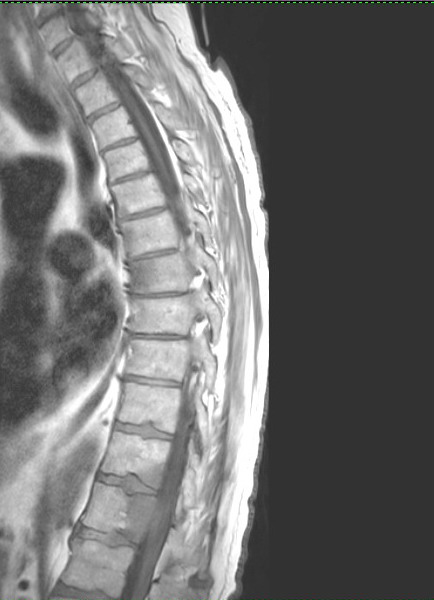 .
. 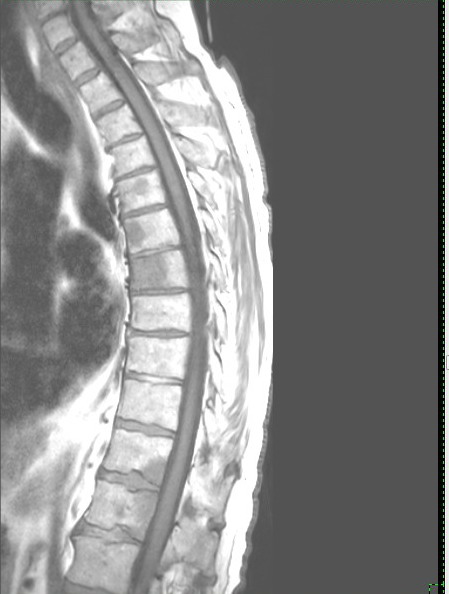 .
.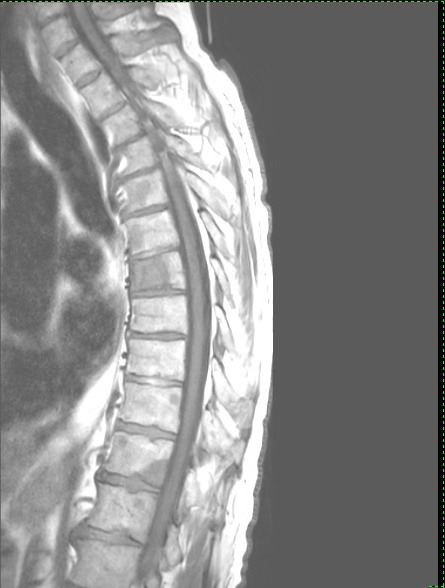
T11 involved? Is this is this real or an artifact?
(It doesn't seem reasonable that a T12 lesion would 'extend' to
T11, which is a separate bone,
and same darkening is seen in T7.)
Inventory
of my MM bone tumors (12/17/15)
'Multiple myeloma'
refers to a characteristic feature of this cancer. It is found at multiple
sites within the bone marrow (myelo-) with accumulations of tumor
(-oma) cells. Unlike solid tumor cancers where cancer cells at least
initially are localized, in multiple myeloma being a blood cancer the cancer
cells spread thoughout the body almost from the start, so a MM patient
typically has bone tumors throughout his body by the time the disease is
diagnosed. (You have to consider you have cancer from "head to foot" I
was informed by a resident leaning over me while being wheeled through
the corridors of the hospital after my neck broke.) Hence the goal of MM
chemo is to try to keep those many bone tumors in check.
For 'fun' I thought I would
pull together all the various references to my bone tumors discovered in
readings of my x-rays, CT scans and MRIs in the fall of 2014 in my medical
record and organized them by location. Why, because other than saying I
have cancer 'from head to foot', I really have no idea where bone tumors
have been spotted in my body.
After taking my inventory
I see my tumors are all in the classic areas that MM tumors are usually
found: head, neck, spine, ribs, pelvis, and upper arm and leg bones. Soon
after my C1,C2 fusion operation I had two weeks of cancer radiation of
my neck and back. How narrowly the beam was focused on C2 and T12 I don't
know, because in both cases there were tumors in adjacent and nearby vertebrae.
----------------------
Update (5/9/17)
A recent pet scan
(in a sensitive setting!) has much of my spine lit up like a christmas
tree! (not clear what this means) Bone pain is common in MM patients, but
I have had NO bone pain (aside from a little neck discomfort associated
with my failed C1/2 fusion). That's good luck with all these bone tumors.
Pet scans have found more tumors like in 2nd rib front and in sphenoid
bone behind my left eye. The recent bone focus has been on the 9th rib,
rear plasmacytoma, my most metabolically active tumor, last measured at
3 cm across (1.95") up from 2 cm just two months earlier.
I had a 2nd round of
head radiation to irradiate a tumor in the sphenoid bone behind my left
eye that was affecting my vision, and I insisted that the nearby tumor
on my jaw also be irradiated at the same time, which it was. Later scans
show a huge chunk of my T12 vertebrae is just gone. For the last two years
I have been getting in infusion of a drug monthly (Zomata) that works well
to strengthen bones, same drug given to older women once a year to prevent
osteoporosis.
----------------------
Head and skull
-- skull has "multiple"
tumors ("well-defined lucent lesions")
-- upper right jaw near
the pivot has a tumor ("focal lesion in the right mandibular ramus")
Spine, cervical (neck)
-- C2 has a "diffuse infiltrative
tumor" with a pathologic fracture. In english a cancer caused broken neck.
"The fracture line is oblique at the
base of the C2 odontoid process{ (vertical peg). The tumor
involves "most of the C2 vertebrae" including the "superior aspect of
the C2 body as well as part of the lateral masses" and "large lytic C2
lesion with pathologic fracture through the body of C2".
-- C3 has a tumor in "inferior
aspect of its vertebral body and inferior endplate"
-- C4 has a tumor in its
"spinous process and inferior endplate" (A biopsy of the C4 spinous
process tumor was taken during my C1,C2 fusion
operation to confirm the diagnosis of multiple myeloma.)
-- C6 has a "small
focus" tumor in it "spinous process"
Spine, thoracic (chest)
-- T1 has a tumor
in its "left superior facet" (identified as the "right superior facet"
in a summary). (Facets are small flat sliding cartilege
coated joints between vertebrae.)
T1 also has scattered bright spots that might be tumors, but "given the
small size of these lesions, these are equivocal"
-- 1.46" egg shaped abnormal
growth (destructive lesion) in T12 vertebrae body, left side and rear.
T12 has not compressed or fractured.
-- one note says T12 tumor
has expanded and is 'impinging' on the spinal cord (without compression),
elsewhere it says tumors
are 'moderately' narrowing the canal openings of T12 and L1
-- tumors of T12 and L1
are extending into the left nerve canal ('neural foramina', or canal between
vertebrae where nerves leave
the spinal cord) (This is not the same as the large hole (canal)
in the center of vertebrae for the spinal cord.)
-- tumors ("destructive
lesions") in T7, T11, and L1. (vertebrae near T12)
Spine, lumbar (lower back)
-- diffuse abnormal growths
in entire lumbar spine
-- tumor in L1 (directly
below T12)
Spine, sacrum
-- posible tumor in S1
Pelvis
-- several turmors in the
pelvis, most notably within the ('iliac wings' are the large flaring surfaces
of the pelvis)
Ribs
-- lower rib on right side
(9th rib) appears to have been broken by the cancer. (This might be the
cause of some chest pain I had while
exercising weeks before my neck broke.)
Arms
-- several small tumors
(well-defined lucent lesions) in both upper arm bones ("proximal humeri")
(humeri is the plural of humerus)
Legs
-- large 1.5" (top-bot)
well defined tumor in left femur (middle, outside edge, about 30% of dia).
Possibly other small tumors in the left
and right femurs, but not visible in later x-rays of right femur. (I included
x-rays of this femur tumor in this essay)
Details
of cancer in my bones from MRI and CT scans during my hospital stay (Aug
30, 2015)
Reading through my medical
records on MyLaheyChart recently I was surprised to find a lot of information
from tests taken during the time I was in the hospital (Sept 2014). (Not
sure if this historic material has been newly made available online, or
I just missed it.) I found two references (below) to my T12 vertebrae in
a write up of a lumbar spine MRI (with and without gadolinium contrast)
done 9/18/14, which was the day of my C1,C2 fusion surgery and prior to
it. There is also a reference to T12 in a 9/16/14 abdomen and pelvis CT
with contrast. This needs some translation, a work in progress.
MRI
-- Bones: Diffuse, enhancing,
neoplastic infiltration of the entire lumbar spine with deposits ranging
from punctate through expansile, 37 mm (1.46") ovoid left T12 pedicle and
posterior vertebral involvement. No lumbar compression or apparent sacral
insufficiency fracture.
-- Thoracolumbar junction:
There is impingement upon without compression of the conus medullaris due
to the large, dominant, left posterolateral T12 vertebral body and pedicle
expansile. (Wikipedia says the 'conus medullaris' is a name for the spinal
cord near the lumbar vertebrae L1 and L2. L1 is immediately below T12.
Wikipedia says injury to 'conus medullaris' can cause back pain and bowel
and bladder dysfunction.)
CT
1. Multiple additional osseous
metastases, the largest involving the left posterior lateral aspect of
the T12 vertebral body, likely amenable to biopsy. Probable pathologic
fracture posterior right 9th rib with adjacent overlying atelectasis.
(What! A broken rib. No one has ever mentioned this. I did have some rib
pain prior to my neck breaking.) (Atelectasis is lung tissue that is compressed)
2. T12 lesion demonstrates
moderate canal narrowing and extension into the T12-L1 left neural foramina.
Recommend correlation for clinical symptoms and consideration of thoracolumbar
MRI for complete characterization of spinal metastases.
Osseous structures:
Scattered lucent destructive
lesions among multiple vertebral bodies, the largest within the T12 vertebral
body at the left posterior lateral aspect extending into the pedicle with
associated canal narrowing and likely extension into the left neural foramina
at the T12-L1 level. Additional lucent lesions noted in T11 and T7, possibly
also S1. Probable pathologic fracture posterior right 9th rib with adjacent
overlying atelectasis. Additional lucent lesions in the pelvis, most notably
within the left iliac wing. Degenerative changes lumbar spine.
IMPRESSION:
1. Multiple
additional osseous metastases, the largest involving the left posterior
lateral aspect of the T12 vertebral body, likely amenable to biopsy. Likely
pathologic fracture right 9th rib with overlying atelectasis.
2.
T12 lesion demonstrates moderate canal narrowing and extension into the
T12-L1 left neural foramina. Recommend correlation for clinical symptoms
and consideration of thoracolumbar MRI for complete characterization of
spinal
metastases.
C2 descriptions (few days prior to C1,C2 fusion operation)
-- Metastatic lesion to
C2
INDICATION:
Acute pathologic fracture
of C2
FINDINGS:
There is diffusely abnormal
signal intensity involving almost the entire C2 vertebrae including the
odontoid process and most of the superior aspect of the C2 body as well
as part of the lateral masses. There is diffuse enhancement of the C2 vertebrae
except for the oblique fracture line at the base of
the odontoid process. The alignment of the fracture fragments is significantly
improved compared with the CT scan. The tumor is corresponds to the lytic
lesion seen on CT. There is no cord impingement. There is extensive prevertebral
edema from the anterior atlanto occipital membrane level to the C5-6 level.
Joint effusion is noted at the atlantodens interval. There is also edema
between the opisthion and the posterior arch of C1 as well as extending
posterior to the occipital bone.
The above findings are consistent
with diffuse infiltrative tumor involving C2 with pathologic fracture.
Other focal areas of tumor involvement include the following:
Anterior inferior aspect
of C3 vertebral body, C4 spinous process, inferior endplate of C4, small
focus in the C6 spinous process and left T1 superior facet. There are other
scattered tiny foci of hypointense signal on T1 weighted images which also
could represent tumor although given the small size of these lesions, these
are equivocal. There is also focal lesion in the right mandibular ramus.
The above findings are most likely due to metastatic disease although multiple
myeloma or lymphoma can have a similar appearance and clinical correlation
is recommended. PET-CT scan or bone scan could be obtained to evaluate
for an accessible site for biopsy. (Yikes, lesions in other bones
of the neck: C3, C4, C6 and T1)
IMPRESSION:
1. Tumor involving most
of the C2 vertebrae including the odontoid process with pathologic fracture
through the base of the odontoid now with satisfactory realignment. Extensive
prevertebral edema from the level of skullbase to C5.
2. Multiple other areas of
tumor involvement including C4 spinous process, inferior endplate of C4,
inferior endplate of C3, spinous process of C6 and right superior facet
of T1. Neoplastic (abnormal growth) lesion in the right ramus of the mandible.
('ramus of the mandible' is the upper section of the lower jaw) Findings
most consistent with metastatic disease, although lymphoma or multiple
myeloma can have a similar appearance. Clinical correlation is recommended.
(The bigger picture of this write up is that the cancer is affecting nearly
all the bones of my neck C1,C2,C3,C6, T1 and even my jaw.)
Post operation
Again noted is a a large
lytic C2 lesion with pathologic fracture through the body of C2. Alignment
of the fracture fragments is markedly improved status post fusion and is
similar to the preoperative MR examination. Lytic lesions of the C4 spinous
process and inferior endplate of C4. Postoperative air is seen in the region
of the C4 spinous process which was also biopsied. Multiple other lesions
are better delineated on recent MRI cervical spine examination. (My
surgeon later told me that the biopsy of the C4 spinous process lesion
(chunk of bone taken from the projection of the C4 vertebrae out the rear)
taken during the operation was used to confirm my MM diagnosis.)
IMPRESSION:
1. Immediate postoperative
examination status post posterior C1-C2 fusion. No evidence of immediate
hardware complication. Metallic streak artifact limits soft tissue evaluation,
however no large hemorrhage is identified.
2. Lytic C2 lesion with pathologic
fracture. Alignment of the odontoid fracture is satisfactory and improved
compared with prior CT scan.
Extremities: Several small
well-defined lucent lesions proximal humeri (upper arm bone).
IMPRESSION:
1. Multiple well-defined
lucent lesions seen in the skull, proximal humeri (upper arm), proximal
femurs (upper leg), and C2 vertebral body where there is a known pathologic
fracture. Findings are most consistent with multiple myeloma.
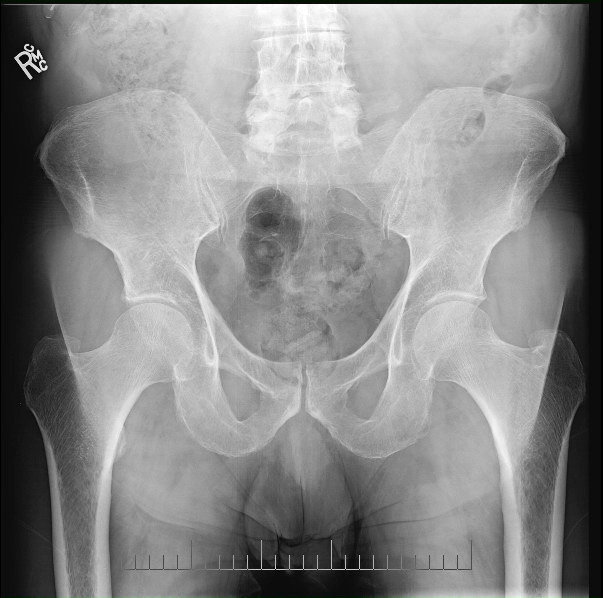
Is that a lesion in my pelvis upper right? (10/21/14)
At first I thought maybe, but now I don't think so.
One, a similar density difference above it indicates it's probably
in another plane, and
two, when I review male pelvises online, I find small density differences
like this on the right side.
However, write up finds a tumor in "left iliac wing", which if this
is a rear view, agrees with the density thing in the upper right.
(Nice view of my ball and socket hip joints, which seem clean)
One year
follow up cervical CT scan (9/16/15)
Prior to meeting with my
surgeon for a one year follow up to my C1,C2 fusion operation to stabilize
my pathological C2 dens fracture I had a new cervical CT scan (wo contrast).
(This scan takes only 5 min.)
I now understand I was not the best (or was maybe a poor) candidate
for a fusion operation to succeed, though no one ever said this to me.
Here are a list of my negatives:
1) Neck bones weakened by cancer --- C2 body (or
dens) broke in my sleep. Also C4 had a tumor that was biopsed during operation
2) Radiation -- I had two weeks of daily radiation on my neck
soon after the operation to kill the cancerous marrow cells. Apparently
the radiation is a negative for fusion to succeed. (I need to research
this.) The surgeon during the review asked if I had had radiation, implying
it was a negative, but not saying so. I don't remember any of my doctors
at the time mentioning that radiation might affect the ability of the bone
to regrow.
3) Cadaver bone graph material --- Best source of bone graph
material for a cervical or spine fusion is from your own body. The raw
bone is usually obtained from an incision in the hip and then powered.
I had no hip incision. The surgeon specifically told me the bone came from
a cadaver.
4) Age --- 72
5) Screw placement issues? --- There is reference to the one
of the screws to being oriented properly, that it first penetrated the
spinal opening. I presume that it had to be redrilled, but if this were
in issue it should affect only one of the screw seatings.
The key specifics are that bone
has grown into only one of the four screws. The lucency around three screws
is suggestive of screw loosening. (It would need to grow into all four
screws for any motion between C1 and C2 to be removed.) The fracture
of the C2 body has only partially healed. Bone graph material (from
cadaver) between the rear side arches of C1,C2 (interlaminar space) has
not been well incorporated. [Note in this review the C2 fracture (or fractures)
is described as in the body of the vertebrae. Does this means the
'dens'? My guess is probably yes, as the dens projects up from the body
of C2.]
Failing or failed C1,C2
fusion
The big picture here as
I see it is that my C1,C2 fusion has failed (or is failing) though my surgeon
did not use this word. It's 12 months and I read that 90% of cervical fusions
have succeeded by this time. On the other hand my bones began in a weakened
state, C2 fracturing while I was sleeping. Perhaps the first six months
should be discounted. I think it's possible (but maybe not likely) that
another six months may show some improvement. It was only a few months
my chemo coticosteroid was stopped, and I can sense my body getting back
to normal in a lot of small ways, also I am 7-8 months (of planned 24 months)
into zometa infusions for bone strengthening. So there's a chance that
another six months may show some improvement and that is the plan.
Here is the (complete) analysis
of the CT scan (1yr post operation) by a radiology resident obtained from
my online medical record (with text excerpts and notes below).


INDICATION:
Evaluate status of arthrodesis
(surgical fixation of a joint to promote bone fusion), status post C1-2
spinal fusion. History of multiple myeloma with pathologic fracture of
C2.
FINDINGS:
Patient is status post C1-C2
laminar screw and rod fixation for treatment of pathologic C2 vertebral
body fracture. The left C1 and bilateral C2 laminar screws demonstrate
periprosthetic (near hardware) lucency (opposite of opacity), suggestive
of hardware loosening. Right-sided C1 laminar screw appears well seated.
Persistent geographic lucency in the C2 vertebral body compatible with
previously imaged neoplastic processes with partial interval healing of
the anterior and posterior vertebral cortical lucencies, although residual
cortical lucencies persist (Lucency shows up as a dark shadow around the
screws.)
Posterior-lateral bone graft
material within C1-2 interlaminar space demonstrates inadequate bony incorporation.
(Laminar is a name applied to a region of the vertebrae. It is the relatively
thin bone that forms the rear arch around the spinal column.)
No acute fracture or traumatic
subluxation is identified.
Straightening of physiologic
cervical lordosis (normal curvature of the neck), unchanged. Vertebral
body heights are maintained. Intervertebral disk spaces and facets demonstrate
multilevel degenerative change. Disc height loss and uncovertebral hypertrophy
(enlargement) at the C3-4 through C6-7 levels causing multilevel neural
foraminal narrowing without high-grade central canal stenosis (narrowing).
IMPRESSION:
1. Postsurgical changes
of posterior C1-C2 screw and rod fixation for treatment of pathologic C2
fracture.
2. Inadequate incorporation
of C1-2 posterolateral graft material.
3. Periprosthetic lucency
surrounding left C1 and bilateral C2 laminar screws suggestive of hardware
loosening.
4. Geographic lucency within
body of C2 correlates to neoplastic lesion with partial interval healing
of anterior and posterior vertebral
cortical fractures of the C2 vertebral body.
5. Degenerative changes
of the cervical spine, as detailed above.
References
The jargon and abbreviations
used in many papers on MM is intense, so here's some definitions:
induction therapy jargon for standard initial chemo
treatment
refractory jargon for disease that has become resistanet
to (existing) chemo
sCR stringent Complete Response
normalization of the free light chain ratios
as well as the absence of monoclonal plasma cells in the marrow.
CR Complete Response --
> 95% reduction in monoclonal spike
VGPR Very Good Partial Response -- 90% to 95% reduction
in monoclonal spike
PFS Progression free survival
OS Overall survival
RR Response rate
FLC Free light chain ratio
ASCT Autologous stem cell transplant
TRM Transplant related mortality
A 2012 open source MM book,
very technical, each chaptor by different authors.
http://www.intechopen.com/books/multiple-myeloma-an-overview
======================================================================================
Appendix
History
and info on the thalidomide class of drugs
My main chemo drug, lenalidomide
(brand name Revlimid), is basically thalidomide, the drug that fifty years
ago caused a whole bunch of babies to be born with no arms and fingers
sticking out of their shoulders.
Thalidomide
Thalidomide must have a
curious history. It became famous decades ago when Life magazine published
pictures of babies born with no arms and fingers sticking out of their
shoulders! It must have been considered a safe drug at the time as it was
being given to pregnant women (to relieve anxiety I think). It had been
developed in Germany in 1957. The baby disaster resulted in the drug being
banned in 1961, but in 1998 it was (re)approved for the (chemo) treatment
of multiple myeloma. Not so many years ago thalidomide itself was used
as chemo for multiple myeloma, and lenalidomide (revlimid) is the result
of an effort to modify it a little to make it more effective and reduce
side effects.
Brief history of thalidomide (from Wikipedia)
"Four years after thalidomide
was withdrawn from the market (1961) for its ability to induce severe birth
defects, its anti-inflammatory properties were discovered when patients
suffering from erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) (complication of leprosy)
used thalidomide as a sedative, and it reduced both the clinical signs
and symptoms of the disease. Thalidomide was discovered to inhibit tumour
necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in 1991. TNF-alpha is a cytokine produced
by macrophages of the immune system, and also a mediator of inflammatory
response. Thus the drug is effective against some inflammatory diseases
such as ENL. In 1994 Thalidomide was found to have anti-angiogenic activity
and anti-tumor activity which propelled the initiation of clinical trials
for cancer including multiple myeloma. The discovery of the anti-inflammatory,
anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities of thalidomide increased the
interest of further research and synthesis of safer analogs."
Revlimid
What is revlimid (lenalidomide)?
The Celgene sheet says, "REVLIMID, a thalidomide analogue, is an immunomodulatory
agent with antiangiogenic (angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits
the growth of new blood vessels) and antineoplastic (acting to prevent,
inhibit or halt the development of a neoplasm, i.e. a tumor.)" Wikipedia
says it also has anti-inflammatory properties. It's a relative small small
molecule consisting of three carbon rings with the formula C13H13N3O3.
(Thalidomide is very close with the same three carbon rings and the formula
C13H10N2O4.) Under Wikipedia 'immunomodulatory' I find this:
"There are three
generations of immunomodulatory drugs, with each successive generation
being better tolerated and more active against inflammatory and malignant
conditions.
First generation
- Thalidomide
Second generation - Lenalidomide (revlimid) and pomalidomide
Third generation - Apremilast (brand name, Otezla). Approved to treat arthritis.
"Their mechanism of action
is not entirely clear, but it is known that they inhibit the production
of tumour necrosis factor, interleukin 6 and immunoglobulin G and VEGF
(which leads to its anti-angiogenic effects), co-stimulates T cells and
NK cells and increases interferon gamma and interleukin 2 production. Their
teratogenic (development problems, i.e. no arms!) effects appear to be
mediated by binding to cereblon. Apremilast, on the other hand, inhibits
PDE4."
Translation: The thalidomide
class of drugs messes around with a lot of the functions of the immune
system, and we don't have a clue as which of these effects makes it work
against multiple myeloma cancer cells, but clinically we know it works.
"Lenalidomide (revlimid)
is the first analog of thalidomide which is marketed. It is considerably
more potent than its parent drug (thalidomide) with only two differences
at a molecular level, with an added amino group at position 4 of the phthaloyl
ring and removal of a carbonyl group from the phthaloyl ring. Development
of lenalidomide began in the late 1990s and clinical trials of lenalidomide
began in 2000. In October 2001 lenalidomide was granted orphan status for
the treatment of MM. In mid-2002 it entered phase II and by early 2003
phase III. In February 2003 FDA granted fast-track status to lenalidomide
for the treatment of relapsed or refractory MM. In 2006 it was approved
for the treatment of MM along with dexamethasone." (So there's nine years
of history for the dex/rev treatment of MM.)
Half life of lenalidomide
in the body is 3-4 hours. It is removed by kidneys.
Pomalidomide
Until I started reading
up thalidomide in Wikipedia I had never heard of Pomalidomide. "Pomalidomide
(3-aminothalidomide) was the second thalidomide analog to enter the clinic
being more potent than both of its predecessors. First reported in 2001,
pomalidomide was noted to directly inhibit myeloma cell proliferation and
thus inhibiting MM both on the tumor and vascular compartments. This dual
activity of Pomalidomide makes it more efficacious than thalidomide in
vitro and in vivo. This effect is not related to TNF alpha inhibition since
potent TNF alpha inhibitors such as Rolipram and Pentoxifylline did not
inhibit myeloma cell growth nor angiogenesis. Up regulation of Interferon
gamma, IL-2 and IL-10 have been reported for Pomalidomide and may contribute
to its anti-angiogenic and anti-myeloma activities." Wikipedia shows it
was approved in Europe in 2009 ('orphan designation') for treatment of
MM.
"Lenalidomide is believed
to be about 1,000 times more potent in vitro than thalidomide in anti-inflammatory
properties and pomalidomide about 10 times more potent than lenalidomide.
It is worth noticing however that, when comparing lenalidomide and pomalidomide,
clinical relevance of higher in vitro potency is unclear since maximum
tolerated dose of pomalidomide is 2 mg daily compared to 25 mg for lenalidomide,
leading to 10-100 times lower plasma drug concentration of pomalidomide."
Here's the bottom line on
pomalidomide from the FDA site. It's another Celgene drug that can be used
with dexamethasone to (maybe) give a few more months after dex/rev has
stopped working. Below seems to say it only worked in about 1/3rd of patients
with a median extension of 7.4 months. (Another clinical trial data point
showing that dexamethasone greatly enhances the effectiveness of this class
of thalidomide drugs.)
"On February 8,
2013, the U. S. Food and Drug Administration granted accelerated approval
to pomalidomide (POMALYST capsules, Celgene Corporation) for the treatment
of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least two prior
therapies, including lenalidomide and bortezomib, and have demonstrated
disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy.
The approval was based on
the results of clinical trial CC-4047-MM-002; a multicenter, randomized,
open-label study in 221 patients with relapsed and refractory multiple
myeloma who had previously received lenalidomide and bortezomib and were
refractory to the last myeloma therapy. The treatment arms were pomalidomide
alone or pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone. The efficacy results
demonstrated an overall response rate of 7% in patients treated with pomalidomide
alone, and 29% in those treated with pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone.
The median response duration was not evaluable in the pomalidomide alone
arm and was 7.4 months in the pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone
arm."
Who gets what
"Thalomid-based therapy:
Currently more than 70% of newly diagnosed patients receive a combination
that includes Thalomid. Results of clinical trials indicate that combination
treatment with Thalomid and dexamethasone produces anticancer responses
in approximately two-thirds of patients, which is significantly improved
over dexamethasone treatment alone.
There are a large number
of effective chemotherapy drugs now available for initial, standard-dose
treatment of patients with multiple myeloma. The main goal of initial therapy
of multiple myeloma is to produce a complete or near complete disappearance
of myeloma cells in the body. Approximately 30-50% of patients can expect
to achieve this goal.
Alkeran-based therapy (melphalan):
Prior to the widespread use of Thalomid the most frequently used regimens
were Alkeran and prednisone and Oncovin, Adriamycin and dexamethasone (VAD).
Alkeran-based therapy is still the most common treatment for patients who
do not plan to undergo autologous stem cell transplant at some point in
their disease course." (outdated info from Texas Oncology)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lahey Hospital and
Medical Center
My hospital is the headquarters
of Lahey Hospital (formerly Lahey clinic) in Burlington MA (suburb of Boston)
located about five miles from where I live. My broken neck was operated
on in this hospital, and my oncologists works out of this hospital. This
hospital is the teaching hospital of Tufts University School of Medicine
and many of its staff member bios list them as Assistant professor of medicine
at Tufts Medical School, which I have been told is something of a formality
and does not mean they are doing any regular teaching in the medical school.
Their wb site adds that besides Tufts "many of our physicians hold teaching
assignments at Harvard Medical School and Boston University School of Medicine".
Lahey Hospital & Medical
Center, Burlington MA includes a 259-bed hospital (elsewhere it says 317
beds) with all private room accommodations; a 19-room operating suite;
seven inpatient units; and medical, surgical, and cardiac intensive care
units. Lahey web site says over 500 physicians and over 5,000 nurses and
support staff. 24 hour emergency room (Level II Trauma Center). Lahey web
site says 3,000 patients a day are treated at the Burlington headquarters.
As a research center, Lahey Hospital & Medical Center offers patients
access to clinical trials of new therapies for diseases such as cancer,
diabetes, heart disease and cataracts. Research programs at Lahey Hospital
& Medical Center encompass more than 200 clinical trial protocols and
participation in numerous national and international studies.
An article in the Boston
Globe (2013) says acquistions have reduce the number of independent hospitals
in the state to just 12 with only 2 remaining in the region north of Boston
(Anna Jaques Hospital and Lawrence General Hospital). Competing with Lahey
in the acquiring of hospitals is North Shore Medical Center, a member of
Partners HealthCare, associated with Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts
General Hospital.
Lahey is a non-profit (501(3)
charity) whose IRS filing shows revenue over 700 million, assets over 400
million, and over 4,000 full time employees. They have been buying up local
hospitals. Besides a Lahey satellite location in Peabody, they own, or
are 'affiliated' with,' Winchester hospital, Beverly Hospital, BayRidge
hospital (Lynn) and Addison Gilbert hospital (Gloucester). Latest online
annual report is for 2011 (!) shows 20,000 admissions, 21,000 surgeries
(about 60/day) and 7 million in contributions. In 2011 there were 463 medical
center physicians plus 143 interns and residents supported by 1,100 nurses.
The rest of the 5,000 staff are health and administrative staff. 8,000
inpatient surgeries, 52,000 emeergency room visits. Operating revenue about
1,000 million dollars with 400 million in assets. Salary and benefits about
600 million and 'profit' (excess of revenue over expenses) 60 million (6%).
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Details
of my neck C1,C2 fusion operation
This information
comes from my surgeon's Medicare billing records (09/18/2014, 10k total).
It shows during the operation some bone was removed and used for a graft.
My surgeon has never described to me the operation to me in any detail,
so I don't know (for sure) what this graft was for. My understanding is
that neck hardware will fatique in time, so that it's main job is to stabilize
the bones to allow them to fuse. Hence my guess is that the graft was probably
tiny pieces of bone inserted between C1 and C2 to encourage them to fuse.
Something else I don't understand
is how the screws into C1 and C2, which are into the (thick) sides,
holds in place the C2 (dens) projection, which is in the center and which
my surgeon told me is what broke. (Is the C2 dens, which as I understand
it normally touches and slides along the C1 front arch, perhaps glued to
C1 to hold it in place?)
Fusion Of Spine Bones At Skull Base, Posterior Approach (3.9k)
(rear entry, fusion high in neck)
Partial Removal Of Spine Bone And Growth At Upper Spinal Column (2.1k)
(probably the notch (biopsy) of C4 lesion for MM diagnosis)
Insertion Of Posterior Spinal Instrumentation At Base Of Neck For Stabilization,
1 Interspac (2.4k) ('1 Interspac'
I think means one fusion)
Harvest Of Bone From Same Spine Incision For Graft (1.0k)
(?? ask surgeon about this)
Donor Bone Graft For Spine Surgery (0.6k)
(surgeon later told me bone for fusion came from a cadaver)
The hospital's billing Medicare
record for the week of my neck operation also has some interesting details
(50k total):
MRIs --- brain (3.2k), spine (5.4k, 2.9k)
CT --- body scan (2.6k)
Blood administration (transfusion) --- (1.7k) (I was not aware
I had a blood transfusion)
Room and board (7 days, private room) --- (5.3k)
Billing for monthly
visits with my oncologist or follow up visits to surgeon
15 min --- Medicare approves $53
25 min --- Medicare approves $81
Youtube C1-C2 fusion video
Below is a very nice 5 min
video with excellent animation showing how the hardware is inserted in
a posterior C1-C2 fusion operation. The trick (not clear in my x-rays above)
is that the head of each screw has an inside thread and a slot. Rods are
dropped into the C1 and C2 slots, then nuts with outside threads are screwed
in and tightened. In other words the rods are clamped to the screw heads
with sort of an inside-out nut and bolt configuration.
.jpg) .
..jpg)
Scn captures from the C1-C2 fusion video (below) showing
(left) bars flying in
(right) nuts flying in
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fhFSSdjqYtA
Sketches of posterior C1,C2 fusion operation
-- The two vertebrae are
fixed into position by direct screwing of the joints, the so-called transarticular
fixation or fixation with screws into the pedicles and Massae laterles
that are connected to a rod. Ultimately, in addition a fusion of bone is
always required, which is placed between the two vertebrae and secured
with wire. Thereby stability is ensured in the long run, even if the screws
loosen or break; because the bone grows in.
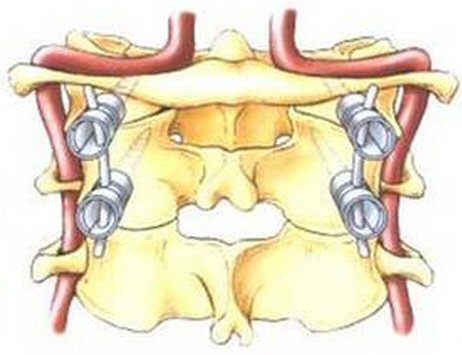 .
.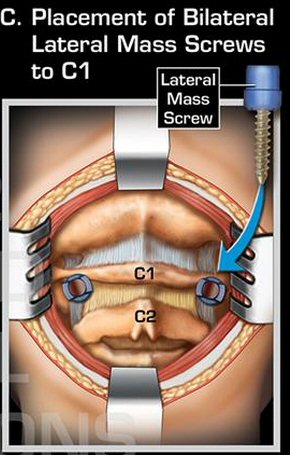
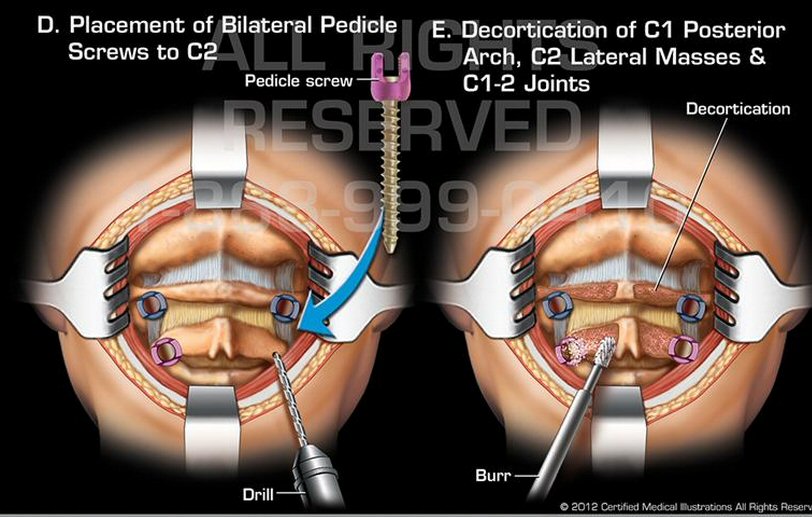
x-rays of my operation show side clamps, lateral mass screw and
pedicle screw shown here
(source -- http://www.certifiedmedicalillustrations.com/c1-c2posteriorfusionsurgery.aspx)
Details of C1,C2 fusion operation, which looks like my procedure, from
International Spine Center, Berlin:
http://www.kreuzschmerzen.org/en/precedures/microsurgery/spinal-fusion/c1-c2-fixation.html
https://kulaga.wordpress.com/2012/10/17/cervical-spinal-fusion-of-c1-c2-vertebrae/
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lahey online patient
'portal'
After doing a lot of reading
and speaking with some people at Lahey about the portal, I have some new
perspectives. Three aspects of the portal data, which I think are piss
poor, can all be 'explained' by a concern to minimize feedback (i.e. questions)
from patients to doctors. This would include
a) Blood data is provided in patient unfriendly format (full of abbreviations
like RBC, WBC, which are not explained)
b) Out of range values are not high lighted
c) 'Sensitive' data is (or may be) excluded
It's possible the patient
history is missing for the same reason. The patient history must exist
inside the hospital database somewhere. The question is does it remain
in the legacy system that keeps running, or has it been migrated to Epic
and simply not been made visible to patients?
(update 3/4/15)
My portal blood data has
this introductory note: "This document contains information that was shared
with Donald Fulton. It may not contain the entire record from Lahey Health."
The first part of this statement is, of course, total crap. It will be
a few days before I meet with my doctor to review the latest blood data
now on the portal, blood collected 5/1/15. Also my 'Current medications'
are all screwed up. The starting date is wrong on three of the four entries.
And my main cancer drug, revlimid, is incorrectly listed twice, once under
its brand name (revlimid) and once under its technical name (lenalidomide)
with different starting dates. Jesus , what a mess!
I suspect the portal ranks
near the bottom of concern in all the changes associated with the big change
over to the new record and billing system. I read all the top executives
at a ME hospital got fired a few months after taking the Epic system live
because billings were not entered properly by staff and fell off 50 million.
Also I read a lot of patients have little interest in the portal.
----------------------------------------
In April 2015 Lahey Hospital
is making a lot of noise about its introduction of a patient online 'portal',
called MyLaheyChart. According to the hospital patients can log on and
get access to their records and lab results, contact their doctor, make
appointments and a lot more. The introduction of the portal is apparently
tied in with a big change in the record keeping at the hospital. My doctor
recently told me the hospital was changing its computer record keeping,
and a MyLaheyChart booklet says Lahey is "transitioning to Epic, a new
electronic health record to improve and streamline your care." A Boston
Globe article a couple of year ago said Lahey was planning to introduce
a new 162 million dollar electronic record system. (What?)
Epic is evidentily
a big name in electronic records. Partner Healthcare (Mass General, etc)
in 2013 announced they were going to go to Epic, but were years away from
going live. A story about Epic and a ME hospital shows that a big change
is the doctors and nurse need to enter into the computer everything they
do, because that is how the charges are figured. In an Epic installation
in UK five years of patient history were transferred to the Epic system.
Quote from NYT article that
electronic records system do no share with those made by other companies:
"Epic and its enigmatic founder, Judith R. Faulkner, are being denounced
by those who say its empire has been built with towering walls, delberately
built not to share patient information with competing systems." "A research
report from the RAND Corporation described Epic as a “closed” platform
that made it “challenging and costly for hospitals” to interconnect with
the clinical or billing software of other companies. Shortly after, Representative
Phil Gingrey, a Georgia Republican and a doctor, assailed the company in
public hearings in Washington for the same shortfalls."
"A sort of Microsoft of the
Midwest, built on a sprawling campus on nearly 1,000 acres of farmland
near Madison, Wis., the privately held Epic has emerged as a leader in
the race to digitize patient medical records. Its systems hold the health
records of nearly half the country." There is a Wiki page for Epic. It
says the company employs 8,000 people! Epic also provides electronic record
systems for Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, the Cleveland Clinic,
Johns Hopkins Hospital, and The Mount Sinai Hospital.[4] [13] Epic software
system (EHR) is a “de facto standard among the more complex academic health
centers and multispecialty medical groups,” says Dr. John D. Halamka, chief
information officer of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston and
a professor at the Harvard Medical School. Only approved healthcare providers
involved in your care can view your record. (So my doctor should be able
to access my portal.)
Medical history
As the info for doctors
below shows, the Epic system has to contain the patients medical history
to be useful to doctors. So where is it? Look at this: "With MyChart, you
can securely access the Internet to view portions of your medical
record." (from Yale hospital that uses Epic)
How does the Epic EMR help
manage patient care for my hospitalized patients? Ans: From the hospital,
their private office or another location, physicians have easy online access
to one centralized electronic chart with all of the patient’s information,
including medical history, medications, allergies, laboratory and radiology
results and more.
Of course I signed up
right away. One feature I like, and is a real step forward, is a simple
way to communicate with your doctor (with a promised answer in two days).
I have used this twice and it has worked well. What is not working well
is the medical side: lab results, medical records, etc.
Perhaps a minor quibble,
because it is a one time thing, but to sign up required a trip to the hospital!
To sign up you needed a (new) ID number, and the only way to get the required
ID number was in person. I don't understand the reason for this nonsense,
this mickey mouse. It didn't bother me personally because I am at the hospital
all the time. My lab data is simple, it's just my blood numbers, should
be totally standard, almost all patients have blood work done at some point
or other. Here's what I found:
1) Database problems --- Most important blood number
to me as a blood cancer patient ('Monoclonal Peak Quant') is MISSING. I
know the missing data is in the hospital computer system because a few
days before I accessed the Epic portal during a visit to my doctor she
handed me a printout of my latest blood numbers, and it's there. I compared
all the blood numbers between the sheets my doctor gave me and the blood
data I downloaded. The numbers are all the same, except the number showing
the amount of cancer in my blood, the number my doctor focuses on at the
end of every cycle, is missing from the portal data. Terrific. The entry
for 'Monoclonal Peak Quant' under 'Protein Electrophoresis' is there in
the blood format, but it's blank.
a) So is there an email or a contact to report problems with
your data? There is not, which I find revealing. I reported the problems
to my doctor asked her to feed it back. I said take a look at my records,
but apparently she is unable to access my account. This is another screw
up and will work to prevent problems from being identified and fixed.
2) Sloppy programming --- Out of range blood values not marked. In
the last six months I have gotten my blood data in several formats from
the hospital and out of range values have always been marked with a 'H'
or 'L', but not in the Epic blood format.
3) History missing --- The implied message to patients about the portal
is that you use it to review your medical records and status, but the reality
is much less impressive. There has apparently been no attempt (at least
to date) to digitize even relatively recent hospital records (say for the
last six months or year). My health status: blank. My operation at
the hospital a few months ago and dozens of follow up visits: missing.
Epic or Lahey never say this, but it looks like the only data that will
be online begins in April 2015 when the portal became available and hospital
began transitioning to the new record keeping system. I like how this issue
is never mentioned, essentially swept under the rug, who needs to look
at their medical history. My portal history has no mention that I
have cancer. Essentially all that's there is my latest blood numbers, and
as I detailed above, even that is screwed up with the key cancer value:
blank
Health Summary:
"You have no health issues on file"
Current Health Issues: "You have
no health issues on file"
Medical History:
"You have no medical history on file"
Surgical History:
"You have no surgical history on file"
4) Crappy format --- I know the blood format well. Having a blood cancer
I am very familiar with the various blood formats Lahey used until recently,
which were quite compact printing out on 2 or 3 pages, which I keep in
a notebook. When my blood data comes up in MyLaheyChart the screen fills
with a SEPARATE link for each blood panel. What? Just to see your blood
data takes 10 clicks, and worse under this are often more links like a
'detail' button, which of course is blank. This is something like 10-20
clicks to see what should take one click. Idiotic!
Digging around on the
portal (there are a lot of links) I found hiding, and it really is hidden,
my blood data in a compact format. And what's the name of this link? If
you can believe it, it is called: 'Lucy' record. If you click 'Lucy' you
don't find it! No, you need to click 'Download my record' and then 'Preview
your Lucy record'. If this isn't riduculous I don't know what is. How is
the patient supposed to know that's where to look to find his compact blood
data? I even keep losing it. Freaking ridiculous. Maybe your doctor
will tell you? Not mine, at my only meeting with my doctor since the portal
opened I got zero info on using it. Nor should I, there are more important
things to discuss in the limited time available with your doctor than getting
a tutorial on the portal.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
About
the Lahey MM clinical trial I was offered
At the time I had to chose
I didn't know much about MM chemo regimens, so I didn't have any real perspective
on this trial. And my memory is my doctors didn't provide any real perspective
either, basically I was just handed the trial paperwork (several pages)
to read. What this trial is testing is an upgrade to the (popular) RVD
regimen (revlimid, dexamethasone, velcade regimen). A big practical problem
with this regimen is that velcade is injected, so it requires a
trip to the hospital every 3-4 days! Also velcade classically caused damage
to nerves in fingers, which has been apparently reduced recently by injecting
the drug under the skin.
Millennium, who makes velcade,
has developed a pill version of it (ixazomib or MLN9708) that they describe
as "first oral proteasome inhibitor". This is one of several trials they
are running to asses its effectiveness. In early 2015 (without giving any
numbers) a press release from the company said that adding the new experimental
drug to dex/rev significantly improved the time to disease worsening for
refractory MM patients (vs rev/dex plus plecbo).
----------------
I had first written the
clinical trial I was offered was being sponsored by Celgene (makes of revlimid).
Wrong! It's sponsored by Millennium Pharmaceuticals of Cambridge MA (now
owned by Takeda of Japan), who make injectable botzezomib (velcade), have
developed its pill equivalent. The pill is called MLN9708 in the trial
documents, but a little digging shows its trade name is 'ixazomib'. It
is taken once a week for 3 weeks of the usual 4 week cycle. The trial I
was offered is for newly diagnosed MM patients and will go on for seven
years! From below it appears the Lehay trial is what Millennium calls the
TOURMALINE-MM2
trial. (I've been told in May 15 that Lahey has dropped the trial I was
offered, maybe they couldn't get anyone to sign up!) Here is the linkto
the trial on ClinicalTrials,gov. Millennium in other trials is testing
the drug not only as chemo for newly diagnosed MM, but for relaped MM and
as mainenance therapy after a stem cell transplant. These are phase 3 trials
with a goal of enrolling about 700 patients, about 5 of which will come
from Lahey hospital. The contact for the study at Lahey is Dr. Tarun Kewalramani,
one of the 14 staff of the dept of Hematology and Oncology.
Trial end date
Trying to figure out when these
trials end is a challenge. The paperwork I was given on this trial says
it runs seven years. The gov site shows the study start date: May
2013, and Estimated Study Completion Date: February 2021, or 8 years. There
is also something called the Estimated Primary Completion Date: June 2018.
Millennium on their site says: The study is estimated to be completed in
May 2019. So there you have it, the study runs 7 or 8 years and it wraps
up in either 2018, 2019, or 2021. Take your pick! Follow up in one spot
is shown as 2.5 years, in another as 5 years. These trials take forever...
And the dose of revlimid and dexamethasone is unchanged for the whole study!
About Ixazomib (Ninlaro) --- pill version of Velcade
"Ixazomib (MLN9708) is an
investigational
oral proteasome inhibitor, which is being studied in multiple myeloma (MM),
systemic light-chain (AL) amyloidosis and other malignancies. Ixazomib
was granted orphan drug designation in MM in both the U.S. and Europe in
2011, and for AL amyloidosis in both the U.S. and Europe in 2012. Ixazomib
received Breakthrough Therapy status by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) for relapsed and/or refractory AL amyloidosis in 2014. It is also
the first oral proteasome inhibitor to enter Phase 3 clinical trials. Four
global Phase 3 trials are ongoing:
** TOURMALINE-MM1, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo in combination
with lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed and/or refractory MM;
TOURMALINE-MM2, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo in combination with
lenalidomide and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed MM;
TOURMALINE-MM3, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo as maintenance therapy
in patients with newly diagnosed MM following induction therapy and autologous
stem cell transplant."
(http://investor.millennium.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=80159&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=2014902&highlight=)
Checking the Millennium web site I find some preliminary information from
the MM1 trial (for relapsed MM) is available now:
"Cambridge, Mass. and Osaka, Japan, February 10, 2015
** Takeda Pharmaceutical
Company Limited (TSE:4502) today announced that the randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled TOURMALINE-MM1 pivotal Phase 3 trial evaluating the
safety and efficacy of ixazomib, the first oral proteasome inhibitor, conducted
in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (MM) achieved
its primary endpoint of improving progression-free survival at the first
pre-specified interim analysis. In the trial, patients treated with investigational
ixazomib plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone lived without their disease
worsening for a significantly longer time compared to patients who
received placebo plus lenalidomide/dexamethasone."
FDA approval
Nov 20, 15 Takeda press
announcment says FDA has just approved its first oral oral proteasome inhibitor,
now called Ninlaro, based on early results of the TOURMALINE-MM1 phase
3 trials. This trial is continuing as are three other TOURMALINE trials
for the drug. The early results of the TOURMALINE-MM1 trial are to be reported
on at the American Society of Hematology on December 7, 2015
A NIH check of clincial trials
(4/15) shows about 20 clincal trials being run at Lahey, but curiously
does not show this one. Only one MM clinical trial is on the list being
run by Sloan with Lahey as a partner. But the listed trial, while it does
use revlimid and dexamethasone, will be only 62 patients and is very different,
it is (on a quick read) randomizing a stem cell transplant vs maitence.
(Clinical trials are linked via Lahey Wikipedia page.)
Update on Ninlaro
here.
Time to progression
Months to 'time to progresssion'
is a common end point in MM literature. But what does this mean? I finally
found a definition in a MM clinical trial (national cancer institute):
Time to progression
(TTP) was defined as the date of transplant to date of progression or death
due to any cause, whichever occurs first. TTP was estimated using the Kaplan
Meier method. Progression was defined per the 'International Myeloma Working
Group' definition as one more of the following:
** 25% increase in serum M-component (absolute increase
>= 0.5g/dL)
25% increase in urine M-component
(absolute increase >= 200mg/24hour
25% increase in the difference
between involved and uninvolved Free Light Chain levels (absolute increase
>= 10 mg/dL)
25% increase in bone marrow
plasma cell percentage (absolute increase of >=10%)
Definite development of
new bone lesion or soft tissue plasmacytomas
Development of hypercalcemia
Defintion of Time to Progression
What does the first one
mean? A 25% increase from what baseline? No, my minimum is low enough that
the absolute increase applies. My minimum monoclonal M spike (after
8th cycle) reached less than the threshold of the M-spike test (done at
Lahey), very close to zero (<0.05 g/dL). So in my case Time to Progression
(TTP) M-spike threshold is 0.5 g/dL absolute (round numbers). This is a
pretty low threshold, about 10% of my pre-chemo original baseline of 5.31
g/dL.
Below is the definition for TTP from the Interntional Myeloma Working
Group:
Increase of > 25% from lowest response value in any one or
more of the following:
** Serum M-component and/or (the absolute
increase
must be > 0.5 g/dL)
Urine M-component and/or
(the absolute increase must be > 200 mg/24 h)
Only in patients without
measurable serum and urine M-protein levels; the difference between involved
and uninvolved FLC levels.
The absolute increase must be > 10 mg/dL. (I have a lambda cancer so this
would be lambda - kappa FLC must be > 10 mg/dL)
Bone marrow plasma cell
percentage; the absolute percentage must be > 10%
Definite development of
new bone lesions or soft tissue plasmacytomas or definite increase in the
size of existing bone lesions or
soft tissue plasmacytomas
Development of hypercalcaemia
(corrected serum calcium > 11.5 mg/dL) that can be attributed solely to
the plasma cell
proliferative disorder. (This is only about 10% above the normal range:
8.4 to 10.4 mg/dL)
MM clinical trials
One benefit of reviewing
MM clincal trial using the chemo I am taking is to see what the thinking
(guessing) is about drug combinations, dosage and cycles. I found a list
of MM clinical trials on the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer center (NYC)
home page and the Dana Farber Cancer Institute (Boston) home page. The
Sloan Kettering list is much more searchable than Dana Farber list.
http://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/adult/multiple-myeloma/clinical-trials
27 MM trials
https://www.dana-farber.org/Research/Clinical-Trials/Clinical-Trials-Search-Result.aspx?q=multiple%20myeloma
41 MM trials
Do stem cell transpants still have merit?
There are several trials
ongoing evaluating whether a stem cell transplant still has merit vs a
modern chemo regimen for newly diagnosed MM patients. Phase 2 trials (50-60
patients) have been encouraging that drugs alone are effective, but phase
3 trials with x10 more patients are needed. Phase 3 trials are the gold
standard by which over time progress in chemo is made. I found two MM phase
3 trials ongoing, but unfortunately both of them won't end for a few years
(2018/20).
This is particularly interesting
to me, because I am (in effect) in the control group with no stem cell
transplant. The general procedure is treat patients with chemo, then randomly
half are assigned to have a stem cell transplant, and both go on maintenance.
The maintenance is sometimes different for the two groups. (Obviously these
are not double blind trials!)
Phase 3 trial --- Lenalidomide
(revlimid), Bortezomib (velcade), and Dexamethasone (RVD). Maintenance
is revlimid 10-15 mg daily for one year. This is for newly diagnosed MM
patients under age 65. Ends Sept 2018, 660 participants. Revlimid is provided
at no charge.
http://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/adult/multiple-myeloma/clinical-trials/12-018
Phase 3 trial --- Study
Comparing Conventional Dose Combination RVD to High-Dose Treatment With
ASCT in the Initial Myeloma up to 65 Years. Ends 2018, 700 participants..
Maintenance phase (12 months): Cycle length: 28 days Dosage: Lenalidomide:
10 mg/day continuously for 28 days during 3 months and if the participant
tolerates 10 mg/day without complication, a dose increase to 15 mg/day
will be allowed. (Reviewing this I wondered if it might be the same trial
as above, but it's not. They have different principle investigators, and
the above trial is run out of the US, while this trial is being run out
of France.)
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01191060
Phase 2 trial --- Lenalidomide
and low-dose dexamethasone (LD) (four cycles). Maintenance is LD
(rev/dex) for non-transplant patients and L (revlimid) for transplant patients.
Standard risk patients up to age 75 qualify. Ends Dec 2015, 62 participants.
Lahey clinic is a collaborator in this trial.
http://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/adult/multiple-myeloma/clinical-trials/08-121
Phase 2 trial --- [Bortezomib
+ dexamethasone] vs [Bortezomib, dexamethasone, and lenalidomide]
Bortezomib, dexamethasone, and lenalidomide are often given together to
treat newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (a cancer of the bone marrow). However,
this combination of three drugs is associated with significant side effects.
Trial is to see if same result can be obtain with two drugs [Bortezomib
+ dexamethasone] for fewer side effects. Lenalidomide would be included
for non-responders.
For relapsed MM
Phase 2 trial --- [Pomalidomide
plus 2nd Autologous Stem Cell transplant] vs [Pomalidomide/Dexamethasone]
End De 2016, 44 participants.
http://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/adult/multiple-myeloma/clinical-trials/12-138
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Salt
My sodium is just a hair under normal at 133 mmol/L or 133 x 0.023g/L =
3.06 g/L. The humam male has about 5L of blood, so stores about 15 grams
of sodium. Salt consumption is about 3.5 g/day of which 40% is sodium,
so 1.5 g/day of sodium consumed (in salt). This means the blood electrolyte
stores of sodium represent about 15g/(1.5g/day) = 10 days worth of salt
consumption. (mmol is a mille-mole, atomic weight of sodium is 23, hence
1 mmol of sodium is 0.023 gram)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Protein Electrophoresis
test
Proteins in the serum (fluid)
component of blood are spread out by atomic weight by a blood test called
'protein electrophoresis'. The proteins driven by an electric field (they
are charged) diffuse along special paper. Smaller molecules diffuse faster
than larger molecules so after a few hours (?) the proteins are spread
out by size/weight. Multiple myeloma patients have a (huge) excess of a
protein of one particular atomic weight which is being turned out
by the marrow plasma cells that have gone cancerous. This produces a band
in the paper (see IgG band below). The density of this band is an measure
of the cancerous plasma cells in the marrow. (I don't know how the density
of this band is measured. It is given to three decimal places in my blood
work. And clinically it is important that it be measured with high resolution
and repeatability because the objective of chemo is a CR (complete response)
which means reducing its value by a factor of 20 or more.)

Multiple myeloma monoclomal peak band in protein electrophoresis
test
MM serum monoclonal proteins
can be one of several types. 1,000 multiple myeloma patients at Mayo clinic
had this breakdown:
IgG kappa
35%
** IgG lambda
18% (I have IgG lambda monoclonal peak)
IgA kappa
13%
IgA lambda
8%
Prior to chemo my initial
'Lambda free light chain blood' density was super high at 379 mg/dl about
x150 normal (0.57 to 2.63 range)! Just two cycles of rev/dex chemo
reduced this value to 2.74, just slightly above normal, and brought the
kappa/lambda ratio into the normal range. After four chemo cycles 'Lambda
free light chain blood' at 1.50 was well within the normal range.
The 'G' and 'A' above refer
to types of Immunoglobulin (there is also M, E and D). 'G' is the most
common antibody as it protects against bacteria and viral infections.
Wikipedia --- Immunoglobulin light chain
The immunoglobulin light
chain is the small polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin).
A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains
and two Ig light chains, which in a given antibody will be the same. There
are two types of light chain in humans:
*
kappa chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin kappa locus (IGK@) on chromosome
2
* lambda
chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin lambda locus (IGL@) on chromosome
22
The approximate length of
a light chain protein is from 211 to 217 amino acids. The normal kappa
to lambda ratio is 0.66 (0.26 to 1.65) when measuring free light chains,
and a highly divergent ratio indicates cancer. My initial pre-chemo ratio
was < 0.01, because my lambda free light chain was a sky high 379 (normal
range .57 to 2.63).
Nice description of M-spike
Very readable, clear description
of M-spike and the underlying (monoclonal) marrow cells that create it
from 'Pathology Student' site (http://www.pathologystudent.com)
written by a doctor. Can you explain to me what the M protein in multiple
myeloma is?
In the bone marrow aspirate above, you can see tons of malignant
plasma cells.
A few look a lot like plasma cells, with clock-face chromatin and
a hof and everything, but others look for all the world like blasts.
(source -- http://www.pathologystudent.com/?p=3007&cpage=1)
A. Multiple myeloma is a malignant, clonal disorder of plasma
cells that originates in the bone marrow. It’s a relatively common disorder,
accounting for 1% of all malignancies and 10% of all hematologic malignancies
in adults. Patients present with painful, lytic lesions of the bones, recurrent
and persistent infections, weakness, renal failure, and hypercalcemia.
The prognosis is generally not great, but new chemotherapeutic agents seem
to hold some promise.
* Patients with myeloma have a
monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow, meaning that
there are a ton of malignant plasma cells that all originated from the
same
initial
cell. In the bone marrow aspirate above, you can see tons of malignant
plasma cells. A few look a lot like plasma cells, with clock-face chromatin
and a hof and everything, but others look for all the world like blasts.
That’s one thing to remember about myeloma – malignant plasma cells don’t
always resemble their nice little benign counterparts.
* The malignant plasma cells almost
always secrete immunoglobulin, and because they are monoclonal, they all
secrete exactly the same form of immunoglobulin. This is very different
than what you see in a patient without myeloma, where there are a bazillion
different types of plasma cells, all making different types of immunoglobulin
molecules. This huge mass of all-the-same immunoglobulin secreted by myeloma
cells is called a “monoclonal gammopathy;” the normal immunoglobulins are
called “polyclonal.”
* Monoclonal gammopathy is so characteristic
of myeloma that you can use it for both diagnosis of disease and follow-up
of patients. You can detect the monoclonal immunoglobulin using serum electrophoresis
(which separates the blood proteins into groups based on charge and size).
There’s a predictable pattern of proteins in normal serum: albumin (the
most abundant protein in the blood) migrates to a certain predictable point;
other proteins migrate to different places (which are given different names
– the alpha 1 region, the alpha 2 region and the beta region). Immunoglobulins
migrate to a unique place called the gamma region, and because they
are all different (in normal patients), they migrate to slightly different
places within that region, giving a gentle bell-shaped curve or smear
(depending on whether you’re looking at a tracing or the actual bands on
the gel).
* In myeloma, the immunoglobulin
is monoclonal, so it all migrates to exactly the same spot on the gel!
Which gives you a big spike (if you’re looking at a tracing) or a very
distinct, crisp, strong band (if you’re looking at the gel itself).
This spike is called an M-spike (you could remember M for either monoclonal
or myeloma), and the corresponding monoclonal protein that it represents
is called an M protein.
A few other things to note about this M protein:
1. You need to do electrophoresis on urine too, not just serum. Some
cases of myeloma secrete only light chains (these are called Bence-Jones
proteins), which are so small that they are passed in the urine (so if
you only looked at the blood, you’d miss them).
2. While patients with myeloma have an increase in the total amount
of immunoglobulin present in the blood (due to the large monoclonal immunoglobulin
spike), they also have a decreased amount of normal, polyclonal immunoglobulins.
So when you look at an electrophoresis, you’ll see this huge spike in the
gamma region, but also a noticeable depression in the amount of the background
normal immunoglobulins.
3. A little trivia regarding the kinds of immunoglobulin expressed by
myeloma cells. The most common heavy chain expressed in myeloma is IgG
(60%); next is IgA (20%). Rare cases express IgD or IgE, and IgM myeloma
is virtually nonexistent (most cases of plasma cell lesions that express
IgM turn out to be Waldenström macroglobulinemia). Almost one-fifth
of all cases of myeloma secrete only light chains. And somewhere between
1 and 5% of all cases of myeloma secrete no detectable immunoglobulin at
all! Which, without the familiar M-spike, would make for a pretty difficult
diagnosis.
Cytogenetics and deletion
13
The cytogenetics literature
is a jungle of complexity. Everyone seems to have their own idea of how
to pair up the DNA abnormalities with risk and prognosis. There is general
agreement some variations are 'bad' [hypodiploid group with t(4;14)(p16;q32)
or t(14;16)(q32;q23)] and a few are 'good' [hyperdiploid], but there is
controversy about deletion 13. The first table on MM cytogenetic variations
I discovered is here:

I have the hyperdiploidy variation (and deletion 13)
(Notice the 'poor' outcome for deletion 13 is when measured not
with Fish, but with the less sensitive conventional test.)
['t' is a translocation, so t(4;14) means chromosome 4 is incorrectly
connected to chromosome 14]
My cytogenetics test results
Here is the key section
of the multi-page written report from Mayo clinic of the cytogenetics test
done on my extracted bone marrow cells prior to chemo (which I finally
pried out of my doctor). It took me a while to understand that what is
being looked at here is the (corrupted) genetics of my extracted myeloma
marrow cells. My good hyperdiploidy variation is indicated by the
extra one or two copies (above standard diploidy) that I have on chromosomes
3, 9, 11, and 15. My not so good deletion 13 (Fish) is shown as only one
copy (monosomy) of chromosome 13.

cytogentics report from Mayo Clinic on my extracted bone marrow
(Wikipedia says 50% of MM patients have abnormalities in chromosone
14 and 50% have a partial deletion of chromosone 13.
I have the latter, but apparently not the former.)
The 'appear' in the comment
on deletion 13 ["Monosomy 13 does not appear to affect this favorable
(hyperdiploidy) prognosis in multiple myeloma."] reflects the clinical
uncertainty of whether or not deletion 13 as measured by the sensitive
Fish test (as here) is unfavorable or should be disregarded. The comment
"plasma cell clone" is, of course, medical jargon for the patient has multiple
myeloma. The Mayo
Clinic MM treatment guidelines have this to say about deletion 13:
"Deletion 13 has long been considered an adverse prognostic marker. When
detected on conventional cytogenetic studies, it does, indeed, portend
a poorer prognosis, but if seen on FISH, in the absence of hypodiploidy,
it doesnot retain its significance."
Some propose three risk levels
with deletion 13 forming an intermediate risk group, others put deletion
13 into the bad category, others think it is not really important as it
is secondary term generally associated with hypodiploid. Also a lot of
the references I find on cytogentics are quite old (2003 to 2008). Here
is data supporting three risk levels with deletion 13 being an intermediate
risk.
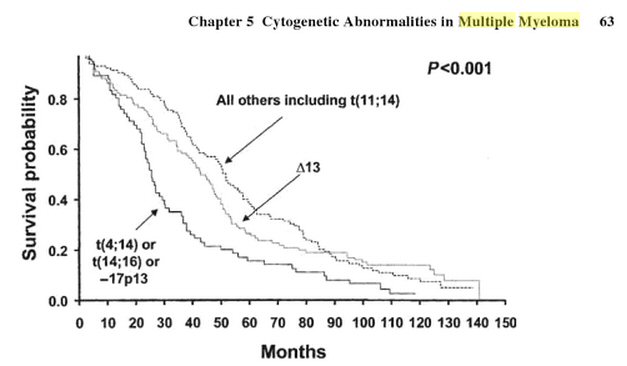
data supporting deletion 13 as an intermediate risk
(Fonseca et al have demonstrated that 3 distinct staging groups
can be defined by the presence or absence of
t(4;14)(p16.3;q32), t(14;16)(q32;q23), deletion 17p13,and deletion
13q by FISH)
(source -- book 'Myeloma Therapy, Pursuing the plasma cell, edited
by Sagar Lonial, 2008)
A big complication
with deletion 13 is how it is measured. The older test was insensitive,
so if it picked up deletion 13 it was a bad sign. The newer Fish test is
much more sensitive, so picking up deletion 13 in this test many think
doesn't mean too much. Some studies showed patients with deletion 13 as
measured by Fish responded to treatment as well as those without deletion
13. [The jargon is intense -- "In summary, the detection of deletion 13
in interphase cells is not as predictive as its observation in metaphase.
One reason for the difference in prognostic value is that deletion 13 seen
in CC (older test) is an indicator of the presence of abnormal metaphases
and infers a more proliferative clone and higher tumor burden. Its role
as a prognostic factor, therefore, could be indirect.] Oh, yea...
All this is important to
me because I have deletion 13 along with the 'good' hyperdiploid variation.
My hematological oncologist focused on the hyperdiploid variation, saying
clinical results indicate that 'good' hyperdiploid variation overrides
the 'bad' deletion 13. What I have been trying to determine is to what
extent my 'good' cytogenetics are compromised by also having deletion 13.
First question is how was my deletion 13 measured? All I got from my doctor
on cytogenetics was an oral summary, 'you have hyperdiploid variation and
deletion 13'.
In May 2015 meeting
I brought up the deletion 13 issue with my doctor, saying I had no info
on this except an oral statement that I had delection 13. In response she
printed out the Mayo clinic report on my cytogenetics tests. While 6 pages
long it has relatively little information, but a few pieces of info in
it are interesting.
Deletion 13 was determined
by the Fish test. The Mayo clinic comment about my deletion 13 says simply:
"At diagnosis hyperdiploidy is associated with a favorable prognosis in
multiple myeloma. Monosomy 13 (deletion 13) does not appear to affect
this favorable prognosis."
No where else in the six
pages does it (clearly) state I have hyperdiploidy (see next). It also
says I have (secondary) DNA abnormalities: trisomy 3, 11, 15 and tetrasomy
9. Wikipedia says, "Trisomy 9 is a chromosomal disorder caused by having
three copies (trisomy) of chromosome number 9", but I doubt that I have
multiple copies of a whole genome, probably just a short stretch correlated
with myltiple myeloma. [Jargon --- normally there are two copies of a DNA
segment (from ma and dad), so its diploid. Monosomy means only one chromosome
of the normal pair is present, so this is a deletion. Trisome means three
chromosomes and tetrasomy means four, so these are both additions.] Wikipedia
say the deletion or an addition of a whole chromosone (46 = 2 x 23 in humans)
generally causes a fetus to be aborted. Down syndrome is a trisomy with
three whole copies of chromosone 21.
Hyperdiploid explanation
-- Karyotypes from multiple
myeloma (MM) patients are complex but may be categorized either as hyperdiploid,
displaying gain of odd chromosomes and some structural changes,
or as hypodiploid or pseudodiploid, displaying
loss of even
chromosomes and frequent structural changes, including IgH rearrangements
(1, 2).
This is useful. My detail cyctogenetics
results show probes for 15 DNA variations, and of these 10 were normal.
The five that were abnormal: +3, +9 +11, +15, -13. OK, I am hyperdiploidy
because I have gains of four odd
chromosones (+3, +9 +11,
+15) plus the deletion of an odd chromosone (-13).
-- Chromosomal hyperdiploidy is the defining genetic signature
in 40-50% of myeloma (MM) patients. We characterize hyperdiploid-MM (H-MM)
in terms of its clinical and prognostic features in a cohort of 220 H-MM
patients entered into clinical trials. Hyperdiploid-myeloma is associated
with male sex, kappa immunoglobulin subtype, symptomatic bone disease and
better survival compared to nonhyperdiploid-MM (median overall survival
48 vs 35 months, log-rank P = 0.023), despite similar response to treatment.
Among 108 H-MM cases
with FISH studies for common genetic abnormalities, survival is negatively
affected by the existence of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) translocations,
especially those involving unknown partners, while the presence of chromosome
13 deletion by FISH did not significantly affect survival (median
overall survival 50 vs 47 months, log-rank P = 0.47). Hyperdiploid-myeloma
is therefore a unique genetic subtype of MM associated with improved outcome
with distinct clinical features. The existence of IgH translocations but
not chromosome 13 deletion by FISH negatively impacts survival and may
allow further risk stratification of this population of MM patients. (2006
paper showing a slightly lower survival time with deletion 13, but
for only 100 patients).
Variability of
patient response to chemo
These curves from a 2013
Italian MM clinical trial with 400 patients (comparing revlimid maintenance
vs no maintenance) are broken out by category. The gentle downward slope
(as opposed to a more rectangular shape) in nearly every category clearly
shows that individual patient response to chemo has a very wide variability.
Only the CR response (top center) shows a partially rectangular response.
While the categories clearly matter, as far as I know the individual responses
within them is entirely unexplained. It could be just random or due to
so many small effects that it might as well be random. [Maintenance in
this trial was 10 mg revlimid 'cycled' (21 days of 28), and maintenance
started about ten months after high does chemo.]
Only the CR response (top center) shows a partially rectangular
response.
Two curves right are without/with three known 'bad' cytogenetic
variations
Revlimid maintenance in this trial was 10 mg cycled (21 days out
of 28)
Ten months of high dose chemo preceeded maintenance.
(data from a 2013 Italian MM clinical trial with 400 patients)
http://www.myelomabeacon.com/docs/asco2013/Boccadoro-MPRvsMEL200.pdf
As I wrote in an email
Ok I have achieved CR (complete
response), but the 64 dollar question now is how long before my cancer
comes back? The answer is that the data in papers shows the time in an
individual case is wildly variable. It could be 6 months, or 1,2,3,4 years,
who knows. Good genetics, achieving complete response, right choice of
maintenance chemo all improve the time on AVERAGE, but it's in an individual
case it is a statistical game. Once you have done all you can, you just
have to take it a day at a time.
Spectrum of MM patients
Some useful perspective
of my numbers is provided by Mayo clinic who have published data on about
1,000 of their MM patients when diagnosed. Most relevant is about 1/4th
of all MM patients present with a broken bone (pathologic fracture) like
me, and my staging beta2microglobulin of 6.9 puts me in the highest quarter
of MM patients. The normal range for hemoglobin is 13.8 to 17.4. The data
below shows 70% or so of MM patients have anemia with (oxygen carrying)
hemoglobin about 30% low. This is similar to me where my (minimum) hemoglobin
prior to chemo was 9.9.
 .
.
Accessing medical articles
To have a say in what chemo
regimen I am on I want to read underlying papers. I find summaries to be
totally useless. One resource worth looking into is the New England
Journal of Medicine. This journal has published a lot of stuff on MM, and
its homepage, at least for some papers, shows a link to 'free full text'.
This info below on PubMed
from Wikipedia (PubMed') is worth following up on. Many PubMed records
contain links to full text articles, some of which are freely available,
often in PubMed Central and local mirrors such as UK PubMed Central:
The National Library
of Medicine leases the MEDLINE information to a number of private vendors
such as Ovid, Dialog, EBSCO, Knowledge Finder and many other commercial,
non-commercial, and academic providers.[26] As of October 2008, more than
500 licenses had been issued, more than 200 of them to providers outside
the United States. As licenses to use MEDLINE data are available for free,
the NLM in effect provides a free testing ground for a wide range[27] of
alternative interfaces and 3rd party additions to PubMed, one of a very
few large, professionally curated databases which offers this option.
Lu[27] identifies a sample
of 28 current and free Web-based PubMed versions, requiring no installation
or registration, which are grouped into four categories:
* Ranking search results, for instance: eTBLAST;
Hakia; MedlineRanker;[28] MiSearch;[29]
* Clustering results by topics, authors, journals
etc., for instance: Anne O'Tate;[30] ClusterMed;[31]
* Enhancing semantics and visualization, for instance:
EBIMed;[32] MedEvi;[33] (Note: CiteXplore was withdrawn from service on
15 February 2013,[34] replaced by Europe PubMed Central.[35])
* Improved search interface and retrieval experience,
for instance, askMEDLINE[36][37] BabelMeSH;[38] and PubCrawler.[39]
* GoPubMed is a knowledge-based (Gene Ontology and
MeSH) search engine for PubMed. GoPubMed is the semantic search engine
for the life sciences.
* Expertscape provides search and ranking of medical
and biomedical expertise by specific diagnosis, technique, or other terminology.
Results are based on analysis derived from most recent ten years of PubMed
data.[40]
* Search term forwarders like "OssiPubMed online".
O. Groth., which runs searches on multiple external platforms derived from
the original boolean search terms.
* Reference-to-PubMed transcriptors like "OssiPubMed
online". O. Groth., which retrieves the PMID from one-letter coded journal
abbreviations to get the full-text articles.
* Link-Out arborizers "OssiPubMed online". O. Groth.,
which tries to retrieve available PDF's from additional hosts.
As most of these and other
alternatives rely essentially on PubMed/MEDLINE data leased under license
from the NLM/PubMed, the term "PubMed derivatives" has been suggested.[27]
Without the need to store about 90 GB of original PubMed Datasets, anybody
can write PubMed applications using the eutils-application program interface
as described in "The E-utilities In-Depth: Parameters, Syntax and More",
by Eric Sayers, PhD.[41]
What bones are affected
by MM?
-- "Meloma affects
the places where bone marrow is normally active in an adult. This marrow
is in the hollow area within the bones of the spine, skull,
pelvis, rib cage, and the areas around the shoulders and hips. The
areas usually not affected are the extremities: the hands, feet, and lower
arm/leg regions. This is very important, since the function of these critical
areas is usually fully retained."
(Ref: Multiple Myeloma Handbook, http://myeloma.org/pdfs/PHB_2015.pdf)
-- "Even if the myeloma cells
are at a higher level of 10%–60% of the total bone marrow, the growth rate
can be very slow and represent asymptomatic or smoldering multiple myeloma
(SMM)" (My number pre-chemo was 70% of marrow cells in my hip extract were
myeloma cells.)
Antibody proteins
The monoclonal M-spike that
is tracked to assess the cancer level in the body is specific type of protein
made by the cancerous plasma cells. Each plamsa cell can export into the
blood thousands of these molecules/sec! While antibodies are considered
'large' proteins, they are tiny in comparison with the dimensions of a
plasma cell, which is visible under a light microscope. Like all proteins
an antibody is composed of a string of amino acids. An antibody string
has a specific Y shape and is composed of two 'heavy' chains and two 'light'
chains.
-- "Each immuno globulin
(antibody) is made up of two (identical) heavy chains and two (identical)
light chains. There are five types of heavy protein chains: G, A, D, E,
and M. There are two types of light protein chains: kappa and lambda. The
typing of myeloma, done with a test called immunofixation electrophoresis
(IFE), identifies both the heavy and light chains. Most myeloma patients,
about 65%, have IgG myeloma with kappa or lambda light chains. The next
most common type is IgA myeloma, also with either kappa or lambda light
chains. IgD, IgE, and IgM myelomas are quite rare." (I fall into the 65%
category with an M-spike of IgG lambda, meaning my monoclonal antibodies
have G heavy chains and the lambda light chains.) "IgG myeloma has the
usual features of myeloma."
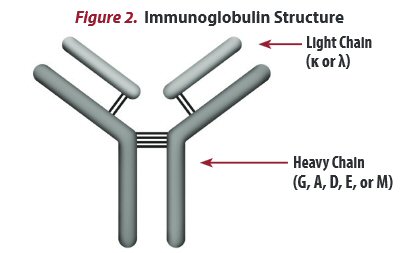
Y shaped antibody protein
(Heavy chains are built up from about 500 amino acids and light
chains from 215.)
An important point, which
is obvious from the structure (above), is that an immumoglobinm protein
cannot not come from a ribosome (molecular machine) in one go. Almost for
sure (though I have not found a reference that says this explicitly) it
is made in four pieces (two heavy chains and two light chains), and the
four pieces are post assembled into this Y shape. The two heavy chains
are supposed to be the same and the two light chains are supposed to be
the same, but are they always?
Note there's a balance issue.
Do the number of light chain molecules that are made match the number of
heavy chain molecules? The answer is in a normal person they don't. One
references says, "In normal circumstances, and for unknown reasons, plasma
cells produce an excess of light chains compared to heavy chains"
with the result that a small amount of (free) light chains can be measured
in normal blood (0.57 - 2.63 mg/dL lambda).
My own blood work shows clearly
that MM (prior to chemo), for reason which I have not seen explained, caused
the amount of free light chain in the blood to be extremely high (379 mg/dL),
nearly x400 times the normal average, and the kappa to lambda ratio correspondingly
very far from normal.
-- ** Most people with
multiple myeloma produce increased amounts of either kappa or lambda free
light chains, which can be measured in blood. Consequently, the ratio of
kappa to lambda light chains is abnormal in most people and is a sensitive
indicator
for this disease. This test is used to monitor progression and/or
treatment.
More on 'Complete Response'
I admit to being uncertain
as to what constitutes a 'complete response' (CR). Was there more than
one definition? Maybe one for blood, but a more stringent criteria used
by clinical trials? From my initital reading it appeared that a reduction
in M-spike of > 95% was considered a CR, and a reduction of (90% to 95%)
was considered a 'very good partial response' (VGPR). My primary hemotological
oncologist did not correct me when I referred to my M-spike reduction of
95.5% as a complete response, but a consulting hemotological oncologist
implied that was not sufficient.
The definitive word should
probably be that of the 2006
International Myeloma Working Group, which was constituted just for
the purpose of standardize MM terms and criteria. The section in the report
on categories starts with: "Changes in the M-component level are
the principal indicators
used for response evaluation", with the caveat that "M-component is
a surrogate marker". So changes in M-spike is the 'principal indicator
of chemo response with the caveat that it is a surrogate marker.
Let me start with their definition
of VGPR, one level down from CR:
VGPR --- "Serum
and urine M-protein detectable by immunofixation but not on electrophoresis
or
90%
or greater reduction in serum (plasma) M-protein plus urine M-protein
level <100 mg per 24 h".
Note from the definition (above)
the VGPR criteria can be met in two ways, either by meeting an absolute
criteria [M-protein not detectable on electrophoresis] or by a change
criteria
[> 90% reduction in serum M-protein combined with an absolute criteria
on M-protein in urine]. Now in six months of chemo my doctors have never
once tested my urine. I once asked about this and was was told it wasn't
necessary, monitoring M-spike in the blood was sufficient, but apparently
the international working group felt otherwise. With that caveat my 95.5%
reduction (from baseline) in M-spike says I (at least) qualify for VGPR.
Now here is the working groups definition of CR:
CR --- Negative immunofixation on the serum
and
urine
and disappearance of any soft tissue plasmacytomas
and<5% plasma
cells in bone marrow.
This is a triple criteria, all
of them absolutes: no soft tissue tumors, and immunofixation test on the
serum must be negative and <5% plasma cells in bone marrow (2-3% is
normal level). Now my bone marrow was extracted only once and that was
at the beginning of chemo for cytogenetics testing. However, the M-protein
in the blood is considered a stand in for the cancer in the marrow because
within some (unspecified) tolerance it must track it. My pre-chemo analysis
of my marrow showed 70% of the cells to be cancerous, so would it not be
reasonable that a 95% reduction in the monoclonal antibodies in the blood
means the marrow cells generating these monoclonal antibody proteins cells
have also dropped by about 95%? This would mean an absolute cancer level
in the marrow of 70% x 0.05 = 3.5%, which is less than the 5% criteria
and just about normal.
But what about the 'negative
immunofixation on the serum'? At this point I don't know how this relates
to M-spike levels. This gets into details of the thresholds of various
tests. In table 4 of the report I find below:
'Measurable disease
(except for CR) in the report is defined as a serum M-protein >1 g/dl'.
This is a pretty high level. My M-protein after five rev/dex chemo cycles
is at 0.24 g/dl, so it is, what, unmeasurable?
-- 'Serum FLC (free light
chain) assay is a highly sensitive marker of light chains in circulation
that are unbound to intact immunoglobulin. The FLC ratio is an excellent
indicator of clonality. Thus, normalizing of serum FLC ratio is a stricter
indicator
of CR'.
My lambda free light chain
pre-chemo was super high at 379 (.57 to 2.63 normal), which made my kappa/lambda
free light chain ratio virtually zero (<0.01) (.26 to 1.65 normal).
After five cycles of rev/dex chemo my lambda free light chain is 1.84 well
centered within the normal range (.57 to 2.63 normal), and my kappa/lambda
free light chain ratio is 0.82 also well centered within the normal range
(.26 to 1.65 normal). So the report text says 'normalizing of serum FLC
ratio is a stricter indicator of CR' and I meet that, but in the
tables in the report there is no mention of the free light chain ratio!
'Complete response'
discussion
The Multiple Myeloma Research
Foundation gives the following defintion of (chemo) responses:
Complete response (CR) --- A treatment outcome where there
are <5% plasma cells in the bone marrow and no evidence of myeloma proteins
in the serum or urine as measured by standard laboratory techniques.
Near Complete Response (nCR) --- A treatment outcome when there
are <5% plasma cells in the bone marrow but there are detectable myeloma
proteins in the serum or urine as measured by standard laboratory techniques.
Near complete response (near CR) --- Response to therapy where M protein
is no longer detectable in the blood and/or urine using conventional tests,
but is detectable with the more sensitive immunofixation test, and there
are less than 5% plasma cells in the bone marrow.
Very good partial response (VGPR) --- Treatment outcome where there
is a greater than 90% decrease in M protein; also known as very good partial
remission.
Partial response (PR) --- Treatment outcome where there is a greater
than 50% decrease in M protein; also referred to as partial remission.
Notice the definition of 'Complete
response' ["A treatment outcome where there are <5% plasma cells
in the bone marrow and no evidence of myeloma proteins in the serum or
urine as measured by standard laboratory techniques."] is poor (read crappy).
It may be usefully clinically, but to the patient the threshold value of
the proteins (presumably monoclonal spike) is hidden. It depends on how
sensitive the standard tests are and that is hidden away in some footnote.
Tom Brokaw perspective
The most famous person in
the public eye with multiple myeloma is the retired NBC newsman and evening
news anchorTom Brokaw. He's two years older than me and was diagnosed with
multiple myeloma just about a year before me when he was age 73. This is
a guy who for a non-medical person is embedded deeply in the the medical
system. He is on the board of several famous clinics (like Mayo clinic),
one of his own daughters is a physician.
As he tells the story when
he got a back ache that wouldn't go away he makes two trips to see famous
back guys at these top institutions. All these super specialists did is
take an x-ray of this back and tell him to slow down. Pain persists, only
on a later 3rd visit (yikes!) does someone actually take some blood, about
the most benign of 'invasive' procedures, and they discover he has multiple
myeloma. He returns home to Montana and immediately travels 150 miles to
a fishing trip, big mistake he says. On the trip his back pain is so bad
he barely makes it back home, and just four days after being diagnosed
he can't get out of bed and has to be medivacked out of his Montana home
to the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, where he is found to have a compression
fracture in his back. The irony here is that I discover I have cancer when
a bone in my neck breaks, Brokaw in spite of being treated by multiple
big names in the field fares little better, four days after his diagnosis
he also has a broken vertebrae!
He was advised by some to
get a stem cell transplant, but as he tells the story, Ken Anderson of
the Dana Farber in Boston advised that he skip the stem cell transplant
and be treated with drugs and that's what he did. [We are going to go to
"war" and various other nonsense.] I made the same decision to not do a
stem cell transplant, the difference being that I (essentially) made the
decision on my own based, on my research and my experiences in the hospital
for a week for my neck operation, which was enough time in the hospital
for me! My oncologist comment on my decision: It was not unreasonable'.
Partly Brokaw's and my avoidance
of a stem cell transplant is a function of age. My oncologist told me at
diagnosis that not so long ago the cut off age for a stem cell transplant
was 68 or 70 (I was 72 at diagnosis and Brokaw was 73), but that lately
people older than me had had them. The age cut off being a tradeoff of
the ravages to the body and risk vs benefit of the procedure. And partly,
while not yet definitively proven, there are hints from clinical trials
that the new generation of (so-called) 'novel' drugs, like rev/dex, are
achieving results comparable, or nearly comparable, to earlier trials with
stem cell transplants. Stem cell transplants became the 'gold standard'
for MM at a time when only the first generation of drugs, like thalidomide,
were available as an alternate treatment, and these first generation drugs
were poorly tolerated, so at the time a stem cell transplant offered a
chance, after a long recovery, of getting off drugs for a while. However,
more recent clinical trials are showing that for even for stem cell transplant
patients a maintenance of dose of revlimid, vs no drugs, considerably lengthens
the time before the disease progresses.
As best as I can tell Tom
started on rev/dex and later Velacade was added. His Dec 2014 announcement
about going on maintenance in six weeks indicates that his 'induction'
therapy to drive his numbers down ran almost a year and a half. In my case
I took rev/dex for six months and then went on maintenance (10 mg Revlimid).
So far rev/dex has worked well for me, I achieved a CR (complete response)
based on M-spike, which I am told only 10-15% of rev/dex patients achieve.
When after diagnosis he asked
how long he had, he was told five years. In Jan 2016 I saw Tom Brokaw live
on TV (commenting on a primary election) and he didn't look too good, but
he up and about, and he is one more year into chemo than I am. It's very
frustrating for MM patients that Brokaw is not more forth-coming about
his chemo. He writes a book and give speeches about his disease, but he
never says specifically what drugs he is taking. All he does is drop hints
that those on the MM forums try and interpret.
Roy Scheider
Jaws actor Roy Scheider
was diagnosed at 71 with MM in 2004, had stem cell transplant in 2005 and
made it to 2008 where he died from complications of a staph infection.
He was treated at Univ of Arkansas.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
References
Multiple myeloma
overview arrticles
This paper ('Multiple Myeloma: An Update', 2013) by a doctor from Oman
has a very detailed overview of MM.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3562980/
2015 MM Patient Handook from
International Multiple Myeloma Foundation (good technical reference)
http://myeloma.org/pdfs/PHB_2015.pdf
2013 Mayo clinic MM treatment
recomendations (detailed paper, complete)
http://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-6196(13)00077-3/fulltext
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Multiple Myeloma spectrum
There are two precursors
to MM. The first is 'monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance'
(MGUS), and this can advance to smoulding multiple myeloma (smouldering
MM). When I dig into it, even though the terminology obscures it, MGUS
is really a low level and slow growing MM. It's a lot like the slow growing
prostrate cancer that most older men have that don't give them any symptoms.
It affects 3% of people over age 50, and 5% over 70, so it is quite common.
As these people age, a few of them (about 1% per year) will progress
to full blown MM. The clinical definition of MGUS is these three criteria:
1) Monoclonal spike
on serum protein electrophoresis of less than 3 g/dL
2) Bone marrow infiltration
by monoclonal malignant plasma cells of less than 10%
3) No organ damage related
to multiple myeloma (no renal failure (?), no hyperCalcemia, no anaemia,
no bone lesions)
In other words the patients
have no symptoms, but up to 10% of their marrow plasma cells can be cancerous
and these cells can produce a monoclonal M spike in the blood that can
be remarkably large (3 g/dL). For perspective my pre-chemo M spike was
5.31 g/dL that after six months of rev/dex chemo has been reduced to 0.23
g/dL, which is less than 1/10th of the level that a non-symptomatic MGUS
person may have. If the monoclonal level is above 3 g/dL and/or the amount
of malignant plasma cells in the marrow is above 10%, then the condition
is called 'smouldering MM' and while it is still a classified as precancerous,
50% of these patients will go on to develop full blown MM in five years.
M-spike tracking?
MGUS seems to blow a hole in the
theory that M-spike tracks cancer levels in the body. MGUS by definition
means plasma cells make up less than 10% of the marrow cells (2-3% is normal).
Yet somehow (not explained!) this relatively small level of cancerous marrow
cells pumps out so many clonal anti-bodies that the M-spike can be as high
as 3 g/dL. What? For comparison my M-spike was 5.31 g/dL and bone aspiration
found that clonal plasma cells made up 70% of my marrow cells. (something
doesn't computer here!)
In other words there's a spectrum
where cancer can exist in the marrow plasma cells but is slow growing and
has not yet spread (metastasize) to form bone lesions. Lower levels are
'monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance' (MGUS), higher levels
are 'smouldering MM', and once it has spread and bone lesions have formed
it is (full blown) MM.
---------------------------
'The
Role of CR (complete response) in MM' --- excellent 2009 French
paper
This 2009 french paper (reprinted
2015) from journal Blood discusses in detail 'complete response (CR)',
and its correlation with improved prognosis. They discuss that years ago
the definition of CR was no cancer showing up in the standard electrophoresis
test, i.e. monoclonal spike was below the threshold of the test. The paper
gives the threshold of the electrophoresis test as (0.02 -
0.06 g/dL), which is x4 to x10 lower that my current (and likely plateau)
of 0.23 g/dL. Over time as MM treatments improved (stem cell transplants,
better drugs), the CR threshold was lowered to include that the immunofixation
test also not detect cancer cells. This test is about twice as sensitive
as the electrophoresis test. Even deeper levels of remission beyond CR
have been defined amounting to (in effect) no detectable cancer in the
body (blood, urine or marrow). To sort patients in this domain new and
exotic tests are required.
The reason for the focus
on CR is that it is correlated (somewhat loosely) with improved
prognosis, a longer time before cancer comes back ('time to progression',
and sometimes longer life. The clinical implications of this are not so
clear, and I discuss this elsewhere in this essay. The french authors of
the paper are clearly of the opinion that the correlation of CR to improved
prognosis implies that high risk patients should be treated to achieve
CR, However, the facts are that regardless of the treatment goals only
a minority of patients, often only a small minority, typically achieve
CR.
This paper gives the threshold
of the tests, i.e. "lowest detected level of M component'. My laboratory
tests measure M-spike in units of g/dL, so my 0.23 g/dL after six cycles
is far (x4 to x10) above the threshold of the serum electrophoresis tests,
not to mention immunofixation which is lower still by another factor of
2.
Serum electrophoresis
0.2 - 0.6 g/L (0.02 - 0.06
g/dL)
Immunofixation
0.12 - 0.25 g/L (0.012 - 0.025 g/dL)
http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/bloodjournal/114/15/3139.full.pdf
MM cure vs control debate
According to the MM Beacon
a leading doctor at Mayo clinic (S. Vincent Rajkumar) by been pushing to
make the objective of MM treatment control of the discease and not agressively
attempt a cure. In the important article below he makes a strong case not
to obsess about achieving CR, saying it (probably) makes little difference
for the 85% of patients that are standard risk. In the cure vs control
debate he comes down on the 'control' side, which amounts to conservative
treatment, don't throw everything at the cancer in the beginning trying
to drive down to the CR level. The same OS will likely result, he argues,
if newer and multiple drug combos are held for possible treatment later
with a resultant better overall quality of life.
There's also a link on the
MM Beacon to a 2011 interview with Ken Anderson of Dana Farber discussing
this issue. Anderson comes down firmly on the side of working to achive
CR, so it's a good guess that this is probably the approach of the Dana
MM team.
Here's a 2011 paper by Rajkumar (et al) and below quotes from it"
"Approach
to the treatment of multiple myeloma: a clash of philosophies' (Journal
Blood)
-- "Distressingly, most myeloma phase 3 trials are designed
with surrogate endpoints and typically fail to have well-designed quality-of-life
studies built in that can shed light on how patients in different risk
categories benefit from various interventions." (translation -- clinical
trials are of limited use in deciding how to indivualize treatment for
patients in different risk categories.)
-- "Several papers have emphasized
the importance of CR in MM (ref 26,27,31–35). This is a difficult topic
to cast doubt on because, after all, who can be against CR? The main reason
to be cautious in espousing CR is the correlation between increased response
rates and increased toxicity. Striving blindly for CR may lead to unacceptable
and unnecessary toxicity for some patients and come at too great a price."
-- "However, oncologists
willing to say that CR is not an important endpoint can quickly attain
the pariah status. Despite this, we wish to highlight some important caveats
about CR and illustrate its limited use as a surrogate endpoint in a disease,
such as MM."
-- "Unlike curable cancers,
such as large cell lymphoma, CR in MM is not a surrogate for cure but rather
a marker of profound tumor reduction. It is not a true CR because most
CR patients will relapse with time. Indeed, in most studies that proclaim
the benefit of CR, the median CR duration is short."
-- "Thus, achieving immunofixation-negative
CR status may need eradication of not just MM cells but also any premalignant
monoclonal plasma cell populations present in a given patient. The existence
of such clones is not in doubt and is evidenced by the fact that premalignant
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance almost always precedes
MM (ref 37,38), and MM patients after therapy often achieve a prolonged
remission from malignancy (symptoms and signs of MM) despite the presence
of a residual stable monoclonal (M) protein. (I read 3% of older people
have 'monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance', meaning there
is an excess monoclonal protein in their blood but it's stable or progresses
very slowly into clinical MM, analogous to slow growing prostate cancer
in men, which is best left alone.)
-- ** "Finally, and most
importantly, we now know from ... that not every MM patient needs or benefits
from achieving CR. Data show that patients with standard-risk MM (composing
85% of all MMs) have the same survival regardless of CR status,
whereas achieving a CR appears to be critical for patients with high-risk
disease."
-- ** "Similarly, despite
the doubling of the rate of CR/very good partial response with thalidomide
and dexamethasone, or a tripling of it with the addition of lenalidomide
to melphalan and prednisone induction, there was not even a hint of a difference
in PFS or OS. There was, however, significantly greater toxicity."
-- ** "But prolongation of
PFS alone is not adequate because the seriousness and implications of a
second cancer (from revlimid) are quite different from a rise in the monoclonal
(M) protein by 25% (which is all that it takes to qualify as “progression”
in MM)." (The latter is simply not correct. The international committee
definition of progression is a greater than 25% rise in M-spike, but a
rise that must also exceed 0.5 g/dl, so for anyone with a reasonable
low M-spike (< 2 g/dl), the rise (from mimimum) of 0.5 g/dl applies.
After ten months of chemo my M-spike level dropped below the threshold
of the test (probably <0.05 g/dL), so that would make my M-spike threshold
of progression 0.5 g/dl (round numbers).
** I found a good reference
point here. I looked at what monoclonal spike was needed to qualify for
a clinical trial at Dana Farber for 'relapsed' mulitple myeloma patients.
The qualification threshold includes a monoclonal spike [> 0.5 g/dl].
It would be useful to look at other trials, many are listed on the Dana
Farber site. (Exceeding this round number is probably a good shorthand
for the disease having come back.)
-- "Thankfully, in the case
of lenalidomide maintenance, an OS advantage is emerging in one of 2 randomized
clinical trials, and the risk of second cancers may be overcome if a significant
survival benefit is confirmed." (Saying good things, circa 2011, about
revlimid maintenance.)
Criteria for
my MM progression (Aug 2015)
What are the criteria to
look for to determine if my MM is coming back? (Another 64 dollar question.)
Even though I have been in maintenance for two months with low M-spike
levels my doctor has said nothing about this. (Except in response
to a question of mine that it is generally pretty obvious, whatever that
means!) From the article above and similar references I think the working
definition to use is an M-spike level of 0.5 g/dL. For perspective this
is the level I was at in mid-March 2015 after four months of chemo and
about 0.1 of the level I was originally at prior to chemo (5.31).
The alternate definition
I see widely quoted is a 25% increase in M-spike. Well my M-spike was reported
this month as undectable (below the threshold of the test). So what's a
25% increase from an unmeasurable level?
But looking at the M-spike is
not enough. A possible, or maybe likely, leading indicator, is the lambda
free light chain. The lifetime of the lambda free light chain in the body
is very short (hours), so any rise of this parameter above the normal range
(2.63 mg/dL) should raise alarm. In my first month of rev/dex chemo free
light chain dropped 98% while M-spike, which has a lifetime in the blood
of weeks, dropped 67%.
Summarizing
Here's my best judgement
(as of aug 2015, two months into maintenance) on the blood markers to look
for to judge if the cancer is coming back:
1) Increase of lambda free light chain with a rise outside the normal
range
-- > 4 or 5 mg/dL raise alarm
2) M-spike level rising above a baseline level
-- > 0.25 or 0.30 g/dL raise alarm
-- > 0.50 g/dL clinical threshold of reoccurance
What are
the clinical implications of CR?
This is a 64 dollar question?
I read varying opinions. It's easy to jump to the conclusion that if achieving
CR leads to a better prognosis, i.e. a longer disease free period, possibly
4 years vs 2 years, then patients should be treated more aggressively to
try and achieve CR. But the data only supports a correlation. A
paper from a guy at the Clevland Clinic points this out and argues that
the observed correlation my very well be just be a sorting of patients
according to their genetics. (This makes a lot of sense to me.)
He points out that MM is
a very heterogeneous disease, meaning two seemingly similar patients treated
the same way can have very different outcomes. The Clevland author puts
this down to patient genetics, but I think it could just as well be due
to individual variability that is not at all understood (biological noise).
He argues that the small subset of patients that achieve CR are very likely
just those with good genetics, these are the patients more responsive to
treatment. He thinks it is a logical fallacy to use the known correlation
as an argument to treat longer and more aggressively other patients to
get to the CR level. It might be desirable, but just as well it might not
be, the data doesn't support aggressive and/or extended levels of treatment.
Trying to achieve CR in a wider subset of patients may very well lead to
excessive over-treatment and a reduced quality of life.
My primary hemotological
oncologist and the consulting hemotological oncologist, both at Lahey,
have not pressured me to take more treatment as after six months I am transitioning
to a maintenance does of revlimid (no dexamethasone). Maybe this is a consequence
of my age and choice that I don't want a stem cell transplant and that
I have achieved a result that is probably as good as I can achieve with
standard pill based chemo.
What about
'Very Good Partial Response'?
Where it really gets interesting,
at least to me, since I clearly have not achieved CR in six months of standard
rev/dex chemo, is the 'Very Good Partial Response' (VGPR) category. I may
be in this category. Many papers when they discuss favorable outcomes lump
VGPR together with CR. A paper I read (from Mayo Clinic) discussed in detail
patients' perceived 'failure' to achieve the CR target, and the author
argued for 85% of patients it made no difference to their outcomes.
In other words as he reads the literature only 15% (or less) of patients
may benefit from more aggressive treatment to improve the depth of their
response.
I find definitions for VGPR
are much harder to come by than definitions of CR, but the french paper
(discussed above) has a definition for VGPR, and it is interesting. The
VGPR threshold can be met in two ways, either by having an absolute
level
of cancer below a threshold or by a change in M-spike levels.
I find it rather curious VGPR can be met by an absolute cancer level OR
a reduction in cancer level (due to chemo). I find the absolute level to
be quite stringent (cancer not detectable by electrophoresis), but the
reduction in M-spike (monoclonal spike) less so. I don't meet the absolute
threshold as my cancer is detectable on the electrophoresis test, but I
do (easily) meet the reduction in M-spike level (> 90% reduction), since
6 months of rev/dex chemo has reduced my M-spike level by > 95%, so according
to this formal definition I am in the VGPR category.
VGPR Serum and urine
M protein detectable by immunofixation but not by electrophoresis, or 90%
or greater reduction in serum M protein
plus urine M protein (< 100 mg/24 hours). [Reference is 2006 paper by
Durie et al, "International uniform response criteria for
multiple myeloma', (journal) Lukemia]
I achieve CR (based
on M-spike) (2/16)
After six months of rev/dex
my M-spike had dropped from 5.31 g/dL to .23 g/dL. Two months later (on
maintenance) it suddenly became unquantifyable (meaning it was below the
threshold of the test) and remained unquantifyable for three months.
I found the test threshold hard to pin down, but I think the Lahey M-spike
test threshold was probably about .05 g/dL, since in the succeeding month
a value of .07 g/dL was measured.
Does the M-spike test threshold depend on where the spike
is?
As of 2/16 with both Dana
and Lahey protein electrophoresis results in hand I am less confident that
I know what the threshold of the M-spike test is. I am beginning to suspect
there may be more than one threshold, that it depends on exactly where
in the spread out proteins the monoclonal spike (if any) falls, i.e. it
depends on the background 'noise'. My M-spike data from Lahey does not
identify the region where the monoclonal spike is located.
Dana on the other hand breaks
out the total protein value into five regional subcomponents: albumin,
alpha 1, alpha 2, beta and gamma, with a value (g/dL) for each region.
My one Dana reading that said my M-spike could not be quantified noting
it was within the beta region. My beta region value is outside (to me far
outside) normal region at 1.57 g/dL (normal .60 to 1.20 g/dL). This is
over x30 times .05 g/dL. I asked my Dana doctor what the threshold value
(in the beta region) might be, and got a weak reply (maybe) .1 g/dL.
Both my regular hematological
oncologist and my Dana MM specialist say I achieved CR (based on M-spike).
This is a loose CR definition. It does not meet the more rigorous definition
of CR for clinical trials, which requires, among other things, a marrow
extraction to directly confirm < 5% plasma cells in the marrow. I did
not have a marrow extraction to confirm my low M-spike readings.
My Dana MM specialist looking
at my M-spike results told me I was 'exquisitely sensitive' to Revlimid,
because I had achieved CR on rev/dex. I asked was this unusual? He said
only 10-15% of patients achieve CR on rev/dex.
'Understanding
Protein Electrophoresis' notes
I'm not aware that there
was any attempt to 'correlate' my monoclonal reading with the amount of
cancer in the bone marrow (as advised below). The only reference point
(I presume) is the one aspiration of my hip bone. (review this). I have
a vague memory that the clone cells in the aspiration were 50%? Does the
ratio of M-spike to total protein qualify as calibration?
** -- The level of M-component
on SPEP and UPEP reflects the amount of myeloma present. However, it is
very important to realize that each patient is different. At the time of
diagnosis, some patients have, for example, a very high spike in the serum
but not such a high level of myeloma in the bone marrow
or bones. And the opposite is also true: some patients can have a low
spike, but a lot of myeloma cells. Thus, at diagnosis, it is very important
to
correlate the spike level with the amount of myeloma in an individual
patient. If the spike is low, this can be especially important, since small
changes can be more important in terms of response to treatment as well
as potential progression or relapse. (I don't think my spike was low. Prior
to chemo beginning it was 5.31 g/dl and the threshold for MM diagnosis
I think is 3 g/dl.)
This is justification for
six months of induction chemo
-- If the treatment is working
well, frequently there will have been substantial improvement (reduction)
in the M-protein levels on SPEP/UPEP within the first 2–3 months. As noted
above, the level of response can be quantified as >50% (partial response
[PR]); >90% (very good partial response
[VGPR]); 100% (complete response [CR]). The classification of CR also
requires that no M-protein is detectible using immunofixation (IFE) and
that a bone marrow test shows no evidence of myeloma. Achieving the higher
levels of response such as VGPR and CR will typically take at least another
2–3 months of
treatment (total of 4–6 months at that point). Several additional months
of therapy may be required to achieve maximum response.
-- This protein (M-spike),
which is released into the serum or urine, is called a serum or urine tumor
marker. Only a very few cancers have this type
of a marker which, in this case, makes it possible to assess the amount
of myeloma at the time of initial diagnosis and track the amount of myeloma
throughout the course of the disease. e. One can look at response to treatment,
depth of remission, and, if necessary, the patient’s relapse using exact
numbers, which is a unique advantage. For example, we can determine if
a response is: Partial (PR)=50% reduction of M-protein; very good partial
(VGPR) = 90% reduction
of M-protein; or complete (CR) = no protein detected. We can also identify
a >25% increase in protein level, which we call relapse. (Where is the
caveat tha the increase must be at least 0.5 g/dl!)
M-spike to total
protein ratio (7/15)
The ratio of [M-spike protein/total
protein (both in g/dl)] is an interesting perspective and gives real meaning
to the M-spike number, which is otherwise abstract. This test is done is
plasma, which is what remains of blood when all the blood cells are removed.
Here are my protein numbers for baseline (pre-chemo) and after 7 months
(one month into maintenance), and my calculation of several protein ratios.
Total protein consists of
a large albumin spike with the balance globulin. The albumin spike typically
makes up a little more than half of the total protein [55% (+/- 3%) nom],
but pre-chemo because the (globulin) M-spike was so large the albumin spike
was only 23% of total protein. At my lowest cancer levels (9 months into
chemo) the M-spike fraction of total protein was less than 0.7%, whereas
pre-chemo it was 50%. Pre-chemo nearly all (97%) of the huge excess
of IgG antibodies in my blood were monoclonal M-spike, but at 9 months
< 5% of the much lower amount of IgG antibodies are M-spike. IgG has
a high normal residual (0.75 - 1.4 g/dl), so changes in IgG per se are
likely to be a weak indicator of disease progression, but the ratio of
M-spike to IgG will probably be more useful.
|
|
M-spike
(monoclonal spike)
|
Total protein
(6 - 8.2 g/dl normal)
|
albumin
(3.2 - 4.8 g/dl
normal)
|
IgG
(0.75 - 1.4 g/dl normal)
|
|
M-spike
to
Total Protein
ratio
|
M-spike
to
IgG
ratio
|
albumin
to
Total Protein
ratio
|
albumin
to
(total protein - albumin)
or
globulin
ratio
|
baseline
(pre-chemo)
|
5.31 g/dl
|
10.6 g/dl
|
2.4 g/dl
|
5.46 g/dl
|
|
50.1%
|
97%
|
0.23
|
0.29
|
7 months later
(maintenance)
|
0.19 g/dl
|
6.0 g/dl
|
3.5 g/dl
|
0.64 g/dl
|
|
3.2%
|
30%
|
0.58
|
1.40
|
9 months into chemo
(min cancer
baseline 8/31/15)
|
<0.05 g/dL
|
6.6 g/dL
|
3.7 g/dL
|
0.93 g/dL
|
|
<0.7%
|
<5%
|
0.56
|
1.28
|
|
12 months into chemo
|
0.12 g/dL
|
6.1 g/dL
|
3.4 g/dL
|
0.94 g/dL
|
|
2.0%
|
13%
|
0.56
|
1.26
|
16 months into chemo
(back to rev/dex 5/9/16)
|
0.25 g/dL
|
5.8 g/dL
|
3.4 g/dL
|
0.83 g/dL
|
|
4.3%
|
30%
|
0.59
|
1.42
|
2.0 months into new pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo
(8/22/16)
|
0.20 g/dL
(8/8/16)
|
6.7 g/dL
|
3.5 g/dL
|
0.627 g/dL
|
|
3.0%
|
32%
|
0.52
|
1.09
|
Pre-chemo my large M-spike
of 5.31 g/dl increased the total protein to 10.6 g/dl (above the normal
range), and M-spike was 50% of it. After seven months of chemo, my protein
numbers are (probably) close to normal. Total protein has dropped to 6.0
g/dl, within the normal range, and the M-spike is now only 3.2% of it.
Pre-chemo the normally large dominant albumin spike (see figure below)
was only 23% of total protein, but after seven months with the drastic
shrinking of the M-spike the albumin (spike) is now 58% of total protein.
Immunofixation showed my multiple myeloma cancer puts out an IgG protein
(most common type of multiple myeloma). This is confirmed in that pre-chemo
the IgG in my blood (5.46 g/dl) measured just slightly higher than the
M-spike (5.31 g/dl). The near agreement of these two numbers is reassuring
that both tests look to be accurate. After seven months, IgG has dropped
drastically (factor of x8.5) to 0.64 g/dl and the M-spike (0.19 g/dl) is
only 30% of it.
-- The crucial information
comes from SPEP (serum electrophoresis). By calculating the size of the
“spike”, which depicts the amount of monoclonal protein (done by measuring
the
area between the top of the spike and the baseline of the graph),
one gets the percentage of the total protein that represents the M-protein.
(Translation: while M-spike is reported in absolute units, the value is
actually obtained by measuring total protein in absolute units and then
scaling it by the ratio of M-spike to total protein.) For example:
* Spike is 60% of total protein
* Total protein = 12 grams/deciliter (g/dL)
* Spike level = 7.2 g/dL (60% of 12) (This g/dL value is what would
show up in blood work.)
Both the total protein and
percentage of monoclonal protein change over time. With response to treatment,
the spike can drop to 40%, and total protein to 9 g/dL, for example. This
gives a spike level of 3.6 g/dL, which is a 50% drop in M-protein, or a
partial response. (Note my numbers above are quite consistent with this
excerpt from the booklet by the International Myeloma Foundation on electrophoresis
protein testing.)
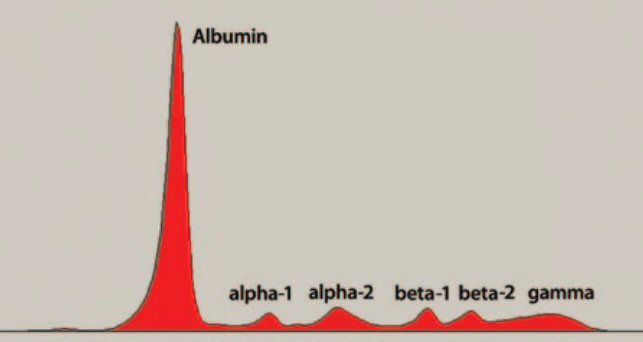 .
. 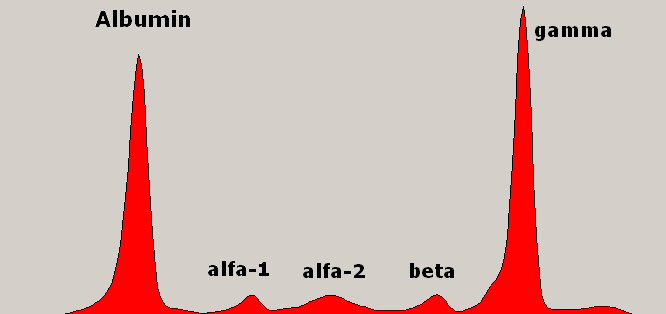
Left: normal
Right: multiple myeloma adds a spike right (in beta or gamma region)
Plasma proteins spread out by electrophoresis.
Albumin (left spike) is normally dominant, a little more than half
the total protein.
All the small spikes together are the globulin proteins.
(source -- http://myeloma.org/pdfs/U-PEP-Eng2012(P)_f1web.pdf)
IgG testing advantage
My type of antibody is IgG.
A paper explains that IgG tends to occur in the gamma region, which from
a testing viewpoint is an advantage because in the gamma region there is
"very little background from other serum proteins". In contrast IgA and
IgM tend to occur in the beta region and are partially obscured by normally
existing proteins, so "there is no reliable way to quantitate the M-spike
in the beta region".
Dana Farber lab breakout of protein data (2/18/16 update)
My Lahey electrophoresis
tests do not identify the region of my M-spike, but my Dana Farber test
result does. While Dana Farber identifies the monoclonal paraprotein as
IgG lambda, it notes that it is in the beta region, and they were
unable to quantified it. The breakout of my total protein at Dana Farber
is as follows: (data taken 2/8/16). (Note Lahey blood work (at least as
reported to the patient) reports only albumin and total protein with no
mention of alpha 1, alpha 2, beta, or gamma.)
albumin
3.19 g/dL (3.20
- 5.30)
low ratio of albumin to total protein (47%)
alpha 1
.26 g/dL
(.10 - .40)
alpha 2
.81 g/dL
(.50 - 1.00)
beta
1.57 g/dL
(.60 - 1.20)
quite high
gamma
.97 g/dL
(.80 - 1.70)
-------------------------
total protein 6.80 g/dL
(6.4 - 8.3)
consistent with past Lahey readings
Two things are odd in the
above numbers, neither of which my doctors have commented on. One, albumin
is only 47% of total protein. This is quite a bit lower that the valued
as measured by Lahey labs over the last year or so. In my Lahey data aftter
the first two months of chemo it has remained in the range of 52% to 58%
or (55% +/- 3%), and this is consistent with what I read that albumin protein
component is normally a little more half of total protein. Two, the beta
range value is quite high, far outside the normal range, and this is where
they found my monoclonal spike, yet still the Dana Farber clinical doctor
said the M-spike was too small to be quantified.
A couple of thoughts come
to mind. I wonder if maybe my IgG (1.06 g/dL) might have 'moved' from its
(usual) gamma region into the beta region? If so, what might this
mean? On albumin maybe the two labs don't interpret what is the albinum
component in the same way. Albumin in online plots is normally shown as
a large isolated spike at the beginning (or end) of the diffusion, and
this is consistent with the above data where the adjacent alpha 1 region
is only .26 g/dL. I would think (guess) that the definition of these regions
would be fairly standardized, but maybe not. If I add the alpha 1 value
to the albumin value, the albumin/total protein ratio is increased to 51%.
Hopefully the picture will
clarify soon because three weeks after these Dana labs I am scheduled to
get a new set of Lahey labs. It might be desirable to meet with one of
the doctors at Lahey who does this interpretation to try and understand
the test better.
I haven't physically seen the
machine that scans the diffusion, but I suspect it displays a curve like
those shown above and automatically measures the area under the
entire curve. This is reported on blood work as 'total protein'. The technician
(or pathologist) then manually moves two markers to define the edges
of the M-spike. This allows the machine to figure the
ratio of the
area of the M-spike to the total protein, and the fraction of the
total protein area under the M-spike is then reported in absolute terms
(g/dL) as the value of the M-spike.
In my table of numbers when
my pre-chemo M-spike was 5.31 g/dL, my total protein was 10.6 g/dL. This
means my M-spike was initially almost exactly 50% of my total protein.
My initially albumin of 2.4 g/dL was down roughly 30% in absolute terms,
but because the total protein was inflated (by the M-spike), it was only
23% = (2.4 g/dL/10.6 g/dL) of total protein vs the 52-58% it normally is.
Useful booklet from International
Myeloma Foundation with some good info about the electrophoresis test for
MM. They have a related booklet on the free light chain assays (see next
paragraph)
http://myeloma.org/pdfs/U-PEP-Eng2012(P)_f1web.pdf
Value
of kappa/lamda ratio in monotoring MM patients for relapse (7/19/15)
On a MM forum I saw reference
to paying close attention looking for signs of relapse to what was called
Free Light Chain Ratio (FLCR). A free light chain in the plasma is a fraction
of the immunoglobulin. The key # to watch turns out to be the kappa/lamda
ratio (normal 0.26 to 1.65). Multiple myeloma clones will either be kappa
or lamda type. So the ratio will go offf on the high side for those with
a kappa MM and off on the low side for those with the more common lamda
MM. My myeloma is the lamda type. My pre-chemo 'lamda free lt chn bld'
was a sky high 379, so with kappa in the normal range, my kappa/lamda ratio
is virtually zero (< 0.01 in my blood work).
(update 1/2/16)
It looks like I am beginning
to see this leading action. While my cancer levels are still low, they
have ticked up for the last three (or four) months. My latest free light
chain reading (12/29/15) shows a big move, and this concerns me. I have
yet to see my corresponding M-spike value (due to new year holiday it is
delayed), but I bet it will be up considerably from .12. I think the significance
of the kappa/lambda ratio should be discounted somewhat as my kappa free
light chain is also rising. Over the last 12 months my numbers have shown
I may have some kappa involvement in my cancer.
Below shows a steady increase
in my numbers, both M-spike and lambda free light chain, over a six month
period while on revlimid maintance. Noteworth is lambda free light chain
exceeding 10 mg/dL which clinal trials use as a threshold for disease progression.
My first remission ended a couple of months later (5/16/16) when an MRI
found a (large) plasmacytoma growing behind left eye that was causing double
vision.
date
M-spike (g/dL) lambda
free light chain (mg/dL) kappa/lamda
ratio
----------
------------------
------------------------------------ ----------------------
9/28/15
< .05
3.11
1.17
10/26/15
.07
3.18
1.00
12/1/15
.12
4.08
0.95
12/29/15
.16
6.41
0.65
1/13/16
.18
6.39
0.70
1/26/16
.16
8.41
0.53
2/23/16
.22
12.00
0.38
3/2/16
.22
13.60
0.28
3/22/16
.31
15.30
0.26
In my blood work the section is called:
Immunoglobulin Free Light Chain Blood, and it has three entries: kappa
free lt chn bld, lamda free lt chn bld and the ratio of the two. Here's
my latest light chain numbers (July 2015, six weeks into maintenance).
Kappa is a tad high, but chemo has driven my lamda (clone) number down
from pre-chemo 379 to 2.37 within normal range, and more importantly the
ratio is well within the normal range too.
kappa free lt chn bld
2.59
(0.33 - 1.94) mg/dL
lamda free lt chn bld
2.37
(0.57 - 2.63) mg/dL
kappa/lamda ratio
1.09
(0.26 - 1.65)
-- M-protein may consist
of intact immunoglobulin, free light chains, or both. (This many
be true, but free light chains are measured in mg/dL while intact immunoglobulin
are measured in g/dL. My highest fraction was before chemo where my M-spike
was 5.31 g/dL while my lambda free light chain was 379 mg/dL. This means
the free light chain was 7% of the total. But just a month into chemo with
M-spike at 1.82 g/L and free light chain at 8.17 mg/dL the free light chain
fraction was only 0.4% of the total, hence it's only significant at very
high levels of cancer.)
-- Patients Who Benefit the
Most From the Serum Free Light Chain Assays Are: People with myeloma who
have abnormal serum free light chain results at the start of treatment.
(that's me) Monitoring with the serum free light chain assays often allows
a rapid assessment of the effectiveness of treatment.
The International Myeloma
Foundation has a related booklet discussing serum free light chain assays
(kappa/lamda ratio), and how it is useful for monitoring MM patients because
it is very sensitive.
http://myeloma.org/pdfs/U-Freelite-Eng2011_g2web.pdf
MM marker
without a measurement of M-spike?
Looking at my protein ratios
(calculated above) I am wondering if a low Albumin to Total Protein Ratio
(23%) is a marker for multiple myeloma that might be picked up by 'routine'
blood testing. In other words is an electrophoresis test ever done as part
of a routine checkup? Or is IgG in the blood routinely measured? Even without
specifically measuring the M-spike (monoclonal) spike my numbers show it
substantially throws off IgG (pushing it far above normal) and the albumin
to total protein ratio (less than half of normal).
A/G ratio
When I research this, I
find that albumin and total protein are sometimes measured in it
routine blood work, so my odd ratio might have detected my multiple myeloma
before my neck broke, which clearly would have been a plus. However the
standard lab test is not the [albumin/(total protein) ratio], it is called
the [albumin/globulin ratio or A/G ratio], which is calculated as [albumin/(total
protein - albumin)]. Total protein is made up of the albumin protein spike
and a bunch of small protein spikes which all together are called globulin.
The multiple myeloma M-spike is a spike in one of the globulin proteins.
(on a quick read it was unclear if the standard blood work requires an
electrophorsis test to measure these proteins)
I read the A/G ratio
is normally a little above 1, which means there is a little more albumin
than globulin. In other words albumin is a little more than half the total
protein. This is consistent with my 7 month data where my albumin measured
58% of total protein.
Platelets
My platelet count has bounced
around but remained in the low end of normal for my six months of chemo.
However, my first month into maintenance my platelet count dropped to 122,
substantially below the normal range (150 - 450). Platelet cells
in blood are responsible for clotting. The lifetime of a platelet cell
is short only 7 - 10 days (much less than my 28 day chemo cycle). Platelets
are made in the marrow all the time by large cells called megakaryocytes.
My infusion nurse recently mentioned that my low platelet count going into
maintenance might be due to stopping dexamethasone. She said some platelet
diseases are treated only with dexamethasone. The excerpts below confirm
that she was right. Corticosteroid (dexamethasone is a corticosteroid)
is the drug of choice to treat some forms of low platlet count.
-- If for any reason your
blood platelet count falls below normal, the condition is called
thrombocytopenia.
Normally, you have anywhere from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter
of circulating blood. Because each platelet lives only about 10 days, your
body continually renews your platelet supply by producing new platelets
in your bone marrow. [Normal range for platelets in my blood work is shown
as (150 - 450 K/uL), so clearly 'K' stands for 1,000]
-- Treatment for low platelet
count (thrombocytopenia): Your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids, also
called steroids for short. Steroids may slow platelet destruction. These
medicines can be given through a vein or by mouth. One example of this
type of medicine is prednisone. (This confirms what the nurse told me that
some platelet diseases are treated with corticosteroids.)
-- If your condition
is related to an immune system problem, your doctor may prescribe drugs
to boost your platelet count. The first-choice drug may be a corticosteroid.
-- Dangerous internal bleeding
can occur when your platelet count falls below 10,000 [10 K/uL] platelets
per microliter. (Nurse told me her concern
is when platelets are less than 100 K/uL)
History of myeloma
Discovered a german site
with a lot of detail about MM including by far the best history of MM I
ever seen. It includes some interesting details of new drugs. It's a good
technical overview of MM. It is written for doctors: 'Phyician's guide
- consise review'. In a table titled: 'Tests Required To Monitor Therapy
Responses' there is the following: blood tests (which I get monthly), but
also urine, bone evaluation (skeletal x-rays, bone density (DEXA scan)
as a baseline to evaluate effectiveness of biphosphonates, bone marrow
(aspiration and biopsy for periodic monitoring).
-- Besides activation of
osteoclasts, the other characteristic feature of myeloma bone disease is
inhibition of osteoblasts, which are responsible for new bone production
and bone healing.
-- * An important
new observation is that the cholesterol-lowering statins (HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitors, e.g., Lipitors; Mevacor'v), can enhance osteoblast activity
and promote bone healing. In addition, VELCADE® (see relapse treatment)
has been shown to promote bone healing, at the same time that it is a potent
anti-myeloma agent. (This is the first I have heard of statins as being
useful in promoting bone healing.)
-- The predisposition
to infections is perhaps the single most characteristic feature of myeloma
patients besides the strong tendency for bone disease. Myeloma patients
are susceptible to both viral infections and infections with "encapsulated"
bacteria such as pneumococcus. However, in the face of neutropenia and
the effects of high-dose chemotherapy, and with the added local effects
of implanted catheters (e.g. Hickman catheter), the whole range of bacterial,
fungal, and opportunistic infections can occur in myeloma patients undergoing
therapy.
-- About 70% of myeloma patients
present with pain of varying intensity, often in the lower back or ribs.
Sudden severe pain can be a sign of fracturing or collapse of a vertebral
body. (I have been lucky, because I have not had this problem, at least
to any significant extent. I did have a few incidences of rib pain
a few months preceeding my broken neck, but it has not reoccurred.)
-- Pneumococcal pneumonia
is the classic infection assoiated with myeloa at presentation, other bacteria,
such as streptococci and staphylococci, are now frequently isolated.
-- Hypercalcemia (excess
calcium in blood) is present in 10% - 15% of patients at diagnosis. (I
did have some elevated calcium in my blood. My first infusion of 2hr increased
by blood volume 11%, thus immediately decreasing the concentration of calcium
by 11%. (Excess calcium is a problem because it affects the kidneys.)
-- A combination of serum
beta2 microglobulin and serum albumin provided the simplest, most powerful,
and reproducible three-stage classification (International Staging System
introduced in 1996)
-- Responding patients go
from a high-risk to a lower-risk status until, ideally, no signs of myeloma
are left, or they achieve a stable plateau phase, but with measurable residual
disease. The time required to achieve the plateau phase is variable, ranging
from 3-6 months (rapid response), to 12-18 months (slow response).
-- Indications for
the need to start treatment can be summarized as CRAB features: Calcium
elevation; Renal problems; Anemia; or Bone issues.
-- There is a strong reluctance
in many centers to harvest stem cells without a clear plan for use, typically
immediate use. This reluctance arises from protocol priorities, cost/utilization
constraints for harvesting and storage, as well as numerous other factors.
Nonetheless, many patients request and want their stem cells harvested,
even though they may not be enthusiastic about immediate high-dose therapy.
-- For patients with severe
local problems such as bone destruction, severe pain, and/or pressure on
nerves or the spinal cord, local radiation can be dramatically effective.
The major disadvantage is that radiation therapy permanently damages normal
bone marrow stem cells in the area of treatment. Wide field radiation encompassing
large amounts of normal bone marrow should be avoided. A general strategy
is to rely on systemic chemotherapy to achieve overall disease control,
limiting the use of local radiation therapy to areas with particular problems.
(This is what I had)
-- Bisphosphonates - Bisphosphonates
are a class of chemicals that bind to the surface of damaged bones in patients
with myeloma. This binding inhibits the ongoing bone destruction and can
improve the chances of bone healing and recovery of bone density and strength.
A randomized study utilizing the bisphosphonate pamidronate (Aredia®)
showed particular benefit in patients responding to ongoing chemotherapy.
It is currently recommended that bisphosphonate therapy be used as an adjunctive
measure in myeloma patients who have bone problems (see Figure 5). Other
bisphosphonates are now available including clodronate, an oral formulation
in use in Europe for the treatment of myeloma, and zoledronic acid (Zometa®),
approved in the U.S. and Europe as treatment of both hypercalcemia and
bone disease. Several new bisphosphonates are in clinical trials. One,
called ibandronate, is now available in Europe.
-- Two new concerns have
emerged related to chronic bisphosphonate use. The first is kidney damage
and the second is a condition called osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ). Both
conditions are fortunately relatively uncommon. Kidney function must be
serially monitored (especially serum creatinine before each treatment dose),
particularly with Zometa use. If the serum creatinine increases by 0.5-1.0
mg/dL, dose and/or schedule adjustments for Zometa® may be required.
-- ** For Zometa, one of
the simplest adjustments is to extend the infusion time from 15 minutes
to 30-45 minutes, which reduces the risk of renal impairment. (2008)
(my infusion time is 15 min)
-- ** The International Myeloma
Working Group (IMWG) recommends discontinuing bisphosphonates after one
year of therapy for patients who achieve complete response and/or plateau
phase. For patients in whom disease is active; who have not achieved a
response; or who have threatening bone disease beyond two years, therapy
can be decreased to every three months. (2008) (As of Dec 2015 I have been
getting zometa infusions monthly for about a year and my schedule shows
them continuing for at least a few more months. Mmy understanding is that
the plan is zometa continues for two years.)
-- Infections are a common
and recurrent problem in patients with myeloma. A careful strategy for
infection management is required. Antibiotic therapy should be instituted
immediately if active infection is suspected.
http://szpiczak.org/index.php?lang=en&vol=szpiczak&part=3
(part 1)
http://szpiczak.org/index.php?lang=en&vol=szpiczak&part=4
(part 2)
Bone remodeling
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts
are the two (factors) that control bone remodeling. (I love these two names,
differing by only one letter.) Osteoblasts build up bones and osteoclasts
'reabsorb' them. The balance between these two is important in MM, because
the cancer somehow shifts the balance to osteoclasts causing (net) bone
destruction. The purpose of Zometa as I understand it is to shift the balance
back. The fact that 'osteoclasts are descended from stem cells in the bone
marrow' may be relevant. Bone destruction leads to high levels of calcium
in the blood of untreated MM patients.
-- Bone may seem to be stable
and unchanging, but in fact, bone is constantly being remodeled. Bone remodeling
is triggered by a need for calcium in the extracellular fluid, but it also
occurs in response to mechanical stresses on the bone tissue.
-- Unlike osteoblasts,
which are related to fibroblasts and other connective tissue cells, osteoclasts
are descended from stem cells in the bone marrow that also give rise to
monocytes.
Bone remodeling site
http://courses.washington.edu/conj/bess/bone/bone2.html
Multiple myeloma drugs
When myeloma chemo drug
combinations are listed by either brand name or technical name it just
looks confusing. How are these drug combinations put together? Actually
it is pretty simple. First group drugs by their class of action. A chemo
drug combination for multiple myeloma is then assembled pretty much the
same way that ordering is done in an old style chinese restaurant: one
from column A, one from column B, etc. In the case of multiple myeloma
each drug in the combination will typically have a different class of action,
a different method of attacking the cancer. (A few drugs are considered
boosters or are added to counter side effects such as deep vein clotting.)
Many of the drugs fall into families.
A drug will be found, perhaps serendipidesly, to be somewhat effective
against the disease, but will often have bad side effects This is a first
generation drug. The drug companies then seach for variations of it that
is some conbination of reduced side effects, easier to administer and increased
effectiveness. If the drug companies results in the lab are confirmed in
clinical trials, then it becomes a 2nd generation drug. And often there
will be 3rd generation drug in the clincal drug pipeline.
For example, the primary
chemo drug I take, Revlimid (lenalidomide) is a second generation drug.
It is a variation on thalidomide, which was a first generation drug and
had a lot of bad side effects. Wikipedia describes these drugs as having
anti-angiogenic (prevention of blood vessel growth) and anti-inflammatory
properties. Specifically, in vitro, lenalidomide has three main activities:
direct anti-tumor effect, inhibition of angiogenesis, and immunomodulatory
role. In vivo, lenalidomide induces tumor cell apoptosis directly and indirectly
by inhibition of bone marrow stromal cell support, by anti-angiogenic and
anti-osteoclastogenic effects, and by immunomodulatory activity. 3rd generation
drug in the same family is pomalidomide, whose brand name is Pomalyst in
the US and Imnovid in Europe. (Yikes two brand names for same drug, same
manufacturer!) [Another recent variant on thalidomide is apremilast (brand
name Otezla), but it is not used in MM and is thought to work via a different
mechanism.] All are manufactured by Celgene.
Another family is Velcade
(bortezomib) from Millennium Pharmaceuticals. This is a first generation
drug, the first proteasome inhibitor approved for humans. Although widely
used to treat MM, it has two bad problems, it must be given by injection
in hospital and it causes widespread peripheral nerve damage. A 2nd generation
version of velcade is carfilzomib (brand name Kyprolis) from Onyx, but
it is also given by injection. A 3rd generation drug in the velcade class,
but which is given by pill, is in development, in fact is was the subject
of the clinical trial I was offered. It is currently known as MLN9708 (ixazomib).
Documentation
with little concern for patients
My complaint here is not
about doctors per se, but the whole medical establishment. Reading postings
on the Beacon Myeloma forum there is continuing confusion about cancer
tracking values, specifically the kappa and lambda free light chain proteins.
The source of the confusion is that the blood work of some patients have
values expressed in mg/L while others report the value in mg/dL. Good grief.
Here we see the medical establishment in action. We see little to no consideration
for patients. Basically they don't give a shit. Nobody can be bothered
to do the simple thing of organizing and standardizing the units on basic
blood work. And while they are at it how about standardizing the names
for the blood tests. When I review my blood work I see several different
formats and names for standard blood tests and this is over only ten months
and all taken at the same hospital!
Don't give a shit #2 (update 2/16)
Celgene is the manufacturer
of my tier 5, 10k/month chemo drug, Revlimid. Before they will allow a
pharmacy to dispense the drug a patient is required to do a telephone 'survey'
with the company, which amounts to three questions and then listening while
they read a long list of the many possible serious side effects of the
drug. This same statement has been read to me over a dozen times.
The statement is a doozy.
Every side effect is described only by its technical name. I remember
a couple of xxxxpenias and myocardial infarction. Clearly this list was
compiled for doctors, yet it is being read to every patient every month.
Why do they do this, when it would be virtually no effort to give both
the technical name and usual name for each side effect? I would suggests
two possible reasons. One, the company just doesn't give a shit if the
patient understands the side effects or not. Two, this is driven by lawyers,
who just want to be able to say in court that the patients were warned,
and who don't care whether the statement is understandable or not.
I saw the same problem in biology.
When I was writing an essay on photosynthesis a while back, I was continually
confused by the various units in different papers. When I looked up one
common biochemical protein in Wikipedia, it told me the protein was also
known by 13 other names, which it proceeded to list. 14 different names
for the same protein! Yikes, idiots. Physicists don't do this. They get
together periodically and standardize notation so students are not confused
by units. For example, when I was in HS the common unit of frequency was
'cycles per sec', but when I was in engineering school an international
meeting decided to change it to 'hertz', and in the classroom frequency
immediately became 'hertz', cycles per second never again mentioned.
And a biggy, where is the
equivalent of the programmer's 'verbose' command? Most of the blood work
pages are totally blank, just white space, the names of the tests on the
left, the normal values on the right and 80% of the center part of the
page is blank. When blood work is provided for a patient it need not be,
should not be, in the shorthand format doctors use. After all they do this
everyday, they know WBC means 'white blood count', but this should be spelled
out for the patient. A large number of blood tests are listed in this cryptic
abbreviated manner. There's plenty of room on the mostly blank page to
add explanatory notes. Of course it's easier to just provide a copy of
the doctor's blood report to the patient, so basically that's what they
do. It hard not too conclude that no one in the medical world gives a shit
about helping the patient understand his blood work, which for someone
with a blood cancer like me is vital.
It gets worse, a few months
after the Lahey portal became active, the 'H/L' out of range markings on
the blood work provided to the patientsuddently disappeared. I know that
in blood work formated for internal hospital use, like in the infusion
lab which I have seen, the H/L out of range markings remain. A lab technician
taking my blood suggested to me that the reason the hospital's new patient
blood work provided no longer labels out of range lab results (H or L)
may be a deliberate choice to minimize questions. I'm betting this is right.
Some patients probably run down the list and ask about every 'L' value,
which the doctors find tendious and likely argue is mostly a waste of value
patient/doctor interface time, and I would agree this has some merit. Still
my point is many serious ill patients, especially those with blood cancers
like me, are ill served by a decsion like this.
Even the protein (anti-body)
in the blood that is the main tracker of MM goes by a bunch of names:
-- M-spike
-- M-protein
-- monoclonal spike
-- monoclonal protein
-- paraprotein
-- monoclonal immunoglobin protein
-- M protein of monoclonal protein (Mayo clnic covers all the bases!)
Good grief!
Abbreviations everywhere
Now that I am sensitive
to customer unfriendly abbreviations I am seeing them everywhere. In the
last few days I stumbled on some beauties.
Cannon camera --- Camera
is connected to my PC via USB, and in Windows Explorer I am searching for
the directory with the pictures. The pictures are in a directory named
'DCIM'. What the hell does this mean? Why can't Cannon label the
directory something like maybe, oh, 'pictures' or 'photos'? I mean,
this is a camera! With a little googling I find 'DCIM' stands
for 'Digital Camera Images' and there's a historical reason for DCIM, and
even on most phones pictures are found in a DCIM directory.
Fidelity Charitable --- If
an appreciated security is donated to charity, the allowable tax deduction
is its 'fair market value', but this can be differeent from the cash the
charity receives when it is sold by them a few days later. Fidelity Charitable
labels the fair market value as 'FMV'. Good grief. (I had to make
a phone call to figure this out.) OK, maybe there is some rational for
this abbreviation, but just like with blood work the online screen could
be expanded to say 'FMV (Fair Market Value)'.
Experiences of others
with MM chemo
One of the problems with
MM chemo is a sense of isolation. I can't get my doctors to tell me about
how any of there other patients respond to chemo or even give a sense of
the process. The information is always just dribbled out as to what to
do next with no overview. I have some understand of why from their perspective
it is better not to say much, but still the patient unless he researches
hard (or perhaps joins a support group) is left with little perspective
on how his treatment is going.
So I set out to try and find
the experiences of others with MM (how their M-spike responded to chemo,
etc), but it is surprisingly hard to find much of anything. I figured people
would plot up their numbers (like I just did) and post them, but an image
search has turned up very little. (One of the problems here, common in
biology, is that there is no standard name for the M-spike also known as
monoclonal spike, paraprotein). Here's an M-spike plotted up apparently
from a guy with smouldering myeloma. This is a precursor to MM with a monoclonal
spike, but not yet the full symptoms of mulitple myeloma. At first I was
puzzled as to why with such a high M-spike his chemo was delayed so long,
but then I noticed it began just after his M-spike exceeded 3 g/dl. This
is one threshold for MM diagnosis, so my guess is that his diagnosis at
this time changed to MM. He's gotten a 'partial response' (> 50% reduction
I think), but from the shape of the curve it doesn't look like he is going
to get to 0.32, which would be a 90% reduction to qualify for VGPR. Unfortunately
there was no info on the site as to what his chemo was.
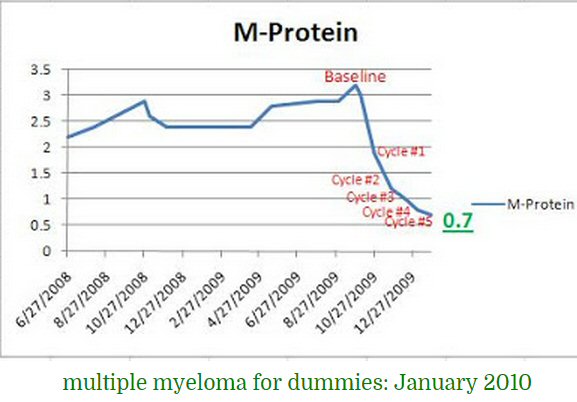
decline from 3.2 to 0.7 g/dl in five cycles
(source -- http://solidalen.net/protein-pattern-in-multiple-myeloma/)
One source is the forum on
the Myeloma Beacon, which is a large dedicated MM resource. The difficulty
here is finding what you want in the thousands of posts. (The Beacon internal
search engine doesn't find much. Google does better if you know the name
of the poster.) Two Beacon posters have caught my attention. One began
his chemo at almost exactly the same time as me, and he has posted a detailed
running commentary (at first day by day). His chemo included velcade and
you can see its problems. A second prolific poster (Chris Hill) was diagnosed
about four years ago and after a few good years on maintenance has begun
to relapse, so this gives a more extended perspective.
Chris Hill
This young guy was diagnosed
four years ago with super bad numbers (8.9 M-spike). [rev/dex + velcade]
drove his M-spike to 0.1 in less than six months. He had a transplant and
was off all meds for a nearly a year. When his numbers ticked up, he brought
them down with rev/dex chemo getting a stable 15 months. This got him to
3.5 years, but then numbers again ticked up, so his chemo was tweaked with
a newer proteasome inhibitor kyprolis (carfilzomib) added to rev/dex (instead
of velcade (bortezomib)), and this drove his M-spike down to 0.1 again.
But this second plateau after his 'relapse' only lasted about six months
and his numbers are ticking up again. He's had a lot of problems and pain
in his four years and for much of the time has been largely tied to the
hospital since both proteasome inhibitors are injected twice a week. (Not
to mention the huge cost of revlimid, 3 weeks in the hospital for the transplant
(150k) and 100k+ for the injections with no medical insurance.)
---------------
Chris is a young man, 43
at diagnosis. When he was diagnosed in 2011, he was in bad shape with a
super high M-spike of 8.9 and lots of bone issues including several compression
fractures in his back . (In 2011 he claims his bones were fine and that
MRI had even shown some lesions healed and that the pain in his back is
from disc issues). He had been feeling very tired and had bad nose bleed
for 8 months (no health insurance) before he went to ER. His hemoglobin
was 7.3, close to half of normal (me 9.9), so they immediately transfused
him, then it dropped to 6.3 and his platelets were really low at 63k and
he was bleeding all over the place. His marrow aspiration was 85% (or 80%)
cancer (me 70%). He says his genetics is good. (He focuses (unfairly) on
how bad deletion 13 is and is glad he doesn't have it. I have deletion
13.) He characterizes his MM as 'aggressive' since it can shoot up fast
when he is off chemo. He posts on Beacon and also on his Facebook page,
which can be accessed. His cancer is IgA.
His M-spike dropped spectacularly
with [rev (25 mg)/dex (20 mg) + velcade] chemo going from 8.9 to 0.1 g/dL,
and he had a confirming 2nd marrow aspiration, showing cancer had dropped
from 85% (or 80%) to 2%. His initial 8.9 g/dL he says was the highest his
oncologist had ever seen and the 2nd highest a MM oncologist at John's
Hopkins had ever seen. It dropped to 2.2 (75%) after two three week cycles
and to 0.5 after four cycles. He could not raise the funds for a transplant,
so he went without chemo for a few months and surpassingly from this low
base (2%) his M-spike rapidly shot up (.76 g/dL) in two months and
to 1.7 one month later with no chemo, and even when chemo (dex + velcade,
no revlimid) was restarted in another month 2.3 then 2.9. When revlimid
was then added to the chemo, his numbers started down.
After he had a bone marrow
transplant (three weeks in hospital at Johns Hopkins). He is told it will
take six months for his immune system to come back (he wears a mask when
out) and a year before his energy returns! Six months post transplant his
M-spike is 0 (which probably means < 0.05). He was off therapy for 10
months and his M-spike stayed at 0.1 and then started to rise. He went
back on rev/dex in 2013 where his M-spike stayed at 0.5 for 15 months and
then began to rise. That's when he added Kyprolis, which is an injection
and requires two trips to the hospital per week. He has pictures of nasty
bruising at the injections sites. One cycle of the new chemo in early 2015
dropped M-spike from 0.8 to 0.4, to 0.2 after two cycles and to 0.1 after
three cycles then to 0. He says Kyprolis is 1,700/dose, which at six per
cycle would be 133k/yr. His platelets are quite low at 82,000, so he bruises
easily. Dexamethasone gives him terrible headaches and bad back pain, and
he claims it is bad for bones and reduced potassium in the body. (I checked
and my potassium in six months slowly drifted down, but remained in the
normal range.)
Note even though his new
[rev/dex + Kyprolis] chemo was effective dropping his M-spike to virtually
zero (0.1 or 0), he still only got a stable five months from a new chemo
regimen after his first relapse before his numbers started to rise again.
This is four years in with a stem cell transplant.
-- End of 2014 I
became refractory (resistant) to the Revlimid and Dexamethasone chemotherapy
I was on. It's common as Multiple Myeloma genetically mutates so it can
overcome the chemo you are using. January 2015 I started a new very promising
new Chemotherapy called Kyprolis, added to the Revlimid and Dexamethasone.
It worked until 2 months ago when my numbers started creeping up again,
showing it wasn't working. So I got about 5 months out of it. Once the
numbers started climbing we decided to try one more month to see if it
was a fluke, if it would slow down, or keep advancing. (7/2/15 post)
-- Wondered why back has
been hurting more the last few months. Partially due to the myeloma making
me osteoporitic, and partially due to the long term use of dexamethasone,
a steroid I take with my chemo as it keeps bones from utilizing calcium
and minerals to build themselves. (Is this true?, research this) Hill is
right about this. Long term usage of dexamethasone can indeed cause "decrease
calcium absorption and increase its excretion" so bones can be affected
leading to "pain and osteoporosis". "You may also experience muscle pains
because dexamethasone can cause you to lose potassium". (http://www.myelomacanada.ca/docs/u-dex-eng_c1-web.pdf)
Carfilzomib (kyprolis)
Kyprolis (carfilzomib) and velcade
(bortezomib) are both proteasome inhibitors. Proteasome inhibitors are
drugs that block the action of proteasomes, cellular complexes that break
down proteins, like the p53 protein. Velcade (from Millenium) was first
and kyprolis (from Onyx Pharmaceuticals) is newer. kyprolis is on fast
track approval (costs 10k/month). At present it is only approved by FDA
as a substitute for velcade.
K_Shash
K_Shash is not too different
from me. He (or she) is diagnosed at age 67 in Nov 2014. His chemo treatment
is almost exactly concurrent with mine. Like me he has multiple bone lesions.
30% cancer cells in his marrow (vs 70% for me). His chemo is RVD, which
is rev/dex (15 mg revlimid, 20 mg dexamethasone, 3 wks on 1 wk off) with
(infusion) velcade added (once a week). His plan is to stay on RVD and
avoid a stem cell transplant.
My initial lambda free light
chain value was x144 higher than the upper end of normal (379/2.63 = 144).
My lambda free light chain response to chemo was rapid and deep with a
98% decrease in the first cycle. My kappa/lambda ratio pulled into the
normal range after just two cycles, and my lambda value was normal in four
cycles. (Curiously my doctor has never talked to me about my free light
chain response!) A comparison is provided by a frequent poster on Beacon
who posts under the name: K_Shash. He apparently is in the minority of
MM patients who doesn't have an M-spike, because he says his main cancer
marker is a free light chain protein, in his case the kappa free light
chain.
He gives the initial kappa
free light chain value as 853 mg/dL, which would make it x440 higher than
the upper end of normal (853/1.94 = 440), and a kappa/lamda ratio of 127
(0.26 - 1.65 normal). (However, he may have messed up his units, so it
might be 853 mg/L or 85.3 mg/dL). He had a reduction in his kappa free
light chain of 80% in his first cycle and 98% after three cycles, whereas
I had a reduction of 98% in my first cycle and 99.3% in three cycles. It
took him 8 months for his kappa free light chain to get into the normal
range, and his kappa/lamda ratio of 1.74, while close, was still not quite
normal (0.26 - 1.65).
Reading K-Shash's posts I
see his doctors treated him like my doctor treated me, in the sense that
they only look ahead to the next month so the patient has no overview of
where the chemo process is going or how long it is likely to take before
maintenance. And with velcade, which requires a trip to the hospital probably
twice a week (because it is an injection), a switch to maintenance and
less (or no) velcade becomes a BIG deal.
rafaelmsantiagomd
Here's another interesting
Beacon poster. This guy (Rafael M Santiago) is an MD age 62 diagnosed with
MM in Sept 2014. He is stage 1 with no chromosomal abnormalities. Like
me he is on rev/dex taking zometa (25 mg revlimid, 40 mg dexamethasone).
In his first cycle he is having terrible problems with side effects. He
says he passed out three times after meals, so after one cycle his revlimid
was reduced to 20 mg.
MM for Dummies
This site has MM stories
from about 50 people:
http://mmfordummies.blogspot.com/2009/03/myeloma-mondays-archive-survivorpatient.html
Other blood cancers
The three main blood cancers
in terms of frequency are
Lymphoma
52%
74,000 cases in US/yr
Leukemia
34%
48,000 cases in US/yr
Multiple myeloma
14%
20,000 cases in US/yr
Overview
Half of all blood cancers
are lymphomas, but they are quite different from multiple myeloma because
they are based in the lymphatic system, whereas leukemia and MM are both
based in the bone marrow. As far as I can tell, neither leukemia or lymphoma
has a blood marker like the M-spike of MM. Protein electrophoresis test,
which is used to measure the blood marker for MM, is not used in other
blood cancers.
This is significant in a
clinical setting because it means this test is used only for a minority
of patients a hematological oncologist treats. It means scheduling blood
collection a week or so before results are needed is probably unique to
MM patients, since it takes four days or so for the results to become available.
(This may explain why the scheduling of my blood collection sometimes gets
screw up.) This test not only has a diffusion, but it is not fully automated,
a a doctor is needed to examine and interpret the resulting protein band.
Discussion
With a little digging I
find there's an interesting similarity between MM and lymphomas, but with
a twist. In lymphomas the cancer making cells (lymphocytes?, a type of
while blood cell) are in the lymph system, so the lymph system serves the
roll the marrow in bones does for MM! The cancerous cells in the lymph
system feed lymphomas into the blood, but because the marrow is unaffected
the normal blood cell production is unaffected, so what happens is that
the blood is essentially normal except that many clonal cells from the
cancerous lymph system added to it. This explains why when the lymphoma
cancer making cells congregate we don't get a bone lesion as in MM, but
instead a solid tumor in one or more of the lymph nodes.
In leukemia the cancerous
cells are in the marrow as with MM, so normal blood cell production is
affected. In other words MM is more closely related to leukemia than lymphoma
because in both cases the cancerous cells reside in the marrow of the bones.
Marrow based cancerous cells in leukemia put lymphoma cells into the blood
too. The difference between leukemia and lymphoma being the source of the
monoclonal lymph cells in the blood.
-- Hematological malignancies
may derive from either of the two major blood cell lineages: myeloid and
lymphoid cell lines. The myeloid cell line normally produces granulocytes,
erythrocytes, thrombocytes, macrophages and mast cells; the lymphoid cell
line produces B, T, NK and plasma cells. Lymphomas, lymphocytic leukemias,
and myeloma are from the lymphoid line, while acute and chronic myelogenous
leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative diseases are
myeloid in origin.
Lymphoma
One reference lists
35 (!) subtypes of lymphoma. Lymphomas are types of cancer derived
from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that populate lymphatic system.
While lymphoma is called a blood cancer, it appears most commonly as a
solid
tumour
in the lymph nodes of the neck, chest, armpit or groin. This localization
makes it treatable with radiation (as well as chemo). Hodgkin's lymphoma
is usually found in the lymph nodes of the neck and head. 74,000 people
in USA are diagnosed with lymphoma (65,000 non-hodgkins and 8,500 hodgins)
each year (about x3.7 times the number of MM cases).
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
The Aug 2015 news story
that the Red Sox manager, John Farrell, in the middle of the season was
suddenly leaving due to a diagnosis of lymphoma piqued my interest in looking
into other blood cancers. All three types of blood cells (really the marrow
cells making them) can go cancerous. A doctor at Dana-Farber said Farrell's
cancer is probably B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and will be treated with
9 weeks of chemo and radiation. Farrell's case is probably stage 1, which
means it is in only one lymph node and has not spread. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
is the 5th most common cancer in US (about 70,000 cases/yr in USA). There
are many variations of this cancer. The overall 5 yr survival rate is 69%,
but some types are considered highly curable (90%). Wikipedia says the
suspected cause of some lymphomas is a virus.
Multiple myeloma, a cancer
of the blood plasma cells, make up only 10% of blood cancers. Is
this important to me clinically? I suspect it is. It is my understanding
that hematological (blood) oncologists treat all the blood cancers. If
that is right, it means MM patients with their unique problems make up
only a small fraction of the patients these doctors are treating, though
I see hints that some of them my specialize in specific blood diseases.
Hodgkin lymphoma
A lymphoma identified long
ago by a doctor named Hodgkin is today (surprise!) known as Hodgkin's lymphoma
and all other lymphomas are as a group called non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Hodgkin's lymphoma differs from the other lymphomas is that it is particularly
radiation sensitive.
Leukemia
Leukemia is a cancer of
white blood cells. Leukemia is based in the bone marrow, whereas lymphoma
are based in the lymphatic system. 48,000 people in USA are diagnosed with
leukemia each year (about x2.5 times the number of MM cases). One reference
lists 9 subtypes of leukemia. Abnormal white blood cells of leukemia can
come either from lymphoid cells or myeloid cells.
-- Leukemia is cancer of
the blood and bone marrow. It develops when bone marrow, which produces
blood cells, forms abnormal white blood cells that divide out of control.
Normal white blood cells are the body's infection fighters, but these abnormal
white blood cells, called leukemia cells, don't die at the same rate as
normal blood cells. Instead, they accumulate and crowd out normal cells,
like red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells and their
precursors, in the bone marrow.
-- Two categories of immature
precursor cells produce white blood cells: myeloid cells and lymphoid cells.
Myeloid cells produce red blood cells, platelets, and several white blood
cells types, known as granulocytes. Granulocytes circulate in the blood
and fight infections by killing and digesting bacteria. Lymphoid cells
develop into lymphocytes, another type of white blood cell that is found
in both the blood and the lymphatic system.
Multiple myeloma
There are many subtypes
of lymphoma and leukemia cancers, and for that matter multiple myeloma
(MM) too. In MM the monoclonal anti-bodies can have either lambda or kappa
light chains. In some MM patients there is no (significant) M-spike just
an excess of lambda or kappa free light chains.
-- B lymphocytes start in
the bone marrow and move to the lymph nodes. As they progress, they mature
and display different proteins on their cell surface. When they are activated
to secrete antibodies, they are known as plasma cells.
-- Multiple myeloma develops
in B lymphocytes after they have left the part of the lymph node known
as the germinal center. The normal cell line most closely associated with
MM cells is generally taken to be either an activated memory B cell or
the precursor to plasma cells, the plasmablast.[14]
Above seems confusing,
but I think the explanation is that there are an extra steps in the simplified
view that cancerous marrow cells turn out identical antibodies. From these
comments in Wikipedia it seems the marrow turns out B cells (or B lymphocytes)
that are released into the blood. When they encounter an infectious agent
(technically bind to a specific antigen), they turn-on (jargon is they
get activated), proliferate and begin to turn out anti-bodies. The process
is actually extremely complicated. Wikipedia (B cell) list 7 (!) steps
in the development of B cells.
-- Antigens are usually
proteins and polysaccharides, and less frequently, lipids. This includes
parts (coats, capsules, cell walls, flagella, fimbrae, and toxins) of bacteria,
viruses.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Excerpts
from 'Multiple
Myeloma Patient Handbook' Myeloma Canda
MM biochemistry
-- When myeloma cells enter
the bone marrow, they attach to other, structural cells of the bone marrow
known as stromal cells. Once attached to stromal cells, interactions occur
that stimulate the myeloma cells to continue reproducing.
-- Chemical messengers called
cytokines are produced that stimulate the growth of myeloma cells and prevent
the cells from dying naturally. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is one of these chemical
messengers.
-- The myeloma cells secrete
chemicals called growth factors that promote the creation of new blood
vessels that usually accompanies the growth of malignant cells (a process
called angiogenesis). One of the most important of these growth factors
is vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
-- As the myeloma cells invade
the bone, they may cause multiple areas of damage that weaken the bone.
Thes areas are known as osteolytic lesions, or lytic lesions for short.
Drug mechanisms
Thalidomide is an immunomodulatory
agent. Instead of destroying myeloma cells (like chemotherapy drugs), thalidomide
interferes with the underlying processes that promote the growth and reproduction
of myeloma cells. Lenalidomide (Revlimid) like thalidomide is an immunomodulatory
agent but is more potent and has a different side effect profile from thalidomide.
Lenalidomide has multiple mechanisms of action that affect both the cancer
cell and its microenvironment. Thalidomide:
• inhibits factors that promote the growth of blood vessels (Vascular Endothelial
Growth Factor or VEGF and basic Fibroblast Growth Factor or bFGF) that
help to feed tumours
• modulates the level of several chemicals (called cytokines) that the
cancer cells use to communicate with one another and orchestrate growth
and reproduction (e.g., Tumour Necrosis Factor – alpha or TNF-alpha, interleukin
6 or IL-6, interleukin 2 or IL-2, and interferon-gamma or IFN-gamma)
• alters the expression of chemicals involved in acute rejection, such
as cytokine secretion and cell growth
Bortezomib (Velcade) is a
proteasome inhibitor, one type of the new generation of “biological treatments”.
It works by acting on the myeloma cells and the cells with which they interact
to inhibit plasma cell growth and reproduction and to promote cell death.
A number of new therapies
are in development. At the time this handbook was printed, among the clinical
trials underway in Canada were a new proteasome inhibitor (carfilzomib),
a monoclonal antibody (elotuzumab), histone deacetylase inhibitors (panobinostat,
vorinostat) and pomalidomide, a new immunomodulatory agent.
Spine fractures
-- Vertebral fractures (fractures
in the spine) have traditionally been treated by a procedure called vertebroplasty,
in which cement is injected into the affected vertebrae to stabilize it.
A newer alternative is kyphoplasty. In kyphoplasty, a balloon is inserted
into the compressed vertebra and inflated to raise
up the collapsed section. The cavity is then filled with a bone cement,
stabilizing the vertebrae and preserving the reestablished height.
M-spike
-- The M-proteins produced by
myeloma are cleared from the body in the kidneys. Over time, the elevated
levels of abnormal M-proteins in the blood and urine can damage the kidneys.
This is why renal function is assessed regularly by creatinine testing
of the blood.
Pain killers
-- Although non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Motrin® or Advil®), naproxen
(Naprosyn® or Aleve®) and diclofenac (Voltaren®) are common
and effective painkillers, people with myeloma should avoid them, particularly
if they have kidney damage.
Dental
-- Because of the increased
risk of infection, myeloma patients may require antibiotics before any
dental work.
-- A review of patients at
one of Canada’s largest myeloma centres, the Princess Margaret Hospital
in Toronto, found that 2% of patients taking
pamidronate developed osteonecrosis (jaw death). It can occur spontaneously
but appears to be more likely following dental work, particularly traumatic
work such as extractions. The risk of osteonecrosis appears to be higher
among those taking zoledronic acid (Zometa®), compared to pamidronate
(Aredia®).
--- Restorative work such
as fillings, bridges and crown and root canals are probably safe, provided
wounds are as small as possible and all rough edges are carefully smoothed.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Blood test machines
Flow cytometry or (fluorescence based flow cytometry)
This is a fluorescence based
procedure to count and identify cells. It is used to diagnose some blood
cancers like leukemia. It is an automated way to identify characteristics
of individual cells at high speed. Cells are excited with a laser and how
they fluoresce is measured. The cell identification can be made very specific
by uses of anti-bodies with fluorescing tags that bind to proteins of the
cell membrane.
FISH
Another technique that uses fluorescence.
FISH or Fluorescent in situ hybridization s not a blood test but a cytogenetic
test. It uses probes that bind to the DNA and fluoresces can identify translocations,
etc.
Free light chains ---
Plasma cells output both
anti-bodies (2 heavy chains + 2 light chains) and free light chains. MM
plasma cells make a lot of free light chains, a higher ratio of free light
chains to anti-bodies than normal plasma cells. Kidney problem can
cause both the lambda and kappa free light chain levels to rise. The ratio
will separate out cancer from kidney problems. At low (normal levels) variations
of 25-50% can occur. Warning sign cancer is coming back is progressive
increases, especially > 50% increase on successive readings.
Freelite is trademark of Binding Site Group, Birmingham UK
Half life of IgG
-- Under normal circumstances,
most serum proteins that are too large for renal filtration (> around 60
kDa) are removed by pinocytosis, a process that occurs in all nucleated
cells as they obtain their essential nutrients from plasma. This accounts
for the half-life of IgA and IgM, which is constant at around 5 - 6 days.
By contrast, IgG has a concentration-dependent half-life of approximately
21 days due to recycling by FcRn receptors.
-- At low IgG concentrations,
when FcRn receptor protection is maximal, the IgG half-life extends to
several months. In such cases, serum IgG levels are particularly slow to
indicate responses to treatment, and sIFE (serum immunofixation) may remain
positive long after a tumour has been eradicated (as demonstrated by bone
marrow immunophenotyping). Serum IgG concentrations may therefore be an
unreliable indicator of tumour production rates in patients with IgG MM.
(see figure)
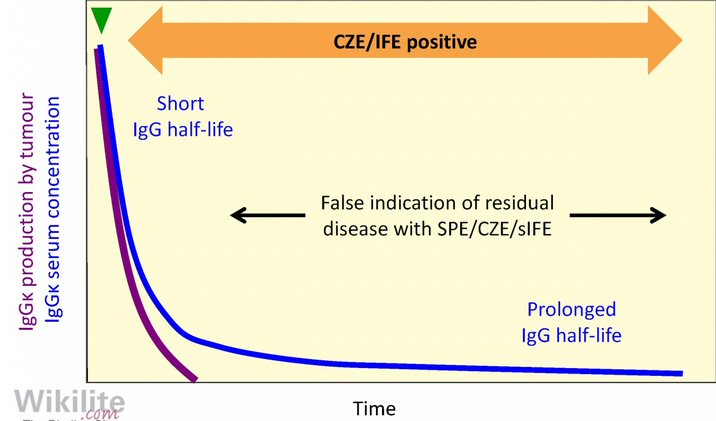
Wow, looks a lot like the graph of my numbers!
CZE = capillary zone electrophoresis
IFE = serum immunofixation
SPE = serum protein electrophoresis
(source -- http://www.wikilite.com/wikilite/index.php?title=File:18.15.jpg)
-- Orlowski et al.
reported that rapid normalisation of the FLC kappe/lambda ratio - after
the first or second cycle of therapy - was highly predictive of prolonged
time to progression. (My ratio was nearly normal after two cycles).
The fast response of free
light chains can be very useful to evaluate if a new chemo regimen is working.
Freelite (wikilite) gives this example (below):
Blue is the free light chain and as new chemo is begun it quickly falls.
They point to the interval of 2-3 months were the IgG (red) is falling
and that in isolation would be considered a good sign, but the blue has
not pulled into the normal range giving advance warning that the chemo
is not working and sure enough after 6-7 months the IgG and free light
chain start to rise.
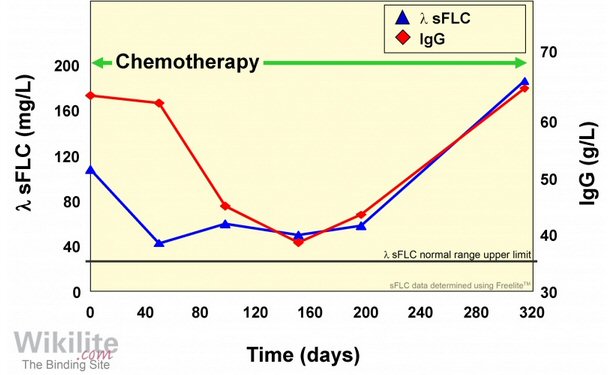
(blue) Lambda free light chain responds rapidly to new chemo,
but critically it settles out around 5-6 mg/dL, substantially above
normal range.
This is a leading indicator that the new chemo regimen is not working.
(source -- http://www.wikilite.com/wikilite/index.php?title=File:A_rapid_drop_in_%CE%BB_sFLCs_provides_an_early_indication_of_response_to_treatment.jpg)
** The not so subtle message
from the free light chain people is if a new chemo regimen doesn't quickly
bring the free light chain into the normal range it's a bad sign,
and it may be time to change chemo soon rather than waiting for the slowly
responding IgG to show a rise.
Clincial
indicators of disease progression
** -- Difference
(involved - uninvolved) free light chain --- French viewgraphs
(2014) use absolute difference [(involved - uninvolved) free light
chain > 10 mg/dL] as in indicator of disease progression. (yes)
This seems to fit with nicely with my data so I added this column to my
numbers table.
-- M-spike absolute increase > .5 g/dL (no)
-- new bone lesion, plasmacytoma (yes)
-- hypercalcemia (> 2.65 mmol/L, attributable to MM) (no)
-- increase in >25% (absolute increase > 10%) in bone marrow plasmocyte
(not tested)
Clinical indicators
of disease relapse
-- One
of more of
- new soft tissue plasmacytoma or bone lesion (yes)
- and/or increase in size of existing plasmacytoma or bone lesion
- and/or hypercalcemia (> 2.65 mmol/L) (no)
- and/or decrease in hemoglbin (< 2 g/dL) (no)
-and/or rise in serum creatine (> 2 mg/dL or 177 micromol/L) (no)
https://www.ebmt.org/Contents/Data-Management/Helpdesk/Documents/Myeloma%20-%20evaluating%20response%20to%20treatment%20and%20relapse.pdf
Patients blog about free light chain
I found an interesting discussion
from a MM patient with undetectable M-spike (few years following a stem
cell transplant) who is carefully monitoring his free light chains and
is beginning to see a (small) increase. The comments to the blog posting
are interesting too because others are reporting their free light chain
numbers. Here is his plot of his free light chains. He has a kappa cancer,
so both his numbers tend to rise, whereas I have a lambda cancer, so I
need to watch for my lambda free light chain rising and my kappa/lambda
ratio falling. In four months his free light chain ratio has roughly doubled,
but at 2.08 it is barely above the high end of normal (1.65). (In normal
anti-body proteins the light chains are twice as likely to be kappa vs
lambda, which might explain why the basic light chain ratio has kappa in
the numerator.)
In the comments discussion
someone says (circa 2014) until the ratio is greater than 10 no doctor
will recommend treatment, except perhaps a bone marrow check, and that
it takes a ratio greater than 50 to really get their attention. (This strikes
me as doctors not fully cognizant of the power of a leading indicator.)
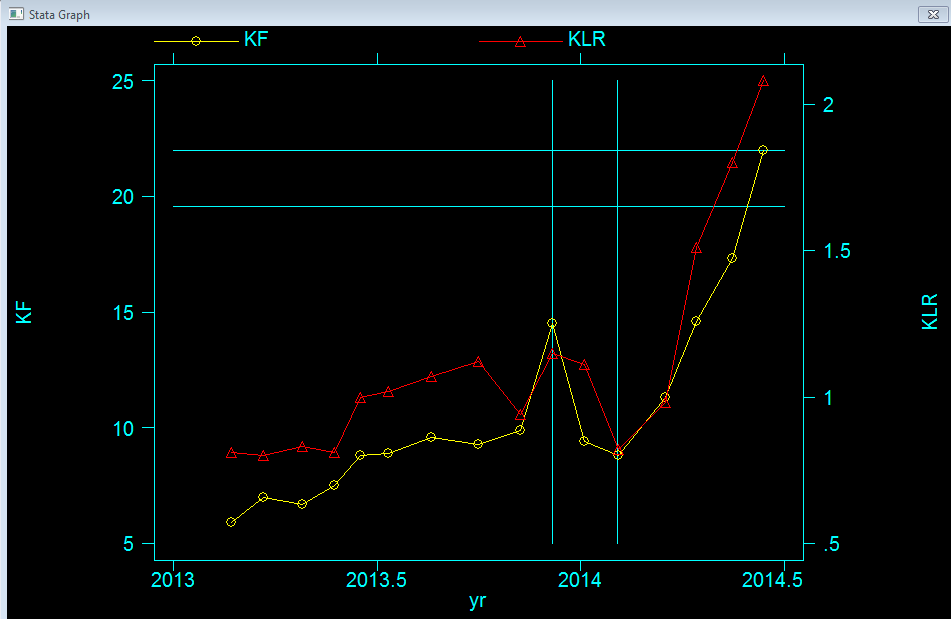
MM patient plotting up his free light chain data over 18 months.
red -- kappa/lambda free light chain ratio (1.65 normal upper range)
yellow -- kappa free light chain (1.94 normal upper range)
(soure -- http://multiplemyelomablog.com/2014/06/more-about-alternative-ways-to-monitor-myeloma.html)
Hevylite Assay -- heavy free chain test
The Freelite chain people
(The Binding Site in UK) have developed a new sensitive test to measure
heavy free chains (hevylite assay). It was approved by FDA in 2014 for
IgG. In 2014 a poster reports to getting this test done by going to his
doctor to discuss this, and then his blood sample was sent off to the Mayo
clinic. (Mayo clinic is one of only two labs doing the test according to
the Hevylite site.) Another possible leading indicator to keep an eye on.
The Mayo clinic new HevyLite/Binding
Site test is called: 'Immunoglobulin Heavy and Light Chain (HLC) Pairs,
IgG Kappa and IgG Lambda '. From this name it looks to me like this test
is measuring excess 1/2Ys of antibodies, i.e. equal number of IgG heavy
chains paired with a light chain, and the test will measure both kappa
and lambda light chains paired with the IgG heavy chain. (Mayo offers similar
tests for IgA and IgM heavy chains.
Hevylite testing is useful for:
• Distinguishing between
broadly migrating monoclonal proteins and restricted polyclonal immunoglobulin
responses
• Quantitating monoclonal
IgA, IgG, or IgM proteins that are difficult to quantitate on serum protein
electrophoresis
• Providing a more specific
quantitation of the monoclonal protein than quantitating total IgA, IgG,
or IgM
These results can be used
when monitoring previously diagnosed IgA, IgG, or IgM multiple myeloma
patients and is used in conjunction with other laboratory findings
Drugs used in Multiple
Myeloma (sept 15)
Starting from lists of MM
drugs at www.cancer.gov
and a booklet on myeloma from the Leukemia and Lymphona society I pulled
together this list of MM drugs. Combinations are assembled with drugs from
different classes.
At the present time the main
cancer drug for a newly diagnosed MM patient is generally revlimid (an
anti-angiogenic and immunomodulator) or a general cancer drug like melphalan.
They tend to be paired with either a corticosteroid, like dexamethasone,
or a proteasome inhibitor, like velcade, or both. Two new classes of drugs
on the horizon are Panobinostat (histone deacetylase inhibitor) and
humanized monoclonal antibodies, like Elotuzumab and Daratumumab. Both
monoclonal antibodies are still experimental (no FDA approval). Elotuzumab
is further along, now in phase III trials. The monoclonal antibodies, being
antibodies, are huge molecules (20,000 atoms) compared to the other drugs.
MM drugs organized by class
Here's are all the MM drugs organized
by their mechanism of action. When I do this, it's discouraging that there
are only two classes of MM drugs with any track record: anti-angiogenic
& immunomodulators and proteasome inhibitors. The other two classes:
histone deacetylase inhibitor and humanized monoclonal antibody have just
gotten their first (limited) FDA approval in 2015 and can only be used
in relapsed patients. At present (1/16) I have only taken one drug from
the anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator class. My preferred proteasome
inhibitor would be Ninlaro, the only proteasome inhibitor that's a pill,
but I need to do some research to see how available it really is.
Anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator
* lenalidomide (Revlimid, rev) (2006)
anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator 2nd generation
thalidomide Celegene Corp
pill, + dex
(Revlimid is a multiple myeloma monster that dominates in first-line and
second-line indications with
$5.7 billion billion (Celgene?) in expected sales this year. (business
press)
(several beacon posters report good results with only rev + dex. Tom Brokaw
is though to have
taken rev/dex for six months and then added velcade for a year (RVD) to
get to a CR.)
* pomalidomide (Pomalyst) (2013)
anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator 3rd generation
thalidomide Celegene Corp
pill, + dex
(Imnovid in EU)
GoodRx says, 100% of Medicare Part D and Medicare Advantage plans cover
Pomalyst.
pom: 4 mg (1,2,3 mg), cycled 21 of 28 days cycle, take between meals
dex: 40 mg/wk (20 mg on two consecutive days/wk of carfilzomib)
Proteasome inhibitor --- Proteasome inhibitors come in two forms,
boron based (Velcade, Ninlaro), and epoxyketone based (carfilzomib, oprozomib)
bortezomib (Velcade, BTZ)
(2003) proteasome inhibitor (boron)
injection Millennium Pharmaceuticals
(owned by Takeda)
(one beacon poster reports neuropathy worse after being off velcade
two months, doctor is
sending her to pain doctor and it looks like velcade caused nerve damage
is permanent.)
Velcade is given at a dose of 1.3 mg/m2 intravenously or as an injection
under the skin on days 1, 4, 8, and 11
of a 28 day cycle.
cyclophosphamide added to Velcade/dex (VCD or CyBorD) has proven effective
in several trials
* ixazomib (Ninlaro) (2015)
proteasome inhibitor (boron) in pill form (once weekly) approved
by FDA 11/20/15 Millennium Pharma
(MLN9708)
(doses: 4 mg, 3 mg, 2.3 mg, recommended dose 4 mg, three pills in 28 day
cycle, to be used with rev/dex)
Ninlaro is considered to be a second-generation proteasome inhibitor because
it has improved characteristics
and activity over Velcade. Laboratory and animal studies show that Ninlaro
inhibits the growth of
myeloma cells, including those that are resistant to Velcade. Ninlaro and
Velcade differ from
carfilzomib in that they are boron based.
* carfilzomib (Kyprolis) (2012)
proteasome inhibitor (epoxyketone) FDA approved in 2012 for MM
injection Onyx Pharmaceuticals
(further FDA approval (2nd line) in July 2015) (Onyx was recently bought
by Amgen for 10 billion.)
Amgen web site describes carfilzomib as a second generation proteasome
inhibitor.
(one beacon poster had port installed for Kyprolis and reports bad pain)
infusion (10 min) six times a month (days 1,2 8,9 15,16 of
28 days cycle)
(two consecutive days for three weeks, then week off)
dexamethasone is given prior to the infusion (to minimize side effects
of the infusion)
One treatment widely discussed on Myeloma Beacon is [carfilzomib + daratumumab
(Darzalex)]
oprozomib (ONX 0912)
proteasome inhibitor in pill form, (epoxyketone), phase 1/2 trials
reported Dec 2013, Onyx Pharmaceuticals
(PR-047)
Oprozomib is an orally bioavailable analog of carfilzomib (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22763387)
"In summary, similarly to bortezomib, carfilzomib and oprozomib exert potent
cytotoxic effects
on myeloma cells under continuous and physiological dosing conditions."
Blocks the 20S proteasome.
Oprozomib was granted orphan drug status for the treatment of multiple
myeloma in 2014.
In November 2013 Onyx Therapeutics initiated a randomised, double-blind
phase Ib/III trial to assess the
maximum tolerated dose, safety, tolerability and efficacy of oprozomib
in combination with pomalidomide
and dexamethasone ... in patients with primary refractory or relapsed and
refractory multiple myeloma
(NCT01999335). The trial completed enrolment of planned 314 patients in
the US in June 2015.
marizomib (NPI-0052)
marizomib is in the same class of agents as Velcade® (bortezomib),
but it has a different structure.
Given by infusion. Being developed by Triphase Accelerator. In phase I
trials.
Proteasome inhibitors can be purchased with prices at Selleckchem.com
pharmacy, The site also shows a lot of chemical information about each
drug
with links to literature
and clinical trials.
http://www.selleckchem.com/products/oprozomib-onx-0912.html?gclid=CI724Kya4dQCFRBMDQodUSUIsA
Humanized monoclonal antibody Monoclonal antibody
drug (MoAbs). Side effects with this class of drugs are quite minimal
and are similar
to other chemo drugs. They are widely used in other cancers, but just beginning
to be used in MM.
Infusion reactions are common.
Immunotherapy is a new cancer treatment approach that is receiving a lot
of press. It activates the body's immune
system to fight diseases, including cancer. Darzalex (daratumumab) is the
first drug of this type for MM.
* daratumumab (Darzalex)
humanized monoclonal antibody targets proteins on the surface of myeloma
cells. Used as single agent
(HuMax - CD38)
or in combination with revlimid + dexamethasone, or velcade + dexamethasone.
Daratumumab is a human
monoclonal antibody (mAb) with broad spectrum cytotoxic activity. It targets
the CD38 molecule,
which is highly expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells.
Once daratumumab is bound
to the CD38 protein on cancer cells, it signals for the immune system to
kill the cells. Infusion.
Phase I/II. Jassen Biotech (subsidiary of Johnson and Johnson) with
Genmab (Danish, who developed
the drug). Daratumumab is a human IgG kappa monoclonal antibody.
Myeloma Beacon ; "Since there are CD38 positive cells in the lung tissue
and especially in the bronchial
lining, why did they even decide to try Darzalex for a patient with COPD?
Why not start with Empliciti,
which primarily affects cells with SLAMF7 (the second most prevalent marker
on myeloma cells)?"
Preliminary results of an ongoing multicenter Phase 1b study showed that
the combination of Darzalex and
Pomalyst-dex resulted in a high 71% overall response rate in heavily pretreated
patients.
Approved (really preliminary approval) by FDA in Nov 2015 to "treat
patients with multiple myeloma
who have received at least three prior treatments." (FDA
site) "Darzalex was approved under the agency’s
accelerated approval program (breakthrough designation and a priority review),
which allows the approval
of a drug to treat a serious or life-threatening disease based on clinical
data showing the drug has an effect
on a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit to
patients. (business press says Johnson
& Johnson wants to position this drug as a front line treatment for
MM.) Some data from two phase 3 trials
are now available: Pollux and Castor. Ph 3 clinical trials compared [rev/dex
+ daratumumab] to [rev/dex].
Percent with VGPR (or better) was 74.5% (17% had a partial response). (This
is far better than elotuzumab's
33%!) It looks like daratumumab PFS (prgression free survival) time will
be better than elotuzumab because
at 18 months its response curve is flattening out at 75%.
---------------------------
At the time of disease progression, various options will be available to
Mr. Fulton. Among them I would prefer
a daratumumab-treatment regimen such as daratumumab plus bortezomib (Velcade)
(plus dex) based on the
CASTOR trial. Bortezomib could be administered on days 1, 8, 15 of the
28 day treatment cycle to minimize
the risk of toxities, expecially peripheral neuropathy. The dose of bortezomib
could also be reduced from 1.3
to 1.0 mg/m2 if there's a progression of neuropathy symptoms.(consulting
Dana Farber hematological oncologist)
--------------------------------
Note, the mention of a 28 days cycle.. This indicates the writer is not
that familiar with Castor trial because
the trial and also the current daratumumab prescribing document use a threee
week (21 day) cycle when
the drug is paired with Velcade.
-------------------------------
Outline of ph3 Castor clinical trial
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1606038?rss=mostEmailed#t=article
New England Journal of Medicine paper on Castor trial results Aug
2016 -- 'Daratumumab, Bortezomib,
and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma'
http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1606038
Slide
talk on the Castor trial
New England Journal oct 2016 paper on Pollux trial, 'Daratumumab, Lenalidomide,
and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma'
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1607751#t=article
http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1607751
----------------------------
Infusion once a week for two months, then every two weeks for four months,
then once a month.
(get this!) "The infusion will be completed in 15 hours"!! (Thise infusions
are SLOW. Prescribing sheet shows
1st infusion is 6.5 hr and subsequent infusions are 4 hr! 135k/yr
(first year) to 76k (second year)
Infusion reactions are common, but just on the first infusion, 46% of people
are affected.
As I read the infusion rate table in the presciring document I get
(for 1,000 ml) 5 hr for the 1st infusion and
2.5 hr for subsequent infusions at 500 ml, but there are a host of premeds
required and very often the infusions
are interrupted by complications. One poster says his 1st infusion took
12 hr.
elotuzumab (Empliciti)
humanized monoclonal antibody targets SLAMF-7 proteins on the surface of
myeloma cells. Used in combination
(HuLuc63, Elo)
with revlimid + dexamethasone. Infusion Phase III. Two year results. Bristol-Myers
Sqibb
and AbbVie. Phase III with FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation. Infusion
schedule: every week for
first two cycles, then every other week (until disease progression). A
complication with the infusions is that
dexamethasone pills (28 mg) must be taken 3 ro 24 hr in advance (take
7 pills at home in morning) and 8 mg of
dexamethasone must be infused 45-90 min before elotuzumab (plus a bunch
of other pills in advance).
In Ph III clinical trial [rev/dex + elotuzumab] was conpared against [rev/dex].
Percent with VGPR (or better)
was 33% (46% had a partial response). Mechanism of action: elotuzumab targets
SLAM7 (Signaling
Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family member 7 protein) on MM cells and
natural killer cells, which are
activated by elotuzumab.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Daratumumab vs elotuzumab (3/26/17)
Clear advantage Daratumumab,
far better patient response (74.5% v 33% for VGPR) and likely a longer
disease free progression time too. In choosing a monoclonal antibody drug
for my next chemo my doctors seem to be favoring daratumumab over elotuzumab,
but why? I have not yet had a chance to ask them, so to try and answer
this question I reviewed the ph 3 trial data as given in prescribing documents
of both drugs. In the trials both drugs were used with rev/dex and compared
against rev/dex, so the data can be used to compare them against each other.
Here are PFS plots for daratumumab and elotuzumab.
 .
.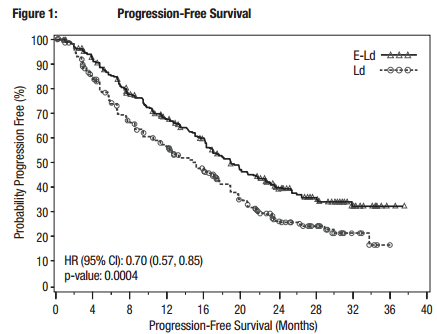
Ph3 trial data from daratumumab prescribing document
Ph3 trial data from elotuzumab prescribing document
74.5% of daratumumab patients had a VGPR (or better) response
33% of elotuzumab patients had a VGPR (or better) response
The PFS plot for daratumumab
looks much better than elotuzumab, at about 18 months (available data)
the daratumumab plot is flattening out near 75%. There is no flattening
in the elotuzumab plot, so it looks likely that daratumumab will have a
longer PFS time, but how much longer is not known because the data is not
in. Probably much more important are the response numbers. Far more patients
responded to daratumumab than elotuzumab. 74.5% % of daratumumab patients
reported a VGPR (or better) response, while only 33% of elotuzumab patients
achieved a VGPR (very good partial response) or better.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[rituximab (Rituxan)]
MD Anderson cancer site mentions this monoclonal antibody in connection
with MM, but the manuf web site makes
no
mention of MM, just lymphomas and leukemias. References in the literature
for this drug to back 18 years!
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against the protein CD20, which is primarily
found on the surface of immune
system B cells. Manuf by Genetech/Biogen.
MDX-1097
Denosumab (for bone disease)
Siltuximab (Sylvant)
Monoclonal antibody that binds to interleukin-6. Evaluated for other cancers.
Encouraging results have been reported
in 2009 from a phase II trial for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
In 2014 FDA approved for another
cancer. Jannsen Biotech. By infusion.
pembrolizumab (Keytruda)
Phase 3 trials for other cancers (melanoma and lung cancer), but being
evaluated in early trials for MM
( MK-3475)
Being deveoped by Meerk
Histone deacetylase inhibitor
panobinostat (Farydak) (2015)
inhibits enzymes known as histone deacetylases (HDAC), causes apoptosis
of malignant cells. Oral capsule.
FDA approved for MM in Feb 2015. "Farydak is the first HDAC inhibitor approved
to treat multiple myeloma.
It is intended for patients who have received at least two prior
standard therapies, including bortezomib
(velcade) and an immunomodulatory agent (revlimid). Farydak is to be used
in combination with bortezomib,
a type of chemotherapy, and dexamethasone, an anti-inflammatory medication."
(FDA
site) Marketed by Novartis
Pharmaceuticals.
“Farydak has a new mechanism of action that distinguishes it from prior
drugs approved to treat multiple myeloma."
This drug appears to have a lot of risk. (toxic) In Nov 2014 an FDA panel
decided the advantages did not out
weight the risks. The manuf then resubmitted, and got approval by more
tightly restricting the candidate MM
population. The clinical trial (193 participants) showed only that adding
Farydak was better (by 5 months) than
(velcade + dexamethosone). This FDA "accelerated" approval is really only
preliminary approval. The manuf is
required to do more tests demonstrating clinical benefit. "The (FDA) accelerated
approval
program provides
earlier patient access to promising new drugs while the company conducts
confirmatory clinical trials."
Yikes --- "73% of patients had dose interruptions or modifications, 87%
experienced Grade 3/4 adverse events, and
33% were hospitalized due to adverse events. The efficacy advantage was
modest" (FDA farydad
summary review). This is a drug that can be used only after revlimid and
velcade (or ninlaro) have been used.
vorinostat (Zolinza)
2011 Merck reported phase III results. Trial tested (Zolinza + Velcade)
against Velcade alone in relapsed MM patients.
As I read the results, the benefits were modest with significantly more
side effects. This is a pill. It is not FDA
approved for MM, but it is for a lymphoma. The Wikipedia (Zolinza) page
makes no mention of this drug
for MM. This drug is not new, it has been around since 2006, and since
it has a wide spectrum of possible
anti-cancer uses the manufacturer keeps trying it on different cancers,
many (or several) of the tests it has failed.
Since I see nothing on the Merk site after 2011 or on Wikipedia about MM,
I suspect its MM response was a failure too
or its benefit too small (even though that's not how Merck describes it
to this day on its site!). Yup, I find this
on the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation site --- "Merck is no longer
pursuing an FDA indication
in multiple myeloma. However, since Zolinza is FDA-approved for another
cancer, doctors may prescribe it
off-label for myeloma based on the data supporting its effectiveness."
Wikipedia describes its mechanism of action this way:
"Vorinostat has been shown to bind to the active site of histone deacetylases
and act as a chelator for zinc
ions also found in the active site of histone deacetylases. Vorinostat's
inhibition of histone deacetylases results
in the accumulation of acetylated histones and acetylated proteins, including
transcription factors crucial for the
expression of genes needed to induce cell differentiation."
azacitidine
(Vidaza) Cytotoxic drug FDA-approved for the treatment of myelodysplastic
syndromes (MDS) being evaluated in combination
with Revlimid-dex in relapsed or refractory myeloma. From Celegene. Chemical
analog of cytidine. Approved
by FDA in 2004 for myelodysplastic syndrome.
General anti-cancer drug used for MM
Doxil (Doxorubicin)
Doxil is a chemotherapy drug used in myeloma treatment. Doxil is an anthracycline
antibiotic that works by
intercalating the DNA found in multiple myeloma. The drug has been used
in traditional chemotherapy regimens
for many years. Phase 3 MM trial showed that used with Velcade it extended
time to disease progression from
6.5 months to 0.3 months, Janessen Products
Experimental (nov 16)
bb2121 from BlueBird bio (Cambridge) (financed by 10 million from Celgene)
is reporting Phase 1 (CRB-401) trial results.
of a customized T cell theapy. Just 9 patients, but good response. Bluebird's
infused treatment is a member of an
emerging potent new type of cancer therapy called CAR T cells. Patients
T cells are removed and genitically altered
to target the protein called BCMA found on cancerous blood plasma cells,
then infused back in.
(individual gene therapy)
Excellent overview of most of these drugs
https://www.themmrf.org/multiple-myeloma-knowledge-center/myeloma-drugs-guide/velcade/
Drugs marked '*' I have taken.
Revlimid with the corticosteroid dexamethasone (rev/dex) was my initial
chemo. When I relapsed and became refractory to Revlimid after about 20
months, Pomalyst was substituted as the anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator,
dexamethasone was continued and the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib (injection)
was added (pom/carfilzomib/dex).
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Drugs
to counter chemo 'side effects' (9/21/17)
After three years on continuous
chemo drugs, my quality of life is affected more by the so-called 'side
effects' of the chemo drugs than the underlying cancer. Every time my chemo
has been changed the new drugs brings a (largely predictable) new set of
side effects that attacks the body. I am jittery (cause ???), my
lungs have taken a lot of damage (from carfilzomib), and my feet are numb
(from proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro).
Extreme shortness of breath
In recent weeks (9/21/17) the
biggest impact on my quality of life is a crippling shortness of breath.
When I get out of the shower, I need to lie down for 5-10 minutes before
I have the energy to comb my hair. After walking slowly around the market
picking up a few groceries, I feel the need to sit down for a few minutes
on a bench in the market before I have the energy to carry my packages
out to the car. Yet when I am sitting down, or driving a car, I feel totally
Ok.
Low hemoglobin levels in blood
I am pretty sure I know (physically)
the reason for this. My latest blood work shows my hemoglobin as of (9/13/17)
is only 8.4 g/dL. This is only 60% of the lower edge of normal (13.8 g/dL),.
This is far lower than in my whole three years of taking chemo drugs. My
lungs have tested Ok, my heart has tested Ok. With this low number of red
blood cells in my blood (RBC is also 60% of low normal) my blood just does
not have the oxygen carrying capacity to get the oxygen from my lungs to
the muscles that need it.
Low number (or poor quality) red blood cells
While I read that normal red blood
cells have a 'lifetime' (how defined?) of about four months, my blood work
for aug 2017 into early sept 2017 shows a decline of hemoglobin of 38%
[13.5 g/dL (near normal) => 8.4 g/dL] in just under five weeks. Either
something is destroying my red blood cells, or more likely they are emerging
from my chemo damaged marrow not fully formed or in an immature state.
In fact my memory is the blood technicians looking at my blood under a
microscope have commented that the size and shape of some of my red blood
cells do not look normal. Red blood cells are basically just bags of hemoglobin,
so there is a close relationship between red blood cell count (and quality)
and the amount of the oxygen carry molecule hemoglobin in the blood.
Drugs
to increase hemoglobin and RBC (red blood count)
With this introduction to
the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood I recently learned from the recent
book of the chief hematological oncologist at MGH (Mass General Hospital)
that he speaks of treating multiple myeloma patients with this problem
using a drug called erythropoietin. This is a manufactured drug that is
apparently the same (identical?) as a hormone the body naturally manufactures
(in the kidneys primarily) to regulate hemoglobin in the blood.
Eerythropoietin (EPO) blood test
One thought that immediately jumps
to mind is that low hemoglobin might be due to the kidney damage, the kidneys
not putting out the required level of erythropoietin. The good news is
there is a special blood test that can measure the level of erythropoietin
in the blood called the 'erythropoietin (EPO) test'.
Erthropoietin (brand names: Epogen and Procrit) --- hemoglobin raising
hormone
Ryan, the chief hematological
oncologist of MGH (Mass General Hospital), in his new 2017 book 'Living
with Cancer" suggests a common alternative to a blood transfusion for cancer
patients when hemoglobin levels are low is a drug called erthropoietin
(short hand 'epo'). This is actually a hormone the body produces mostly
in the kidneys (10% in the liver) to encourage more red blood cell production.
Seems likely this is a key part of feedback loop that regulates the level
of hemoglobin in the blood.
Risk of deep blood clots
Ryan notes that a significant
drawback to giving this drug is that it can cause deep blood clots (which
means strokes when they move), but that recent data has shown that the
risks are lower than once thought. However, the clear implication of Ryan's
language in his book is that he is using (and recomending) this drug in
his treatment of cancer (mulitiple myeloma?) patient at MGH to treat anemia,
low red blood cell counts.
--
Erythropoietin is a protein with an attached sugar (a glycoprotein). It
is one of a number of similar glycoproteins that serve as stimulants for
the growth of specific types of blood cells in the bone marrow. There is
a blood test for this hormone called the 'epo test'. It requires an overnight
fast.
This drug can be given as
a subcutaneous injection (It was used by Lance Armstrong as an (illegal)
way to improve his performance.), but to cancer patients it is given intravenously
weekly.
Epogen (Amben) and Procrit (Janessen)
Erythropoietin is
sold under brand names: Epogen (Amben) and Procrit (Janessen). This
appears to be the exactly the same drug (it has been on the market for
28 years) sold by two different manufacturers. The Epogen and Procrit prescribing
documents say it can be given intravenously weekly to cancer patients:
40,000 Units weekly. This would fit nicely with my weekly daratumumab infusion
chemo. Threshold for use: hemoglobin <10 g/dL. At 8.5 g/dL I meet
this threshold easily. The response time is relatively slow, something
like 0.5 g/dL.
Epogen
-- Epogen® (epoetin alfa) Injection, for intravenous or subcutaneous
use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
Procrit® (epoetin alfa)
-- Procrit® (epoetin alfa) Injection, for intravenous or subcutaneous
use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
Aranesp® (darbepoetin
alfa) (a long acting version of Procrit). Approval 2001
There appears to be less emphasis in the prescribing document for cancer
patients. For cancer patients it is given weekly subcutaneously, or at
a higher dose subcutaneously every three weeks.
I wouldn't be opposed
to the idea of Procrit or Aranesp (a long acting version of Procrit), but
I have seen a number of blood clots induced by these drugs, several in
myeloma patients, so though the risk is less than they originally thought,
it is still not zero. That in combination with the risk of blood clots
on Pomalyst (which you will be starting again soon, hopefully) may compound
the clot risk. Again, I am not opposed, but we should discuss it further.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Huge risks of activated immune system (12/3/16)
Long article in NYT details
how 20% for single drugs (and 50% for combination of drugs) of cancer patients
being treated with 'immunotherapy drugs' that activate the immune system
are having major organs destroyed: 'Immune System, Unleashed by Cancer
Therapies, Can Attack Organs' By MATT RICHTELDEC. 3, 2016. Doctors tend
to shrug, and say this is evidence that its workng, and diabetes (with
destroyed pancreas) is better than dieing.
-- “We are playing with fire,”
said Dr. John Timmerman, an oncologist and immunotherapy researcher at
the University of California, Los Angeles, who recently lost a patient
to side effects." The promise comes with real risks. A 2015 paper in The
New England Journal of Medicine showed that use of these drugs carried
a risk of side effects that were severe, required hospitalization or were
life-threatening 54 percent of the time. “It’s at least that high, at least,”
Dr. Kluger said. But, she noted, most of the side effects are manageable
through immune suppression, such as with steroids.
Proteasome inhibitors
-- Proteasome inhibitors
are drugs that block the action of proteasomes, cellular complexes that
break down proteins. Multiple mechanisms are likely to be involved, but
proteasome inhibition may prevent degradation of pro-apoptotic factors
such as the p53 protein, permitting activation of programmed cell death
in neoplastic cells dependent upon suppression of pro-apoptotic pathways.
For example, bortezomib causes a rapid and dramatic change in the levels
of intracellular peptides.[1] Proteasome inhibitors are being studied in
the treatment of cancer, and three are approved for use in multiple myeloma.
(Wikipedia -- Proteasome inhibitors)
-- Bortezomib's boron atom
binds the catalytic site of the 26S proteasome. Bortezomib (Velcade) was
approved in 2003, the first proteasome inhibitor for use in the U.S. Carfilzomib
irreversibly binds to and inhibits the chymotrypsin-like activity of the
20S proteasome. It was approved by the FDA for relapsed and refractory
multiple myeloma on July 20, 2012 under the brand name Kyprolis.
-- Proteasomes are protein
complexes inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. The
main function of the proteasome is to degrade unneeded or damaged proteins
by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds.
-- The ability of proteasome inhibitors
to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in rapidly dividing cells has
been exploited in several recently developed chemotherapy agents such as
bortezomib (Velcade). (Wikipedia)
-- Proteasome inhibitors
have effective anti-tumor activity in cell culture, inducing apoptosis
by disrupting the regulated degradation of pro-growth cell cycle proteins.
This approach of selectively inducing apoptosis in tumor cells has proven
effective in animal models and human trials.
-- The results highlight
that the proteasome is a novel biochemical target and that inhibitors such
as PS-341 represent a unique class of antitumor agents (1999 paper).
-- Notably, multiple myeloma
has been observed to result in increased proteasome-derived peptide levels
in blood serum that decrease to normal levels in response to successful
chemotherapy.
2011 review of Proteasome Inhibitors
Bortezomib (Velcade)
---- based on boron atom, Millennium/Takeda
MLN9708 (ixazomib)
(Ninlaro) --- also based on boron atom, Phase 3 trials, Millennium/Takeda
http://mmrf.pub30.convio.net/living-with-multiple-myeloma/relapsed-refractory-patients/treatment-options/mln9708.html
Carfilzomib --- based on
ONX 0912
NPI-0052 -- Marizomib, infusion
CEP-18770
http://www.cancernetwork.com/oncology-journal/current-advances-novel-proteasome-inhibitor%E2%80%93based-approaches-treatment-relapsedrefractory-multiple
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pomalyst and Kyprolis (6/13/16)
FDA approval of both Pomalyst
2013 and Kyprolis 2012 is for patients previously treated with velcade,
but doctors are free to ignore that.
GoodRx reports Pomalyst is
covered by all Medicare Part D plans.
Comments from 2013
Vincent Rajkumar, Mayo Clinic
says Pomalyst is an important addition for the treatment of multiple myeloma,
and it is very well tolerated.
In a large clinical trial of Pomalyst
in heavily pretreated patients, nearly all of whom were refractory (resistant)
to Revlimid, about 1/3rd had some response (most a partial response) to
Pomalyst, but the effected lasted only a few months. So there's some evidence
that Pomalyst makes sense as a replacement for Revlimid, if Revlimid has
stopped working.
Kyprolis will be mainly used
for patients who have pronounced neuropathy (nerve damage) due to Velcade.
-- The investigators note
that the efficacy of the Revlimid (lenalidomide)-Velcade-dexamethasone
(Decadron) combination appears to be lower than that of the three-drug
combination of Kyprolis (carfilzomib), a newly approved drug in the same
class of drugs as Velcade, combined with Revlimid and dexamethasone.
-- In a trial of the Kyprolis-Revlimid-dexamethasone
combination involving patients similar to those in the current study, 77
percent of patients responded to treatment, and the median progression-free
survival was 15 months.
-- Phase 2 trial (2014,
64 patients) Revlimid-Velcade-Dexamethasone (rev/vel/dex) Trial In Relapsed
Multiple Myeloma,. The median progression-free survival was 10 months after
the start of treatment. The median overall survival was 30 months
from the start of treatment.
-- Initial results of a large,
head-to-head clinical trial (2015) show that relapsed myeloma patients
treated with high-dose Kyprolis and dexamethasone had twice the progression-free
survival of relapsed patients treated with Velcade and dexamethasone. Median
progression-free survival in the Phase 3 trial was 18.7 months in trial
participants treated with high-dose Kyprolis (carfilzomib) and dexametason
(Decadron), compared to 9.4 months in in patients treated with Velcade
(bortezomib) and dexamethasone.
-- In particular, patients
who received Kyprolis during the study were more likely to experience heart
failure, kidney failure, high blood pressure, and breathlessness than the
Velcade-treated patients. At the same time, peripheral neuropathy occurred
less frequently in the Kyprolis-treated patients in the ENDEAVOR
trial than the Velcade-treated patients.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Immunotherapy
In November 2015, the FDA
granted accelerated approval for Darzalex, which is a first-in-class immunotherapy
treatment (a monoclonal antibody), which works by helping your immune-system
cells attack cancer cells. Darzalex is approved for patients who have received
at least three prior treatments for multiple myeloma, meaning the disease
has become resistant to the other treatments or has progressed within a
short period of time after the last treatment.
Dana Farber is researching Darzalex
Darzalex clinical trial
investigator Paul G. Richardson, M.D., Clinical Program Leader and Director
of Clinical Research, Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center, Dana-Farber
Cancer Institute, said:
“Multiple myeloma is a highly
complex disease and remains incurable, with almost all patients relapsing
or becoming resistant to therapy … With DARZALEX, we have a promising new
immunotherapy, which has shown pronounced efficacy as a single agent with
an acceptable adverse event profile. This is especially important for treating
these heavily pre-treated patients in whom all of the major classes of
currently available medicines have failed.”
The FDA accelerated approval
was based on two open-label studies: In a study of 106 patients receiving
Darzalex, 29 percent experienced complete or partial reduction in their
tumor burden, lasting an average of 7.4 months. In a study of 42 patients
receiving Darzalex, 36 percent had complete or partial reduction in their
tumor burden. (Note only a minority of patients responded at all,
and this is typical of immunotherapy, and survival time was 7 months.)
Darzalex is given as an infusion;
potential side effects included the following: Infusion-related reactions
(experienced by half of patients): Fatigue,
Back pain, Fever and nausea, Cough, Low white blood cell count, Low
red blood cell count (anemia), Low levels of blood platelets (thrombocytopenia)
-- Advanced options
include immunotherapy to help your body fight the cancer and new methods
for stem cell transplantation. In addition, we are actively pursuing answers
to reducing the side effects of multiple myeloma and its treatment. For
instance, we were instrumental in finding that bisphosphates often can
decrease bone-related events in multiple myeloma.
Chemotherapy -- Drug therapy
is the usual starting point in treating multiple myeloma. MD Anderson offers
the most up-to-date and advanced chemotherapy options. Liposomal drug delivery
is an innovative method that can help chemotherapy be more effective.
Immunotherapy -- MD Anderson
is among just a few cancer centers in the nation that are able to offer
targeted therapies for some types of multiple myeloma. These innovative
new drugs stop the growth of cancer cells by interfering with certain proteins
and receptors or blood vessels that supply the cancer with what it needs
to grow. Possibilities may include:
Monoclonal antibodies, including
Rituxan® (Rituximab)
Biological therapies that
develop antibodies to destroy cancer cells
Proteasome inhibitors, such
as bortezomib (Velcade®)
Immune modulators, such
as thalidomide and lenalidomide, that modify the environment of the tumor
cell and allow it to die
Small molecule treatment,
such as panobinostat
Cytokine therapies
Vaccine therapy
Bisphosphonates help reduce
high calcium levels and decrease the risk of bone fracture
-- Celgene and Juno Therapeutics,
Inc. agreed on a long-term collaborative partnership to bring CAR T-cell
therapies and T cell receptor technologies to market for cancer patients.
(aug 2015)
-- For the study, the patient’s
T cells were genetically engineered to contain a receptor for a tumor antigen
known as cancer-testis antigen (CT antigen), two of which are present in
about 60 percent of patients with advanced myeloma. With the CT antigen
receptor, the T cells were equipped to spot the myeloma and subsequently
employ the immune system to find and destroy it. The results showed that
14 out of 20 patients (about 70 percent) had a near-complete or complete
response three months after treatment; median progression-free survival
was 91.1 months, while the overall survival lasted 32.1 months. (study
by University of Maryland Medical Center) (This study first did a
stem cell transplant before injecting the modified T cells.)
-------------------
(from a NYT article on immunotherapy (July 2016)
Drugs called checkpoint
inhibitors are the most widely used form of immunotherapy for cancer. They
block a mechanism that cancer cells use to shut down the immune system.
This frees killer T-cells — a critically important part of the immune system
— to attack the tumor. Four checkpoint inhibitors have been approved by
the Food and Drug Administration and are on the market. They are given
intravenously.
Another form of immunotherapy,
called cell therapy, involves removing immune cells from the patient, altering
them genetically to help them fight cancer, then multiplying them in the
laboratory and dripping them, like a transfusion, back into the patient.
This type of treatment is manufactured individually for each patient, and
is still experimental.
Bispecific antibodies are
an alternative to cell therapy, one that does not require individualizing
treatment for each patient. These antibodies are proteins that can attach
to both a cancer cell and a T-cell, that way bringing them close together
so the T-cell can attack the cancer. One such drug, called Blincyto, has
been approved to treat a rare type of leukemia.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
new drug I've read about
filanesib (Arry-520)
(novel mechanism!) Filanesib is a highly
selective, targeted KSP (kinesin spindle protein) inhibitor with a mechanism
of action distinct from currently available myeloma therapies such as immunomodulatory
drugs (IMiDs®) and proteasome inhibitors. In phase 2 trials (2014-2016)
& (13-16) for Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma . Being tried
on patients with disease refractory to carfilzomib and/or pomalidomide.
(?? conflicts with trial data) Intravenous. Anderson cancer center
testing
Potential selection marker for
filanesib is (alpha 1-acid glyycoprotein (AAG). Never heard of this. Described
as an "acute phase serum protein used to diagnose and monitor inflamatory
disorders." This protein binds to filanesib. They seem to be saying this
protein has to be low for filanesib to work because it attenuated
filanesib in vitro. AAG is measured in g/L (graphs show 0 to 2.8 g/L).
http://www.arraybiopharma.com/product-pipeline/filanesib/
21 slides http://www.arraybiopharma.com/files/5913/9810/8038/PubAttachment592.pdf
being investigated alone and with dexamethasone (booster)
Being tested (phase 2) as
a supplement to carfilzomib (proteasome inhibitor): carfilzomib (Kyprolis)
vs (carfilzomib + falanesib)
Criteria for entry into phase 2 trial
** -- A monoclonal
Ig (M-protein) concentration on serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) of
> 1.0 g/dL.
**
-- Involved serum free light chain (FLC) level > 10 mg/dL, provided the
serum FLC ratio is abnormal.
Papers (3/16)
(Velcade + rev/dex)
vs rev/dex ** velcade extended PFS from 1.5yr (rev/dex) to
2.5 yr 800 patients Conclusions:
The use of KRd after first relapse led to a 1-year improvement in median
PFS vs Rd (rev/dex). six infusions (10 min) per month
800
http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/150495-156
------------------------------
Cyclophosphamide (cytoxan) (1959) nitrogen mustard alkylating
agent, Cyclophosphamide induces beneficial immunomodulatory effects,
quite toxic (substitutes for Revlid in patients that can't tolerate
Revimid)
Melphalan (1964)
alkylating agent, nitrogen mustard alkylating agent
Vincristine
general anti-cancer drug, hair loss
Liposomal Doxorubicin (doxil) (2007) anthracycline antitumor
antibiotic, general cancer drug, hair loss. Used with velcade.
* Dexamethosone
synthetic corticosteroid drug (used with Revlimid as popular 'rev/dex'
and Pomalyst as 'pom/carfilzomib/dex' )
Prednisone
synthetic corticosteroid drug
* Zoledronic acid
bisphosphonate, Zometa is used to prevent skeletal fractures in patients
with cancers such as multiple myeloma
Pamidronic acid
nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate, used to prevent osteoporosis
Plerixafor
(mobilizes stem cells for later transplant)
Carmustine
alkylating agent in chemotherapy, (used in preparation for stem cell transplant),
general cancer drug
* acyclovir (generic Zovirax)
anti-viral used to prevent the chickpox virus (varicella-zoster) remaining
in the body from becoming active
again and causing shingles (herpes zoster). Available 400 mg and 800 mg
pills.
My dosage: 400 mg, three times a day (1,200 mg daily).
Usual Adult Dose for Varicella-Zoster (chickenpox): 800 mg/four times a
day (3,200 mg daily dose)
Usual Adult Dose for Herpes Zoster (acute): 800 mg orally every 4 hours
(5 times a day) (4,000 mg daily dose)
Usual Pediatric Dose for Herpes Zoster (12 years or older): 800 mg orally
every 4 hours (5 times a day)
valacyclovir (Valtrex)
available in 500 mg and 1,000 mg pills. My dosage: 1,000 mg daily
Anti-viral pill size
To prevent a proteasome
inhibitor (like calfilzomib) from activating the chickpox virus which many
people have in their body (including probably me) an anti-viral need to
be taken daily. Recommended for me by my Dana Farber consultant is acyclovir
400 mg TID (TID means in latin 'ter in die' or three times a day) or valacyclovir
1,000 mg daily.
The (heart shaped) pill size
of 400 mg acyclovir I obtained from my local pharmacy is 11 mm (largest
dimension). For reference my pomalyst capsule is 17 mm long (measured),
and I have no problem swallow it. Some valacyclovir 1,000 mg capsules are
even bigger (21/22 mm long). Valacyclovir 1,000 mg may be available
in 17/18 mm capsules, but I know valacylovir 500 mg is available in a 17/18
mm long capsules. Ref: (1/2^.333 = .79 and .79 x 21.5 = 17)
A trip to my local CVS shows
that their 500 mg valacyclovir is the 17/18 size capsule (M122, white)
and their 1,000 mg is the 21/22 size capsule (M123, white).
So options for fewer easier
swallowing anti-viral are either take two (moderate size) 400 mg acyclovir
morning (with food) and one 400 mg evening with pom (no food). I
see 800 mg is the usual adult and even pediatric dose when treating chickenpox
and shingles, so 800 mg does not seem unreasonable. Or switch prescription
to (relatively large) valacyclovir 500 mg and take one morning and one
evening. The former is preferred.
I asked my doctor about taking
acyclovir 2 x 400 mg morning (with food) and 400 mg evening (no food) and
the response was 'perfectly reasonable', so that's the plan.
Combinations used in clinical trials
Revlimid and dexamethasone
(Rd)
(rev/dex)
* Pomalyst, carfilzomib, and dexamethasone
(rev/carfilzomib/dex)
Melphalan, prednisone, and
Revlimid (MPR)
(added alkylating agent (Melphalan) and prednisone substitutes for dex)
earlier version was Melphalan, prednisone, and Thalidomide (MPT)
Cyclophosphamide, prednisone,
and Revlimid (CPR)
(added alkylating agent (Cyclophosphamide) and prednisone substitutes for
dex)
Mar 2016 paper with 600 patients showed adding an alkylating agent to Revlimid
did not improve progression time.
(http://www.myelomabeacon.com/forum/revlimid-triplets-no-better-than-doublets-t6879.html)
(http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/127/9/1102?sso-checked=true)
Toxic side effects of various MM drugs (6/10/16)
Kyproli --- seems to have
a ton of toxic side effects. Most worrying is that a #1 serious side effect
is pneumonia, which I read causes 20%
of MM deaths.
Ninlaro --- just added to
cycled rev/dex whose schedule doesn't change. Ninlaro is taken just three
days a month, three of the same days dex
is taken. Most serious side effects are diarrhea and low platlets, but
peripheral neuropathy (nerve pain) is also listed.
Velcade --- can be given
once a week for 2 or 3 weeks a month. Velcade can reactive shingles virus
in body (causing painful rash), so a
'medication' may need to be taken to prevent shngles.
** -- List of serious side effects in much longer with velcade than Ninlaro.
-- "Prompt dose reduction and a change in the schedule of Velcade
administration are essential in managing peripheral neuropathy
should it develop."
-- once-weekly Velcade dosing is used more frequently because it has been
associated with fewer side effects
-- Subcutaneous administration of Velcade may also lessen the development
of peripheral neuropathy.
Hence this argue for velcade once a week, subcutaneous (in theigh or belly
fat) with a rapied dose reduction it nerve pain
develops. Poster report this nerve pain (hands and feet) is often permanent
nerve damage.
Revlimid --- Common side
effects of rev/dex include the following, all of which I have: Diarrhea
and constipation, fatique, insomnia, back pain.
"Some side effects such as mild or moderate diarrhea can be managed with
additional medications."
"Revlimid significantly decreases the risk of myeloma disease progression.
" (didn't work well for me)
Good reference for side effect of many MM drugs (seems to be just a
compendium of manuf proscribing statements)
https://www.themmrf.org/multiple-myeloma-knowledge-center/myeloma-drugs-guide/kyprolis/kyprolis-side-effects/
Ninlaro -- Recent status change
On 11/20/15 Millennium Pharmaceuticals
announced
that its pill version of velcade, which has been in phase III clinical
trials (experimental name MLN9708), has been approved by the FDA for use
with rev/dex in relapsed MM. It's the only FDA approved oral proteasome
inhibitor in pill form. This FDA approveal is based on (early, partial)
results of the TOURMALINE-MM1 phase 3 clinical trials, which are to be
reported on at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology
on December 7, 2015. This study is continuing and there are three more
TOURMALINE phase 3 clinical trials of this drug in progress (related to
MM).
TOURMALINE-MM1, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo, in combination
with lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed and/or refractory multiple
myeloma (early results have resulted in FDA approval for ixazomib in Nov
2015 and are to be reported at a hematological annual meeting Dec 5, 2015)
(TOURMALINE-MM1 phase III clinical trial (relapsed MM) uses 4 mg Ninlaro
pill, three
pills/28 day cycle. Revlimid is cycled)
TOURMALINE-MM2, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo, in combination with
lenalidomide and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed multiple
myeloma (clinical trial I was offered)
TOURMALINE-MM3, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo as maintenance therapy
in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma following induction therapy
and autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT)
TOURMALINE-MM4, investigating ixazomib vs. placebo as maintenance therapy
in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who have not undergone
autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) (Millennium press announcement of
may 2015 says first patients enrolled in this study.)
Looks to me like Ninlaro is
probably available, or will be soon, because a detailed (23 page) prescribing
document is online here.
I left a note with my oncologist asking if this FDA approval means it is
likely to be available soon.
Millennium says protease inhibitors
(by which they mean velcade) have a long established history treating MM,
and with the TOURMALINE clinical trials they are exploring the use of their
new protease inhibitor in oral form (ixazomib) in "every major multiple
myeloma patient population", so clearly they have expectations (or hope)
that this pill will be useful as a general MM chemo drug. The TOURMALINE-MM-4
trial, which just began enrolling patients in 2015 (may 2015), is of particular
interest to me because I didn't have a stem cell transplant and am now
on (revlimid) maintenance. My understanding is that when the FDA approves
a drug clinicians are free to use it 'off label'.
A MM blog has an interesting
discussion of Ninlaro, including its cost, and other new MM drugs:
http://multiplemyelomablog.com/2015/11/ninlaro-should-be-a-great-drug-but-storm-clouds-on-the-horizon.html
Ninlaro update
(4/5/2016)
Ninlaro (ixazomib) price (4/5/16)
Ninlaro is now showing up
in drug price search sites. This is a once a week pill, three pills per
28 day cycle. The MA drug discount site shows the price
without
insurance is $3,000/pill (round numbers) or (8,694 to 9,214 for a
three pill cycle). It is available through local pharmacies, the lower
price (500 saving is Stop and Shop pharmacy). It is available in 4 mg,
3 mg and 2.3 mg. Price is same for all doses. Blink Health gives a comparable
price (90k for 30 pills).
My medicare part D insurance
coverage is provided by Cigna. I find (see below) Ninlaro is in Cigna's
list of covered drugs. It's appoval is for use with rev/dex. I spend 11
months of the year in part D catastrophic coverage, so this reduces my
out of pocket cost 95% (9k/month to 450/month).
Ninlaro in Cigna pharmacy list (prior approval), capture 4/5/16
Medicare Part D insurance coverage
Next day (4/6/16) I called Cigna,
my Medicare part D insurer, to confirm Ninlaro is in the Cigna formulary.
It is, but with two restrictions. One is three pills/28 day cycle. (Why
is this not shown online!) Two, is prior approval required. It was explained
to me on the phone that either I, or my doctor, can request this approval.
Cigna then consults with doctor before granting approval. This can be expedited
to 24 hrs. The number to call to request coverage is: 877-813-5595.
Ninlaro update (2/1/2016)
As I write it is 2.5 months
since FDA approval of Ninlaro, and I still had no idea if was available,
so I decided to make some phone calls. Today I called a speciality pharmacy
where I am a customer (Cigna Speciality Pharmacy), a pharmacy I know handles
expensive tier 5 cancer drugs because I get my Revlimid from them monthly.
Ninlaro wasn't on the list of drugs that the customer service person had
available, but she said it might be in limited distribution, so she contacted
the pharmacists. When she returned she said the answer was good news and
bad news.
She said it could be ordered,
but was not presently in stock. However, Cigna would require 'prior approval'
for this new drug, which formally means the doctor must contact the pharmacy
and (typically) explain the patient need for it. Now what this means in
practice is hard to say. Is the 'prior approval' requirement here a low
or high barrier? If Ninlaro is viewed as interchangeable with Velcade (from
the insurance company point of view, not mine), a prior approval bar might
be tricky. For example, they might decide to only approve it if you live
xxxx miles from an infusion facility. I suspect the only way to find out
if it's really available would be with prescription in hand. Maybe I can
find info on MM forums. I did find a forum posting about the wholesale
price given by someone at Takeda at the time of the FDA approval to inquires
by the forum.
Here's what I know about
Ninlaro as of 2/1/16
Available
maybe (can be ordered, but not in stock says Cigna Speciality Pharmacy)
Covered by Part D
maybe (prior approval required at Cigna)
Price
8,670 (wholesale) for 28 day cycle (forum posting 11/21/15 on MM Beacon)
Dosing
3 pills in 28 days cycle (beginning of week 1,2,3)
National Drug Code
63020-078-02, 63020-079-02, 63020-080-02
(indentifies: manuf - drug & dose - package)
FDA
search, (Wiki,
National drug code)
She also gave me the National
Drug Code for Ninlaro and said she was marking it on the paperwork, so
if I called again, the drug could be found. (As I wrote it, it was only
for lowest dose, above is from FDA site.) This is an FDA list of regiestered
and approved drugs. Entering 'Ninlaro' in the 'FDA search' link (above)
as proprietary name brings up three entries for Ninlaro [078 (2.3 mg),
079 (3 mg), 080 (4 mg)].
Farydak
FDA in 2015 gave "accelerated"
approval to Farydak, which has a new mechanism of action, but it has only
been clinically tested with Vecade (not revlimid) and is to be used with
Velcade. "Accelerated" FDA approval means the drug is available on the
hope
that it will prove clinically beneficial, but the phase 3 clinical trials
are still ongoing (with I guess no reported results yet)!
Compassionate Use (1/10/16)
There's a way to access
new drugs in the pipeline, those without FDA approval, via what is known
as FDA Compassionate Use program (see link below). I first heard about
this in the long PBS series on cancer, and recently it was mentioned in
a NYT front page story about the head of the FDA drug approvals. A request
to access a drug must be filed with the FDA. The article said the FDA receives
about 1,000 compassionate use requests a year and approves 99% of them.
The requests have to come from a physician.
Here's an FDA site on its
compassionate use (also called expanded access) program:
http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/PublicHealthFocus/ExpandedAccessCompassionateUse/default.htm
MM treatment history
"Prior to 2003, the prognosis
for a patient diagnosed with multiple myeloma was very grim, as the standard
therapies were largely ineffective. People diagnosed with multiple myeloma
rarely lived beyond three years. However, in 2003, the FDA approved bortezomib
(Velcade®), a new therapy for myeloma, advanced with LLS support. This
marked the first new effective treatment for myeloma patients and more
than tripled survival rates for some patients. Other promising therapies
followed, including lenalidomide (Revlimid), an oral therapy, and thalidomide
(Thalomid ®), approved within a month of each other in 2006, giving
myeloma patients even more options and more hope, extending lives and improving
quality of life. Over the past 15 years, approximately 40 percent of therapies
approved by the FDA to treat cancers have been specifically for blood cancers."
(I find it very odd that thalidomide was approved the same time as revlimid
as revlimid is a 2nd generation thalidomide that is more effective and
with far less side effects.) (from
Leukemia
& Lymphoma Society, which supports MM research)
FDA approval 'zoo'
What does FDA approval mean
anyway? According to the FDA web site FDA approval is required to market
a drug in the USA. So in practical terms I would expect once a drug in
the developmental pipeline gets FDA approval, it will soon be available
for doctors to prescribe. A Q&A web site on this topic says how long
it takes for commercial availability of a drug after FDA approval depends
on the company. If the company is pretty certain that it will get FDA approval,
say with a generic where it is only necessary to demonstrate equivalence,
it may stockpile the drugs in advance. Other times a company may wait for
FDA approval before beginning to ramp up the manufacturing and distribution
process.
The general requirement for
FDA approval of new drug is that the company submit data showing that the
drug is both safe and effective. In the 'old days' this meant
a new drug would typically would get FDA approval only after successfully
completing phase 1,2 and 3 clinical trials.
Phase 1 is to establish
dosage and can be just a dozen people
Phase 2 is larger and the
goal is to establish the drug (at the dose determined from phase 1) is
safe, though it may sometimes provide 'hints'
that a new drug is effective
Phase 3 is a large, long
trial demonstrating effectiveness over existing regimens. In chemo drugs
for MM this is often a double blind trial with
700 or so participants where the new drug is compared against a placebo.
Trials for MM often extend five years or more. When the
time is added to set up the trial, recruit hundred of patients, and write
up the results, the total time for a large phase 3 trial can be
7-8 years.
Such a long pipeline for new
drugs has resulted in consumer groups and politicians pressuring the FDA
to expedite the drug approval process. The result is a 'zoo' of FDA approvals,
some of them quite surprising. A drug my gain FDA approval from early results
of a phase 3 trial (while the trial continues), or even FDA approval from
phase 1 and phase 2 alone with phase 3 trial acting as a "confirmation"
of the 'hints' of effectiveness from the phase 2 trial. Both of these approvals
have been seen in MM drugs gaining FDA approval in 2015. The FDA granted
'priority review' and 'orphan drug' designations for Ninlaro.
Accelerated FDA approval
FDA Accelerated Approval
Program allows for earlier approval of drugs that treat serious conditions
... based on a surrogate endpoint. A surrogate endpoint is a marker,
such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign or
other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit, but is not itself
a measure of clinical benefit. The use of a surrogate endpoint can considerably
shorten the time required prior to receiving FDA approval. (Farydak
received an accelerated FDA approval though I can't determine what the
surrogate marker is.)
Drug companies are still
required to conduct studies to confirm the anticipated clinical
benefit. These studies are known as phase 4 confirmatory trials. If the
confirmatory trial shows that the drug actually provides a clinical benefit,
then the FDA grants traditional approval for the drug. If the confirmatory
trial does not show that the drug provides clinical benefit, FDA has regulatory
procedures in place that could lead to removing the drug from the market.
Breakthrough Therapy
Intended .... to treat a
serious or life threatening disease ... and preliminary clinical
evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement
over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints,
such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development.
If a drug is designated as breakthrough therapy, FDA will expedite the
development and review of such drug.
Priority review status
Priority review status is
granted if a drug would be a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness
in the treatment of a serious condition. (Ixazomib was given priority review
by the FDA. It also has orphan drug status.)
Options for relapsed
muliple myeloma
While my cancer numbers
are now low, driven down by rev/dex chemo, and I am on revlimid maintenance
(10 mg), but at some point virtually guarenteed this regimin is going to
stop working, and my cancer levels are going to start to rise. So this
is the time to research chemo options for patients who are relapsing from
rev/dex chemo. (search term: 'relapsed multiple myeloma')
I asked my hemotologist about
this, and she suggested go back to rev/dex but supplement it with velcade
(This was a few weeks before the FDA appoval of Ninlaro, the pill version
of Velcade.)
I read one option is go back
to the chemo option that worked initially.
*** A 2015 article in Mayo
Clinic newsletter discusses "New 3-drug treatment for relapsed multiple
myeloma" which was recently published in the New England Journal of Medine:
"In the treatment
of relapsed multiple myeloma, the addition of carfilzomib (proteasome inhibitor
like velcade) to a currently accepted two-drug combination produced significantly
better results than using the two drugs alone." "Patients taking three
drugs — carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone — stayed free of disease
progression for 26 months on average," he said. "No one has reported anything
like this before for relapsed multiple myeloma." "Researchers found that
adding carfilzomib to standard treatment with lenalidomide and dexamethasone
resulted in an additional 8.7 months of remission, bringing it to 26.3
months — almost 50 percent longer than the 17.6 months of remission under
the standard two-drug combination. This was a phase III clinical trial
with 792 patients. (This is encouraging, two more years after a relapse.)
Note Mayo is the lead researcher of this drug, so is not unbiased.
So a key issue is the pros and
cons of velcade vs (newer) carfilzomib, since both are injectable proteasome
inhibitors made by different companies. Certainly carfilzomib comes with
a long list of serious side effects.
Injection protocol
Onyx
web site shows the recommended injection protocol is six injections
during a four week cycle: two consecutive days for three weeks of a four
week cycle. The infusion (into a vein) is fast, just 10 minutes. This is
for one year, then for next six months it's scaled back a little to four
injections per cycle: two consecutive days every other week.
Of course, the little shits
at Onyx on the many web pages devoted to kyprolis carefully conceal the
cost of the drug, but you can be sure it is expensive. So much for republicans
claiming that medical costs will come down if patients shop around. The
drug companies make this very difficult.
Will Medicare pay?
After 15 months of dealing
with Medicare and my cancer I still don't have a clue as to how to check
for whether a drug, a test, a consultation, or procedure would be paid
for my Medicare. With new (and likely super expensive) cancer pills being
appoved by the FDA for MM this could be 100,000 dollar issue for me in
the future. I find this on the Medicare.gov
web site:
"Talk to your doctor
or other health care provider about why you need certain tests, items or
services, and ask if Medicare will cover them. For more information, call
1-800-MEDICARE."
All I get from my oncologist
is warning that a test or drug I inquire about may not be paid for by my
insurance, but no hard specific information. In over a year I have never
gotten any specific medicare costing or coverage information from any of
my Lahey doctors who I sense avoid the topic like the plague. My local
GP is different. Last winter I needed two routine vaccines, one was give
to me in his office, but he told me I would be better off getting the other
from a pharmacist, because that way it would be covered by Medicare.
Vertebrae terminology
and anatomy
Vertebrae have a basic shape,
described by a common terminology, that is consistent through the whole
back and neck. The center hole, of course, is for the spinal cord, which
is protected by being enclosed in a flexible bony sheath. In the neck (cervical)
vertebrae two additional small holes on the sides are for blood (artery)
vessels to the brain. The bulk of the bone, which is toward the front of
the body, is called the 'body' and provides weight bearing. Notice it is
more massive in the lower (lumbar) vertebrae, which must bear the weight
of the chest, arms and head, and smallest in the neck (cervical) vertebrae
which only bears the weight of the head.
The bony loop around the
spinal cord has three main regions: 'body' (front, bot in figure), 'pedicle'(s)
(side extensions) and 'lamina'(s), which form the rear section of the loop.
Also in the main loop in the upper back and neck between the pedicle and
and laminar are 'facets'. The figure below left shows that the facet is
sort of a flattened (lubricated) area of the lamina as its joins the pedicle.
The figure below right shows the facets of the vertebrae align and slide
on each other (sort of like the knee). Bony projections that stick out
from the loop tend to be called processes. These projections serve as attachments
points for ligaments and muscles. All the vertebrae have a projection (process)
to the rear of the body, and as the figure below left shows these (spinous
process) tilt downward. Notice in the figure below left how tightly interlocking
the rear projections are and how their upper and lower facets line up allowing
each vertebrae some (controlled) motion relative the vertebrae above and
below.
In the neck I know these
rear projections form a mechanical stop which determine how far back you
can tilt your head, and very likely the rear projections of the vertebrae
in the spine provide a hard limit as to how far back you can arch your
back. Holes are called foramen, both the big one for the spinal cord and
little ones for the blood vessels. The holes for the blood vessels (transverse
foramen) in the neck are (in effect) created by the pedicle regions splitting.
The inside split is then called the pedicle and the outside split the lamella.
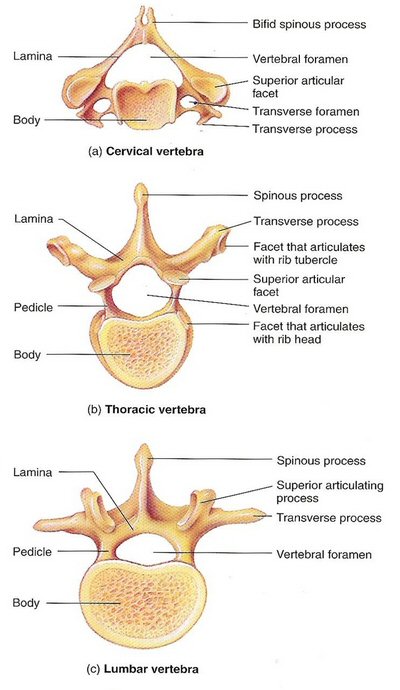 .
.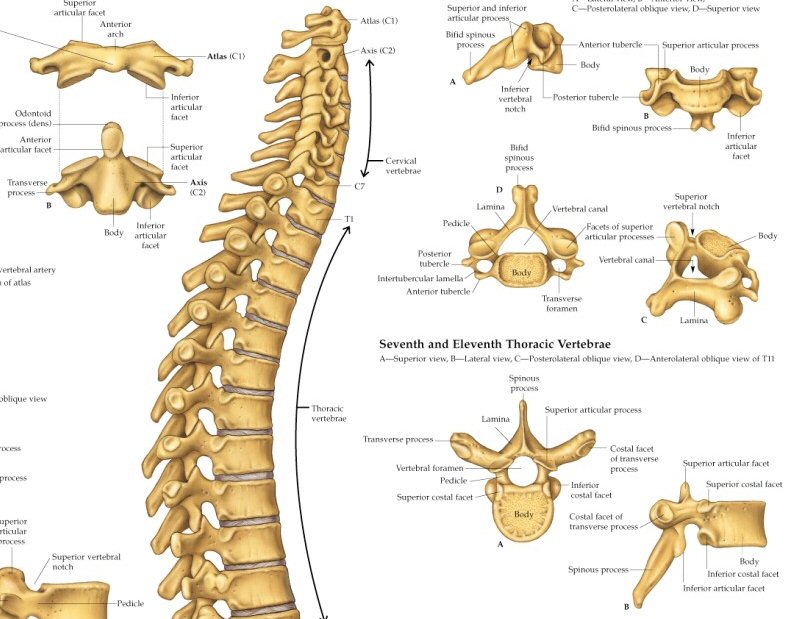
Vertebrae terminology
(source (left) -- http://anatomysystem.com/vertebrae-labeled/)
(source (right) -- http://www.anatomicalproducts.com/images/P/9850.jpg)
Cervical anatomy
My main interest is of course
C2 (axis) which in my case is what the cancer broke. In terms of the terminology
of vertebrae C2's vertical 'dens' projection sits right on top of C2's
'body'. C2's dens projects up into the main hole of C1 (atlas) forming
a pivot about which C1 (and the skull) rotate as the head turns side to
side. As a pivot it cannot be weight bearing. So the weight of the skull
(via C1) is born by the two large facets on the upper side of C2 that mate
with matching lower facets on C1, the facets providing a sliding joint
that allows +/- 45 degrees rotation between C1 and C2, rotation that I
have lost permanently because of my C1,C2 fusion operation.
The interface between the
C1,C2 vertebrae is quite unusual. A striking feature of spinal anatomy
diagrams is a (spongy) disk exists between each of the bony vertebrae,
but that is not true of the C1,C2 interface. There is no C1,C2 disk.
A fundamental reason is that the C1 vertebrae has no body, and disks go
between the (weight bearing) vertebral bodies! The video I saw about C1
and C2 called them 'atypical' vertebrae. The weight of the head presses
down on flat spots toward somewhat to the sides of C2, and it transmits
that force to C3 through C2's body and C2,C3 disk. The distance between
the C2 weight bearing facets and the C2 body forms a lever arm, and the
stress on this lever arm is lowered by the facets being toward the front
not too far from the body and dens.
The C1,C2 weight bearing
interface rather than being a disk is a sliding (cartilage like) joint
on both sides of the bony loops that allows C1 (and the skull) to rotate
+/- 45 degrees with respect to C2. These sliding joints support
allthe
weight of the head. In all other vertebrae interfaces the weight bearing
is through the 'body' of the vertebraes and the intervening disks. The
fact that the body of the C2 vertebrae on the top side is not weight bearing
allows its shape to be modified and to project up in the front forming
a 'dens' that servers as a pivot point around which the front rounded arch
of C1 turns. And C1 is unusual too in that it has no body. Where the body
would normally be, which is toward the front, it has an anterior arch that
pivots on the C2 dens as the head rotates.
Notice in the figure above
right how at the rear all the vertebrae seem to interlock. A side view
shows between the body and the large rear processes (projection) the bones
neatly line up. At this interface both the top and bottom vertebrae are
flattened and have cartilage (forming a facet) such that two (small) sliding
joints are created one each side of each vertebrae. This helps interlock
the vertebrae together, but still allows some (limited) movement between
them.
This is particularly important
to me as I have had C1,C2 fused, so I need to get as much rotation as possible
from my other other neck (and back) vertebrae facet joints. Eleven months
after my operation, a physical therapist has begun to work these C2 to
C7 facet joints to as she says 'stabilize' and 'loosen' them up.
Fracture of dens (Wikipedia 'Axis')
I either had a type II or
III fracture of C2 dens, though I would need to confirm this will my surgeon.
At my one year follow up I asked my surgeon this question. He said it was
a type II fracture, or (maybe) type II/III since it looks like there was
some extension into the body.
-- C2 (axis) forms the pivot
upon which the first cervical vertebra (C1, atlas), which carries the head,
rotates. Fractures of the dens, not to be confused with Hangman's fractures,
are classified into three categories according to the Anderson–D'Alonso
system:
Type I Fracture - Extends through the tip of the dens. This type is usually
stable.
Type II Fracture - Extends through the base of the dens. It is the most
commonly encountered fracture for this region of the axis. This type is
unstable and has a high rate of non-union.
Type III Fracture - Extends through the vertebral body of the axis. This
type can be stable or unstable and may require surgery.
How the C1,C2
dens joint really work
My cervical surgon says
the dens does not provide lateral support, but when he described
how lateral support was provided, I'm not sure he understood I was asking
about how the head is supported when the head is horizontal.
--------------------
Found an excellent video
(see under picture) focusing on C1,C2 that shows how the C1,C2 dens joint
provides lateral support for the head. C1's front (anterior) arch and the
C2 dens projection are touching, so the skull cannot move to the rear.
But I have always wondered how the skull is prevented from moving laterally
forward. The narration in the video provides the answer. A ligament runs
across C1 between its two side lateral masses that goes around the back
of the dens! To keep it from interfering with the spinal column this C1
ligament must be attached to the side masses quite far forward. This ligament
also protects the spinal cord by keeping the dens off to the side (really
the front) of the C1 large center hole. So there's the answer: C1 (and
hence the skull) is supported laterally by the big, strong C2 den with
a C1 bony arch on one side and a C1 ligament on the other. The C2 dens,
of course, is structurally connected to the spine.
C1 dens encircling ligament
After writing about the
C1/dens ligament (above), I found the figure below (right). It clearly
shows that C1 has a thick side to side ligament that does (as I had presumed)
wrap closely around the C2 dens. Thus it's clear the lateral stability
of the head is provided by this encircling of the C2 dens. In this way
the strength of the spinal column can support the weight of the head when
the bending over with the head horizontal.
This understanding helps answer
another question that has been bothering me since the operation. How did
the C1,C2 fusion operation, fixing the C2 to C1, hold the dens (and weakened
bone) in place so the fracture could heal? I can see now that with the
body of C2 attached to the body of C1 with hardware the dens in held in
place laterally by the C1 anterior (front) arch and a C1 right to left
ligament on the back side, and at least when the body is upright, gravity
will pull the dens down.
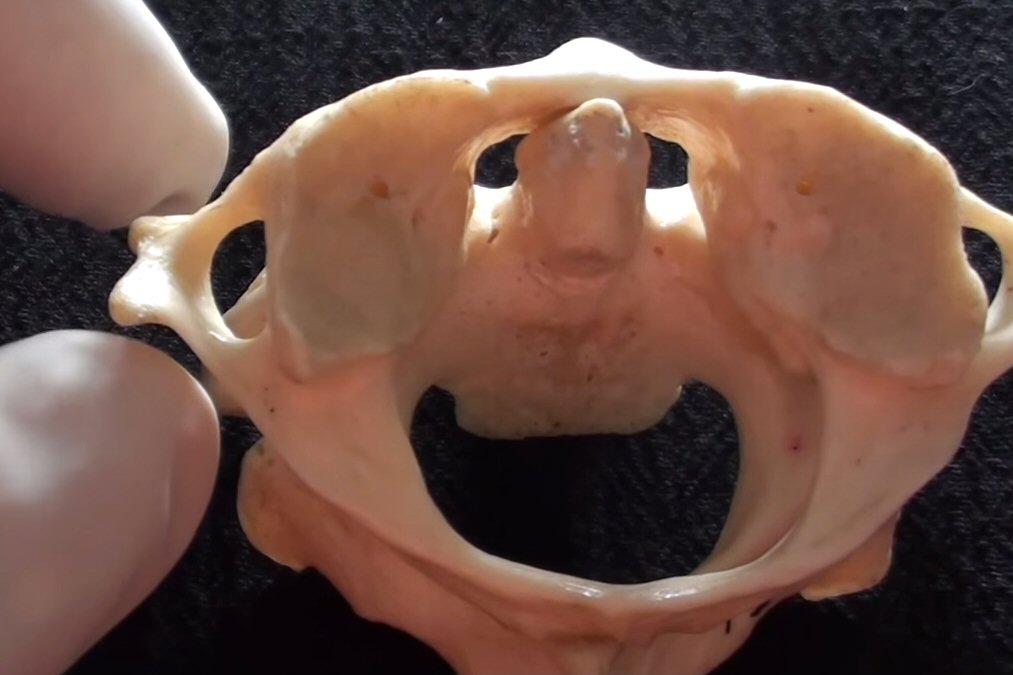 .
. 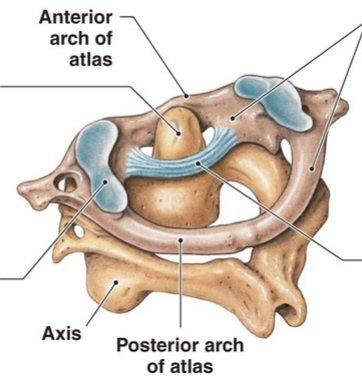
Left: C1 (atlas),C2 (axis) dens joint (video screen capture)
(these look like real bones)
Right: C1 ligament that wraps arund the C2 dens
(source, left -- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ebYFDTbtfUI)
(source, right -- https://sites.google.com/site/jointsofthehumanbody/cervical-vertebrae-by-priyanka)
Here's C1 rotating about the C2 dens
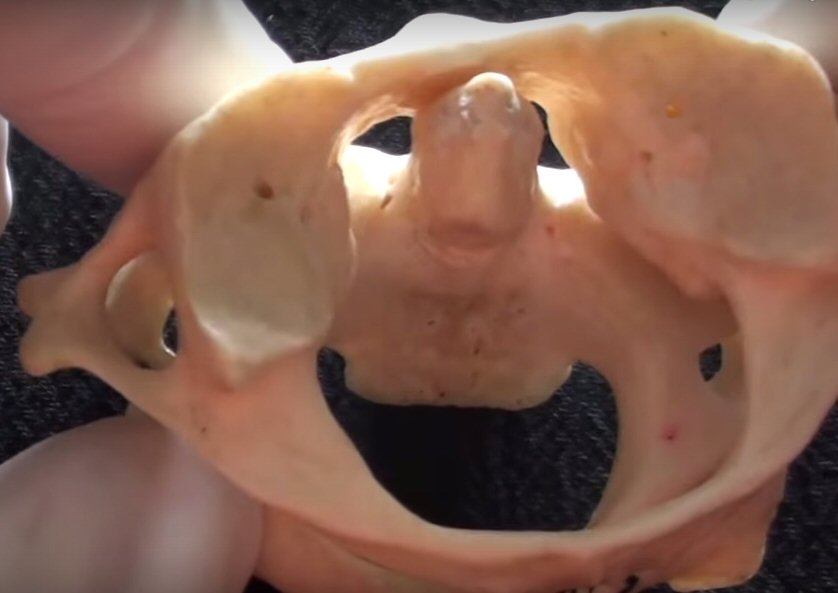 .
. 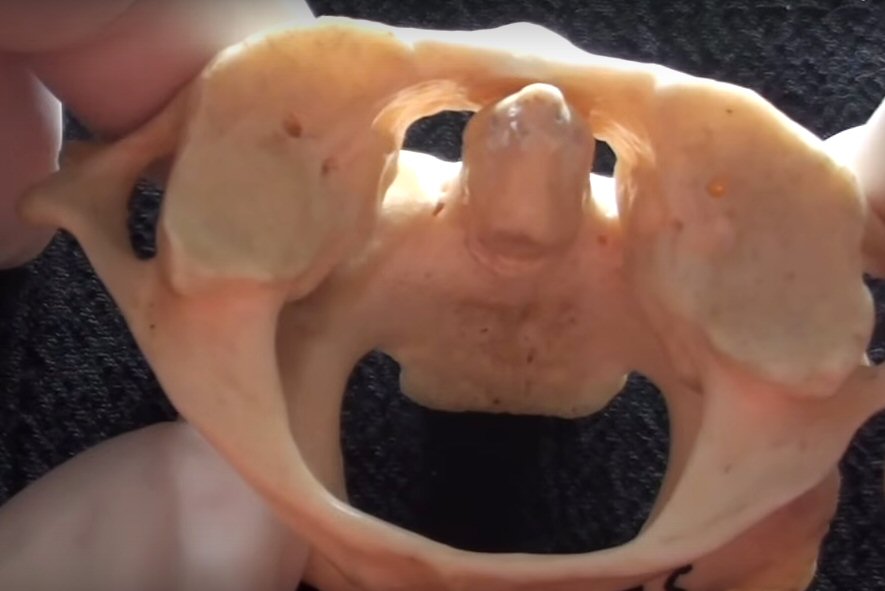
C1 pivoting on C2's upward projection (dens) allows the head to
substantially rotate
(C1's anterior (front) arch has an inside round facet joint with
cartilage where it mates with C2's dens)
(source -- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ebYFDTbtfUI)
Reviewing my scans
I have figured out something
about reviewing my scans (CT scans, MRI scans, and x-rays) at home. Lahey
records charges a lot for copies of my medical record, but (weirdly) they
provide DVDs of patient scans for free. However, there's a problem with
reviewing scans on your home computer, and I am pretty sure I have figured
out what the problem is.
The problem was clearly demonstrated
with the CT scan of my neck done 9/16/15, one year after my C1,C2 fusion
operation, and just an hour prior to my visit with my neck surgeon. The
CT scan was on the screen in the room where I was waiting for the doctor
to come in, and I was using the mouse to move it and look at it. The screen
display at the hospital was very nice with the screws clearly standing
out as they were (automatically) hi-lited in a different color. The whole
neck was displayed in 3D and with the mouse I was able to easily rotate
the image. When the doctor come in, he zoomed into the screws and showed
me a dark shadow near one of them indicative of lack of bone growth into
the screw. However, when I got the DVD of this CT scan I saw nothing like
what I had seen in the doctors room. The same thing happened in Oct 14,
where the excellent view of my T12 bone loss showed to me by my radiation
oncologist, I could never find on the DVD provided.
Primitive viewing software provided to patient
I think what is happening is this.
The hospital has state of the art, expensive, software that can take the
raw CT and MRI images and create polished 3D images for viewing. But what
the patient gets included, when his images are requested from the hospital,
is a very basic (primitive) software package that can only step through
the raw images and make contrast adjustments. No 3D modelling software
is given to the patient. The result is little information is available
to the patient from CT scan and MRI images. For example, I couldn't see
the screws at all at home, whereas in the hospital they stood out clearly,
much less the luciencies around the screws. X-rays may be the exception,
I don't know how much more the hospital software can process x-ray, though
I could hazard a guess that one thing it may be able to do is take calibrated
measurements. I should research this. I might be able ot find better
display software online.
Free healthcare software
A quick Google shows there
are free software viewing packages for CT scans available (geared to doctors),
though I would think it likely that the manufacturers of CT machine have
proprietary package. Below are a few that showed up searching 'ct
viewing software'. Some of these call themselves 'Dicom Viewers' as a common
file format is Dicom.
Wikipedia lists the following
Dicom viewers: 3DSlicer DicomIR Drishti GIMIAS
Ginkgo CADx InVesalius ITK-SNAP OsiriX
Voreen Xebra. These all have their own Wikipedia pages.
Scrolling down brings up a box of 'Free healthcare software', see
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OsiriX
http://unbeknownst.net/archives/466
patient posting recommending Mango for Windows
http://ric.uthscsa.edu/mango/
Mango (big package, lots of options)
https://beta.jackimaging.com/demo
simple viewer -- For those of you looking to view medical images without
having to download or install any software, try Jack's Imaging. Its a web
based drag and drop viewer that works with all medical images!
http://www.radiantviewer.com/
http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/
ImageJ is an java/nih viewer poster uses it with CT and MRI images
(customer unfriendly)
http://www.osirix-viewer.com/
OsiriX is the standard, open source free (?) viewer. Powerful 3d viewer.
Apple only.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Protein electrophoresis
equipment
General overview of protein electrophoresis equipment and procedure
I stumbled onto a maker
of equipment for protein electrophoresis (Bio-Rad). Their 47 page document
showed me there is a lot of scientific use for electrophoresis equipment.
The cells of every living thing (plants, animals, bacteria) are made up
mostly of proteins and with the use of a mortar and a centrifuge the proteins
can be extracted so they can be put into electrophoresis equipment. Electrophoresis
can be used to determine a lot of things, for example the molecular weight
of an unknown protein, hence there are literally hundreds of variables
in the process. In its 47 pages there was no mention of using Bio-Rad equipment
to analyze blood.
The impression I get is that
there is a lot of manual technician steps in this process: sample preparation,
loading and unloading the gel case, fixing and staining the developed gels,
digitizing the stained gels. Below are notes from Bio-Rad's 47 page overview
of their equipment and procedures (Guide to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
and detection):
-- sample preparation: solids
(mammal tissue, plant leaves) ground to fine powder in nitrogen cooled
mortar then centrifuged;
bacterial samples centrifuged (several times to remove all the cellular
material);
blood samples must be prepared by removing all the blood cells, but surprisingly
blood is not mentioned in sample preparation
-- table top box might contain
a dozen vertical each 6-8 inches long, 1 mm thick
-- samples (pre-heated to
100C!) are entered at the top and diffuse downward
-- voltage 10-20 V/cm or
(200 V across gel (@ 30 ma, 6 watts)
-- operating voltage is
limited by ohmic heating of the gel
-- 30-40 min typical diffusion
time
-- diffused gels are floated
off the gel plastic holder into water (washed for 15 min)
-- separated proteins in
a gel can't be seen with naked eye so they are stained with a protein stain
-- staining requires: solution
to fix the protein, exposure to a dye, wash to remove excess dye (30 min
wash)
-- most popular stains are
a blue dye (Coomassie Blue) and florescent stains
-- florescent stains seem
like they are more specialized, more expensive and need a camera or florescent
scanner
-- staining time typically
2.5 hr
-- 10:1 variation in sensitivity
of the various blue stains
-- Bio-Rad offers a 'stain-free'
florescent system too
-- after staining (blue)
bands visible to naked eye
-- in modern labs the blue
stained gel (electropherogram) is digitized by dedicated equipment
-- three ways to digitize:
flat bed densitometer, which is a modified document scanner;
CCD camera with a light box illumination (CCD can be cooled to reduce
noise);
laser scanners are used with florescent dyes (powerful as frequencies can
be matched to specific proteins)
-- specialized software processes
the digitized gel image
Bio-Rad electrophoresis equipment
http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/Bulletin_6040.pdf
Blood electrophoresis
-- Supporting media fall
into two main classes: 1) supports which allow separation of molecules
solely on the basis of net molecular charge (e.g. cellulose acetate, agarose
gel); 2) supporting media exerting a sieving effect on the compounds
being separated (e.g. polyacrylamide gel): the gel can be considered as
a porous medium in which the pore size is of the same order as the protein
molecules. The result is that a molecular sieving effect is observed in
addition to the electrostatic separation and hence the resolution power
of these gels is much greater
-- There are about
25 or more serum proteins bands observed on polyacrylamide gel in comparison
with six bands observed on agarose gel. The many bands seen with polyacrylamide
support medium present a complex picture that is hard to interpret and
appears to help little in routine clinical laboratory diagnosis. Except
for specialized purposes, polyacrylamide cannot be recommended for routine
serum protein electrophoresis.
-- Proteins are amphoteric
molecules: they are either uncharged or negatively or positively charged
particles, depending on the pH of a buffer used for analysis. The buffer
helps to maintain a constant pH, and it ensures that each protein will
maintain a constant charge throughout the course of the separation.
-- If the buffer of pH 8.6
is used the most of proteins are negatively charged and move toward the
anode at a rate dependent on their net charge
-- ** Albumin has the highest
mobility from all of the fractions. (This explains which way the diffusion
goes. Albumin is a small mobile molecule so it ends up at the far end of
the diffusion, whereas the gamma and beta regions, where the IgG monoclonal
spike is found, are at the near end near the buffer, gamma being the nearest.)
-- Proteins therefore, are
usually denatured (unfolded) in the presence of a detergent such as sodium
dodecyl sulfate (SDS) that coats the proteins with a negative charge. (Wikipedia)
-- In most proteins, the
binding of SDS (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) to the polypeptide
chain imparts an even distribution of charge per unit mass, thereby resulting
in a fractionation by approximate size during electrophoresis. SDS is a
strong detergent agent used to denature native proteins to unfolded,
individual polypeptides. When a protein mixture is heated to 100 °C
in presence of SDS, the detergent wraps around the polypeptide backbone.
In this process, the intrinsic charges of polypeptides becomes negligible
when compared to the negative charges contributed by SDS. Thus polypeptides
after treatment become rod-like structures possessing a uniform charge
density, that is same net negative charge per unit length. The electrophoretic
mobilities of these proteins will be a linear function of the logarithms
of their molecular weights. (In other words this technique with heating
and a detergent unfolds the proteins and critically imparts a charge on
the protein proportional to its length.)
-- The gamma band - immunoglobulin
(IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM). Paraproteins (in multiple myeloma) usually
appear in this band. (Wikipedia) (However, this is apparently not the case
for me where Dana Farber labs reports my monoclonal (IgG) spike is in the
beta region.)
-- The types of gel most
typically used are agarose and polyacrylamide gels. Each type of gel is
well-suited to different types and sizes of analyte. Polyacrylamide gels
are usually used for proteins, and have very high resolving power for small
fragments of DNA (5-500 bp). Agarose gels on the other hand have lower
resolving power for DNA but have greater range of separation, and are therefore
used for DNA fragments of usually 50-20,000 bp in size, but resolution
of over 6 Mb is possible with pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE).
Polyacrylamide gels are run in a vertical configuration while agarose gels
are typically run horizontally in a submarine mode.
-- ** Agarose gels (extracted
from seaweed) do not have a uniform pore size, but are optimal for electrophoresis
of proteins that are larger than 200 kDa. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
(PAGE) is used for separating proteins ranging in size from 5 to 2,000
kDa due to the uniform pore size provided by the polyacrylamide gel. (Wikipedia)
(In other words polyacrylamide gel works over a wike range of protein mass
(5 - 2,000 kDa) whereas agarose gel only works well for larger proteins
(> 200 kDa).
-- * Question: what is kDa
(weight) of blood proteins? Human albumin has a molecular mass of 66.5
kDa. In the region between beta and gamma is found C-reactive protein
(110-144 kDa). IgG is 150-170 kDa (144 kDa = heavy chains 50 kDa each,
light chains 23 kDa each).
-- ** (My IgG monoclonal
falling in the beta region must mean is it a little smaller than typical
IgG protein. There's an easy explanation of this. IgG antibodies may have
a range of sizes, so the IgG mass numbers given are averages, whereas an
M-spike is a clone of a particular IgG antibody.)
Electrophoresis for multiple myeloma
A 2005 article
(for medical types) says the gel used when serum proteins is spread is
agar.
-- Gamma region is composed
predominantly of antibodies of the IgG type.
-- An M protein is characterized
by the presence of a sharp, well-defined band with a single heavy chain
and a similar band with a kappa or lambda light chain. (I don't understand
this. Isn't the M-spike a complete antibody? They seem here to be describing
free light chains, but that can't be right because concentrations of those
are tiny, measure in mg.)
-- Definitive diagnosis of
multiple myeloma requires 10 to 15 percent plasma cell involvement as determined
by bone marrow biopsy. At MM diagnosis the M-spike is normally 3 g/dL or
higher. Less than this and the dignosis is usually Monoclonal gammopathy
of undetermined significance.
-- Monoclonal antibodies
cannot be excreted by the kidneys, but free light chains are excreted by
the kidneys into the urine, so a small fraction of MM patients whose cancerous
plasma cells to not secrete (monoclonal) antibodies, their MM diagmostic
signal is high levels of free light chains in the urine.
-- A liter is the volume
of a cube 10 cm on a side, hence 1 uL (or 10^-6 L) is a cube 1 mm on a
side. There are more than a million red blood cells in 1 uL of blood!
Beckman Coulter
Paragon CZE 2000 was a pioneering
automated (capillary) electrophoresis system for clinical use made by Beckman
Coulter. Their site claims nearly all electrophoresis system use their
technology. For capillary electrophoresis they redirect to Sciex
http://sciex.com/products/capillary-electrophoresis-instruments
==============================================================================================================
Big picture
of MM treatment options
(8/27/16)
Now about two years into
chemo for MM, I have some perspective on treatment options for MM. While
doctors tend to tell patients here are a lot of drug options for MM, that's
not really true. For those patients avoiding a stem cell transplant and
going down the newer route of what is often called 'novel agents' of targeted
MM drugs, the treatment choices are few. Sure there are a lot of drugs,
but when you look at their mechanism of action, you find there really
are only TWO established classes. By established I mean MM drug classes
whose original members have a decade or more track record. Within each
class there are first, second and sometimes 3rd generation of drugs as
the manufacturers tweak the formulaS working to make the drug more effective
with fewer side effects.
One class is the anti-angiogenic
& immunomodulator typified by thalidomide and its various improved
analogues Revlimid and Pomalyst. This class of drugs are all from
Celgene,
which have them wrapped up in patent protection. The second class of drugs
are proteasome inhibitors typified by Velcade (bortezomib) and a second
generation competitor carfilzomib (Kyprolis). Here there are two companies,
Millennium
Pharmaceuticals (now Takeda)
maker of Velcade and Onyx Pharmaceuticals
(now Amgen) maker of Kyprolis, both
of which have an infusion version and are working on a pill version. Only
one pill (Ninlaro
from Takeda) at this point has been approved by the FDA and is on the market
(2015), the other proteasome inhibitor pill (from Onyx) is still in clinical
trials.
I figured out this
class arrangement by every time I heard mention of a MM drug I added it
to this essay and did a little research on it, which is easy to do since
most drugs have a wikipedia page and drug manufacturers are quick to set
up web sites dedicated to their 'hot' new drugs. And was surprised to see
that time and time again the 'new' drug fell into a well established class.
(see MM drugs organized by class)
The headline news
in 2015 is that after Amgen bought Onyx for 10.4 billion it layed off 300
of the 500 Onyx staffers. Well that's encouraging..., especially since
I am now on infused carfilzomib (Kyprolis) made by Amgen.
(Patient sharing web
site from Amgen for carfilzomib.)
It's sort of a dirty little
secret but your MM oncologist really only has a two step plan to
offer you. At least two steps that have a track record and work fairly
well for a lot of MM patients. Sure there is always the cutting experimental
edge but this is the end game, response rates are low and added survival
time is measured in months. I have talked to three cancer doctors, my regular
haematological oncologist, who I see frequently, a consulting haematological
oncologist at a world famous MM research center, who I see ever few months,
and another haematological oncologist from which I sought a second opinion.
Not one of them laid out this big picture, that MM treatment is essentially
a two step process.
The goal of both steps is
a remission, i.e. driving the cancer load in the body down to low levels.
With MM patients this is critical as the cancer is ussually widespread
throughout the body (metastatized) before the cancer is even diagnosed,
so the patient depends on the chemo holding the cancer levels low enough
so that his bone (and other) tumors do not grow. The first remission is
statistically the longest and probably with the best quality of life as
you are taking fewer drugs and they may be all in pill form. The median
(50%) remission time for the common rev/dex (Revlimid + dexamethasone)
chemo is roughly two years. (I got only 1.5 yrs) When the cancer outruns
your initial chemo, your first remission is ended and you transition to
a new class of drugs to try for a second remission. Statistically this
remission will be shorter and not as deep.
The nature of clinical
thinking here can be glimpsed by the jargon the doctors use among themselves
to describe this step one to step two chemo transition for MM, but which
I will bet is rarely told to patients. My doctors notes after my first
remission ended read like this: "Relapsed and refractory IgG lambda myeloma
with multiple new sites of bone lesions/plasmacytomas." Recommendations
for new chemo are describes as "salvage therapy".
This is where I am now. I am
still less than two years from diagnosis (23 months), but my first remission
already ended a few months ago, and I am a couple of months into step two
hoping for second remission. In step two I take three drugs, not two as
before, and one of them is by infusion, so I much more tied to the hospital
and spend a lot of time there.
==============================================================================================================
End of 1st remission,
switch to new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
(6/27/16)
4.5 month overview -- 2nd remission
(11/18/16)
It's time to sum up. How
am I doing on the new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo after 4.5 months? The answer
according to my blood work is pretty well. A quick perspective is just
look at the movement of two key blood numbers for MM (free light chain
and M-spike): up is 'bad' and down is 'good'. The general pattern of both
of these numbers since the chemo change has been downward and their settling
in to what appears to be a new and relatively low plateau, a '2nd remission'
if you will. So the big question going forward is how long this '2nd remission'
will hold. And since blood work is only an 'approximation' of what
is happening in the body, what will the next Pet scan show?
Free light chain (11/18/16)
Using the plotting function
in MyLaheyChart here are my free light chain values from the first of the
year. I have had from the beginning an IgG lambda cancer so the relevant
curve below is the orange one at the bottom. Notice the dramatic drop in
lambda free light chain at 7/1/16 when chemo was changed from rev/dex.
During the first six months of 2016 while on rev/dex, it was bouncing around
near 10 mg/dL (8 to 15 mg/dL), far above normal and at a level which clinical
trials use as a threshold of disease progression. Later an MRI showed at
this level a large plasmacytoma had grown behind my left eye that was affecting
my vision. With the change in chemo it dropped quickly to the upper end
of the normal region and in the 4.5 months since it has settled nicely
into the normal region.
Free light chain is important
to track because prior to the chemo change, which my (consulting) oncologist
at Dana Farber was recommending, he said he was looking to drive the free
light chain down into the normal region, and the new chemo has done this.
In the last two months my IgG lambda monoclonal spike has been joined by
a smaller IgG kappa monoclonal spike (two cancerous cell lines!) The kappa
free light chain (blue, top) was down in the normal region months before
the chemo change. The small pop up (one data point and only to 4 mg/dL)
on the right I dismiss as most likely noise.
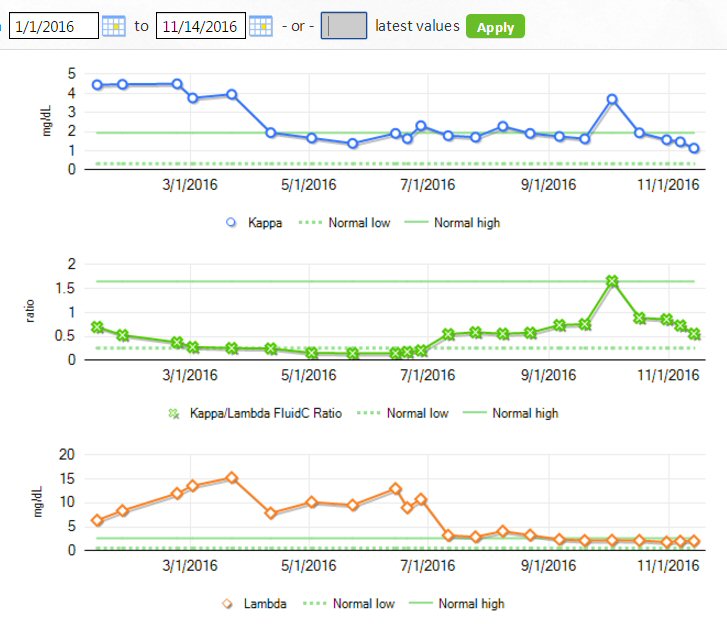
kappa (blue) and lambda (red) free light chains (1/1/16 to 11/16/16)
6/27/16 marks the chemo change, and clearly it caused a big drop
in lambda free light chain (red, bottom)
from 10 mg/dL (disease progression threshold) into the normal region
(< 2..63 mg/dL)
(solid lines indicate the boundry of normal regions)
Plot of my M-spike(s)
numbers for 2016 (updated 12/12/16)

M-spike(s) --- IgG lambda and IgG kappa for 2016 with three
changes in chemo:
rev maintence dose increase (10 mg => 20 mg) (2/29/16)
rev maintence => rev/dex (3/25/16)
rev/dex => pom/carfilzomib/dex (6/27/16)
I've plotted my M-spike data
for 2016 to go with the free light chain plot. I have marked on the plot
the three changes in chemo that occured during the year. It's a complex
plot with two M-spikes. When the IgG kappa spike pops up in recent months
I plot it along with the sum of the two M-spikes. I've included a 0.04
g/dL baseline, my best guess for the quantitative threshold of the test.
The lambda M-spike has come down nicely since the change to pom/carfilzomib'dex
chemo, but SLOWLY taking 4.5 months to drift down from .26 to .07 g/dL
with a recent pop up to .12 g/dL.
It's taken more than four
months but the M-spike has finally following the light chain down. Prior
to the shift from rev/dex chemo my M-spike was running about ,25 g/dL,
which is about half the disease threshold. After a couple of months it
had dropped only a little (.17g/dL), so I was disappointed. then up popped
an IgG kappa M-spike, so now I had two M-spikes! Each spike is monoclonal,
so the cancer load is the sum of the two spikes, and looked at this way
in late sept and early oct the area under the two M-spikes (total) was
back up .25g/dL, no change. But in the last month (oct to nov) the M-spikes
have drifted down. My latest lambda M-spike is 0.07 g/dL, and the kappa
M-spike is there but can't be quantified. However my best guess is the
M-spike measurable threshold is probably around 0.05 g/dL, so the total
of the two M-spikes can easily be .05 + .07 = .12 g/dL. From this point
of view the drop in the M-spike is less impressive more like half (.25
g/dL => .12 g/dL). (For gods know what reason MyLaheyChart won't plot it)
.
Update on new
pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo (8/24/16)
The transition to 2nd chemo regeim
is a crucial point in a MM patient's life, because frankly there aren't
a lot of good options after step two!
As I write it's 8/24/16 and
I have now completed two full cycles of pom/carfilzomib/dex. Pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo was begun on mon June 27, 2016. I am now a couple of days into the
3rd cycle and the data from the completed 2nd cycle is begining to come
in. I had my blood tested every two weeks on the new chemo, so that
has given me four data points for the two cycles, and it's been kind of
a wild ride.
On a change of chemo where
a downward trend is expected the blood component to monitor is the free
light chain. It responds more rapidly, without a lag that affects M-spike.
Here are my recent (lambda) free light chain numbers (in mg/dL). The normal
range for lambda free light chain is (0.57 - 2.63).
|
|
date (2016)
|
lambda free light chain
(0.57 - 2.63)
(mg/dL)
|
comment
|
rev/dex
reference
|
june 27
|
10.80
|
last number on rev/dex
(av of last 7 numbers is 10.0) |
| new chemo --- change to pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo |
cycle 1
of new chemo
|
july 11
|
3.25
|
first number on new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo |
|
|
july 25
|
2.93
|
|
cycle 2
of new chemo
|
aug 8
|
4.11
|
2nd cycle of pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo has +35% dose increase in carfilzomib |
| |
aug 22
|
3.30
|
(average of first 4 new chemo numbers is 3.3) |
Wild ride!
The initial drop from 10.80
mg/dL after just two weeks on the new chemo to 3.25 was very encouraging.
The new chemo looked like it was going to work! The next reading
two weeks later at the end of the first cycle continued the downward trend
to 2.93 mg/dL not far from the top end of the normal range of 2.63 mg/dL.
To put this in perspective free light chain had been hovering around 10
mg/dL for a while on rev/dex, and this is the threshold clinical trials
use to indicate disease progression. A pet scan did in fact show I had
some disease progression at this level, including two plasmacytomas. The
new chemo quickly dropped the free light chain down by a factor of 3, which
looked good.
However the next number two
weeks into the 2nd cycle, where the dose of carfilzomib had increased by
35%, was a shock because it rose 40% (2.93 => 4.11). This looked BAD, because
it seemed to indicate that after just one month into the new chemo the
cancer was already beginning to find a way around it and growing! However,
two weeks later at the end of the 2nd cycle a pleasant and unexplained
surprise, the free light chain dropped down (4.11 => 3.30) close
to where it was initially. A wild ride. So now maybe after two full cycles
a trend is emerging, which is that the new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo has
reduced lambda free light chain by about a factor of three from rev/dex
chemo, taking it from the clinical trial disease progression threshold
of 10 mg/dL down to a level to about 1/3th of it or 3.3 mg/dL. A definite
improvement.
Free light chain is noisy
With more numbers come more
perspective. When I look back in my master table at free light chain values
while still on rev/dex I see it varied around quite a bit. Sure in seven
readings from Apr to June 2015 it averaged about 10 mg/dL, but individual
readings varied from 8 to 13. In other words free light chain is (as an
engineer would day) is noisy, it varies around a little. With this
perspective the four readings under the new chemo average 3.4, and the
bounce from 2.93 to 4.11 and back to 3.30 is probably best explained as
just noise. The new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo looks at this point that
it has decreased my free light chain about a factor of 3. Whether this
is low enough to stop my tumors from growing remains to be see. A new Pet
scan is coming up, which should provide some perspective.
In early oct 2016 the kappa
free light chain shows a marked jump that stands out clearly in the graph
below (blue) to 3.71 mg/dL well outside its normal range (1.94). This combined
with a newly visible kappa M-spike that was still rising (0.11 g/dL) was
worrying, but with two additional readings over the following month it
now appears that this single high kappa free light chain reading looks
more like noise.
-------------------------------
In May 2016 about 20 months
after diagnosis my cancer status changed dramatically. My 1st remission
ended with the discovery of two plasmacytomas (soft cancerous tissue mass)
and several active bone lesions. This is bad....
For about 4-6 weeks prior
to the change in status I began having some vision issues, I couldn't see
my large screen TV across the room clearly. I finally figured out this
was due to double vision when my eyeballs were oriented right in my head.
Looking straight ahead or eyeballs to the left I could see clearly. This
report to my doctors of double vision lead to a brain (head) MRI which
found a large soft cancer mass (plasmacytoma) behind by left eye in the
sphenoid bone. This triggered a full body PET scan which located a second
plasmacytoma in my rear left 9th rib, which likely fractured prior to my
diagnosis, as well as three metabolically active lesions (mandible, pelvis,
2nd rib).
For two weeks (5/23/16 to
6/3/16) the plasmacytoma behind my left eye was treated with radiation
(20 grays) to shrink it, during which at my insistence rev/dex was continued.
An active lesion in my mandible (jaw) was also irradiated at the same time.
The finding of growing plasmacytoma and bone lesions means that even though
my M-spike is still down 95% (.25 g/dL), about half the level normally
defined as disease progression (.5 g/dL), my current rev/dex is no
longer working effectively and a new chemo treatment will be needed. However,
my free (lambda) light chain, which has hovered for months near 10 mg/dL,
is at the about at the level normally defined as disease progression. It
is substantially above normal (2.63 mg/dL), and getting this number down
into the normal range will be a target of the new chemo (said the Dana
Farber specialist).
Timeline of chemo change (summer 2016)
5/16/16
MRI finds large plasmacytoma in sphenoid bone behind my left eye. Triggered
by my reports of double vision.
5/19/16
Pet scan (whole body) finds several metabolically active bone lesions.
5/23/16 - 6/3/16
Two weeks of radiation of left eye plasmacytoma and jaw lesion (rev/dex
chemo continued during radiation)
6/13/16
Meeting with Dana Farber MM specialist who recommends switching to pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo
6/27/16
pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo begins (carfilzomib soft started at 75% of final
strength for first cycle)
7/11/16
first look (1/2 cycle) at lambda free light chain on new chemo shows a
nice drop (10.8 mg/dL => 3.25 mg/dL),
not too far from the upper end of normal (2.63 mg/dL)
(9/12/16)
Follow up appointment scheduled with Dana Farber doctor (8:00 blood, 9:00
doctor)
Relapsed and refractory
Doctors notes from a June
13, 2016 meeting with a specialist at Dana Farber describes my condition
as "relapsed and refractory IgG lambda myeloma with multiple new sites
of bone lesions/plasmacytomas." Recommendations for new chemo are describes
as "salvage therapy".
New
agressive chemo for 2nd round -- pom/carfilzomib/dex
(7/11/16)
First quick look (just two
weeks in) at the switch from rev/dex to pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo shows
a good initial response.
Message to my oncologist (7/12/16)
In just two weeks
(1/2 cycle) into my new pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo my lambda free light
chain, which for the last five months has hovered around 10 mg/dL (8 to
13), a level associated with disease progression, has dropped by a factor
of three to 3.25 mg/dL, getting close to the upper end of its normal range
(2.63 mg/dL). I'll take this as good news.
Doctor's reply
Agreed, I was happy to see
the results. Finally some good news!
Email to family and friends (7/13/16)
My first peek at how my
cancer will respond to my new 2nd generation chemo is good.
The blood objective the Dana
Farber doctor mentioned was to drive my leading cancer indicator (lambda
free light chain) down into the normal region. It was sky high when I was
diagnosed at 379 mg/dL, but for months has hovered around 10 mg/dL, which
clinical trial use as a threshold of disease progression, meaning above
this level bone tumors can grow.
Just two week into the new
chemo, still soft starting at 75% of its final strength, dropped the lambda
free light chain from 10.8 mg/dL to 3.25 mg/dL. A nice drop and not too
far from the top end of the normal region at 2.63 mg/dL.
Some not so bad things about carfilzomib injections
(7/26/16)
Having completed one full
cycle of carfilzomib infusions and the first week on my second cycle I
have some reflections on the need to go the hospital six times a week for
the infusions. The protocol for carfilzomib is two infusions a week on
consecutive days for three weeks followed by a week off. While the actual
carfilzomib infusion is 10 min, with the saline given before and after
the visit to the infusion room, scheduled for 1.5 hr, typically runs long
approaching 2 hrs.
The most important good thing
is that my first preliminary peek at my numbers shows that my new pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo seems to working for me. My lambda free light chain (I have a lambda
MM), which is a leading indicator, in the first two weeks dropped from
10.8 mg/dL (slightly above the disease progression threshold) to 3.25 mg/dL
(not too far above the upper end of the normal range). I was naive to a
protease inhibitor and since my rev/dex first remission ended after after
only 20 months with a bang (finding of two plasmacytomas), my Dana Farber
consulting doctor recommended what he said was the most
active of
the protease inhibitors, carfilzomib, which is taken by infusion as opposed
to the new Ninlaro which is a pill.
The infusions don't hurt
so I take a book and read. The only side effect from the infusions I have
had is some minor black and blueing and muscle swelling near the site of
the needle. When the carfilzomib is delivered by the pharmacy and about
to put into the tubing, the protocol to avoid a mistake is to have a second
nurse come over to verify that the markings on the bag match what is on
the Epic screen and my wristband. I presume the same sort of double checking
happens in the pharmacy, but of course I have no way of verifying this.
So the diffusions don't mess
up my summer travel plans I schedule all my infusions for mon and tues.
For me this works out well allowing me to get to ME mid week for a few
days avoiding the weekend traffic. The infusion room at Lahey hospital
is large and friendly place with nice nurses easy to talk to, and you get
to know each other because you are there so often for so long. That's a
plus.
Carfilzomib risk breakdown
Here is some perspective
on serious (grade 3/4) adverse effects of carfilzomib from a Canadian report
on tht Aspire phase 3 clinical trial. This was a trial that compared (carfilzomib
+ rev/dex) to (rev/dex) for 18 months in relapsed MM patients. The total
adverse effect percentage of 83.7% for carfilzomib looks extremely high,
but the chart below from the Canadian report shows the details. Roughly
17% (72) of the 400 had very serious problems (cardiac failure, deep vein
thrombosis, etc), but about half of the reported events were neutropenia
(low white blood count) and thrombocytopenia (low platlets). The
excess severe events vs control was more like 7.5%,
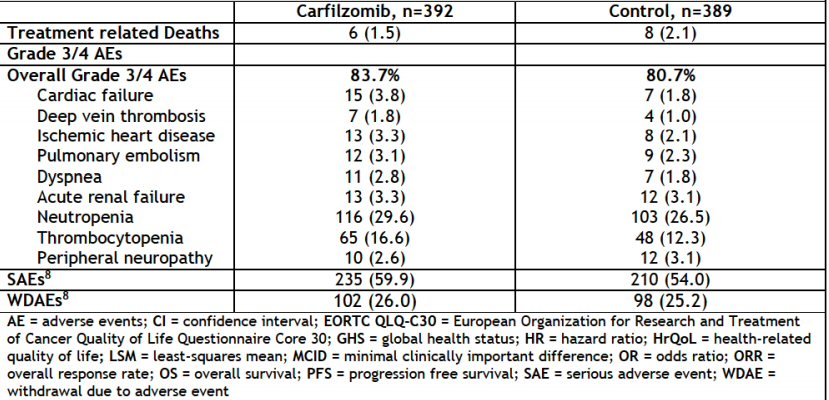
(source --- https://www.cadth.ca/sites/default/files/pcodr/pcodr_carfilzomib_kyprolis_mm_fn_cgr.pdf)
Aspire
phase 3 clinical trial results for carfilzomib (2015)
This phase 3 trial reported
in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2015. One reviewer commented
that "the patient population was predominately a relapsed and early-relapse
population—both features that favor better outcome." Here's the key results
of the Aspire Phase 3 trial, adding carfilzomib to rev/dex vs rev/dex.
Carfilzomib was given for 18 months, rev/dex was continued. (from
the Canadian report). I eyeball the 50% point of disease free prgression
to be 28-29 months (median = 26.3 months). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=N+Engl+J+Med+372%3A142-152%2C+2015
This trial is close to my
personal history. For a few months after my numbers started to rise in
early 2016 I was put back on rev/dex. Withthe discovery of plasmacytomas
in may 2016 the proteasone inhibitor carfilzomib was added to my chemo,
and differing from the trial (slightly), 3rd generation Pomalyst was swapped
in for 2nd generation Revlimid used in the trial. I responded quite well
to the change, see 'Plot of my M-spike(s) numbers for 2016' (above).
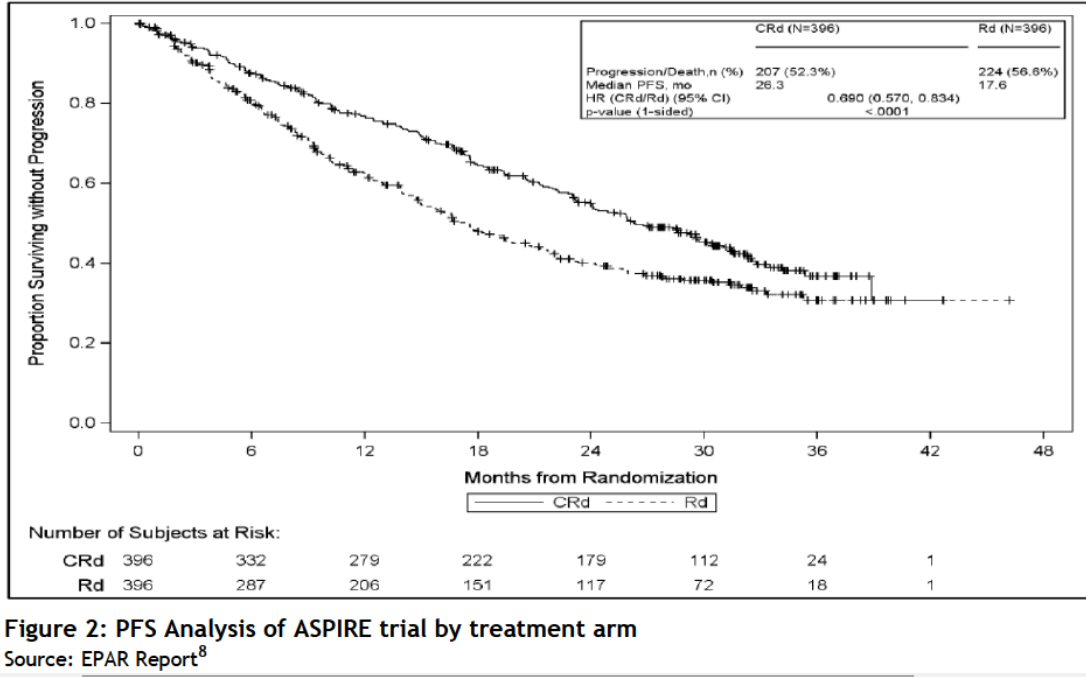
Aspire Phase 3 trial, adding carfilzomib to rev/dex (Crd) vs rev/dex
(Rd)
(source --- https://www.cadth.ca/sites/default/files/pcodr/pcodr_carfilzomib_kyprolis_mm_fn_cgr.pdf)
==========================================================================================================
Dana Farber
update on my cancer (jan 2017)
Latest meeting notes from
Dana Farber say my response to date of therapy, meaning the three drugs
I have been on since the beginning of summer 2016, has "quite impressive",
and I am tolerating them "quite well". It detailed how my blood cancer
numbers are quite low (referencing the M-spike plot I made and brought
with me). surprisingly there was no mention of my good recent Pet scan.
So it says 'ideally' I should remain on these three drugs 'until disease
progression', i,e. until they stop working for me.
The fly in the ointment,
however, is that my shortness of breath and getting run down is worrisome
to him given that carfilzomib (the infused drug) has a known tendency to
damage the heart and lungs. And I know the longer you take drugs like this
the more likely they are to do damage, so he is advising that follow up
tests be done to check out my heart and lungs.
I hope they don't find
anything, because if they do he told me carfilzomib would be swapped out
(in a heartbeat) for the new drug daratumumab, which I know is pretty much
the end of the line for MM chemo (though of course he doesn't tell me this).
In clinical trials its response rate was lousy (only about 1/3rd of patients
responded) and not for very long.
Nothing much new here that
except for the clinical concern for my heart and/or lungs possible being
affected by the chemo and the reason I am run down. It's fully consistent
with my earlier prediction I will 'likely' die in 2017 and 'very likely'
to die in 17/18. Even in the 'ideal case' getting to the end of 2017 without
disease progression would mean I would be on pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
for 18 months, and that is a long, long, time on this chemo with its well
known toxic side effects. I am meeting with my oncologist at Lahey soon,
and my expectation is there will be agreement with the Dana Farber specialist
and will schedule another acoustic flow heart test and a simple lung test
or two.
My oncology history summary
Below is my oncology history
attached to jan 2017 Dana Farber meeting notes. It is a concise summary
of the high points of my voluminous cancer history. I don't really
know who assembled this, but I suspect it was done at Dana Farber either
by my oncologist there, or possibly by a physician assistant. Probably
dictated as my detail history (I have 92 pages) was read through. This
history summery runs from sept 2014, when I was diagnosed, to late june
2016, when chemo was changed to pom/carfilzomib/dex after my first remission
ended with a plasmacytoma found behind my left eye. (The numbers and tests
look right, but missing is a quick (2.5 wk) change in chemo between the
ending of 10 mg revlimid maintenance and return to 25 mg Revlimid/dex in
spring 2016, which was a doubling of Revlimid (no dex) to 20 mg. It had
no effect of the rising numbers, so was quickly abandoned.)

nCR --- near Complete Response (for M-spike)
len --- Revlimid (lenalidomide)
Data Farber meeting notes (1/18/17)
The relevant section on
chemo says, 'It would be ideal to remain on current therapy until disease
progression, but if dyspnea (shortness of breath) prevents this, then daratumumab
could be swapped in for carfilzomib.' As of the date of this meeting I
had been on 'current therapy' (pom/carfilzomib/dex) for about 6.5 months
(since june 29, 2016). While the term 'dyspnea' is used (below) my shortness
of breath cmes only from my history is neither sudden nor very severe.

dyspnea --- Difficulty in breathing, often associated with lung
or heart disease and resulting in shortness of breath.
Creatinine lab values disagree
The Dana Farber notes (above)
refer to a creatinine level of 1.49 mg/dL (on 1/18/17).
This is
higher than Lahey has measured for two years and indicates some impaired
kidney function, yet Lahey labs has measured the same parameter (creatinine)
twice within 30 days, once preceding and once after the Dana meeting,
and both times got 1.1 mg/dL, well within the normal region indication
good kidney function. Puzzled.
It distress me that two major
labs can't agree on a value from what I assume is a highly automated test,
available within the hour.
==========================================================================================================
Two
cancers? -- surprising & discouraging new result
(10/3/16) (10/17/16)
I have an IgG lambda cancer.
This is was the monoclonal anti-body found to be hugly elevated in my blood
when I was diagnosed with MM in sept 2014 and has been tracked for over
two years, But in the last 6 weeks or so another M-spike an IgG kappa has
also appeared and unlike IgG lambda it has been growing: .05, .07, .09,
0.11 g/dL. So as of 10/3/16 two M-spikes nearly the same size are
reported: lambda at 0.15 g/d and kappa at 0.11 g/dL. The increase of the
kappa M-spike to 0.11 g/dL was accoumpanied by a big jump in its associated
kappa free light chain to 3.71 mg/dL well outside of its normal range (1.94
mg/dL is the upper end of its normal range). This was discouraging.
But I have noticed in the
past that my free light chain numbers are noisy, so was somewhat reassured
that two weeks later (10/17/16) my kappa free light chain jumped back down
to 1.95 mg/dL, just a hair outside its normal range (1.94 top). As of this
writing my M-spike numbers for 10/17/16 are not yet posted.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(6/13/16)
Recomended new chemo
A Dana Farber MM specialist
after reviewing my plasmacytomas and blood levels has recommended changing
to a new chemo plan. As a patient naive to a protease inhibitor, he recommends
going to what he calls the most active anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator
(pomalidomide, Pomalyst) plus the most active proteasome inhibitor (carfilzomib,
Kyprolis) plus dexamethasone, the corticosteroid I am now taking.
pomalidomide, Pomalyst
4 mg days 1-21
(pill, cycled, 3rd generation thalidimide, from Celgene)
carfilzomib, Kyprolis
20/27 mg/m2 days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, 16 of a 28 day cycle
(infusion mon/tues at hospital for three wks with a week off, from Onyx
Pharma)
(20/27 means the dose is lower the first cycle, then if well tolerated
increased 35% on following cycles)
dexamethasone (dex)
20 mg on days of carfilzomib (see below)
(40 mg/wk, coordinated with Kyprolis infusion to minimize its infusion
side effects)
(Note I question whether this is correct as it means not taking
dex on the week off! My oncologist
and I have agreed that I will continue with 2 x 20 mg dexamethasone during
the 4th week of the cycle.)
Recently I have been on rev/dex
(25 mg Revimid + 40 mg/wk dexamethasone). The chemo change can be viewed
as follow: an anti-angiogenic & immunomodulator drug remains, but is
upgraded from 2nd generation Revlimid (rev, 25 mg) to 3rd generation Pomalyst
(pom, 4 mg), both are pills from Celegene. In addition a protease inhibitor
is to be added. The recommended protease inhibitor is Kyprolis (carfilzomib,
Onyx Pharmaceuticals), which in an infusion (six times a month). The corticosteroid
I am now taking, dexamethasone (40 mg/wk, ten 4 mg pills), remains but
is to be taken in 'two pulses/wk' (20 mg each) on days of Kyprolis infusion.
Monitoring (7/10/16)
The blood objective mentioned
by the Dana Farber specialist is to drive my lambda free light chain down
into the normal range (< 2.63 mg/dL). In recent months is has been running
about 10 mg/dL, which most clinical trials use as the threshold for disease
progression. In two or three months both Lahey and Dana Farber doctors
speak of repeating MRI and/or Pet scans to see what is happening inside.
Dosing
One of the annoyances of
this new chemo is that Celgene specifies that Pomalyst, unlike Revlimid,
is not to be taken with (two hours separation), and I heard this from my
oncologist too. So while I take the bulk of my pills in the morning, I
need to remember after dinner every day to set a timer for two hours to
take pom (and the 3rd anti-viral acyclovir pill).
Effect of food
The Pomalyst prescribing statement has
this to say about food. Taken as prescribed (without food) the plasma concentration
peaks in 2-3 hours after the dose (pill). Taken with high fat meal or high
calorie meal the peak plasma concentration is delayed by 2.5 hr, which
seems to me totally unimportant in a pill taken once every 24 hours, and
the peak plama concentration is reduced by 27% (high fat) and 8% (high
calorie) when tested in healthy volunteers.
My view of this is that taking
Pomalyst in the morning with a light breakfast of Instant Grits (0 fat,
100 cal, plus milk) would (worst case) result in a very small reduction
(few per cent) in dose in terms of the peak serum concentration.
Wait a minute! (7/29/16)
Poking around the Celgene
web site I find Celgene's Pomalyst food recommendations are
contradictory!
Some Celgene documents do in fact say Pomalyst should be taken without
food (2 hr before or 2 hr after a meal), but other Celgene documents say
explicitly that "Pomalyst may be taken with or without food". This
latter recommendation is in fact found in the Pomalyst detailed prescribing
document from Celgene (link below), marked Revised June 2016, so I tentatively
take this as definitive. Celgene has apparently changed its mind (or is
it a typo?). Or maybe it's just a judgement call since the reduction in
peak serum concentration with food, say a light breakfast, appears to be
fairly small.
http://www.celgene.com/content/uploads/pomalyst-pi.pdf
-------------------------
I question the dosing of
dexamethasone outlined above (copied from the notes of Dana Farber doctor).
Note that it specificies dexamethasone be taken only on the days
of carfilzomib infusion, but this is six times a month for three
weeks with a week off. What no dexamethasone on the week off during the
28 days cycle? This was not the way it was done with rev/dex. And it's
not the way I see the dosing in the two clinical trials of pom that I checked.
The dexamethasone
dosing information in the Pomalyst (section 14.1) speaks only of dexamethasone
as used in clinical trials, which was 40 mg given on days 1,8,15,22. In
other words dexamethasone is continued in the 4th week of the cycle, the
'off' week!
Heart risk of carfilzomib
The detail prescribing sheet
for carfilzomib shows the absolute level of heart attacks of those
taking this drug in clinical trials to be about 6 to 8%. The non-carfilzomib
group had about half this level of heart attacks, so round numbers the
raw odds of carfilzomib causing a heart attack is about 4% or 1 in 25.
Did I recently have a mild heart attack? (6/14/16)
Probably not, but I might
have had some minor heart muscle injury or death. I have had no discussion
of these results with a doctor yet, but my heart numbers are all a little
above normal. What comes to mind is that on 5/30/16 I had an 'episode'
for a couple of hours with distress in my chest that faded away. Was this
maybe a mild heart attack? At the time this did not occur to me, but it
might
fit with the lab results.
Initially I misread troponin I test result
Got faked out here for a
few hours as I initially misread the troponin I rest result as 4
ng/mL. This (high) level would be consistent with already having had a
mild heart attack (probably the chest pressure episode I had on Memorial
day 5/30/16 for a couple of hours), but the actual troponin I result is
0.04 ng/mL (x100 times smaller!) (measured 5/14/16).
Carfilzomib (Kyprolis)
can affect the heart so prior to beginning the new chemo I had several
heart tests: ECG, echocardiogram (ultrasound), and monitoring of blood
related proteins in the blood. I have no baseline here as I have never
had my heart tested. Here are the results:
ECG
(12 lead)
Borderline ECG (same as EKG?)
Sinus bradycardia (pulse < 60 beats/min)
Abnormal R-wave progression, early transition
echocardiogram
This test can show visible
damage to the heart muscle tissue.
troponin
I
0.04 ng/mL ("troponin I is undectable in most healthy individuals")
normal: 0 to 0.30 ng/mL
(blood protein)
(0.30 ng/mL is the 99% percentile)
(one reference: > 0.40 ng/mL means probably myocardial infaction, i.e.
a heart attack)
A troponin test measures
the levels troponin T or troponin I proteins in the blood. These proteins
are released when the heart muscle has been damaged, such as occurs with
a heart attack (ischemia -- lack of blood flow to the heart muscle). The
more damage there is to the heart, the greater the amount of troponin T
and I there will be in the blood. Tropin test is very sensitive and can
pick up minor damage to the heart, which before 1990s was usually missed.
Typically troponin I rises in the blood a few hours after a heat attack
then slowly rolls off, sustaining for a week or two.
Even a slight increase in
the troponin level will often mean there has been some damage to the heart.
Very high levels of troponin are a sign that a heart attack has occurred.
Some people who have ischemia don't experience any signs or symptoms (silent
ischemia). Most common symptom is chest pressure or pain. Troponin elevation
in isolation does not confer a high mortality rate. However, the
presence of increased troponin is one marker of severity of underlying
illness and as such has been used to identify people at higher risk of
bad outcomes
Elevated troponin levels
can persist 1-2 weeks after death to heart muscle (due to blockage of heart
blood vessels). This test was done (6/14/16) 16 days after my chest 'episode'
on Memorial day (5/30/16).
beta
natriuretic peptide (BNP)
113 pg/mL
(6/14/16) (0 to 80
pg/mL normal, < 100 indicates no heart problems)
(brain peptide?) (mean BNP = 31.0 pg/ml in
those aged 65-74 years)
beta natriuretic
peptide (BNP)
23 pg/mL
(update 10/3/16) normal
beta natriuretic
peptide (BNP)
40 pg/mL
(update 2/13/17) normal
BNP is a substance secreted
from the ventricles or lower chambers of the heart in response to changes
in pressure that occur when heart failure develops and worsens. The release
of BNP appears to be in direct proportion to ventricular volume expansion
and pressure overload. BNP increases with right or left systolic or diastolic
heart failure. It is an independent predictor of high left ventricular
end-diastolic pressure. BNP levels decrease after effective treatment of
heart failure. BNP levels of more than 100 pg/ml have a greater than
95% specificity and greater than 98% sensitivity when comparing patients
without congestive heart failure (CHF) to all patients with CHF.
BNP levels below 100 pg/mL indicate no heart failure.
* BNP levels of 100-300 pg/mL suggest heart failure is present.
BNP levels above 300 pg/mL indicate mild heart failure.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
New tests --- Brain MRI and whole body PET scan (5/18/16)
In my regularly scheduled
meeting with my oncologist recently I mentioned that I had had some trouble
coordinating my eyes (double vision) in the last month or two, but curiously
only when watching TV. When I look around the room or are driving, I can
see fine, with the caveat that for the last year or two I have some blurring
in my left eye (which comes and goes) that my optometrist says (after peering
into my eyes with a microscope) is due to some astigmatism visible in the
central region of my left retina.
Why just double vision watching TV? (1/18/16)
I think I just figured out
why I've only sensed double vision while watching my TV, but not in driving
or looking around. I was assuming it had to do with motion on TV, but that's
not it. Tonight I noticed double TV images when there is no motion.
I have two large screen TV's
I watch from my easy chair in the living room. One across the room, where
it has been for years, is a regular TV. The second large screen TV
I use as my computer monitor, and since I have a TV tuner in my computer
it also work as a TV. My easy chair is angled between them. I need to look
right about 30 degrees for the TV and left about 20 degrees for the TV
monitor.
** I now see the double vision
is occuring when I need to look right (relative to the angle of my body).The
proof it is a (right/left) angle thing is that if I reposition myself in
the chair to angle my body slightly to the right of the TV, the double
vision goes away (or pretty much goes away). I can't really figure out
the angle of my eyes relative to my head.
PET scan
My oncologist scheduled an MRI
to check if the cancer was involved with my vision problem. She had another
MM patients with an eye plasmacytoma. The MRI apparently does shows something,
which was described over the phone to me as a possibly a mass pushing
on the left optic nerve, but after two days I have been unable to pry the
MRI report out of the hospital, so I have not read it. Based on the MRI
results a PET scan has been scheduled, which my initial understanding is
that it will (crudely) show how much the mass is growing, really how much
glucose it is extracting from the blood, a measure of its metabolic activity.
Wikpedia says 90% of PET scans are done to see if cancer is metastasizing.
Got not details, but the
MRI seems to show I may have had a possible mini-stroke (no symptoms that
I am aware of), so I will be scheduled to meet with neurology to be checked
out.
Cost of diagnostic tests and radiation treatment (may 2016)
Of course when an MRI and
Pet scan were ordered in may 2015 to assess the state of my MM the costs
of the tests and treatment were never mentioned. I found out the costs
only from Lahey billing received July, 2016. The largest charges on the
July bill are shown below. They mostly hospital services billed related
to the MRI, whole body Pet scan and two weeks of radiation treatment for
the plasmacytoma behind left eye (and at the same session jaw lesion) found
by the MRI. As below shows in round numbers the MRI costs 3.3k, Pet scan
13.3k and two weeks of head radiation (eye and jaw) 10.9k. Really a little
more than this when related physican services are included.. Here are the
largest items on the bill:
MRI (5/16/16)
Pharmacy, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3,328
Pet scan (5/19/16)
Nuclear medicine, Pharmacy, "other imaging services"
12,202
Physician services related to 'Pet imaging for CT attenuation"
1,084
Radiation (5/20 - 5/31) Radiation Theraputic and/or
chomtherophy administration
9,676
(5/23/16)
IV therapy ?
1,223
-------------
total 27,513
Hospital services for May 2016 (total)
26,912
Physician services for May 2015 (total)
3,960
My share of 30,872 total billing for May 2016
1,594 (5.16%)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
High
cost of carfilzomib and daratumumab infusions!
(7/26/16) (10/17/16) (12/1/16) (10/14/17)
I had two infusions of carfilzomib
(pom/carfilzomib/dex) three weeks out of four for about nine months (july
2016 to april 2017) or about 59 infusions total. In round numbers SS paid
the hospital 1,700 per infusion (hospital billed 6,400). This is an annual
cost of about 133k.
In summer 2017 I had nine
weekly daratumumab infusions. Per infusion these were much more expensive
than carfilzomib. My insurance records show that SS approved about 6,400
per infusion (hospital billed 19,000 per infusion!). This is an annual
rate of about 134k (daratumumab infusion rate drops off with time). And
this was for a chemo drug I did not respond to!
Carfilzomib billing decoded (12/1/16 update)
I have been unable to get
the hospital to explain my billing for carfilzomib infusions, but playing
with the numbers I made a breakthrough. Let's look at the funds received
by the hospital for an infusion and ask the question at what billing from
me would the funding for the infusion meet the ideal goal of Part B of
an 80/20 cost split. We just need to solve this little equation where x
is my billing and 1,699 is the payment Medicare provides to the hospital:
x/(1,699 + x) = .2
(set my fraction of total cost as seen by hospital at 20%)
x = .2 x 1,699 + .2 x
.8 x = .2 x 1,699
x = .25 x 1,699
(set patient billing at 25% of the amount Medicare pays provider)
x = 425
(yes, this is what I am being billed)
With the assumption that
the hospital has set its billing to me so that I am contributing 20% of
the cost and Medicare 80% of the cost we find that the amount I should
be billed is just in fact what I am being billed! This cannot be an accident,
it is clearly intended. Why it is intended is another question. It is my
understand is that under Part B the hospital is allowed to charge 20% of
'Medicare approved' charges, and since Medicare (for whatever reason) approves
nearly the entire hugely inflated billing (in excess of 6,000) I could
be getting billed about x3 more than I am, up around 1,200. So the question
on the table now is this. Is the hospital doing this out of the goodness
of their heart, or perhaps fairness for someone without Medigap coverage,
or are they constrained somehow by Medicare rules? (See the answer below)
I see this phrase
being used for Part B: 'reasonable charge' --- Medicare (Part B) pays 80
percent of what Medicare considers a "charge" for the item or service.
-- If the provider participates
in Medicare, he or she "accepts assignment," which means that the provider
agrees that the total charge for the covered service will be the
'amount approved' by Medicare. Medicare then pays the provider 80 percent
of its 'approved amount', after subtracting any part of the beneficiary's
annual deductible that has not already been met. The provider then charges
the beneficiary the remaining 20 percent of the approved "reasonable" charge,
plus any part of the deductible that has not been satisfied.
In other words the hospital
(assuming it 'accepts assignment' which it must because it is taking Medicare
patients) must accept that the 'total' charge for a procedure under
Part B is what Medicare has determined to be 'reasonable'. Since
Medicare then pays the provider 80% of the total charge, the hospital is
constrained. The maximum the hospital can bill the patient is the
remaining 20% of the total cost (or equivalently 25% of the
payment it accepts from Medicare).
Must collect about 25 percent of Part B expenses from beneficiaries
"By law, (Medicare)
must collect about 25 percent of Part B expenses from beneficiaries", (PBS.org).
Note this is another equivalent way to look at the usual Part B cost sharing
usually quoted as 80/20 of total cost. A patient billed at 20% of
the total cost is being billed at 25% (20/80 = .25) of the cost
to medicare. This is consistent with how I am being billed for carfilzomib
infusions, but it doesn't explain why the "Medicare Approved" amount for
each carfilzomib infusion (as shown on my Medicare account) is more than
x3 higher.
Reasonableness check (12/1/16)
We can also do a reasonableness
check on the numbers for my carfilzomib infusion.
2,124 Medicare 'reasonable charge' is 1.25 x 1,699
(Medicare paid provider)
- 1,699 Medicare paid provider
----------
425 patient billing (max) (20%
of total cost)
So is 2,124 in funds collected
by the hospital from Medicare and the patient sufficient to buy the drug
and pay for the infusion? Ans: yes. I am familiar with discount drug
search engines and some of them include carfilzomib. With the MA drug discount
card search engine (below) I found 30 vials of 60 mg carfilzomib (my dose
is 56 mg = 2.07 x 27) for sale with 'discount' coupons for 59,270. This
is 1,976 per vial. 1,976 for a vial means the drug cost is 93% of the Medicare
reasonable cost, a nice fit, and close to the ratio that was billed. After
purchasing the drug for the discount price of 1,976, the hospital has (148
= 2,124 - 1,976) to pay for the cost of the infusion. The reasonable
test is passed.
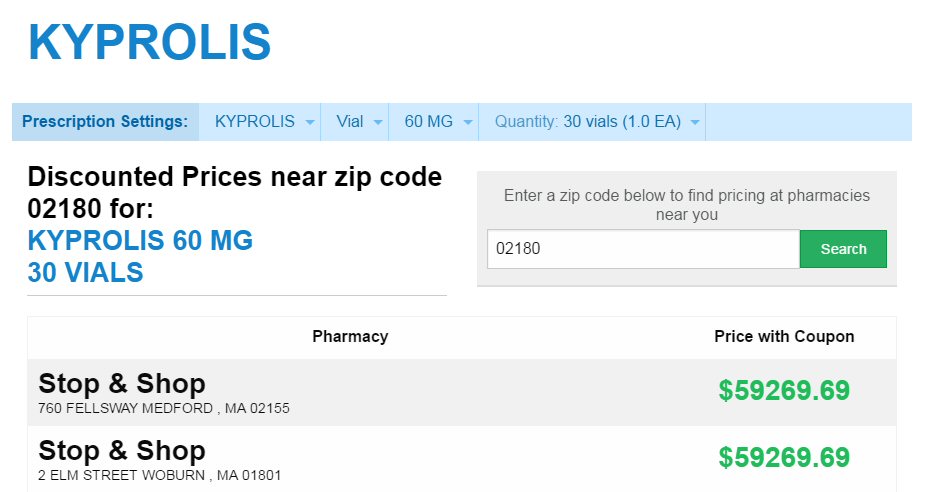
infusion drug carfilzomib discount price
(Kyprolis is the brand name of carfilzomib)
(60 mg vial is correct for me as my dose is 56 mg = 2.07 x 27 mg)
(10/17/16 update)
Why am I being charged $450
(425 to 475) out of pocket for every carfilzomib infusion? Typical
numbers are shown in the June 28,16 entry below: Total charges 6,375 with
Medicare paying 5,940 leaving a patient balance of 433. Total [6,375 =
5,754 pharmacy (drug) + 621 various hospital services]. My fraction of
the drug cost should be 5%, because it is covered by part D catastrophic
coverage .05 x 5,754 = 288. If I am being charged 20% of the hospital charges,
it would be .20 x 621 = 124, and 124 + 288 = 412 (close, but still less
than the 433 on my bill. (1.24 is for supplied dexamethasome pills that
medicare A/B does not cover, but I would think part D should cover.)
I checked the details
of the June 28, 16 charges by logging onto my Medicare account. The key
Medicare numbers agree with the hospital billing, but adds a (puzzling)
detail that is missing from the hospital billing [Amount paid to provider
= 1,699]. This looks to be the typical Medicare mark down. It is 26.7%
of hospital 6,375 total charges. If so, then my 5% part D share of drug
cost (288) is being inflated by nearly 4:1!
Medicare.gov says
"Part B covers chemotherapy for hospital outpatients. This is me. Medicare
part B usually pays only 80% of approved charges, but in a detailed list
of coverage (https://www.medicare.gov/Pubs/pdf/10116.pdf)
it says for chemotherapy give in a doctor's office or free standing clinic'
the patient pays applies 20%, but for chemotherapy given in a "hospital
outpatient setting", which is me, it says a "copayment" applies. It doesn't
detail the copayment, but the definition section says a copayment is "usually"
a set amount. I never make a cash copayment. On a later nearly identical
infusion billing my 433 payment is labelled "coinsurance"
Here's the billing details of
the 6/28/16 infusion (typical of my carfilzomib infusions summer/fall 2016))
as shown on in my Medicare account. Note the 1,699 is in the column labelled
'paid to provider'. 'Paid to provider' looks like the typical Medicare
markdown. The hospital bills 6,375 (including 5,754 for the drug
carfilzomib) and medicare only pays 26.7% of this, a x3.75 markdown.
Somehow this doesn't
smell right. If Lahey is accepting 1,699 for an infusion, which apparently
is both the drug cost and the infusion labor, why is not the 20% part B
coinsurance not much lower. Is my copay being figured on the inflated 'retail'
price? However, I don't know how to separate the drug cost (95% part D
coverage) from the infusion labor (628). [Note at this point I did not
understand that the drug costs for an infusion given in a hospital outpatient
seting are covered by Medicare Part B not Medicare Part D. Medicare Part
D applies to drugs the patient buys from drug manuf via pharmacy, but with
an infusion it is the hospital that is buying the drugs.]
---------------------------------
Lahey carfilzomib infusion billing for 7-26-16 and Medicare payment
(10/25/16)
The 7/26/16 infusion is
a simple case, no labs or other extra charges. For this one outpatient
infusion the hospital billed medicare 6,375.29. Medicare approved virtually
the whole amount (6,373.65) excluding only 1.64 for five steroid pills
I am given prior to the infusion.
The key question is how is
the 429.73 "coinsurance" calculated. There is no information on the Lahey
billing nor my account on the Medicare site that explains the 429.73. It
seems to come out of thin air. I sat down with Lahey billing people today
and was assured this infusion billing is covered under medicare Part B
that Part D is not involved and that is consistent with what it
says on the bill (Medicare A and B). I made a follow up phone call to the
billing people (Tayla, ext 5918) same day after reviewing my billing and
was unable to make sense of the numbers. (If Medicare part B only pays
80% of medicare approved charges, which is what medicare tells patients,
why was I not being billed 1,274.73, which is 20% of 6,373.65? I
was told Lahey hospical has a contract with Medicare and that where
the coinsurance number comes from.
So today (10/25/16 ) over
the phone I made a specific request of Lahey billing to detail how
the 'Adjustment, coinsurance' of 429.73 for the infusion on 7/26/16 (below)
was calulated. Break it out, detail the contract they have with Medicare.
This will require analysis and a follow up letter (hopefully by next week).
Playing around
Playing with the numbers (as engineers
are wont to do) I see something interesting. Lahey was paid 1,684.47 by
Medicare, and they billed me (and I paid) 429.73. If I add these two payment
together and ratio it to the total approved medicare charges of 6,373.65,
I get an interesting ratio: very close to 33% [(1,684.47 + 429.73)/6,373.65
= .3317]. (The unapproved medicare charge is nothing, just
1.64 for the five corticosteroid pills.)
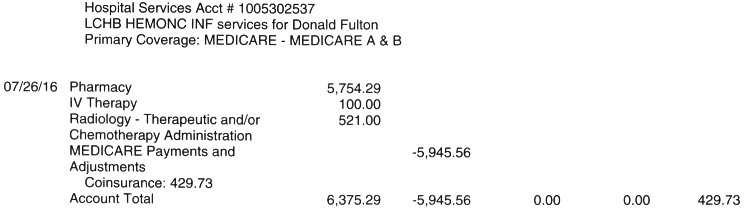
Lahey billing for infusion 7/26/16

my medicare account showing infusion costing detail for 7/26/16
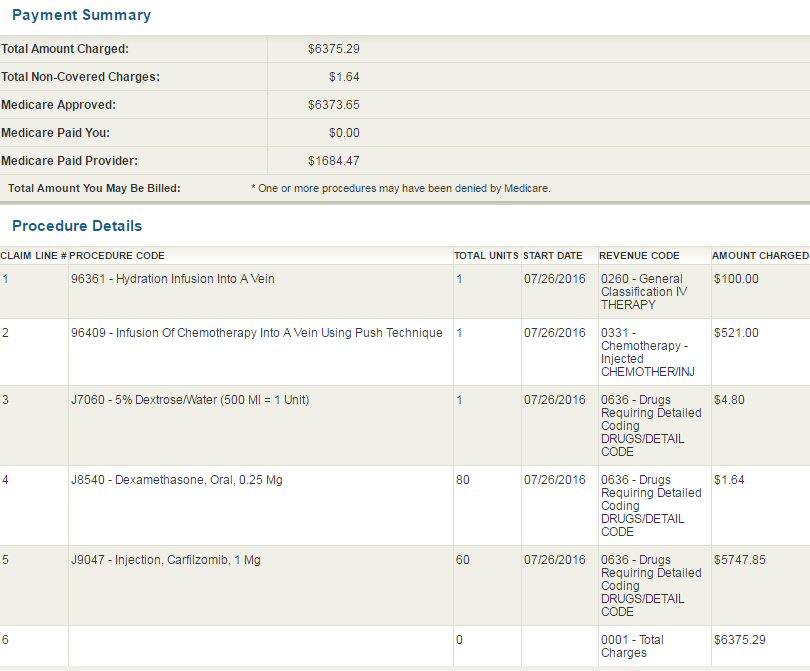
my medicare account showing infusion costing detail for 7/26/16
Note here a single carfilzomib infusion is billed as 60 mg.
This is the size of the a full vial (see above), even though based
on my surface area I am only given 55 mg or 56 mg
of the 60 mg, the balance is discarded.
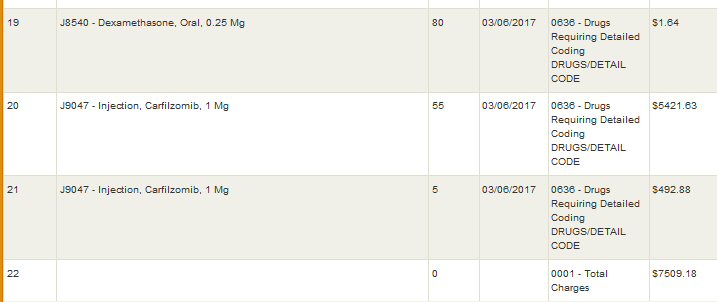
my medicare account showing infusion costing detail for 3/6/17
Note here the cost of a single carfilzomib infusion cost has two
billing entries: 55 mg (5,422) and 5 mg (493).
Based on my body surface area my dose is 55mg (or 56 mg). This billing
makes it clear that the discarded 5 mg is billed at about 500.
For a part B 80/20 split this would mean I am being billed about
100 for the discarded 5 mg of the 60 mg vial.
Note also that the total cost of the 60 mg carfilzomib vial here
is [5,422 + 493 = 5,915],
whereas about eight months earlier (7/26/16) the cost for the same
60 mg vial was 167 less (5,748).
--------------------------------
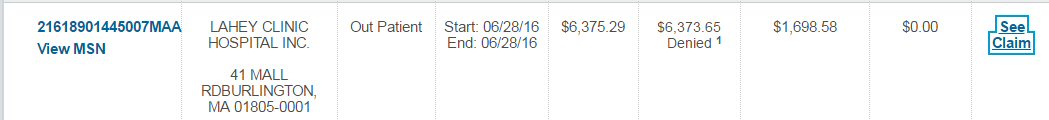 from my account Medicare web site
from my account Medicare web site
..
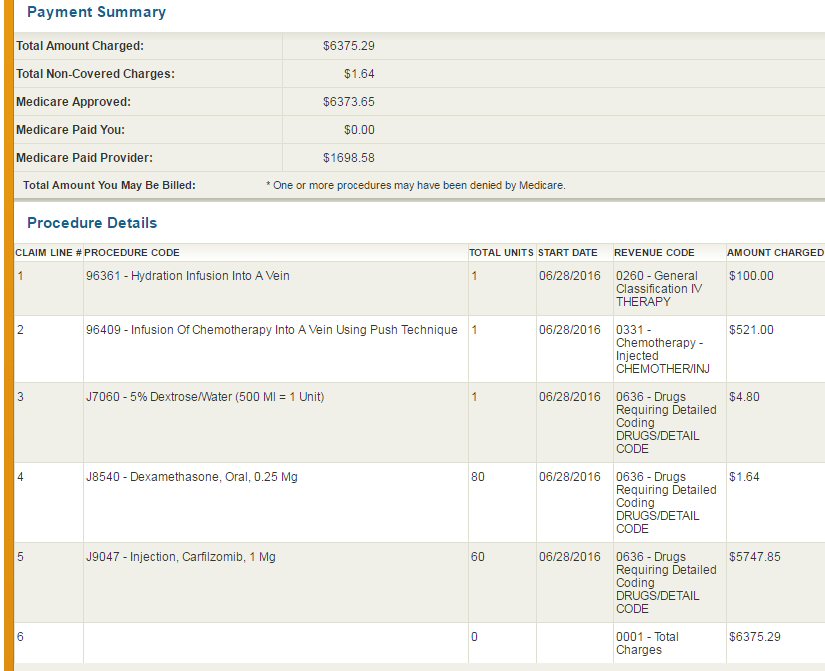
details from my account Medicare web site
I'm always a little confused
by the difference between 'Medicare Approved' and 'Paid provider', which
here is huge, but I think the explanation is the former applies to the
details of the medical care provided, while the latter applies to the cost
of that medical care.
44.2k/yr out of pocket cost of
new chemo! (10/23/16)
My cost for six infusions
of carfilzomib of a 28 day cycle is 2.7k (6 x 450), which is far in excess
of my cost for pom (688)! This means my 2nd generation pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo is costing me (out of pocket) [(6 x 450) (carfilzomib + 700 (pom)
= 3.4k/cycle] x 13 cycles = 44.2k a year. Yikes!
Total new chemo retail cost
Total new chemo costs (excluding
doctor appointments), most of it paid by the taxpayer, can be figured as
follows:
carfilzomib
5,754/infusion x 6 infusions per cycle x13/cycles/yr = 448.8k
pom
688/cycle x 20 (part D) x 13 cycles/yr = 178.9k
-------------------------------
627.7k (total retail cost for pom/carfilzomib/dex)
I am picking up 44.2k (7.0%)
of the 627k total and 93% is being picked up by the taxpayers in the form
of medicare part B and part D.
Medigap?
I need to investigate
for 2017 if a medigap ( or supplemental) policy, which claim they cover
coinsurance and copayments of medicare part B, would reduce my infusion
costs. Medicare.gov gives the price of a medicare policy is 8-9k if in
good health, and 13-14k if in poor health.
I have been looking at my hospital
billing for my carfilzomib infusions and trying to make sense of them.
Here is the online (Epic) billing for the first four pairs of my carfilzomib
infusions which occur on adjacent days. Where their are three entries for
a pair of days, there was also a meeting on the day with a doctor or a
nurse practicioner.
hospital 6/28/16 infusion billing
(shows my out of pocket cost for this single infusion is 433)
..
6/27 and 6/28
7/5 and 7/6
..
 .
. 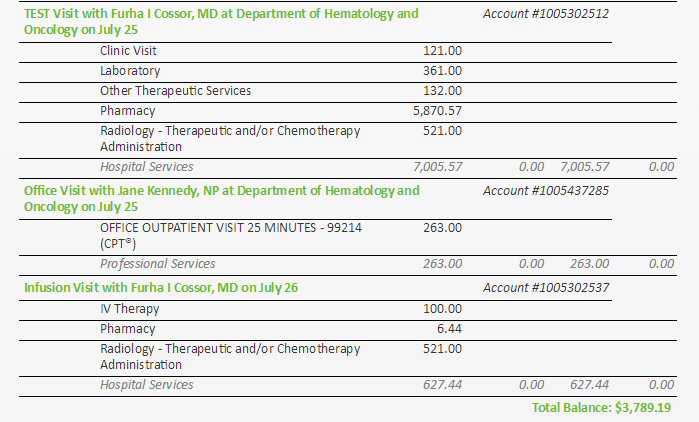
7/11 and 7/12
7/25 and 7/26
It appears that the hospital
charge for a single carfilzomib infusion is between 6,275 and 7,008,
though why it would vary day to day I have no idea since the process appears
to me to always be the same. Where there is doctor or nurse practitioner
office visit associated with reviewing the infusion this added charge is
253 to 495, and it includes the associated blood lab test that precedes
the office visit. The first infusion of the second cycle at a 35% higher
dose is 5,870. (The last infusion (7/26) is the day I am writing this and
the cost doesn't look like its completely billed.)
Note the bulk of the charge
is loaded onto 'pharmacy'. Each infusion in the first cycle shows a pharmacy
charge of 5,754. Add some handling cost in house for the pharmacy and that
seems to imply that the hospital is saying it is paying Onyx about 5,500
dollars for each dose of carfilzomib! Does Onyx really charge 5.5k
per dose of carfilzomib? (research this)
So bottom line for a cycle of six
carfilzomib infusions the hospital is billing roughly 40 thousand dollars
(36 -47k) about 33k of which is for the drug itself! I am covered
by basic Medicare and I am pretty sure as an inhouse hospital procedure
the cost of these infusions, both the drug cost and infusion cost should
be covered by Medicare B.
Medicare billing games?
It my observation from reviewing
other of my hospital bills that hospitals, at least my hospital, plays
a little game with Medicare, billing far higher than what it knows Medicare
will pay and what it will have to accept (typically x3 to x5 higher). The
only Medicare entry in the online billing above is labelled Medicare payments
and adjustments. This doesn't help because the adjustments are not broken
out from the payments.
Description errors
Some of the description
of the charges are just plain wrong.
Flat wrong --- July 12 was
an infusion day the charges reflect that with pharmacy showing a 5,754
charge, yet the title is "Hospital Encounter with Klaudia Hunter at the
dept of Radiation .... on July 12. The charges are right, but the title
is flat wrong. Dr. Hunter is my radiation oncologist. My records show I
did have a brief office visit with her on this day (July 12) preceeding
the infusion to review my earler two weeks of radiation, but Dr. Huner
has no connection
whatsoever with calfilzomib infusions. Lahey billing
seems to have merged two unrelated visits here naming the radiation doctor
in the name of infusion apparently because her office visit preceded it
within some time window. But scheduling was done this way for travel convenience.
Of course if I have a review meeting is coming up, I schedule it on a day
and time near an infusion to save another trip to the hospital. Lahey billing
seems to be totally confused by this!
Some flat wrong naming happens
on July 11. On this day I did have both an office visit with my oncologist
preceding the actual infusion. On the billing for July 11 we find the office
visit charge and infusion charge with identical
names. "Office Visit
with", but showing the usual 5,754 pharmacy, so a very strange "Office"
visit, the other billing (for the real office visit) has no pharmacy charge.
Misleading --- Even the usual
names for the charges is poor and misleading. The name of my Lahey oncologist
appears in most of the charges as follows: "Test Visit with" or "Office
Visit with". Gees. Sure my oncologist has authorized all my carfilzomib
infusions, but during an infusion session there is no "visit" with her,
I meet only with the infusion nurses.
Pattern emerging ---
More than once in these charges I find Lahey billing naming getting 'confused'
(if that is the word) by closely scheduled procedures, which it conflates
or mixes. This makes patient review of charges a nightmare. I really
don't see how this is possible in a properly set up fully electronic system,
unless is done specifically to make review of charges by the patient difficult
or impossible. On short form list of charge, which is what is first presented,
the name for a charge is all that is visible. The billing images included
here are rom a charge "detail' window I had to bring up.
Continuing... I will come back to this when I get
later more date. At some point the cost of the infusions will show up on
the Medicare site and that should be more revealing.
------------------------------------------------------------
Transient ischaemic attacks (or mini-stroke)
Minor strokes and TIAs (transient
ischaemic attacks or mini-strokes) occur when there is an interruption
of blood flow to the brain - they can cause weakness to the limbs or problems
with speech or vision and symptoms usually disappear within days. Transient
ischaemic attacks (also known as mini-strokes) - symptoms resolve within
24 hours but the majority resolve within 10-60 minutes. The chance of going
on to have a major stroke - with more permanent symptoms - is higher in
the days after an attack.
A new study in the Lancet
recommends that in the event of a mini-stroke take aspirin
immediately,
saying that the benefits of 'immediate aspirin' are "highly underestimated".
Their study shows it can reduce the risk of a major stroke later by factor
of five (from one in 20 to one in 100 per day).
MRI results (5/16/16)
Here's an image from the
recent MRI of my head with the bad news that I have a (likely) plasmacytoma
behind my left eye that was not present when I was diagnosed about 20 months
ago. The plasmacytoma is the white region in the upper right of the image.
(MRIs use an outside perspective, so the left eye as seen from the
outside is on the right side of the image.) A call from my oncologist tells
me the growth is not in the brain, but between the eye and a bone behind
the eye orbit called sphenoid bone. A radiation doctor tells me the plasmacytoma
is inside the sphenoid bone where the marrow should be.
This bone can clearly be
seen bowing outward in the image below and pressing on a long white structure
behind the eye, which is likely one of the long muscles (lateral rectus)
that moves the eye right/left. This is the likely explanation of why I
have double vision when look right with my eyes. The plan is to use radiation
(10 sessions over two weeks @ 20 Gy) to kill the cancer cells that make
up the plamacytoma and shrink the mass. Whether the bone will unbow remains
to be seen.
Radiation level of 20 Gray (Gy)
My radiation doctor told
me, confirmed by the Wikipedia article Gray (unit), that radiation dose
used in cancer treatment ranges from 20 to 80 Gy, but blood cancer cells
are quite sensitive to radiation allowing a relatively low dose of 20 Gy
to be used. This is enough to kill them and has the benefit that burning
side effects of radiation treatment are mild.
However, my plasmacytoma
is in a bad spot for radiation right between the eye and brain. Radiation
to the eye is likely to cause dry eye and over time (years) cause a cataract
to grow (darkening of the cornea). Technically one Gy is a "derived unit
of ionizing radiation dose in the International System of Units (SI) defined
as the absorption of one joule of radiation energy per kilogram of matter."
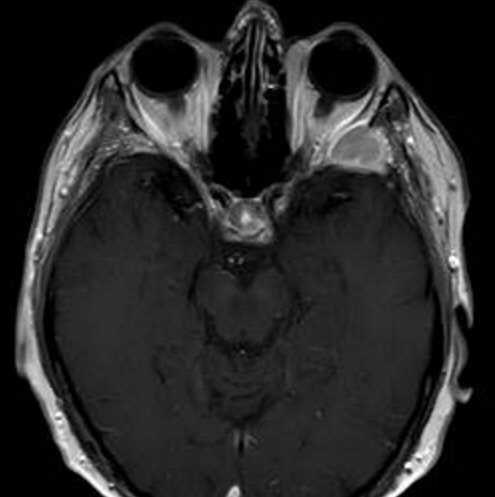
(5/16/16) Plasmacytoma is (large) white area behind my eye in upper
rught corner.
It is apparently INSIDE the (greater wing) of the sphenoid bone
displacing the marrow.
Similar area behind the other eye that is dark and is the marrow
of the bone.
The right sphenoid bone can be seen bowing outward into the eye
area.

MRI findings
1) "Etraconal mass on the
left. This is suggestive plasmacytoma."
(The plasmacytoma is the white mass in the image, in (or associated with)
the sphenoid bone that separates the eye from the brain.)
2) "Small calvarial met
versu myeloma in the right parietal region."
('Parietal calvarial lesion 'is a bone lesion in the large top/rear of
the skull. Here it is on the right measuring 5 mm appearing since last
study.)
3) "Small left frontal infarct
which is acute to subacute in the region of the superior frontal gyrus
posteriorly."
(Infarct is medical jargon for stroke, a localized area of dead
tissue resulting from failure of blood supply, either a blockage
or breaking open and bleeding into the brain.)
The medical jargon here is
pretty intense and requires translation.
diplopia (subacute) --- just the technical term for double vision (which
is what I see when looking a little left at TV)
greater wing of the sphenoid (bone) --- flat bone that forms the back of
the eye socket toward the outsides
(it doesn't appear that the optic nerve goes through it, it goes through
a bone toward inside)
lateral rectus (muscle) --- a muscle that moves the eyeball right and left
parietal calvarial lesion --- a lesion in the large top/rear of the skull
(right, 5 mm, new)
MRI: "Small right parietal calvarial lesion, 5 mm has appeared
since last study. Previously described lesion
is no longer present.
T2 bright focii centrum semiovale ---
calavarial --- skull (or skullcap)
parietal --- major bone of the skull in the top and back of
the head
infarct --- a small localized area of dead tissue resulting from
failure of blood supply (in other words a stroke)
superior frontal gyrus --- one third of the frontal lobe of the brain.
All Wikipedia says about the function of this region of the brain is that
it involved with self awarness and when stimulated an awake patient could
be made to laugh.
stroke --- Stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident (CVA), cerebrovascular
insult (CVI), or brain attack, is when poor blood flow to the brain results
in cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack
of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. If symptoms last less
than one or two hours, it is known as a transient ischemic attack.
sagittal (plane) --- right/left vertical plane
axial (plane) --- horizontal plane
coronal (plane) --- front/back vertical plane
MIPS --- maxium intensity projection (volume rendering of 3D data)
Diverticulitis (May & Sept 2016)
Note finding (above) in
May 2016 PET scan report --- "Colonic diverticulosos, most prominently
within the sigmoid colon." Reference to diverticulosos has (apparently)
also shown up in the report of the 2nd PET scan of sept 2016.
-- Diverticulosis happens
when pouches (diverticula ) form in the wall of the colon . If these pouches
get inflamed or infected, it is called diverticulitis.
(source -- http://www.medicinenet.com/diverticulitis_diverticulosis_pictures_slideshow/article.htm)
My oncologist thinks the
two episodes I have had in recent weeks of a few days of abdominal distress
coupled with a low grade fever may be due to diverticulitis, which is pouches
in the (sigmoid) colon getting infected. She has proscribed a seven day
course of two antibiotics: ciprofloxacin (twice a day) and metronidazole
(Flagyl) (three times a day). They are typically given together because
they kill a much wider range of bacteria (aerobic and anaerobic as well
as protozoa). This is five more pills a day as both of these antibiotics
come in (huge) 500 mg tabs. These drugs are very inexpensive.
Diverticulosos and diverticulitis basics
References say diverticulosos
(little pockets in the colon) are common, that 50% of people have them
by age 60, and about 10% of people with these pouches will develop diverticulitis
(infection). Diet recommendations to help avoid diverticulitis are all
over the map. Most say a high fiber diet (with a lot of water) is preferred
as it softens the stool, but a few sources say exactly the opposite avoid
high fiber foods. I love popcorn and it would seem logical that it should
be avoided due to its hulls, but references point to a paper in JAMA (Harvard
study with 47,000 people, aug 2008) that says popcorn did not increase
the risk of diverticulitis.
1st PET scan results (5/19/16)
The pet scan identified
two soft tissues masses ("likely plasmacytomas") and four MM lesions that
are metabolitically active. The report notes T12, where I had significant
bone loss prior to being diagnosed and which was irradated in Sept 2014,
says has minimal FDG uptake. Also identifed hyperdensities in the pancreas
and liver (possible cysts) with recommened follow up on 1-2 years for the
pancreas.
SUV --- 'Standardized
Uptake Value' used to characterize Pet scan hot spots
Dr, Hunter told me Pet scans displays are normalized to some reference
part of the body and what is displayed is the differential.
As I suspected, she said Pet scans results are somewhat crude (approx,
windowed, etc).
Soft tissue massses
1) same mass seen in the MRI (in) left sphenoid wing (behind the left eye)
SUV 16.2 (intense focal uptake), 2.2 x 1.6 cm (very high SUV)
2) soft tissue mass associated with 9th posterior right rib, 4 x 3.2 cm
[Sept 16, 2014 --- "Probable pathologic fracture posterior right 9th rib
with adjacent overlying atelectasis."]
(In other words 9th rib likely had broken prior to my diagnosis in sept
2014. This lesion has probably been metabolically
active since then and has now formed a huge (4 x 3.2 cm) adjacent soft
tissue mass. Did this bone break ever heal?
Is the rib bone maybe open allowing the monoclonal plasma cells to spill
out? )
MM lesions (active)
3) left mandible (jaw)
SUV 7.6, 1.1 cm (mid-range SUV)
(discussion with radiation doctor places lesion this high up in the madible
near the hinge)
[Sept 16, 2014 --- "Neoplastic (focal) lesion in the right ramus of the
mandible"]
Curiously at staging a mandible lesion in the ramus was found, but on the
opposite (right) side!
4) 9th rib, right posterior (with associated huge soft tissue mass,
4 x 3.2 cm)
(9th rib is low, right rear, attaches to the spinal column at T9)
[Sept 16, 2014 --- "Probable pathologic fracture posterior right 9th rib
with adjacent overlying atelectasis."]
5) 2nd rib, left anterior (2nd rib is high up, left front)
6) left ischium, extending to ischial tuberosity (lowest part of
the pelvis, or sitz bone, two loops)
SUV 5, 2.9 cm
(This ischium lesion appears to be quite close to the left pelvis/femur
ball and socket joint
and extends into the adjacent lower loop of the pelvis called the ischial
tubeosity.)
ischium bone (extending to ischial tubeosity) --- lower part of the pelvis,
below the ball and socket joint, sometimes called sitz bone
because the body sits on it
I got my a disk of my recent PET scan and trolled
(three times!) through the 4,000+ images to find those showing the lesions
(tumors) and plasmacytomas referenced in the PET report. Prior to the test
a radioactive sugar is drunk. The test then looks for areas of the body
have the most radioactivity and displays them in yellow, the more radioactivity
the brighter the yellow. The test is optimized to pick up lesions (tumors)
that are feeding (growing), so it shows where in the body there is active
cancer. (not quite right --- What was drunk prior to the scan was a contrast
material for the CT. The radioactive sugar is injected via IV.)
1st PET scan images (5/19/16)
The report of the PET scan identified six
active areas: four bone lesions (two in ribs, one in lower pelvis, one
in the jaw) and two soft tissue masses (plasmacytomas): behind the left
eye and one associated with the 9th rib lesion. The four thousand plus
images on the disk are arranged in 20 or so views of the body.
I read on a Beacon MM forum
that PET scans can only find tumors that are larger than 1 cm.
Identifying the mandible tumor
After reviewing my PET scans I
have some concern that the right location for the mandible has been chosen
for the radiation. There appear to be three (or maybe two) hot spots. There's
one in the low center about where the teeth are. I first though this was
the mandible tumor, but the alternate radiation oncologist says no, and
I now agree as the location does not look right. I have no idea what his
hot spot really is.
The radiation oncologist
identified the mandible tumor on the screen as a quite dim blurry B&W
spot that I can find on only one scan. He did this quickly identifying
the first image he found. Also he did not do the radiation plan, so he
might be wrong here. In the images below I favor and am showing the 3rd
candidate which is close to what he found, My candidate appears to be in
the right location with one image even seeming to show it high up on the
left mandible (near the hinge) which agrees with what the alternate radiation
oncologist said. Plus my images are quite bright which agrees with the
report said, an SUV of 7.6.
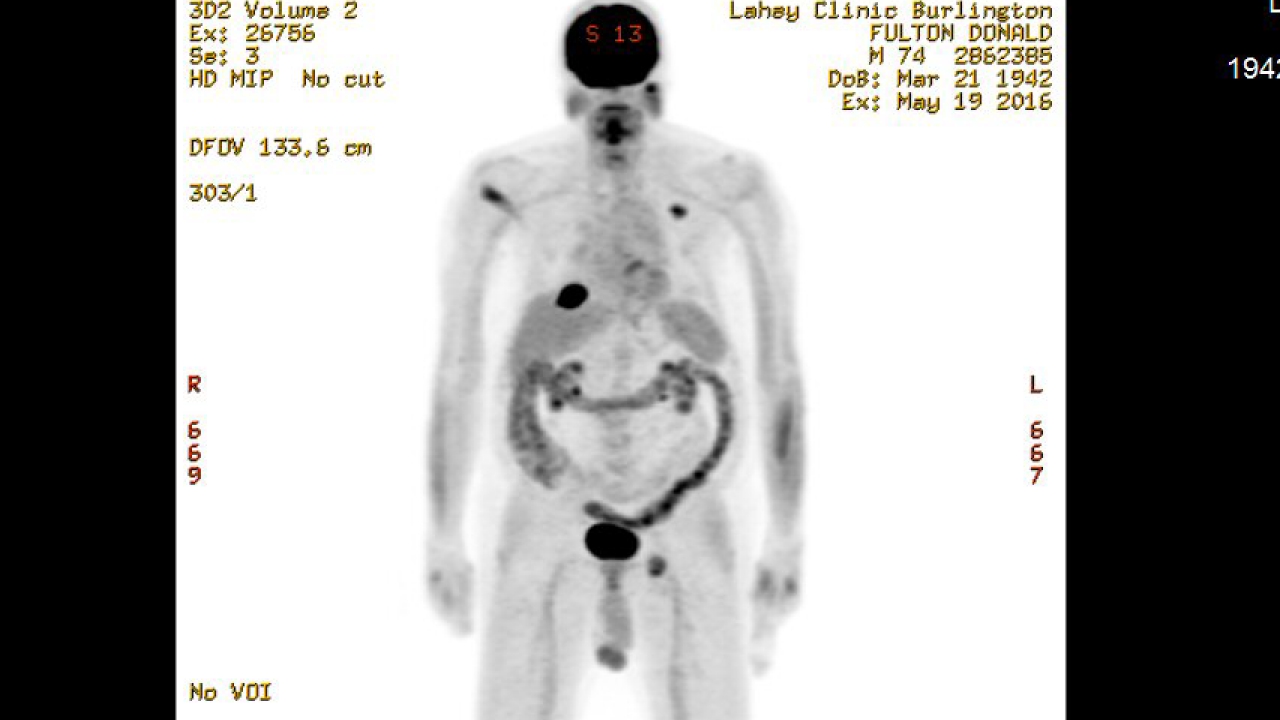
This 1st pet scan iimage shows 4 metabolically active lesions and
plasmacytomas below the head.
-- 9th rib lesion and assoicated plasmacytoma are the larger black
spot in the rib cage on right side of body
[right posterior (near spinal column) with associated large plasmacytoma
(4 cm x 3.2 cm)]
-- 2th rib lesion is the small black spot in the rib cage higher
up on left side of body
[2nd rib lesion left anterior (front)]
-- pelvis lesion is small black spot in crotch on left side of body
(near the pelvis/femur ball and socket joint)
not visible on this image are the two active areas in the head:
left mandible (jaw) lesion and plasmacytome behind left eye
(Report notes "non-specific muscular activity within right shoulder"
(no mention in report of the long radiation stripe in the left lower
arm)
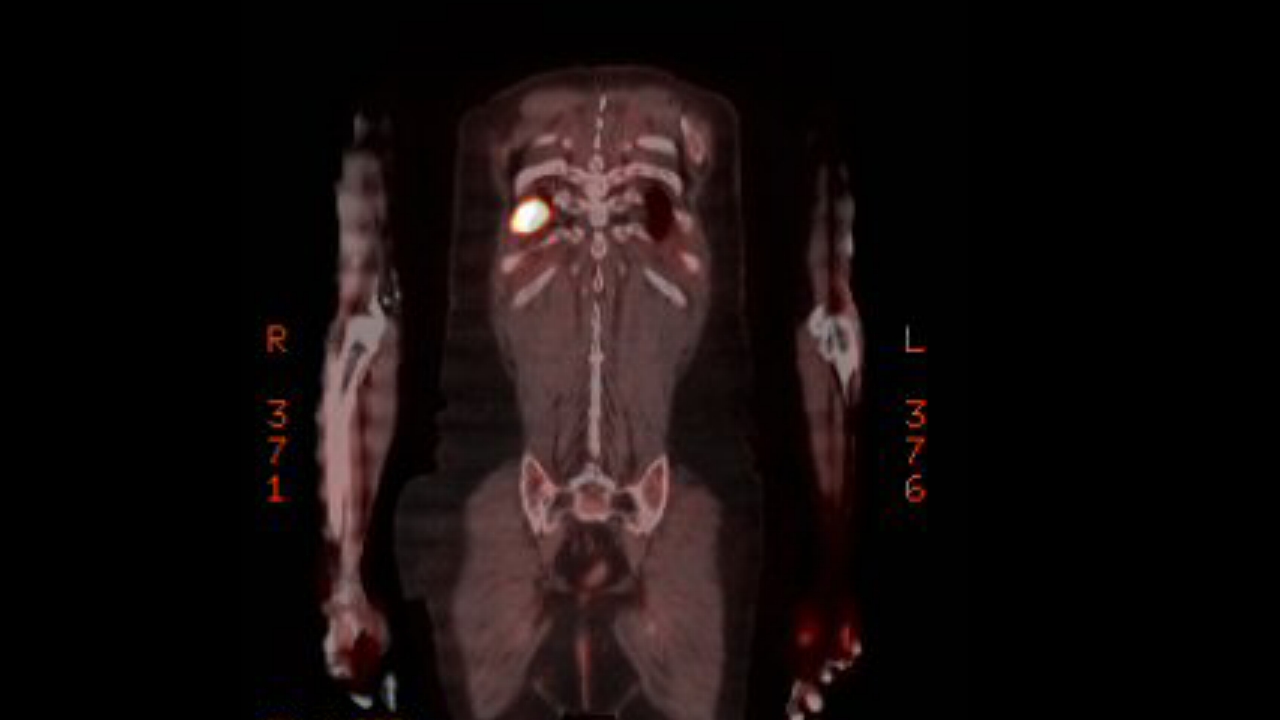
9th rib lesion right posterior with associated plasmacytoma (frontal
view)
SUV 15.1
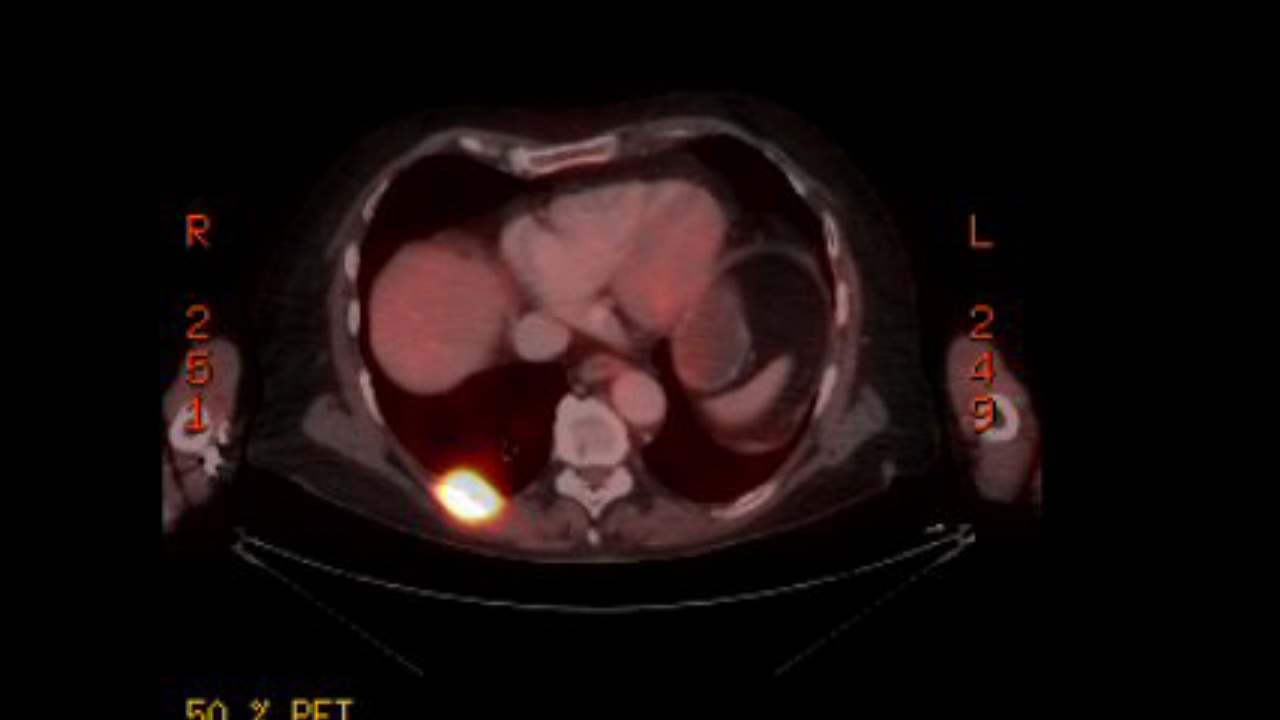
9th rib lesion right posterior with associated plasmacytoma (top
view)
(9th rib lesion and associated soft mass are quite close to T9 in
the spinal column)
Radiologist report on 1st PET scan (may 2016)


---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2nd PET scan images (9/6/16)
Here are new PET scan images
(comparable the images above) taken 2.5 months into new pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo. These are the brightest images I was able to find on the Sept 2016
PET scan CD, and they match up quite well with the images taken earlier
in May 2016 on rev/dex chemo. It's clear the 9th rib plasmacytoma is less
bright,, maybe half, but the definitive reading will come from the radiologist.
The 2nd rib plasmacytoma doesn't now show up, so (if it exists) it is now
below the PET size/brightness threshold.
-- 9th rib right posterier plasmacytoma (upper left in image) in
Sept looks considerable smaller
than in May 2016.
-- Earlier 2th rib lesion (front) was small black spot in the rib
cage higher up on left side of body
but in Sept is does not show up
However, there are three smal dots that are new in Sept 2016
in the body center and near the left elbow
..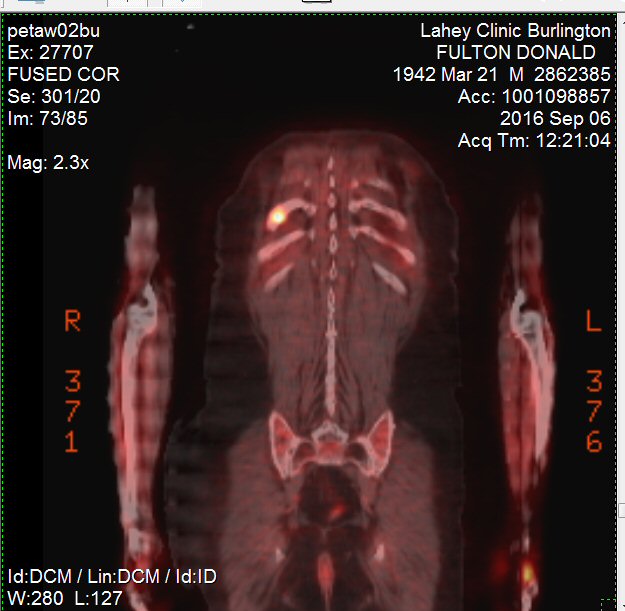
-- 9th rib right posterier plasmacytoma (upper left in image) in
Sept is quite a bit less bright
than in May 2016.
SUV 6.5 (previously 15.1)
..
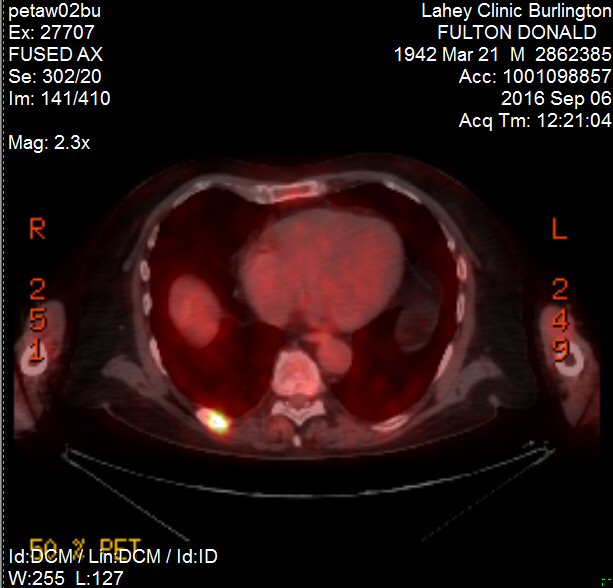
-- 9th rib right posterier plasmacytoma in Sept is quite a bit less
bright
than in May 2016.
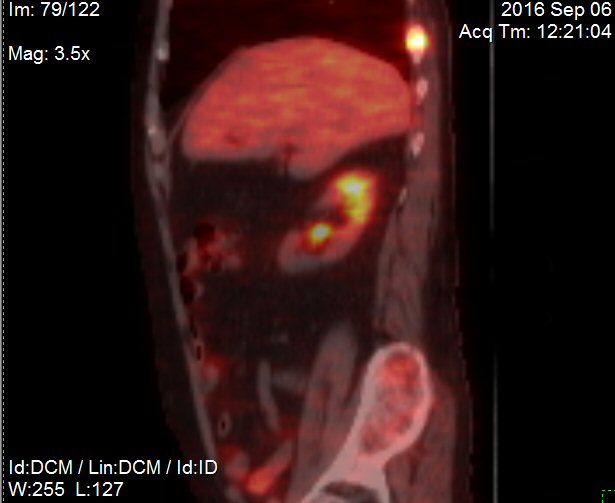
side view of 9th rib right posterier plasmacytoma (upper right)
(Sept 2016)
-- 2th rib left anterior (front) in Sept is quite a bit less bright
than in May 2016 (compare to below)
Radiologist report on 2nd PET scan (sept 2016)

Radiologist report on 2nd PET scan (sept 2016)
Pet scan images of right tibia (sept 2016)
Trolling through the Pet
images here is what I find for the 'suspicious findings' in the report
of the "right tibial and peroneal veins" (names of veins in the lower leg)
Recommends ultrasound to "exclude DVT" (deep vein thrombosis), which is
blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs.
 .
. 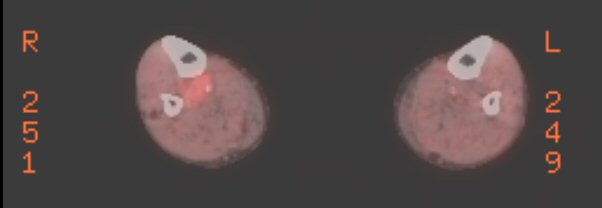
...
Pet scan images of right oral cavity (sept 2016)
Trolling through the Pet
images these are the 'indeterminant findings' in the report of the "right
oral cavity, diving ranula in the differential, correlate with ENT (ear,
nose, throat) exam".
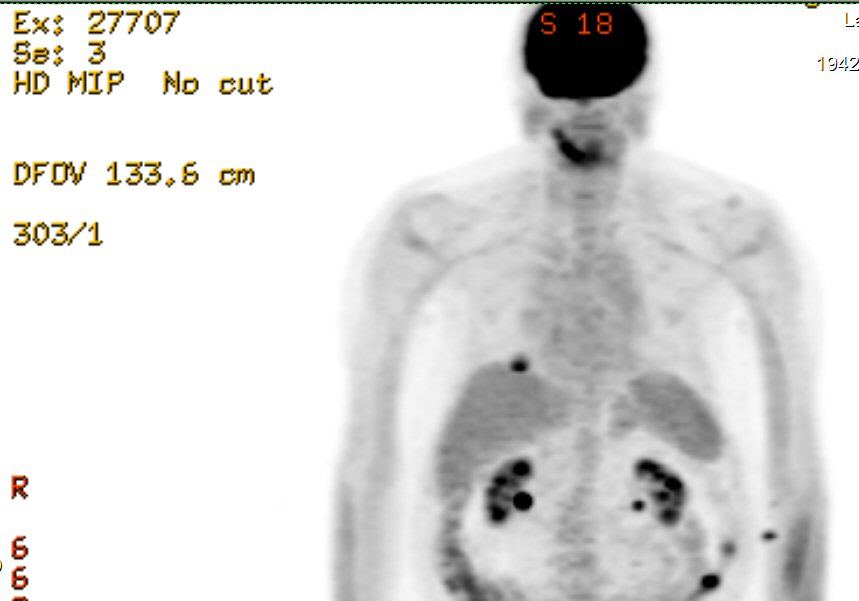 .
. 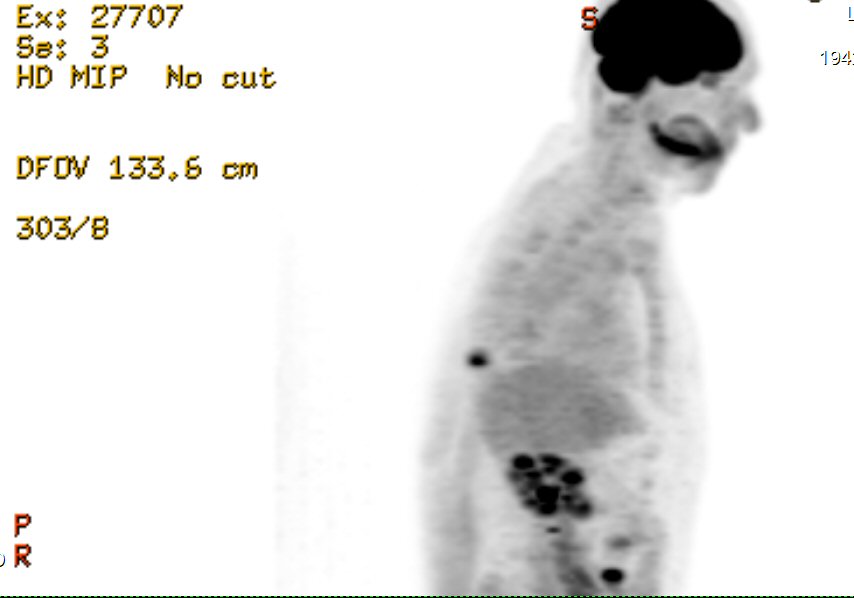
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3rd PET scan images
(1/11/17)
The 9th rib plasmacytoma in the
3rd Pet scan images below looks a little brighter than in the 2nd Pet scan
of sept, but that's because I brightened the image using ADCSee. Prior
to the gamma adjust to my eye the brightness of the 9th rib plasmacytoma
looked basically the same as it did four months ago. I don't see anything
around the head, eyes or jaw, though the resolution of this whole body
scan limits what can be seen in the head.
(1/11/17) (1/16/17)
I have not seen the pathologist
report yet, but I've carefully gone through the images on the Jan 2017
PET disk and the only active cancer area I see is the (pre-existing) 9th
rib posteria plasmacytoma. Need to see what the new SUV reading will
be, but it looks to my amateur eyes that there has been little change in
my Pet scan in the last four months.
Confirmed
Yes, the official read of the
Pet scan pretty much agrees with what I see. Only one plasmacytoma visible
(9th rib right posteria) that is judged to be a little bit brighter and
bigger than four months earlier. When compared with the previous Pet scan
in Sept 2016 (Pet #2), it is just slightly (10%) brighter (SUV 7.1
vs 6.5) and a little larger (2 cm vs 1.5 cm). Of course, it would have
been better if it was smaller, so is this an inflection point pointing
to higher levels to come, or just noise in a stable situation?
"Finding: Slight worsening
of metastatic lesion (bone not identified as a plasmacytoma) posterior
right 9th rib, approx 2 cm max SUV 7.1, prev 1.5 cm, max SUV 6.5. No obvious
FDG Pet evidence active disease remainder of the body."
"Impression: Persistent/slight
worsening metastatic disease posterior right 9th rib. Stable disease the
remainder of the body."

Radiologist's report on 3rd Pet scan (1/11/17)
It is interesting to compare
this 3rd Pet scan after six months on pom/carfilzomig/dex chemo to the
1st pet scan reading prior to this chemo. Even though the resolution of
a full body scan is not good in the head region, the 1st pet full body
scan clearly showed a bright spot (plasmacytomas) behind the left eye,
one on the jaw, and a plasmacytoma on the 2rd rib left front in addition
to the bright 9th rib right posteria plasmacytoma. I had two weeks of radiation
to the head region to treat the plasmacytoma behind the left eye and the
bright spot on the jaw too. Only one of these four plasmacytomas (9th rib
right posteria) are visible on Pet scan #3.
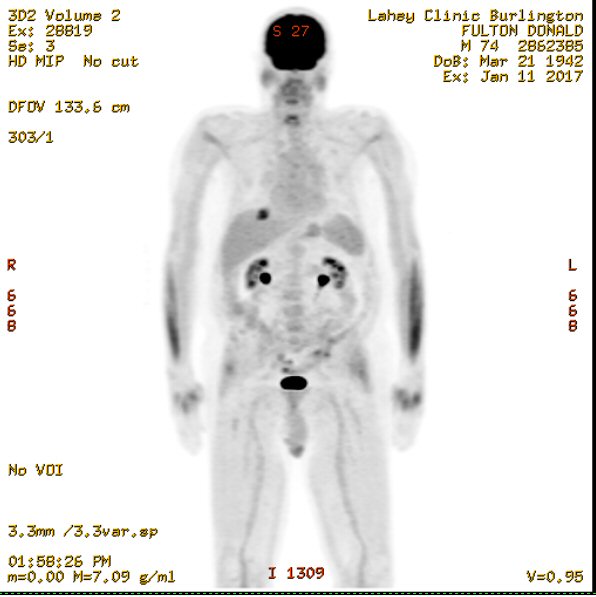
Pet scan #3 (Jan 11,2017)
(6.5 months into pom/carfilzomib/des chemo)
[9th rib right posteria plasmacytoma is the black dot on
left side of image ('R') in the rib cage opposite the mid upper
right arm (humerus)]
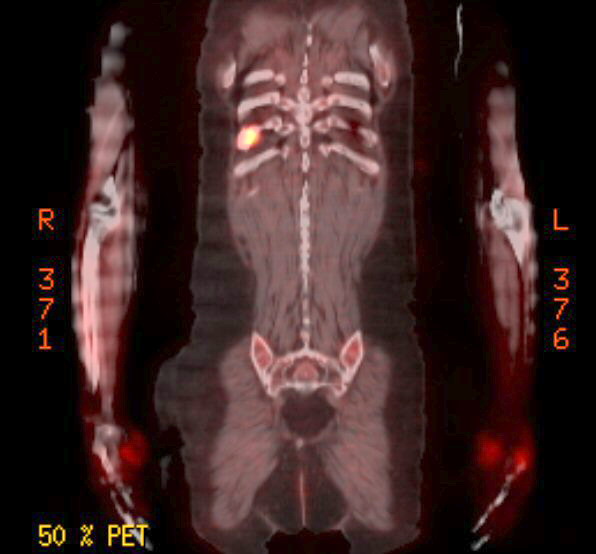
Pet scan #3 (Jan 11,2017)
-- 9th rib right posteria plasmacytoma
(6.5 months into pom/carfilzomib/des chemo)
SUV --- 7.1 (2 cm)
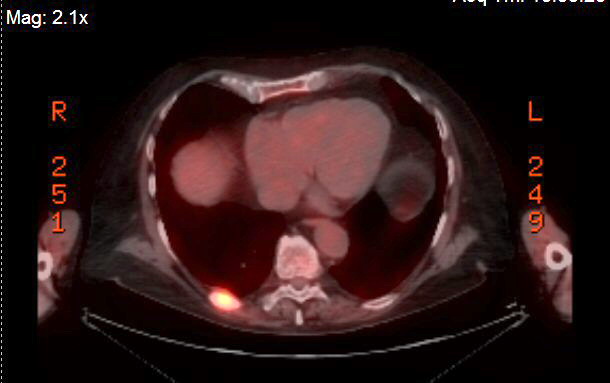
Pet scan #3 (Jan 11,2017)
-- 9th rib right posteria plasmacytoma
(6.5 months into pom/carfilzomib/des chemo)
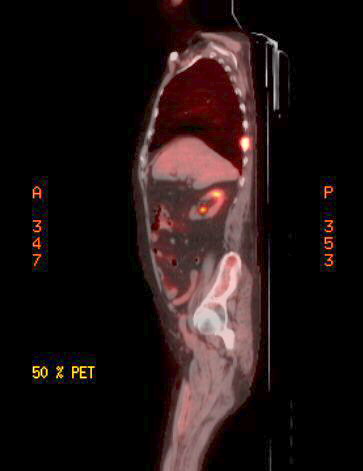
Pet scan #3 (Jan 11,2017)
-- 9th rib right posteria plasmacytoma
(6.5 months into pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo)
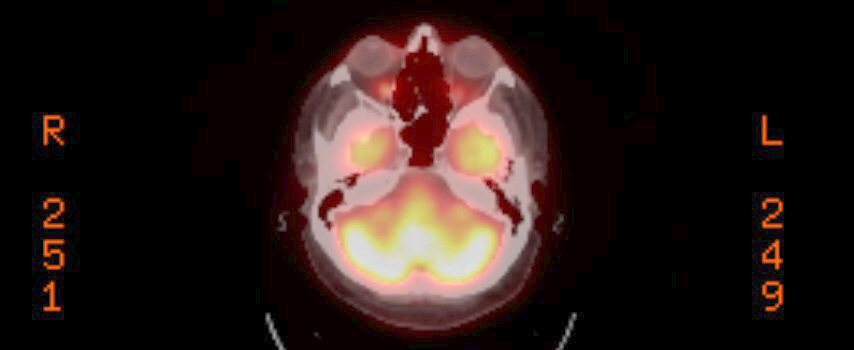
Pet scan #3 (Jan 11,2017)
Area around eyes
(I don't see any indication of a plasmacytoma behind left eye)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4th PET scan images
(3/22/17)
(3/29/17)
The purpose of this 4th
pet scan is to establish a baseline for a pending change in chemo. As evidenced
by rising free light chain (4.55 mg/dL lambda free light chain) and M-spike
(.17 g/dL) readings in the last couple of months my cancer has evolved
around the pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo I have been on since 6/29/16 ending
my 2nd remission of 8.5 months. I have an aggressive form of MM as evidence
by several (five) plasmacytomas (two in ribs, pelvis, jaw, sphenoid bone
behind left eye) seen last spring prior to beginning pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo. Months on this chemo has reduced my plasmacytomas (plus two rounds
of radiation over 2.5 years) seen on a pet scan to one (9th rib posterior),
but my hematological oncologist is concerned that with rising blood cancer
numbers new plasmacytoma may have popped up. Also she wanted a baseline
before beginning an experiment with the proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro substituting
for the protease inhibitor carfilzomib (beginning 4/3/17).
'Metastatic' (right lung) is a reference to a possible
metastasis of the cancer to the lung, i.e. a possible new plasmacytoma.
Right lung is described
as having
" New reticular nodular opacities subpleural distribution superior
segment right lower lobe and posterior segment right upper lobe."
(I disagree that the growth of the 9th rib, posterior plasmacytoma
(in last 9 weeks) is "slight",
since SUV doubled (7.1 => 14.1) and size increased 50% (2 cm =>
3 cm))
Radiologist's report on 4rd Pet scan (3/22/17)
My quick read of the images
(prior to the expert read) is that the only one plasmacytoma is clearly
shown (yup). This is the existing 9th rib, right, posterior. Looks to be
that it is quite a bit brighter than the pet scan two months ago (1/11/17),
perhaps close to where it was at the 1st pet scan last spring prior to
beginning pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo (yup). The SUV reading will tell the
story. It is now about a week since the test and expert analysis of it
has still not been posted on MyLaheychart. But a few days ago my doctor
messaged me after reading the report saying I was right, it has bright
(grown) a lot, I think she implied the SUV had about doubled. If so, all
the shrinkage of 8.5 months on pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo has been lost
in just the last 11 weeks (since the 3rd pet scan). Obviously this
is bad news especially since both free light chain and M-spike are probably
still far below the disease progression thresholds (at least that was true
at the the last blood sampling about three weeks ago)! I am beginning
to wonder if it is a mistake to try Ninlaro for a month and give this plasmacytoma
another month to grow. Would it make sense to schedule two weeks of radiation
to beat it back? Is it just acting as a source of plasma cancer cells that
can more easily spread around the rib cage and the spine? This will a topic
to review with my oncologist at our next meeting in a week (4/417).
There were 3,300 images on
the pet CD. In a couple of hours I pulled the images below from the CD
and posted them online in this essay (below). Something which I doubt any
other patient at the hospital has ever done. I took my time here scrolling
back and forth, I am pretty sure these images are the best views of the
9th rib plasmacytoma.
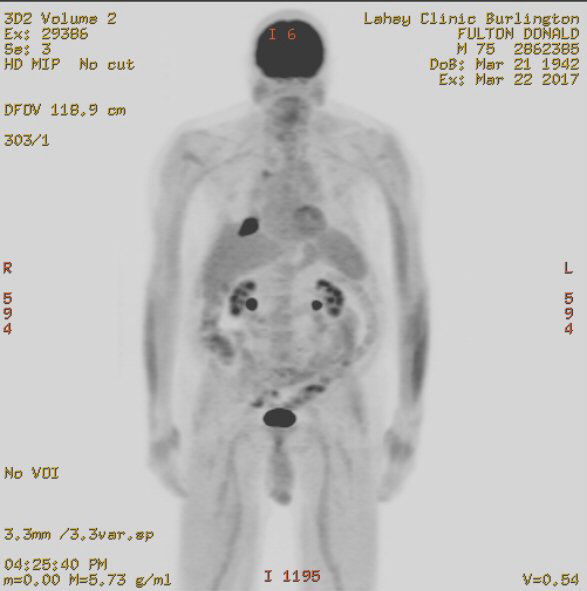
black spot upper left on image is the plasmacytoma 9th rib posterior
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
The front view below also
a weak brightish spot on the left lower down in the ribs that
might
be a (new) plasmacytoma, but it doesn't show in the whole body scan or
other close up views.
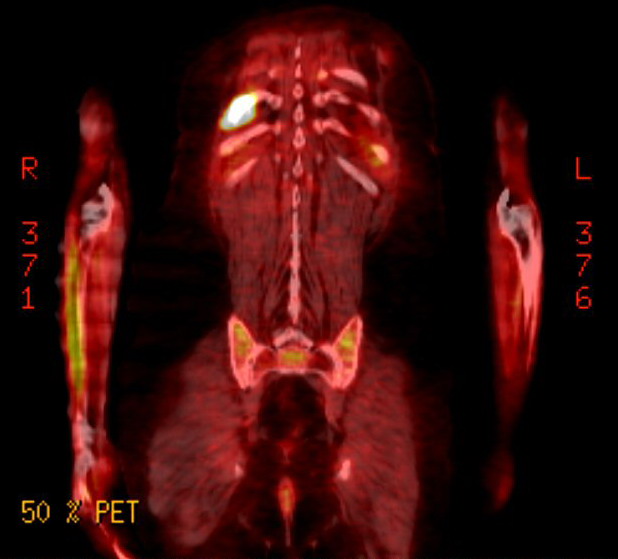
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
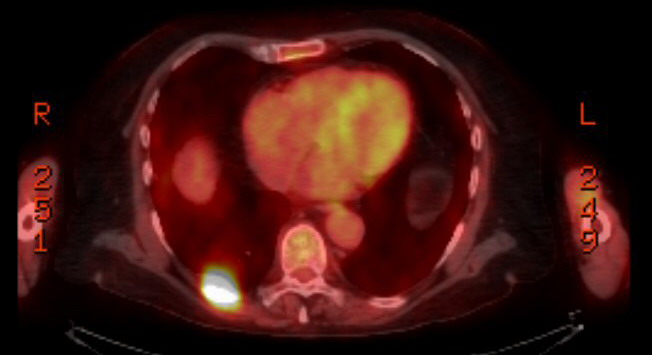
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
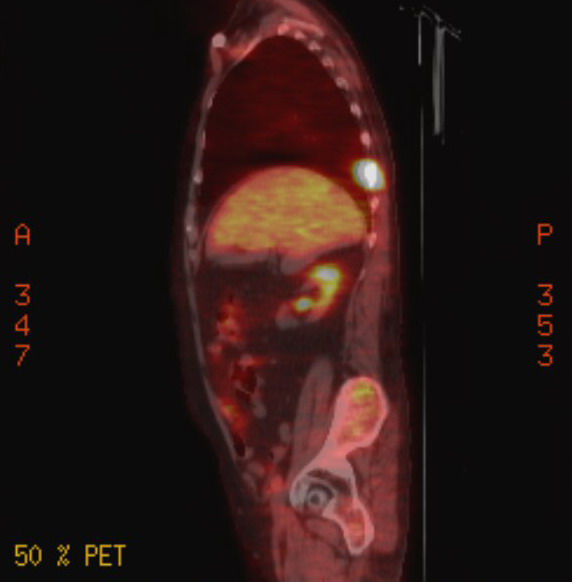
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
Lungs
After
reading the radiologist report, I went back and looked at the lungs. Do
I see opacities in the right lung? When researching my pet images
I at first got faked out. I thought the two large yellow areas were the
lower lobes of the lungs. Wrong! The lungs start high up in the chest and
are pretty much black on pet scans (and trasparent on x-ray). Online pet
scans of a lung with a cancer show a bright yel spot in a field of black.
The two large bright areas I am pretty sure are the right lobe of the liver
and on the left the spleen (or possibly the left lobe of the liver). Below
them the two much smaller, brighter areas are the two kidneys.
The right lung weirdness
that the radiologist noted must be the faint yellow in the large right
field of black. Another look throught the images of the 4th pet scan shows
this is best right lung image I can find, and I am not sure it isn't just
an artifact of the heart.
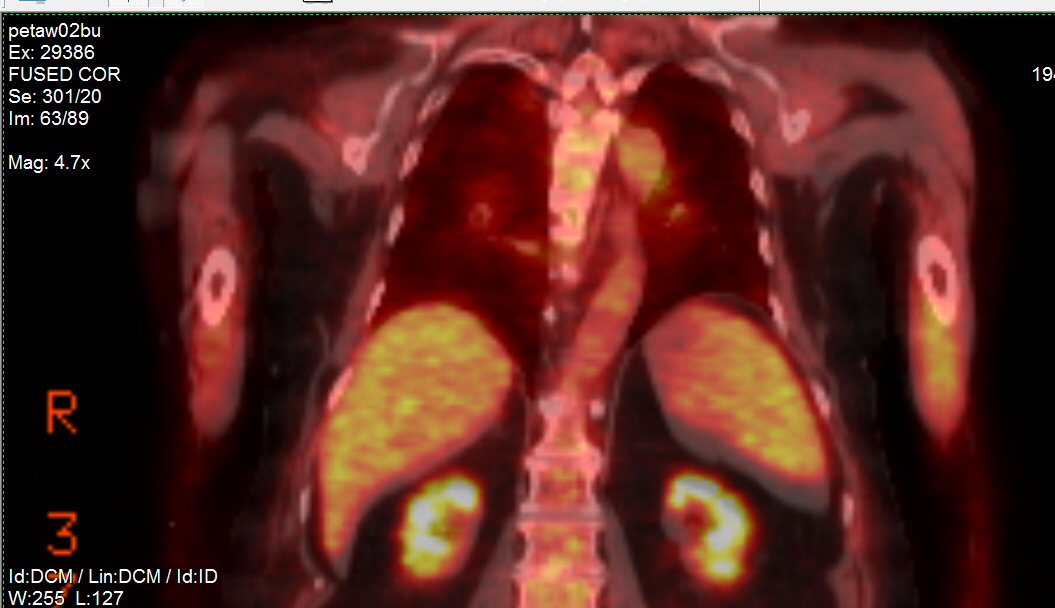 .
. 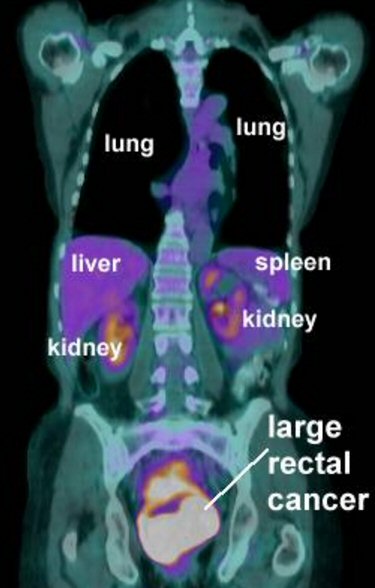
Right lung weirdness noted by diologist is probably the faint yellow
in the black area above the large bright liver right lobe.
(right --- reference online pet chest cavity showing organ locations.)
(source -- http://www.aboutcancer.com/rectal_pet_sah_jan3_2007.jpg)
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
Spine
Lots of false positives
in this side view image (below left), for example just look at the face
and jaw, but it also seems to show possible 'hot spots' running up and
down the spine. When I was diagnosed MM, the cervical surgeon found cancer
up and down my next bones, C2 had broken and the surgeon biopsied
C4 to confirmed my MM diagnosis.
 .
. 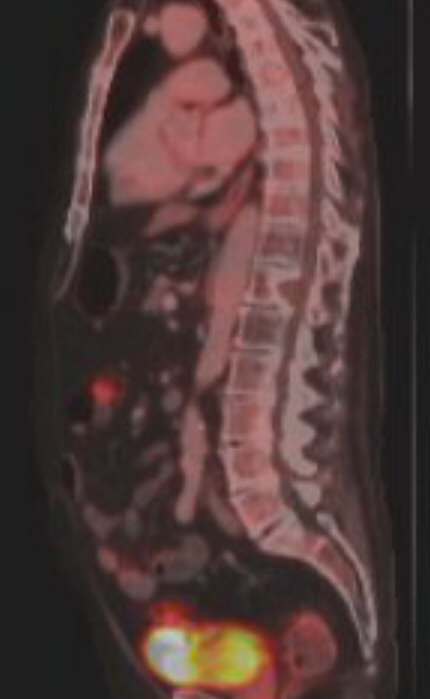
(left) Weak
hot spots along the spine?
(right) T12 notch from 1st pet scan (5/19/16)
Nicely shows the MM caused notch in T12 vertebrae
.
.
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
.
Note the expert read of a
a hi-res CT scan of the lungs taken about the same time reported "lytic
vertebral lesions", in other words evidence of cancer lesions in the vertebrae
of the back, consistent with the left Pet image above.
The images above clearly
shows the 'notch' in T12 vertebrae. A third to half of the supporting part
of T12 had been eaten away by my cancer before I was diagnosed in sept
2014. I saw detailed images of this at the time by the radiologist who
did the radiation of my neck. To date this loss of vertebrae bone and obviously
strength of spine has caused me no problem, but this is a big worry if
chemo stops working. A growth of cancer here would lead to a crushing of
T12, and in fact the radiologist in 2014 said at some point in time this
was likely to happen.
So to keep watch on this
I have carefully compared this 4th pet image of the T12 notch (3/22/17)
to a image showing the T12 notch from my 1st pet scan (5/19/16) about a
year earlier, (side by side above) and to the extent that the resolution
allows, they look the same. I see no deepening of the notch in the last
year, most of which I have been in a second remission on pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo.
Head
The head does not have much
resolution in a full body scan. I still have double vision looking right,
so either the plasmacytoma behind the left eye sill exists or the bending
of the sphenoid bone remained after (or if) the plasmacytoma in it shrank.
I asked about the radiologist on duty about the resolution of the scan
and was told about 5 mm across if bright, which is pretty consistent with
what I found on a MM forum that plasmacytomas have to grow to about 1 cm
across before they will show up in pet scans.
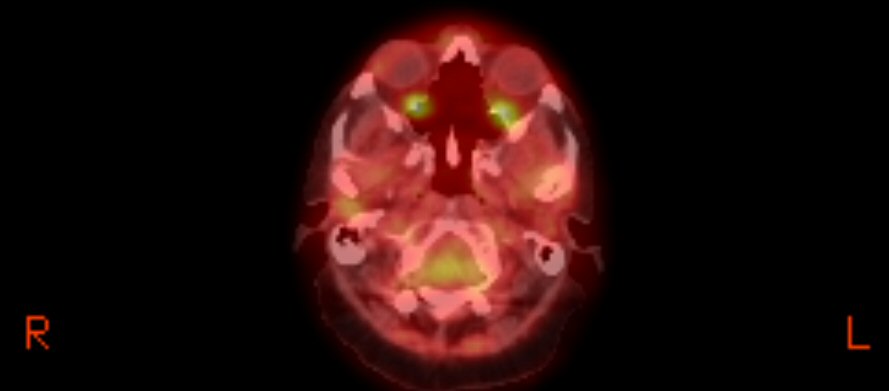
area around the eyes. I don't see anything definitive here.
4th pet scan (3/22/17)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5th PET scan images(7/10/17)
Known rib plasmacytomas
My quick overview
of the 5th pet scan prior to getting the radiologist report is that the
two known rib plasmacytomas are clearly larger. Most significantly
the largest plasmacytoma in my body, 9th rib, right posterior has increased
in size substantially, far larger than it has ever been before. And this
growth has all been since the last pet scan four months ago. The intensity
figures show in addition the known bright core there is a now a surrounding
large area of diffuse brightness. There are hints that the low intensity
diffused area has expanded to (or into) the spinal column (T9). Probably
not good.
Posssible new plasmacytomas
There are
several black dots on the 5th pet scan that were not there four months
ago. Some may be real, others artifacts. One (upper right on image) is
clearly the existing 2nd rib, left front plasmacytoma that was in the 1st
pet scan of 5/19/16, but was reduced enough by the introduction of pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo that for about a year it disappeared from the whole body view in
pet scans 2, 3, and 4, which was the scan of 3/22/17 prior to beginning
the Ninlaro chemo. Well it's back, so it must have grown either after the
cancer became refractory to carfilzomib and/or in the nearly four months
of pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo.
There is a
black dot on right arm near (or below) elbow, probably in the upper part
of the lower arm bones (radius and ulna). This is new, it has never shown
up on earlier scans, so it is might indicate a new plasmacytoma, though
I can't find it on the intensity view.
The are two
interior black dots that are more problematical, both near the large 9th
rib plasmacytoma. The upper one is connected to the large T9 plasmacytoma
and is likely at the T9 vertebrae. The other is below more toward the right,
so it looks like it might be in the 10th or 11th rib.
Curiously the
long narrow black stripe in the right shoulder shown in the 1st pet scan
is now back. Is this activity maybe due to a crack in in the scapula bone?
There is not
enough resolution in a full body scan to see the plasmacytoma behind my
left eye.
Second look at pet5 images --- jaw activity
A second look
at my pet5 images the next day has resulted in five more images posted.
Two of the images show a hot spot in the jaw region. Three side images
were taken without shifting the closeup focus. The left image clearly shows
the one well known vertebrae in my back with the deep notch. This is T12,
and by counting it allows the two spine hot spots to be localized. I count
them to be on T8 and T9.
My 5th pet scan summary (prior to radiologist
report)
The two known
rib plasmacytomas (9th rib, right posterior and 2nd rib, left front) are
definitely bigger with the 9th rib plasmacytoma appearing to have expanded
greatly in a diffuse way including extending toward (or into) the spinal
column at T9 vertebrae. If this is right, it is probably not good. There
is a hint that there might possibly be a new plasmacytoma in the upper
region of the right arm lower bones (ulna or radius), but it doesn't show
up in the intensity images. A black dot in the 10th or 11th rib is unexplained.
More images show activity in the jaw region. The activity in T8 is unexplained.
Confirms a chemo change needed
The big picture
here is that the recent significant growth in my rib plasmacytomas shows
my existing chemo is just not working, things are growing wild inside (with
lambda free light chain at 8.42 mg/dL and M-spike at .15 g/dL). This confirms
my latest blood work that indicated that a chemo change was probably needed
as my lambda free light chain had a big jump to close to its disease progression
threshold of 10 mg/dL. So together they clearly show a change in chemo
is needed at the end of this cycle (another step up the chemo ladder!).
My doctors
prefer changing to a regimen build around the most effective humanized
antibody drug (new drug class for me) daratumumab, and I don't disagree.
What daratumumab should be paired with is another story, and here I don't
agree with my doctors. They perfer pairing it with a proteasome inhibitor
(Velcade), the Castor clinical trial, I want to pair it with an imid (Pomalyst),
the Pollux clinical trial.
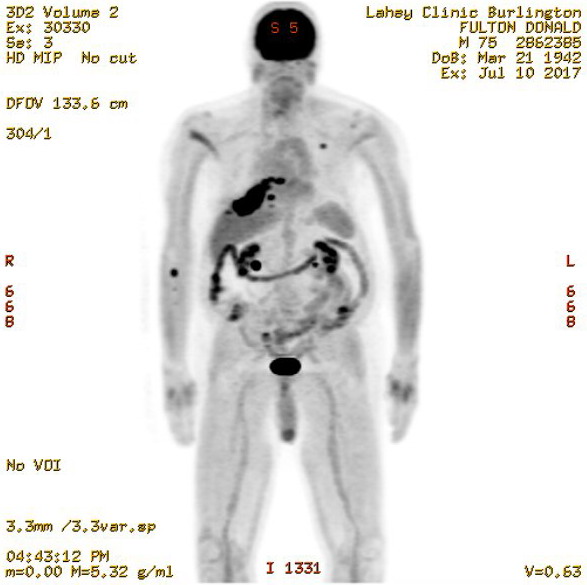
wide black region (upper left on image) is the plasmacytoma 9th
rib right posterior, clearly larger.
small dot (upper right on image) is very likely the 2nd rib, left
front plasmacytoma seen in 1st pet scan
small dot (left side of image) below elbow of the right arm is possibly
a new plamacytoma in right radius or ulna (two lower arm bones)
5th pet scan (7/10/17)
Compare 5th pet full body scan (above 7/10/17) to earlier
pet full scan images below: left, 4th pet scan 3/22/17 and
right, 1st pet scan 5/19/16
 .
. 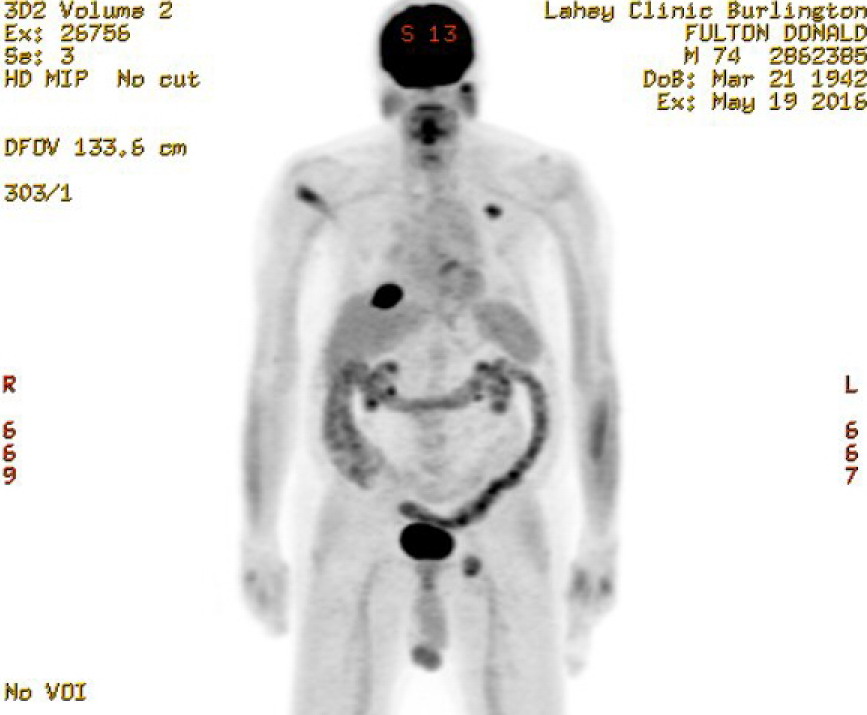
left -- 4th pet scan 3/22/17
right -- 1st pet scan 5/19/16
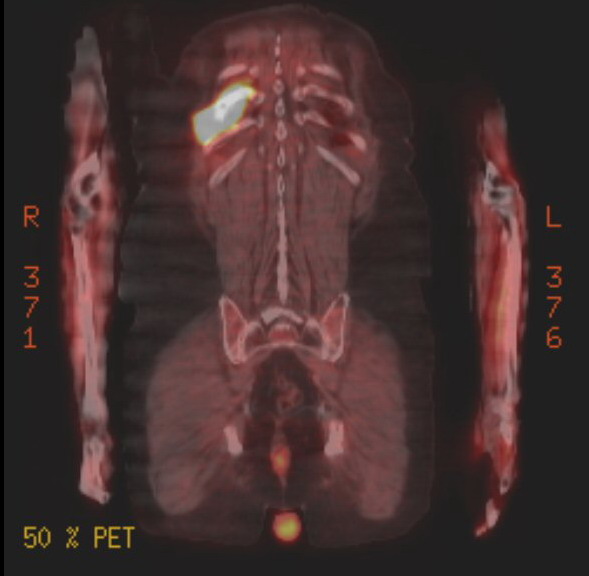
plasmacytoma in 9th right rib posterior showing new low intensity diffused
area
(no hint of activity in right arm in this image)
(5th pet scan 7/10/17)
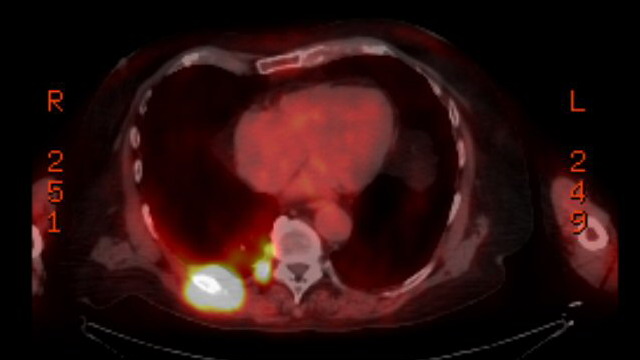
plasmacytoma in 9th right rib posterior showing new low intensity diffused
area
(5th pet scan 7/10/17).
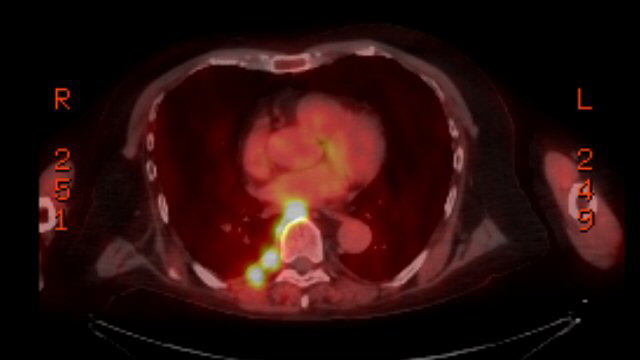
plasmacytoma in 9th right rib posterior
appearing to show its low intensity diffused area extending to spinal
column (T9)
(5th pet scan 7/10/17)
More pet5 images
 .
. 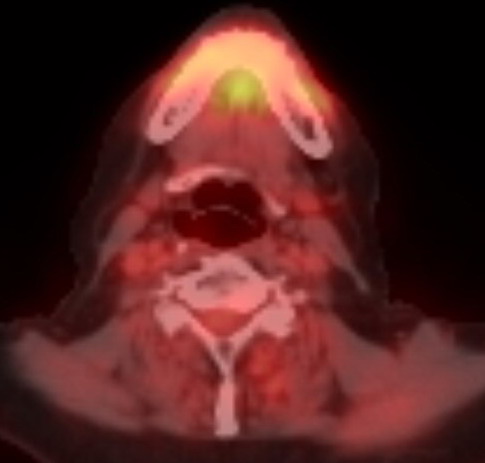
two images showing intesity in the jaw region
(5th pet scan 7/10/17)
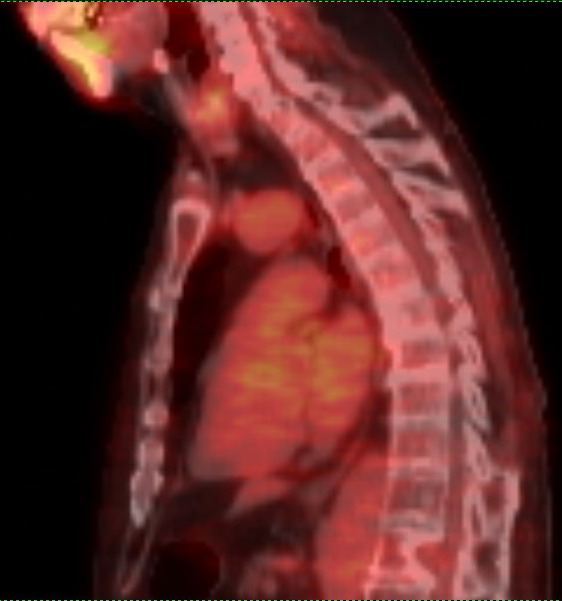 .
.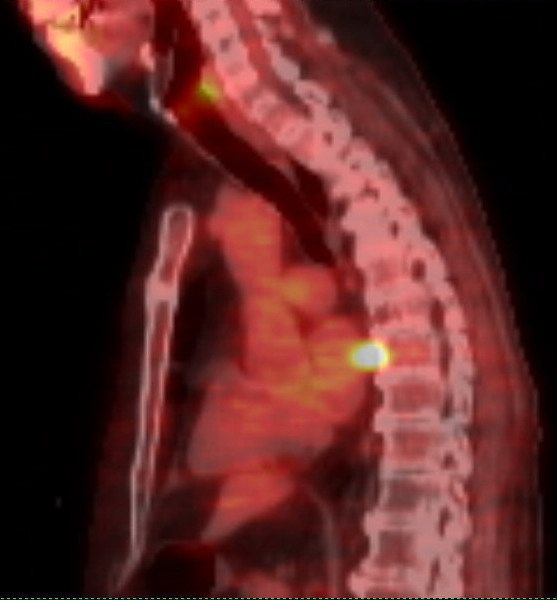 .
.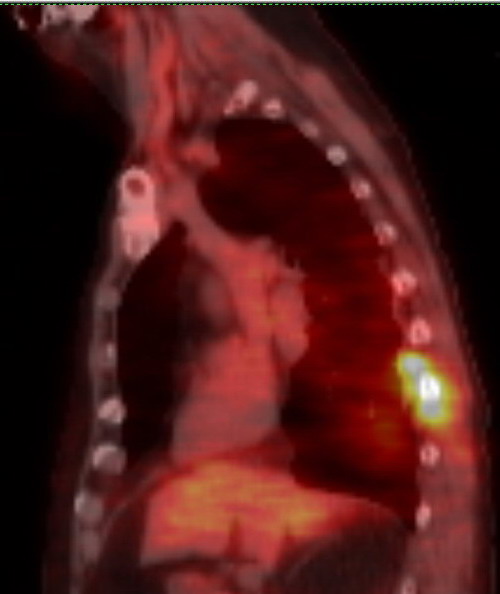
(left) lowest vertebrae with deep notch is T12
(center) hot spot appears to be on (inside of) T8
(right) hot spot appears to be at T9
(5th pet scan 7/10/17)
====================================================================================================================================-
Notes from radiolist report on 5th pet scan (8/18/2017)
The radiologist
report by radiology resident (dictated)) of the 5th pet scan is a disappointment.
Rather than focus on the cancer it's mostly a body review. It fails to
follow up on some new black spots on the initial whole body image. Not
does it comment on what I see as a metabolitically active area in the jaw.
The summary concerns only the known 9th and 2nd rib plasmacytomas. The
extension of the large 9th rib plasma cytoma to the spine, which I have
an image of, it not addressed.
Organs described as normal in appearance in 5th pet
scan
lungs,
liver, pancreas, kidneys, stomach, bladder, small and large bowel
(with moderate colonic diverticulosis), spleen, prostate/ seminal vesticles,
aorta and IVC, biliary ducts, thryoid, adrenal glands, peritoneum (lining
of abdominal caviry)

..

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6th PET scan images (10/18/17)
About 5-6 weeks before this
pet scan I had stopped chemo because I had developed a second cancer (MDS)
that basically shut down my marrow. My body is not making blood, specifically
not making red blood cells and platelets. I have been surviving in recent
weeks only I have been getting twice a week red blood cell transfusions
and platelet transfusions. My M-spike at this time is about .5 g/dL (its
disease threshold) and lambda free light chain a little above 20 mg/dL
(more than double its disease threshold). So it is not surprising that
my long existing right posterior tumor in my 9th rib has clearly been growing.
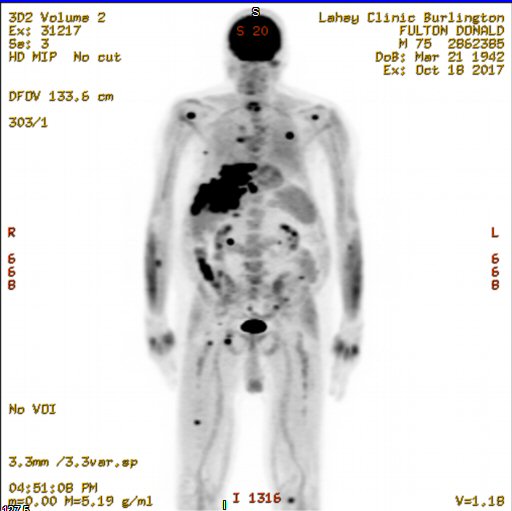

pet6 radiologist report (10/19/2017)
(radiolist text above reordered and expanded)
-------------------------
FINDINGS:
Ribs --- Compared
to prior scan, the (9th rib) right posterior chest wall lesion has markedly
increased in size and intensity. The left anterior 2nd rib lesion has significant
increased in size and intensity of FDG activity.
Lungs --- Right
posterior pleural (thin fluid filled cavity around lungs) lesions have
also increased in size. New lower periesophageal adenopathy (swollen lymph
node in lung) with increased FDG uptake. Right axillary adenopathy (swollen
lymph in arm area) with increased FDG uptake, new since last scan. There
is diffuse increased activity in both lung parenchymal (lung parenchyma
is the portion of the lung involved in gas transfer).
Liver --- Possible
new uptake in the dome of the liver. No other significant focal uptake
in the soft tissue of the abdomen and pelvis.
Bones --- Interval
development of multiple foci of uptake in right humeral head (humerus is
the upper arm bone), left glenoid (shoulder), right side of the sternum
(sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone shaped like a necktie located
in the center of the chest), multiple pelvic bones and bilateral femora
(femur is thigh bone)
IMPRESSION: Interval worsening of metastatic multiple
myeloma.
-------------------------
I suppose
the only 'good' news here is no mention of activity in the tumors in my
back, neck, or head.
====================================================================================================================================
1st Pet images from 5/19/16 (continued)
This image (below) clearly
shows the notch in T12 vertebrae.
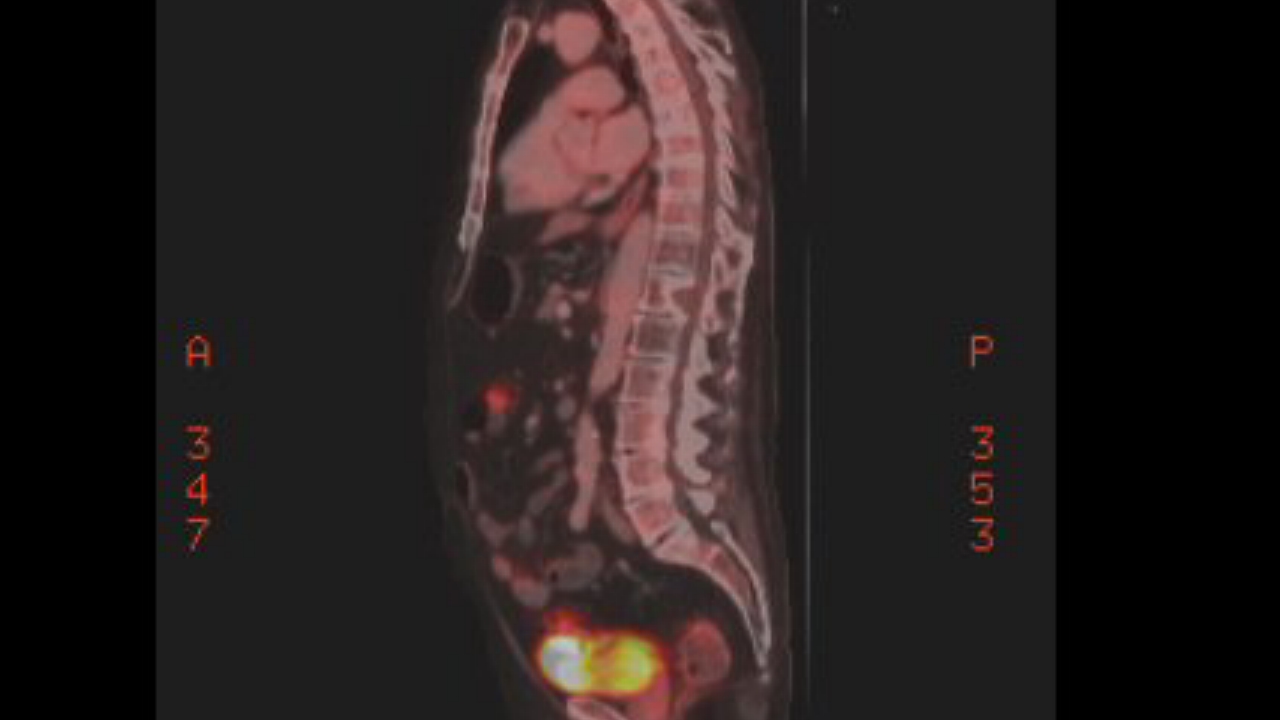
shows (pre-existng) loss of bone in T12 vertebrae (center of spine
in this image)
(T12 treated with radiation in sept 2014)
(No emission from T12, so this lesion does not appear to be metabolically
active)
1st pet scan (5/19/16)
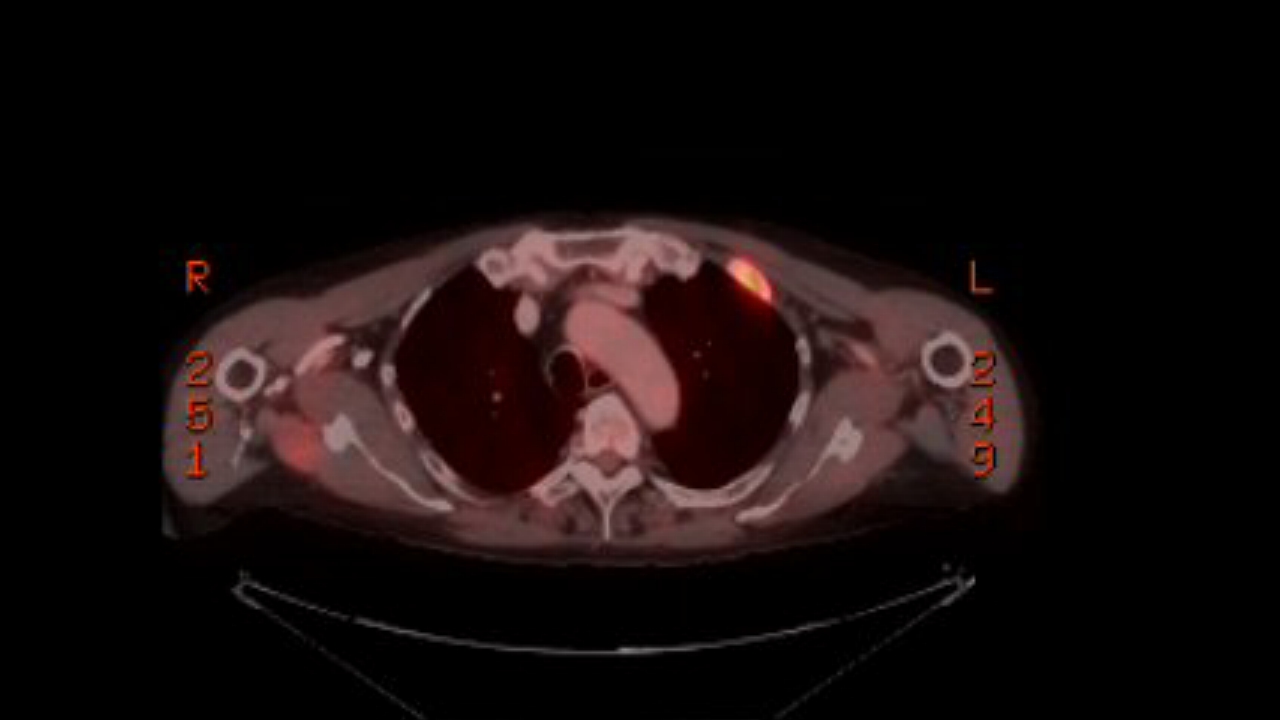
2nd rib left anterior (front) (may 2016)
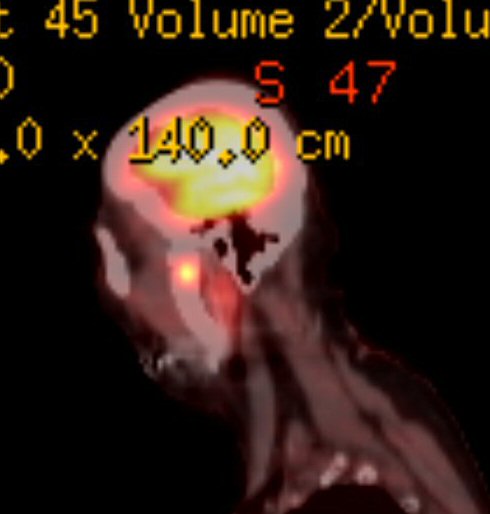
left mandible lesion (near hinge. side view)
(treated with radiation)
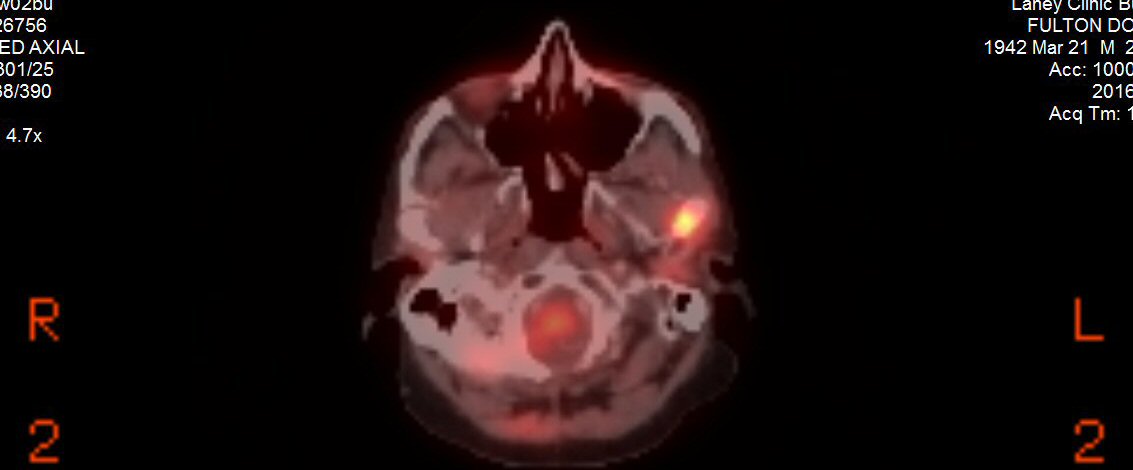
(my candidate for) left mandible lesion (top view)
(treated with radiation)
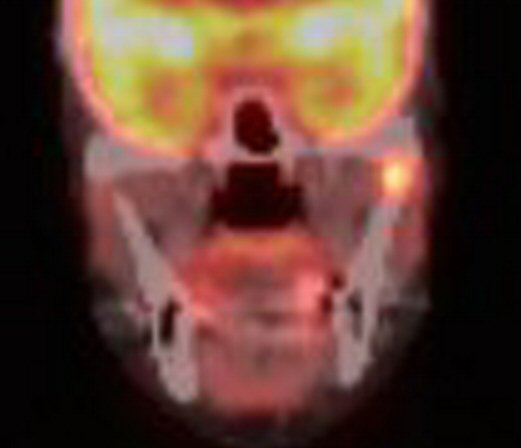
(my candidate for) left mandible lesion (near hinge. front view)
(Note, this view appears to show the hot spot high up on the mandible
near the hinge.)
(treated with radiation)
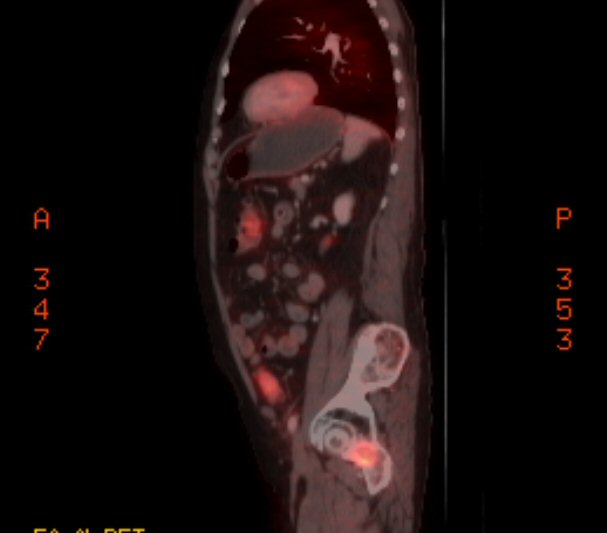
left pelvis lesion (side view)
(near pelvis/femur ball and socket joint)
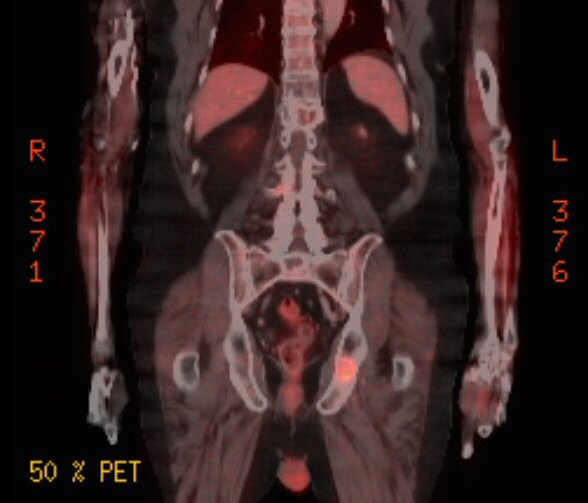
left pelvis lesion (front view)
(near pelvis/femur ball and socket joint)
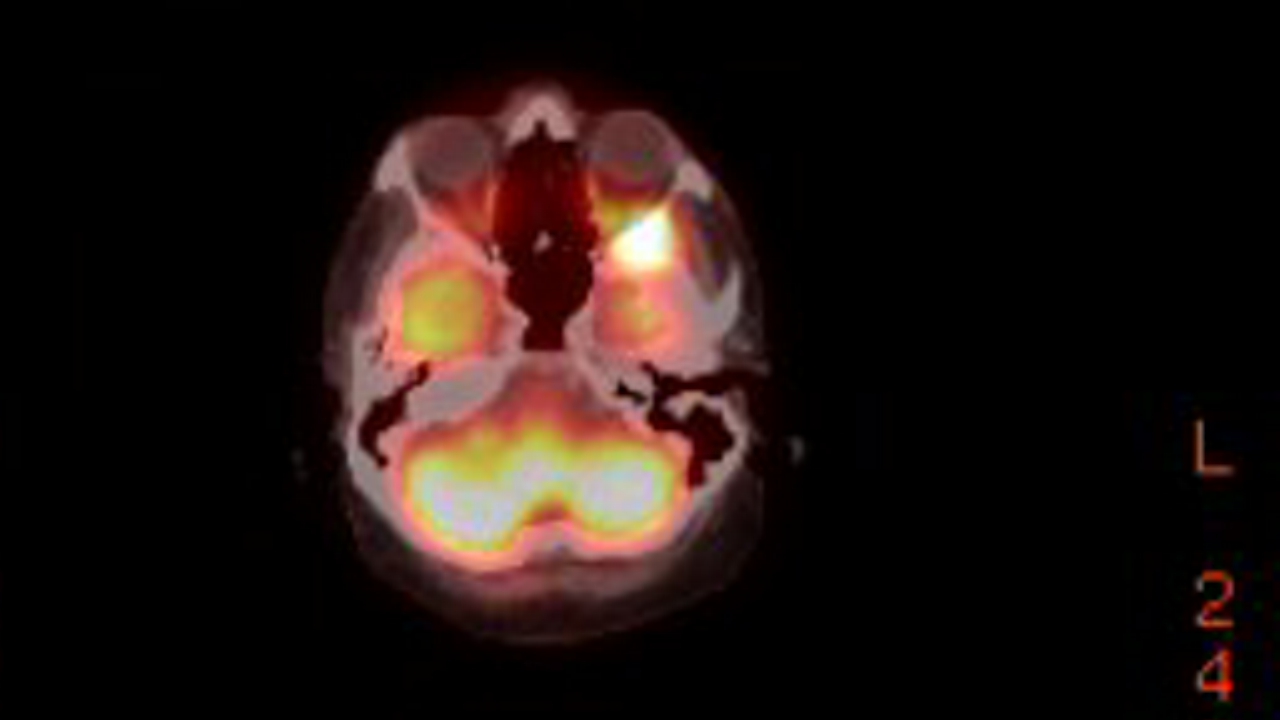
plasmacytoma behind left eye
(bright yellow upper right in this image)
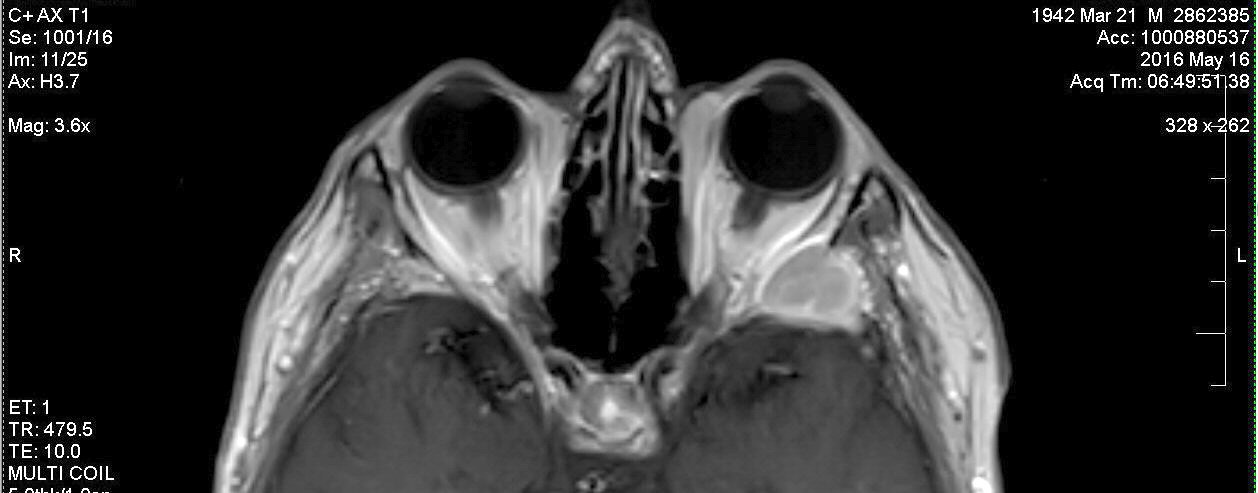
MRI image of plasmacytoma behind left eye ("in the sphenoid bone")
(treated with radiation, june 2016)
MRI faces
Here's some fun MRI images
of my face, as found on my brain MRI disk (may 2016) with only a little
exposure adjust and cropping.
 .
. .
. 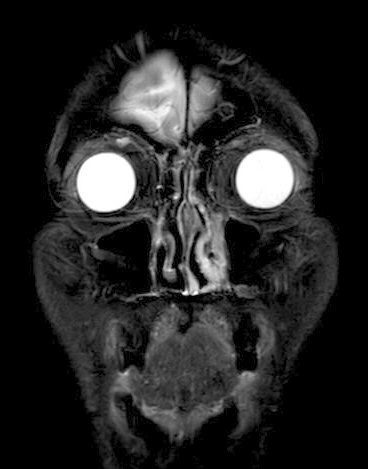
Yup, three sequential MRI images of my face
Pelvis anatomy
My pelvis lesion is described
in the PET report as "left ischium, extending to ischial tuberosity".
The PET reference to 'ischium' to is not clear. The anatomy sketches disagee
about just exactly where the 'ischium' is located. Left shows the 'body
of the ischium' is close to (and (probably) just behind) the hip
ball and socket joint, but right labels as the ischium a region slightly
lower (that left labels as ischial tuberosity!). "Ischial tuberosity' is
the beginning of the lower bone loop which extends down from the body of
the ischium.
 .
. 
PET reports describes active pelvis lesion as
"left ischium, extending to ischial tuberosity, SUV 5, 2.9 cm"
(Report and PET images put the lesion in the lower region of pelvis
(ischium) a little below the socket for the ball of femur
and extending about an inch down the long looping sitz bone (ischial
tuberosity).)
Radiation for 9th rib plasmacytoma?
Could radiation be used
on the 9th rib plasmacytoma? I was initially just assuming it could
be, but then I read in forums that you can't irradiate the same region
twice. So the question is, Is the 9th rib rear plasmacytoma too close to
the T12 area? How close can be figured from the figure below of ribs and
vertebrae. T12 is just above L1. This figure shows that one rib comes into
each vertebrae, that the 9th rib comes into vertebrae T9. The 9th rib plasmacytoma
is a little to side of the spinal column and three vertebrae above the
T12 radiation center. The answer likely depends on how tightly the T12
radiation was targeted.
shows the 12 ribs connect to the spinal column
at T1 to T12 of the thoracic spine.
In other words the 9th rib connects to T9.
(T12 is directly above L1 vertebrae)
Imaging considerations
X-ray
-- Lytic lesions (bone lesions)
become apparent on conventional radiography (X-rays) when 30–50% of the
bone mineral density is already lost.
CT scan
-- CT findings in multiple
myeloma consist of punched-out lytic lesions, expansile lesions with soft
tissue masses, diffuse osteopenia, and fractures.
(CT is better at finding small lesions than x-rays.)
MRI
-- It is important to note that
MRI predominately reflects marrow infiltration, which may or may not be
associated with bone destruction.
(In other words use MRI to look at marrow.)
-- Typical myeloma lesions
are marrow based and have low signal intensity on T1-weighted (MRI) images
and a high signal intensity on T2-weighted sequences.
-- Bone scintigraphy is
of limited use in multiple myeloma. Bone scintigraphy uses technetium 99-m
labelled diphosphonates and relies on the osteoblastic response and activity
of the skeletal system for uptake.
Pet/CT scan
** -- The presence of more than
3 FDG-avid focal lesions was the leading independent parameter associated
with an inferior overall and event-free survival. The prognosis of high-risk
patients in this study not achieving complete FDG suppression was poor,
which supports the use of serial PET/CT examinations in high-risk patients
to individualise therapy and prompt changes to alternative therapies. Importantly,
persistent FDG positivity can occur when bone marrow and M-component markers
are negative.
-- Positron emission computed,
tomography (PET/CT) is a tomographic nuclear imaging technique that uses
a labelled radiopharmaceutical such as 18flouro-deoxy-glucose (FDG) injected
into the patient, followed by tomographic scanning approximately 10–40
minutes later. Tumour cells can be imaged with this technique due to their
high metabolic rate and the resulting high glucose demand, allowing tumour
cells to be distinguished from normal cells.
-- Currently, PET/CT is being
evaluated in patients with multiple myeloma and may detect early bone marrow
involvement in patients with apparently solitary plasmacytoma, to assess
the extent of active disease, detect extramedullary involvement or evaluate
treatment response.
-- Active myeloma is FDG
positive for focal and diffuse abnormities and FDG uptake decreases rapidly
after effective therapy.
-- Persistent FDG positivity
correlates with early relapse as is discussed later. This rapid response
to treatment is converse to that seen with MRI where there may be a time
lag of 9–12 months in the reversal of MRI abnormalities despite successful
therapy.
-- False-positive PET/CT
scans may arise from inflammatory changes due to active infection, chemotherapy
within the preceding 4 weeks, or radiation therapy within the preceding
2-3 months.
-- Later in the disease
cortical breaches may occur, and further local spread from bone may be
seen, producing masses in the surrounding soft tissues.
"Extra-medullary" myeloma plasmacytomas
** -- Overall
survival for patients with extramedullary disease in the soft tissue was
30 months (2.5 yr) from initial myeloma diagnosis, compared to 45 (3.75)
months for patients with extramedullary disease adjacent to a bone. Overall
survival from time of diagnosis for patients without extramedullary disease
was 109 months (9.1 yr). (Extramedullary plasmacytomas are soft tissue
tumors not assoicated with any bone.)
* -- Multiple myeloma is a cancer
in which malignant plasma cells build up and form tumors ("plasmacytomas")
inside
the
bone marrow.
** -- Czech researchers recently
found that extramedullary disease that develops in the soft tissue of a
myeloma patient is associated with poorer prognosis than extramedullary
disease that develops adjacent to a bone.
-- During the course of their
disease, multiple myeloma patients sometimes develop what physicians call
"extramedullary plasmacytomas" or "extramedullary myeloma." In
medicine, when something is described as "extra-medullary," it means it
is located outside of the bone marrow. It occurs when malignant
plasma cells collect together and form tumors in parts of the body other
than a patient's bones. This can occur in any myeloma patient, but it appears
to be more common in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
-- “Extramedullary disease
occurring in a patient with myeloma is generally considered a more aggressive
disease. (These extramedullary lesions can grow quickly.)
-- A large study showed that
85 percent of multiple myeloma patients with extramedullary disease had
a tumor in the muscles, tendons, fat, and other soft tissue surrounding
the axial skeleton, which includes the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column.
-- The Annals of Oncology
study mentioned earlier found that approximately 13 percent of myeloma
patients develop extramedullary disease. Specifically, 7 percent of myeloma
patients have extramedullary disease at diagnosis, and 6 percent of patients
develop the disease during the course of their myeloma.
-- Extramedullary multiple
myeloma is uncommon. In one review of 432 patients with multiple myeloma,
only 19 (4.4%) were identified as having extramedullary multiple myeloma
-- “When a myeloma patient
develops extramedullary disease, it means that the myeloma is relapsing
and is becoming more aggressive.
-- (30 patients from 1998
to 201) Extramedullary disease at relapse was most commonly found in the
liver (25 percent), lungs (21 percent), lymph nodes (17 percent), and mouth
(13 percent).
-- (greek study) From the
time of their initial myeloma diagnosis, the median overall survival for
patients who developed extramedullary disease was 38 months (3.2 yr) ,
compared to 59 (4.9 yr) months for patients who did not develop extramedullary
disease.
-- CT in the followup of
treated disease may demonstrate the resolution of extramedullary disease.
Treatment options for extra-medullary" myeloma plasmacytomas(2011)
-- Results of several clinical
trials have shown that Velcade (bortezomib), Revlimid (lenalidomide), and
pomalidomide may improve outcomes for myeloma patients with extramedullary
disease. However, most of these studies are small, and the role of novel
agents in treating extramedullary disease in myeloma patients is still
unclear.
-- Results of a small study
published in the European Journal of Haematology (abstract) showed that
extramedullary disease disappeared in three out of four myeloma patients
treated with Velcade.
-- Another small study that
also was published in the European Journal of Haematology (abstract) found
that 61 percent of myeloma patients with extramedullary disease responded
to Revlimid, with 44 percent experiencing complete tumor disappearance.
-- In addition, a study published
in the journal Leukemia (abstract) reported that 31 percent of myeloma
patients with extramedullary disease responded to treatment with pomalidomide,
with 15 percent of patients experiencing complete tumor disappearance (see
related Beacon news).
-- (reader comment) Velcade
didn't do anything, he had it the third time. End of August started with
pomalidomide and within only one week the soft tissue manifestations had
disappeared completely. In the first cycle of pomalidomie he developped
a bad rash/itching, but now, in the third cycle it's completely gone. CT
showed, that also inside his body the extramedullary manifestations were
nearly gone right now. Doctors gave him only a few months because of the
very aggressive growth of these extramedullary manifestations - now he
feels really good.
Solitary bone plasmacytoma
Solitary bone plasmacytoma
This is a closely related
disease to MM, but is more limited that usual MM because at diagnosis there
is only single tumor.
* -- Solitary bone plasmacytoma
is a plasma cell disorder characterized by the formation of a single tumor
in the bone. The tumor, also called a plasmacytoma, occurs when abnormal
plasma cells originating in the bone marrow accumulate on the interior
surface of the bone. However, in patients with solitary bone plasmacytoma,
these malignant plasma cells are typically not present throughout the bone
marrow itself or in the soft tissues surrounding the bone.
-- Unlike multiple myeloma,
solitary bone plasmacytoma does not include the presence of abnormal plasma
cells throughout the bone marrow or in the soft tissues surrounding the
bone, a condition known as extramedullary myeloma. It is likely that the
location of the bone tumor is the same location at which the abnormal plasma
cells initially originated in the bone marrow. “That is why in roughly
50 percent of cases, solitary bone plasmacytoma is curable by radiating
that one site alone,” said Dr. Rajkumar.
--A previous retrospective
study involving 206 patients with solitary bone plasmacytoma indicated
that patients who received localized radiation therapy had a lower rate
of relapse (12 percent) than patients who did not receive radiation (60
percent).
-- “Our radiation therapy
specialists advise 40 Gy, similar to most practices elsewhere,” said Dr.
Raymond Alexanian of the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Evidence-based
guidelines published by the United Kingdom Myeloma Forum recommend at least
40 Gy over the course of 20 radiation sessions.
Current Diagnostic Imaging Techniques For Multiple Myeloma (2014)
* -- There have been studies
investigating the value of MRI and PET/CT for evaluating a myeloma patient's
response to treatment. Currently, the evidence suggests that, of the two,
PET/CT may be more effective at tracking treatment response.
-- According to current guidelines
from the International Myeloma Working Group, whole body X-ray skeletal
surveys should be considered the gold standard for detecting lytic bone
lesions in patients. X-ray skeletal survey typically takes much longer
than other imaging techniques because it usually requires at least 20 separate
scans.
-- PET/CT can detect
both extramedullary and medullary (bone) disease.
-- Computed tomography (CT)
is more sensitive than traditional X-rays. CT can detect smaller bone lesions
and can better assess the fracture risk of a patient. CT scans can also
reveal extramedullary disease, which occurs when myeloma cells form tumors
outside of a patient’s bones
-- Whole-body CT scans are
superior to x-rays in the detection of bone lesions in multiple myeloma
patients. “Low-dose, whole-body CT was significantly better than [x-rays]
in detecting lesions in the spine, ribs, sternum, and flat bones,” said
Dr. Princewill.
-- In the United States,
the standard method for detecting bone lesions is through a radiographic
(x-ray) skeletal survey. However in Europe, studies have demonstrated that
whole-body computerized tomography (CT) scans are better than x-rays for
detecting bone lesions.
-- MRI scans are particularly
useful for visualizing the bone marrow in myeloma patients. In this regard,
the technique is considered more sensitive than either X-ray skeletal surveys
or CT scanning.
-- For patients with symptomatic
multiple myeloma, the European researchers believe that screening using
either whole-body x-ray or low-dose CT should be mandatory at the time
of diagnosis. However, they point out that both PET/CT and MRI have
been found to be more sensitive, and have shown a higher detection rate
of lesions in symptomatic patients, than X-rays and CT alone. Based on
these findings, they recommend that MRI be considered as a complementary
diagnostic tool, given that it provides excellent results when used to
image the spine and pelvis.
-- At least two studies have
shown, for example, that patients whose PET/CT scans continue to show a
tumor burden ("abnormal FDG uptake") after treatment tend to have a higher
risk of progression, and shorter overall survival, in comparison of patients
with no abnormal FDG uptake after treatment. (That said, studies on the
use of PET/CT in response assessment have been limited to patients who
have received a stem cell transplant.
-- PET-CT was more
reliable than MRI for evaluating a patient's response to therapy.
http://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmr/2011/583439/
http://www.myelomabeacon.com/news/2011/11/04/extramedullary-myeloma/
http://www.myelomabeacon.com/news/2014/05/02/imaging-techniques-for-multiple-myeloma/
----------------------------------------------------------------
Types of (general) chemotherapy drugs
-- Alkylating agents
Alkylating agents directly damage DNA (the genetic material in each
cell) to keep a cell from reproducing. These drugs work in all phases of
the cell cycle and are used to treat many different cancers, including
leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin disease, multiple myeloma, and sarcoma, as
well as cancers of the lung, breast, and ovary. Because these drugs damage
DNA, they can cause long-term damage to the bone marrow. In rare cases,
this can lead to acute leukemia.
Examples
Alkylating agents are divided into different classes, including:
Nitrogen mustards: such as mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard), chlorambucil
cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), ifosfamide, and melphalan.
-- Other types
of cancer drugs
Other drugs and biological treatments are used to treat cancer, but aren’t
usually considered chemotherapy. While chemotherapy drugs take advantage
of the fact that cancer cells divide quickly, these drugs target other
properties that make cancer cells different from normal cells. They often
have less serious side effects than those commonly caused by chemotherapy
drugs because they are targeted to affect cancer cells, not normal, healthy
cells. Many are used along with chemotherapy.
-- Targeted Therapies
As researchers have learned more about the inner workings of cancer cells,
they’ve created new drugs that attack cancer cells more specifically than
traditional chemotherapy drugs. Most attack cells with mutant (altered)
versions of certain genes, or cells that express too many copies of a certain
gene. These drugs can be used as part of the main treatment, or they may
be used after treatment to keep the cancer under control or keep it from
coming back.
Examples of targeted therapies include:
Imatinib (Gleevec)
Gefitinib (Iressa)
Sunitinib (Sutent)
* Bortezomib (Velcade)
============================================================================================================
Appendix 2
Plasmacytoma (1/8/17)
Plasmacytomas can
only be tracked by Pet scans. My first Pet scan was in 5/19/16 to follow
up on the plasmacytoma discovered behind my left eye by an MRI a few days
earlier. This led to a change in chemo from rev/dex to pom/carfilzomiz/dex.
On the new chemo a follow up Pet scan was done after 2.5 months (9/6/16).
It showed "no new lesions", "interval good response to theapy" and "largest
residual discease posterior right 9th rib, decreased in size and intensity
(max SUV 6.5, previous 15.1)"
A 3rd is Pet scan is scheduled
1/11/17. This will be four months after Pet scan #2 and 6.5 months into
pom/carfilzomiz/dex chemo. The trend of my blood numbers on the new chemo
for the last six months has been good. Free light chains (both) have remained
in the normal region, and my M-spike(s) have shown a general downward trend
with the latest (mid Dec 16) values at 0.12g/dL, or about 1/4th of the
threshold 0.5 g/dL threshold.
My first remission ended
because MRI and PET scan found several plasmscytomas. One behind my left
eye, a big one and a small one in by ribs. My oncologist said plasmacytomas
are rare in MM patients, maybe 5% get them. But more importantly plasmacytomas
are associated with poor survival. A little research confirms that that
is right. My plasmacytomas appear to be confined to my bones (ribs, sphenoid
bone behind eye).
Multiple myeloma
B cell (triggered by invading
'antigens' virus, bacteria, etc) => plasma cells => antibodies. In other
words it seems like plasma cells are the immune systems factories for generating
antibodies, which to into the blood to actually disable the invading antigen.
The antigens cause the B cells generates a particular plasma cell so that's
its immuniglobins will attack the antigen.
Plasmacytomas
The big concern seems to
be plasmacytomas that form away from the bone (extramedullary) in various
organs of the body. It is not clear how this applies to me. All my plasmacytomas
are either in bones, or maybe just spilling out. What are plasmacytomas
really? How bad are they if they are in bones? I did a little research.
-- When plasma cells become cancerous
and grow out of control, they can produce a tumor called a plasmacytoma.
These tumors generally develop in a bone, but they are also rarely
found in other tissues. (www.cancer. org)
-- Plasmacytomas can also
invade soft tissue in the body. Plastacytoma in soft tissue can press on
nearby areas and cause pain such as the throat, tonsils or sinus (multiple
myeloma research foundation)
Extramedullary
-- Extramedullary," it means
it is located outside of the bone marrow. During the course of their disease,
multiple myeloma patients sometimes develop what physicians call either
"extramedullary disease," "extramedullary plasmacytomas," or
"extramedullary myeloma. "Extramedullary" myeloma is myeloma that
is outside of the bone marrow. It occurs when malignant plasma cells collect
together and form tumors in parts of the body other than a patient's bones.
This can occur in any myeloma patient, but it appears to be more common
in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.“Extramedullary
disease occurring in a patient with myeloma is generally considered a more
aggressive disease,” according to Dr. Rajkumar. (Mayo clinic)
-- A large study published
in the Annals of Oncology in 2009 showed that 85 percent of multiple myeloma
patients with extramedullary disease had a tumor in the muscles, tendons,
fat, and other soft tissue surrounding the axial skeleton, which includes
the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column. The remaining 15 percent of
extramedullary disease cases affected the lymph nodes, liver, kidney, airways,
skin, and breast.
-- “When a myeloma patient
develops extramedullary disease, it means that the myeloma is relapsing
and is becoming more aggressive", said Dr. Rajkumar.
-- Results of several clinical
trials have shown that Velcade (bortezomib), Revlimid (lenalidomide), and
pomalidomide may improve outcomes for myeloma patients with extramedullary
disease.
-- Another small study that
also was published in the European Journal of Haematology (abstract) found
that 61 percent of myeloma patients with extramedullary disease responded
to Revlimid, with 44 percent experiencing complete tumor disappearance.
A study published in the journal Leukemia (abstract) reported that 31 percent
of myeloma patients with extramedullary disease responded to treatment
with pomalidomide, with 15 percent of patients experiencing complete tumor
disappearance (see related Beacon news).
-- Plasmacytomas crowd out
normal cells in the bone marrow as well as invade the hard outer part of
the bone and then spread into the cavities of the large bones in the body.(multiple
myeloma research foundation)
-----------------------------
Refractory myelema
I am also a little unclear
about 'refractory' multiple myeloma. Relapsed myeloma I understand. According
to Dana Farber notes I am both relapsed and refractory.
-- Refractory myeloma is
when myeloma is not responsive to therapy. Refractory myeloma may occur
in patients who never see a response from their treatment therapies or
it may occur in patients who do initially respond to treatment, but do
not respond to treatment after relapse. Translation: This seems to
mean a MM patient has tried one (or any) particular chemo and has not responded.
----------------------
Definition
Plasmacytoma is a plasma
cell neoplasm which forms tumors when plasma cells become malignant and
grow out of control. Plasmacytomas crowd out normal cells in the bone marrow
as well as invade the hard outer part of the bone and then spread into
the cavities of the large bones in the body. Plasmacytoma in the bones
may cause pain or broken bones. Plasmacytomas can also invade soft
tissue in the body. Plastacytoma in soft tissue can press on nearby areas
and cause pain such as the throat, tonsils or sinuses.
Note, the definition
of plasmacytoma seems to be a little loose. It's clearly a collection of
grouping together of cancerous plasma cells, but it can be inside
a bone or outside (extramedullary) bone, meaning a tumor anywhere
in the body.
Treatment --- Because these things are localized they can be treated with
radiation (or sometimes surgery). The tumors are radiation sensitive, meaning
that they these cells can be killed with about half the dose used on solid
tumors. Not only does this mean less side effects, but half days needed,
like two weeks vs a month.
Three types
There are three distinct
groups of plasmacytoma defined by the International Myeloma Working Group:
1) solitary plasmacytoma of bone (SPB)
2) extramedullary plasmacytoma (EP)
3) multiple plasmacytomas that are either primary or recurrent.
In medicine, when something
is described as "extramedullary," it means it is located outside of the
bone marrow. So "extramedullary" myeloma is myeloma that is outside of
the bone marrow in the soft tissue and organs of the body.
** When a myeloma patient
develops extramedullary disease, it means that the myeloma is relapsing
and is becoming more aggressive. The results are consistent with those
from previous studies and demonstrate that myeloma patients who develop
extramedullary disease have poorer overall survival than those who do not.
They conclude that myeloma patients with extramedullary disease exhibit
a particularly aggressive and treatment-resistant form of myeloma, posing
unique therapeutic challenges.
** From the time of their
initial myeloma diagnosis, the median overall survival for patients who
developed extramedullary disease was 38 months (3 yr), compared to 59 months
(5 yrs) for patients who did not develop extramedullary disease. (note
these are small studies)
-- A large study published
in the Annals of Oncology in 2009 showed that 85 percent of multiple myeloma
patients with extramedullary disease had a tumor in the muscles, tendons,
fat, and other soft tissue surrounding the axial skeleton, which includes
the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column.
The remaining 15 percent of extramedullary disease cases affected the
lymph nodes, liver, kidney, airways, skin, and breast. Extramedullary disease
at relapse was most commonly found in the liver (25 percent), lungs (21
percent), lymph nodes (17 percent), and mouth (13 percent).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sphenoid bone
Here is the sphenoid bone that
separates the eyes from the brain. The greater wing of this bone is where
the plasmacytoma behind the left eye is located. While it's not clear to
me and is not spelled out in the MRI report, the radiation doctor says
the mass is "inside" the bone.
.jpg)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Proteasome
and 'proteasome inhibitor' drugs
-- Proteasomes are protein
complexes inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes,
proteasomes are located in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The main function
of the proteasome is to degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis,
a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions
are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which
cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded
proteins. (Wikipedia)
Carfilzomib
My interest in the proteasome
protein complex and understanding what it does is because a key component
of my 2nd line chemo has been the infused drug carfilzomib, described as
a 'proteasome inhibitor', which according to it prescribing document "irreversibly
binds to the N-terminal threonine-containing active sites of the 20S proteasome,
the proteolytic core particle within the 26S proteasome." Specifically
it causes the suppression of proteasome chymotrypsin-like (CTL) activity.
One of the major side effects
of carfilzomib is lung toxicity, which after taking it for a few months
became a concern as I began to develop shortness of breath (dyspnea) that
slowly got worse. After about 8 months (7/16 to 3/17) on carfilzomib a
pulmonary functional test DLCO (Diffssion capacity of lung for CO) showed
my oxygen intake per breath was only about half of what it should be for
someone my age. According to the prescribing document 28% of patients on
carfilzomib report dyspnea (shortness of breath) with it reaching grade
3 in 4% of patients. I think this probably includes me, but clinicians
don't talk to patients about grades so it's hard to be sure, but after
8 months on carfilzomib and a very low DLCO measurement I was sent to a
lung doctor for a lung evaluation that is to include a high resolution
CT scan to evaluate damage to the small air sacs of the lung.
Side effects 'grades' 1-4
Grade 1
Mild -- Transient (goes away after a short time) or mild discomfort; no
limitation in activity;
no medical intervention/therapy required
Grade 2
Moderate -- Your daily activity is affected mild to moderately – some assistance
might be needed;
no or minimal medical intervention/therapy required.
Grade 3
Severe -- Your daily activity is markedly reduced – some assistance usually
required;
medical intervention/therapy required, hospitalisation or hospice care
possible.
Grade 4
Potentially life threatening or disabling -- Extreme limitation to daily
activity, significant assistance required;
significant medical intervention/therapy, hospitalisation or hospice care
very likely.
(Grade 5)
Fatal
Fatique example
Grade 1 -- Normal activity
reduced by less than 25%
Grade 2 -- Normal activity
reduced by 25% - 50%
Grade 3 -- Normal activity
reduced by over 50%, can't work
Grade 4 -- Unable to care
for yourself
Ninlaro (Ixazomib)
Another proteasome inhibitor I
will be giving a quick trial to is Ninlaro, the pill equivalent of (injected)
Velcade, which has been a staple in MM chemo for a decade. It too is a
proteasome inhibitor, but it contains boron and attacks a different target
on the proteasome to inhibit it. It's prescribing document says, "ixazomib
is a reversible proteasome inhibitor. Ixazomib preferentially binds and
inhibits the chymotrypsin-like activity of the beta 5 subunit of the 20S
proteasome".
So both of these proteasome
inhibitors inhibit chymotrypsin-like activity, but Ninlaro does it by targeting
the beta 5 subunit of the 20S, which is different from carfilzomib's target
(N-terminal threonine-containing active sites of the 20S proteasome).
Prroteasome complex
Wikipedia has this
sketch (right) of a proteasome complex showing a cylindrical structure
made up of four (blue) rings and red end caps. Its job is to rip apart
damaged proteins, which are fed into its hollow core aided by enzymes called
proteases. It's cell clean up to prevent junk and damaged proteins in the
cell from hanging around. Each of the four stacked rings that make
up the core consist of seven proteins. The inner two rings contain seven
betasubunits,
and this is where the destruction of the degraded protein occurs. The outer
two rings contain seven alpha subjunits and form a gate through
which the protein to be degraded enters. Note that Ninlaro targets the
beta 5 subunit. Where on the proteasome are the carfillzomib targets (N-terminal
threonine-containing active sites), is not clear though Wikipedia says
the alpha subunits N-termini form a gate that suggests that this may be
the target of carfilzomib.
My infused cancer drug
carfilzomib is described in its prescribing document as a 'proteasome inhibitor'
(not a protease inhimitor). Multiple myeloma cancer cell death is
somehow promoted if operation of the the proteasome is shut down, so loosely
speaking cell protein clean up is inhibited. Since this appears to be a
general cell function, why this would more strongly affect cancer cells
than normal cells I have never seen explained. It seems complex, and I
get the impression the biochemical pathways affected are not fully understood.
-- ** Notably, multiple myeloma has been observed to result in
increased proteasome-derived peptide levels in blood serum that decrease
to normal levels in response to successful chemotherapy with Velcade.
-- Lactacystin (precursor of Velcade) covalently modifies the amino-terminal
threonine of catalytic beta subunits of the proteasome, particularly the
beta5 subunit responsible for the proteasome's chymotrypsin-like activity.
This discovery helped to establish the proteasome as a mechanistically
novel class of protease: an amino-terminal threonine protease.
-- * Proteasome inhibitors have effective anti-tumor activity
in cell culture, inducing apoptosis (cell death) by disrupting the regulated
degradation of pro-growth cell cycle proteins. This approach of selectively
inducing apoptosis in tumor cells has proven effective in animal models
and human trials.
-- proteasome inhibition may prevent degradation of pro-apoptotic
factors such as the p53 protein, permitting activation of programmed cell
death in neoplastic cells dependent upon suppression of pro-apoptotic pathways.
Since proteases exist widely I
can't figure out why inhibiting them works against MM. I'm not sure the
researchers do either. as they end up saying in vitro Velcade can dramatically
change the peptide balance of the cell. And this is reflected clinically
in peptide levels seen in the blood. Velcade major side effect has been
that it also affects nerve cells leading to numbness and damage of nerves
apparently in the fingers and toes. Ninlaro has been formulated to minimize
this nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy). |
 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Heart tests (6/14/16)
Here are the test results
of several tests done on my heart prior to starting pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo. The reason for these tests is assess the health of my heart and
establish a baseline since the proteasome inhibitor of my new chemo (carfilzomib)
has a real potential to cause heart attacks. (I need to research this).
The reason given below is stated: Baseline prior to cardiotoxic chemotheapy.
None of the first three tests
are entirely normal.
BNP at 113 pg/mL is out of the normal range (0 to 80 pg/mL)
Troponin, which is 'undetectable in most health individuals', has a low
but measurable value of 0.04 ng/mL (0 to 0.30 ng/mL)
ECG (same as EKG) is described at 'boderline' (abnormal R-wave progression)
but the (ultrasonic) echocardiogram,
which takes a detail look at the motion of the valves and ventricles of
the heart, looks pretty good.
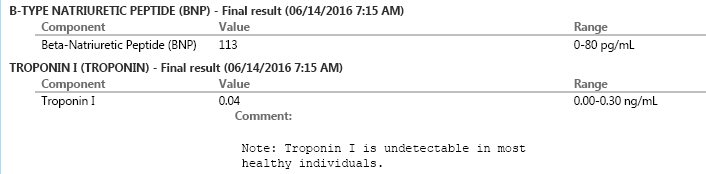
..




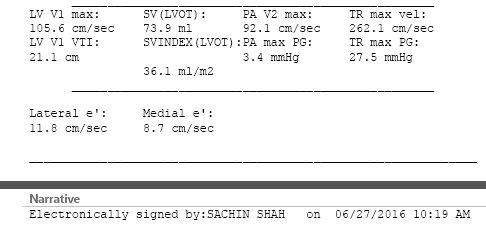
...
====================================================================================
My 'one minute' right eye blindness
(8/9/16)
1 min vision loss symptoms (8/9/16)
Upon waking and opening
my eyes in bed I was horrified to find that I was essentially blind in
my right eye. The lower half of the visual field was blank, the upper half
had images, but very abnormal with high contrast and sparkly noise. After
one minute or so while sitting on the toilet the problem resolved, normal
vision fully returned in my right eye in just 1-2 seconds. All during
this time vision of my left eye remained normal. Also there was no pain.
It's now been a week and the problem has not returned.
Result of eye tests (8/22/16)
The many detailed eye tests, including
a retina tomography machine that combines with many images of the retina
from different angles with a computer into a 3d images of the retina, showed
both my eyes are in good condition, "structurally sound". However, while
I didn't ask, I think the focus of all these tests was the retina. The
images of the retina nerves rising to form the optic nerve bundle looked
normal.
Best guess of cause of transient vision loss (8/22/16)
The best guess from my neuro-opthomologist
was that I most likely had transient reduced blood flow to the right eye
in one of the branching arteries (see below) between the carotid (neck)
artery left and the eyeball right. (Below is actual image the doctor
pointed to, which I later found online.)
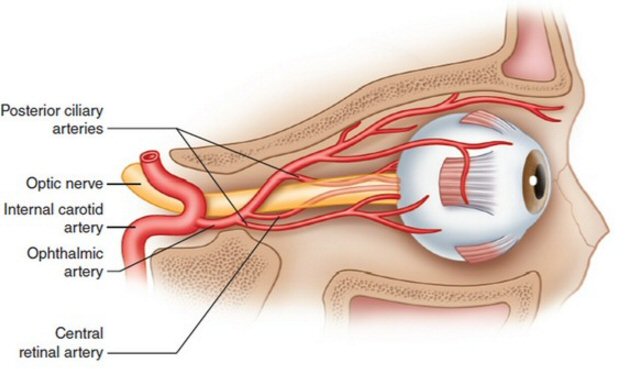
Doctor's initial guess of the cause of my one minute vision loss
in my right eye:
a transient blood blockage in one of the small branching arteries
between the carotid artery (left) and the retina in the eyeball
(right).
(source -- http://www.emdocs.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/anatomy.jpg)
One reference says a (permanent)
blockage of one of the ophthalmic arteries is an ophthalmic emergency,
but prognosis is poor, only 20% of eyes will retain any useful vision.
Translation: You are screwed. Before treatment can clear any blockage,
critical structures in the eye will have died from lack of oxygen and you
are blind in that eye.
Eye-brain visual pathway
Images below show the pathway
from the eyeballs to the back of the head, where the occipital lobes of
the cerebral cortex are located. The optic nerves from the two eyes pair
up at the optic chiasm about 1" behind the eyes and then the optic nerves
of the two eyes travel across the brain in the same bundle to the back
of the brain where the visual cortex is located. So this limits where
a blood clot or possible tumor (plasmacytoma) could be located so that
it affects only one eye with the the other eye normal. Looking at these
images I see two possibilities for the loss of vision in only eye. Something
affects the optic nerve somewhere between the retina and the optic chiasm,
or two a reduction in blood flow to the right eye where nerves of the retina
bundle to form the optic nerve.
Sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone behind the right
eye is another possible candidate given my cancer history. The sphenoid
bone has two holes through which optic nerves from the right and left eye
passes. Three months ago plasma cancer cells were running riot in the sphenoid
bone behind the left eye, in that case producing double vision by pushing
the bone out to press on muscles that move the left eyeball. While the
sphenoid bone forms in pieces during development, these pieces are merged
in an adult, so it may very well be that the marrow sections of the regions
of the sphenoid bone behind the two eyes are merged into one chamber. (However,
I don't know that this is true.) The radiologist reading my recent MRI
taken 9 hr have the transient vision loss did not see any impingment of
the optic nerve as it passes through the hole in the sphenoid bone.
Pituitary gland
I read one source of visual problems
in the brain that commonly affect only one eye arises from problems with
the pituitary gland. This small gland is located just below the optic chiasm.
It can develop tumors causing it to expand and squeeze the optic chiasm,
or bleed which can put pressure one of the still separate optic nerves
as they approaches (or enter) the optic chiasm. However, I have not seen
any info that this would cause a transient visual problem lasting just
a few minutes. So an obvious question is do I have a plasmacytoma in the
pituitary gland. (The radiologist reading my latest (Aug 2016) brain MRI
makes no mention of a the pituitary gland.
Oxygen to the optic nerve
Surprisingly the optic nerve
as it exits the eye is described as a bundle (1 million or so) of very
long axons of nerve cells originating in the retina. (Axons of nerve cells
in some animals are known to be feet long.) The Wikipedia page on the optic
nerve is horrible technical, but it seems to say the retina axons do not
end at the optic chiasm, but continue right back to the optical cortex
at the rear of the brain. So how is oxygen supplies to the optic nerve?
Is is supplied by the source in the retina?
 .
.
(left image) --- nerves from the right and left eyeballs pair up
at the optic chiasm,
and then travel together in a bundle to the visual processing region
in the back of the brain.
(right image) --- shows the location of the pituitary gland relative
to the optic nerve
(source left -- http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_i4f5qTnXK2I/TIJWSh6m4gI/AAAAAAAAAWc/e-0OhlkXTIo/s1600/optic_pathway.+1.gif)
(source right -- http://www.cancer.gov/images/cdr/live/CDR689771-750.jpg)
MRI images from 8/9/16
Quick call from my
oncologist says the radiologist review of these MRI images was negative.
Nothing new of interest was found. The plasmacytoma in the sphenoid bone
behind the left eye, which was irradiated, is seen to have shrunken from
three months ago.
So that means we have no
clue as to the cause of the 1 min loss of vision in the right eye.
====================================================================================
New Test Results (aug 2016)
Updated
view of the plasmacytoma behind my left eye
(8/9/16)
Four images I captured from
8/9/16 MRI disk. The first pair shows almost no difference between the
right and left eyes (second is just a contrast change). This is after two
weeks of radiation and 6 weeks of (new) pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo. The
lower pair of images shows the plasmacytoma is still present though smaller
(maybe 50%) than in May 2016. The bowing of the sphenoid bone is gone.
The fifth image below for reference is the view of the left eye plasmacytoma
in May 2016 while on rev/dex chemo and prior to radiatiion.
(update 11/8/16)
Even though these Aug 9,
2016 images show the bowing of the spenoid bone seems to be gone after
two wks of radiation and 6 wks of pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo my double vision
as of Nov 8, 2016 when looking right remains about the same as prior to
treatment. Is the plasmacytoma growing, has the bowing returned?
On a second look at the 4th
MRI image below it may be that the white triangle of the plasmacytoma,
even without the sphenoid bone bowing, is pushing a little on the eyeball
muscles acting like a wedge?
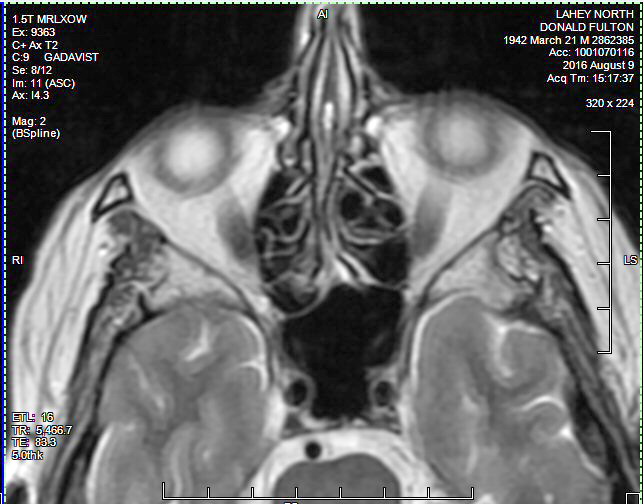 .
. 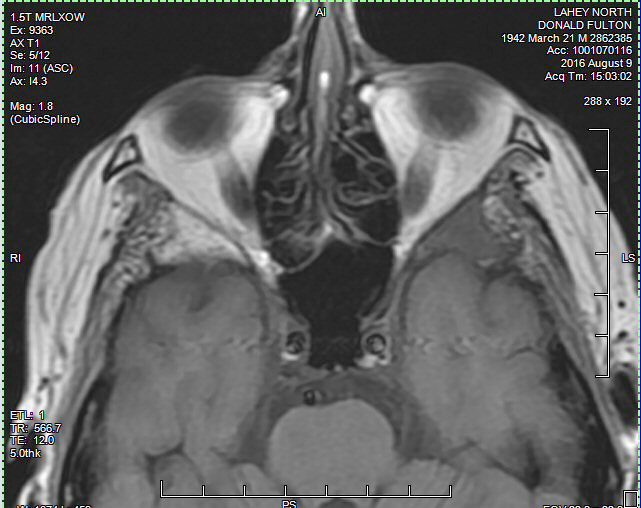
(left) Image shows the spheoid wings behind the two eyes and they
are virtually idential.
Also the well defined boundary between the eyes and the sphenoid
bone is nearly identical.
(right) Here there is a contrast difference between the two eyes.
..
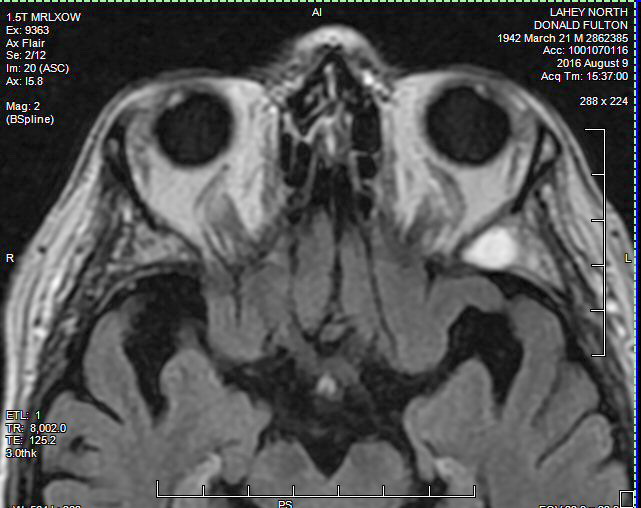 .
. 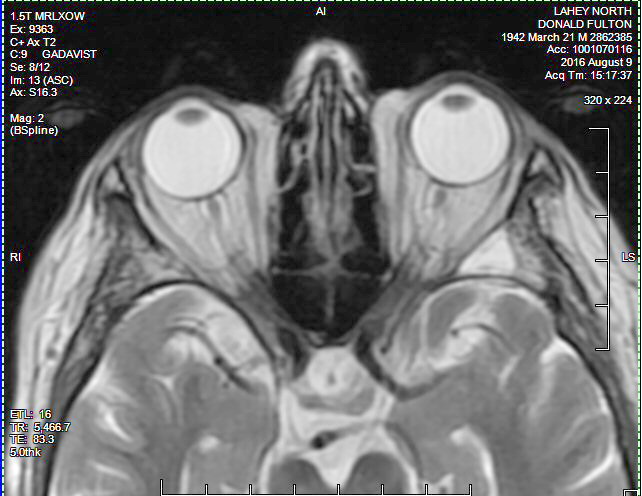
(left) Image shows the round (hot) spot plasmacytoma behind the
left eye. This is probably the 'round spot' the radiologist mentions in
his report.
(right) Another view of the hot spot plasmacytoma between the left
eye.
The bowing of the left wing of the sphenoid bone (evident in the
May 2016 image below)
into the lateral muscles of the left eye is now gone.

For reference -- comparable MRI image taken 5/16/16 prior to radiation
and change in chemo
showing large plasmacytoma (white) behind left eye.
Shows the sphenoid bone bowing out interfering with muscles moving
the left eye
Radiologist
report on my 8/9/16 brain MRI
The summary of my right
eye loss of vision symptoms in this report is pretty accurate, but it's
also important because it is the first look at the plasmacytoma behind
my left eye since it was irradiated and chemo was changed.. (signed by
Philip Kousoubris MD)

..

Retinal tomography
--
3d
images of retina (8/23/16)
I don't remember the exact
name of the hi-tech retinal test I had, but I know it involved using a
laser to take images of the retina from different angles and tomography
combining those images with a computer to get a 3d look at the retina.
From what I see online this may be 'Heidelberg Retinal Tomography' which
specializes in looking at the retina around the hole (optic disc) where
the retina nerves (about a million) come together to turn down into the
hole (in sphenoid bone) and form into the optic nerve. I got print out
of my test results from this test (scans belows). Note green indicates
no problem and nearly all the test results are color coded green.
I have not researched this
tomographic test, so I have no idea what these individual views of the
retina mean, but they are nearly all color coded green, indicating the
images are normal. The neuro-ophthalmologist in charge looking at these
results, which were part of a huge bank of eye tests on the same day, said
my eyes are "structurally sound".
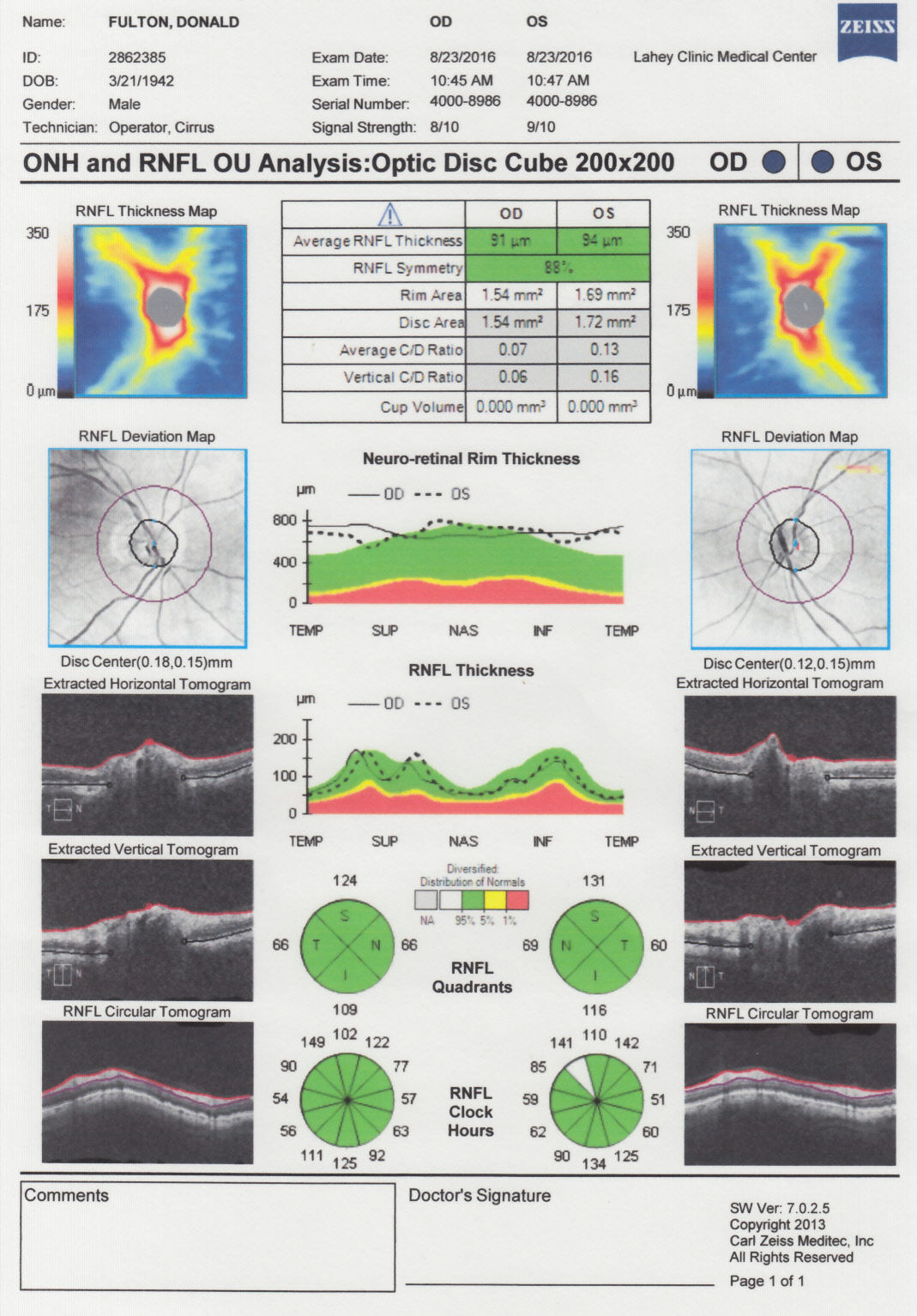
..
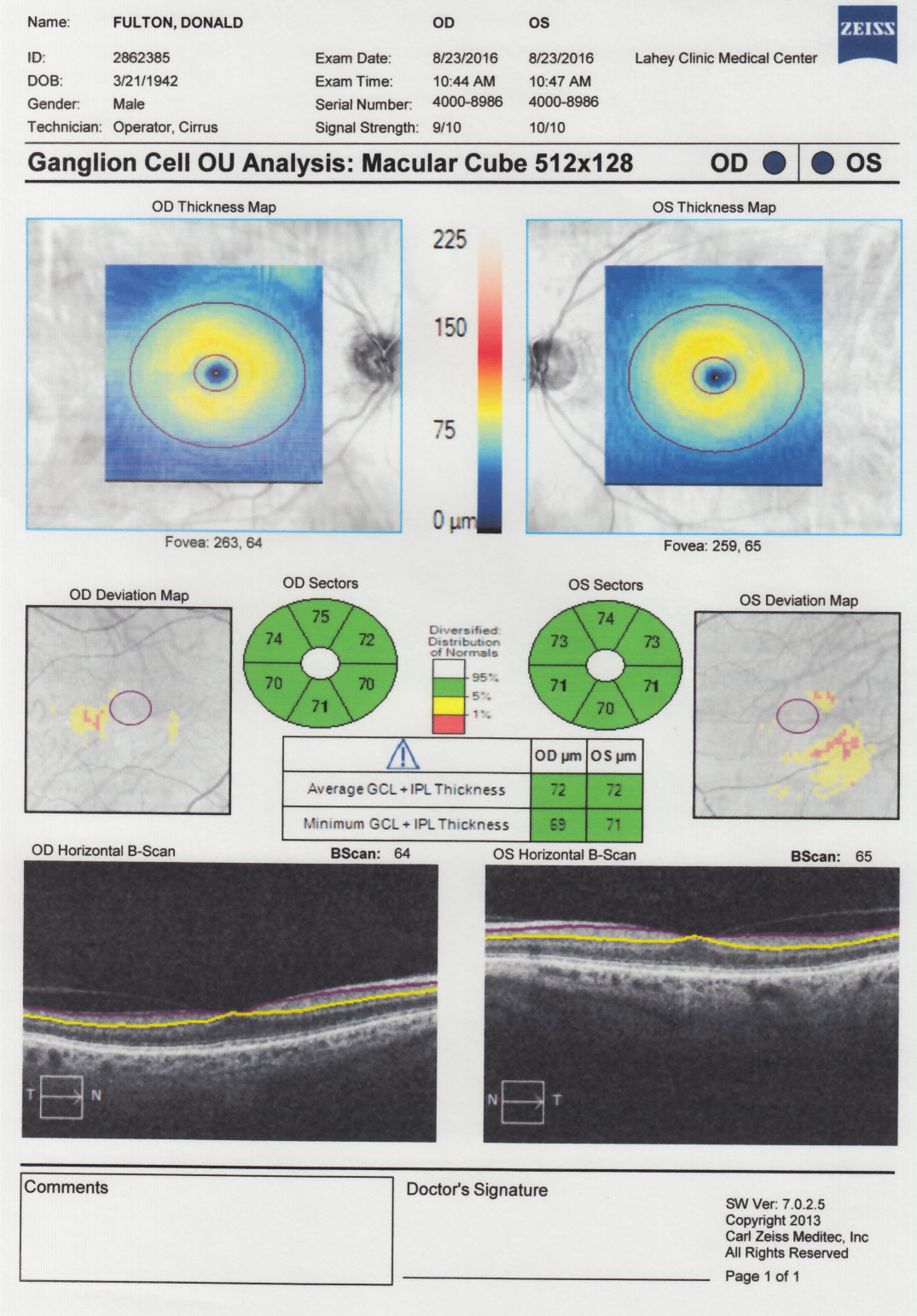
==============================================================================================================
Arteries and veins
of the neck
(8/29/16)
I recently had an ultrasound
test of the carotid arteries of the neck, which turned out to be "normal",
which must mean no blockages found. The technician told me the test measures
the
(local) velocity of the blood (correct). The reason for this test
is to see what blockages I have (if any), because plaques in the neck if
broken off could have been responsible for the 1 min blindness I had in
my right eye (upon waking) a few weeks ago.
What to
do if this happens again?
Amazingly, I was never advised
by all the eye people I saw what to do if this happens again! It's a stoke
or a mini-stroke, what do you do when it begins, while it is happening?
I didn't think to ask. You have no way of knowing initially if this is
a TIA and will resolve itself in minutes (with no harm), or if this will
continue and leave you blind or with permanent brain damage. Is there nothing
effective you can do, or are there things worth trying?
Is this a legal issue, like
we told you do X, you do X and still you go permanently blind, so you may
sue the doctor for malpractice. So if medically there isn't any reliable
strategy to recommend, doctors are advised to say nothing? There
is essentially nothing about this online ('What to do while waiting for
the ambulance') except call 911 because you get to the hospital faster
taking ambulance. How long does it take the tissue of the eye to die. No
idea.
Raise blood pressure in head?
(update)
I think the reason there
is no universal advice as to what to do if you think you are having
a stroke is that there's two possible causes for a stroke. It can be blocked
artery, but it can also be a bleeding artery in the brain, and their treatments
conflict. A pressure increase may make sense if it's a blockage, but it
may make a bleeding problem worse. So the first thing an emergency doctor
would want to determine is what is the cause of the lack of blood.
There's an effective drug
for dissolving a clot, but it can only be given within the first 3 hours.
This is the reason to hustle to the hospital.
Ischemic Stroke Treatment.
The only FDA approved treatment
for ischemic strokes is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA, also known as
IV rtPA, given through an IV in the arm). tPA works by dissolving the clot
and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived of blood
flow. If administered within 3 hours(and up to 4.5 hours in certain eligible
patients), tPA may improve the chances of recovering from a stroke.
---------------------------------
Using common sense I would
think the best thing to do for a stoke or mini-stroke while it is happening
is increase the blood pressure in the head. You are trying to force blood
by a blockage, or break the blockage free. Lie down, or even better
lie down with the feet raised. In my case the most effective way to do
this would be to lie on my couch with my feet high up on the back. Or maybe
lying in bed let your head dangle off the bed. Or is it better to run around
to raise the heart rate? It probably would hurt to take an aspirin
or two, thought this is going to take a while to 'thin' the blood. References
for a heart blockage says getting to the hospital within even 3-5 hours
after the attack can help minimize damage.
In my TIA blindness incident
I got out of bed then for a few seconds laid down flat again (no change).
Since I had to go to the toilet and had no further idea what to do, I went
and sat on the toilet. It was while sitting on the toilet (bent over a
little) after a minute or so that my symptoms resolved and in 1-2 seconds
my normal vision returned to my right eye. Does the blood pressure in the
head go up a little sitting rather than standing because when sitting less
pressure should be required to pump blood in the legs back up to the heart?
Don't know. A review of the blood flow diagrams shows all the arteries
going up the neck to the head branch right off the big aortic arteries
coming out of the top of the heart. They should have the highest peak blood
pressure in the entire circulatory system.
Veins
So I started doing some research
into arteries of the neck that supply blood to the head and brain. I soon
found the answer to one question, where are the veins? Turns out the arteries
and veins pair up in bundles (see image below left). This is true for the
big carotid arteries in the front and the smaller arteries running in the
holes in vertebrae. Note the outside holes in all the vertebrae have both
an artery and vein in it.
I soon realized I had
a misconception. I was aware from studying the cervical vertebrae
that they all have outside holes (transverse foramen) for a blood vessel,
and I had assumed this was the (big) carotid artery, the major supplier
of blood to the head and brain. Wrong, well partially wrong! Images online
show this artery, called the 'vertebral artery' and its paired vein, looks
like it might supply 1/3rd of the blood. Wikipedia says this better protected
artery/vein pair supplies (as the vertebrobasilar system) the upper spinal
cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain. The much larger
artery/vein in the front of the neck and not in the vertebrae holes
is called the 'carotid artery'. It is where you can feel your pulse. It
goes about half way up the neck as without branching, this lower section
called the 'common carotid'. About half way up the neck it divides into
two equal branches called the 'internal carotid' and 'external carotid'.
Three sets of arteries (on each side)
So the brain and head (on
each side) get blood from three sets of artery/veins: 'vertebral
artery' (in the vertebrae holes), 'internal carotid' and 'external carotid'.
The latter two are the two major branches of the carotid artery. Some of
these arteries actually join up in a loop, called the 'circle of willis'.
The blood flow diagrams here are difficult to interpret, but it looks like
the 'circle of willis' ties together arteries from both sides of
the head, specifically the 'internal corotid arteries' and the combined
'vertebral arteries'. This allows blood flow up the neck to shift among
the neck arteries if there are pressure differences. This is important
because it means that if an artery blocks in the neck, the another arteries
can at least partially take over for it. I say partially because
the connecting loops in the circle, called the 'communicating arteries',
are rather small. This provides some redundancy for the brain/head blood
flow. Wikipedia says this shift can sometimes supply enough blood to prevent
symptoms of eschemia (restriction in a blood supply).
Internal carotid artery
Which of these three sets
of artery/veins supplies the eyes? Ans: 'Internal carotid artery' (see
image below right). This is the figure my eye doctor used and other
references agree with it. This probably good news for testing for blockages
that would affect the eye with ultrasound, because I suspect the vertebral
artery enclosed as it in the hole of the vertebrae is very difficult (if
not impossible) to image.
Video of carotid ultrasound test
The youtube videos linked
below are a good introduction to the carotid ultrasound test. The first
has a lot of images taken in real time that would be useful for evaluating
an ultrasound images or CD (if available). It shows clearly that the test
follows the 'common carotid' up to where it splits, the operator looking
especially for blockages in this region, and then following the two branches
('internal' and 'external') upward until they are obscured by the bones
of the skull and jaw. The videos also show the 'vertebral corotid' can
be "sampled", but since only the regions between the vertebrae can be seen
only the blood flow direction is shown being measured. Of course
the imaging is done on both sides of the neck. The velocity of the blood
is directly measured, as my technician told me, by use of the doppler technique.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W-SJxeMInDM
actual exam with commentary (8 min)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r5XhVVL6dDE#t=59.026529
viewgraph lecture (29 min)
I'm a little pissed, because
the video shows a patient looking at the screen, while the operator explains
the images. I was not given the option of looking at the screen.
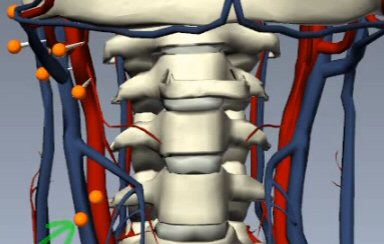 .
.
(left image) -- arteries (red) and veins (blue) pair up including
in vertebrae holes
(right image) -- arterial input to the eye is provided 'internal
carotid artery' via the ophthalmic artery and its branches
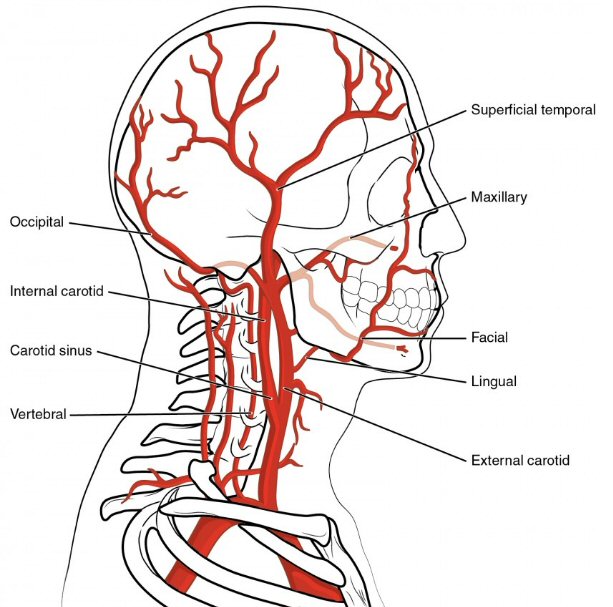
carotid artery below the internal/external branch is knows as the
'common carotid'
Note 'internal carotid' feeds brain and eye,
'external carotid' feeds face
=========================================================================================================
End
of my 2nd remission -- New Test Results (mar 2017)
(shortness of breath)
Overview
Pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo started off strongly with a big drop in free light chain in the first
cycle, but after 8.5 months my lambda free light chain was rising strongly
as was M-spike and worse a little later a pet scan showed my 9th rib plasmacytoma
had also brightened substantially in just the last 9 weeks, so clearly
the cancer has evolved around this chemo. My 2nd remission has ended after
just 8.5 months. Not only that by I appear to have acquired a lot of lung
damage in the last few months, blamed on the carfilzomib as it has as a
side effect that it has a toxic effect on the lungs. This lung damage is
really affecting my quality of life as I now tire easily and have shortness
of breath. This was confirmed by a lung test showing I am only taking in
half the oxygen I should on each breath.
Searching for a 3rd remission.
Before going to a humanized antibody drug (daratumumab), I didn't want
to bypass anther proteasome inhibitor, Ninlaro (equivalent to Velcade with
a ten year good track record) that could easily be slotted in in place
of carfilzomib, so that is the plan with a swap in of Ninlaro for carfilzomib
beginning 4/3/17.
Photos
from last day of carfilzomib infusion (3/21/17)
Here are photos taken in
the Lahey infusion room on the last day of my carfilzomib infusion showing
me with my main infusion nurse, Marci. I found the large infusion room
to be a friendly place, the four infusion nurses who attended me very skilled
and a pleasure to be around. I got of lot reading done during the two hours
of the carfilzomib infusion, and free WiFi too, so I sometimes brought
in my android tablet to surf the web.
 .
. 
Here is my main infusion nurse, Marci.
Note the needle in my arm. The tubing was long enough so I could
move the arm quite a bit, holding a book was no problem,
The drug is in the bag above, the pumping controlled by the programable
controller next to me.
 .
. 
Bad news --- Free light chain is rising fast (3/6/17)
At my meeting with my doctor
to discuss these latest test results (heart and lung) because of my shortness
of breath our working assumption had been that the pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo was continuing to work very well as it had for the last 8 months.
New cancer tracking data from labs the day before was not yet available.
However I had noticed that the lambda free light chain had been slowly
creeping up for a few months (from a low level) and had just recently exited
the normal region at 2.83. Unfortunately when free light chain from the
blood work the day before dribbled in after the meeting the upward climb
of lanbda free light chain continued strongly reaching 4.55 mg/d (60% one
cucle rise). This is nearly half way to free light chain disease progressing
threshold of 10 mg/dL, where it was when pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo was
begun. M-spike data is not yet available to me yet, but it should be in
a day or two to my doctor.
This free light chain rise
in my opinion could strengthen the case for a one cycle test of Ninlaro
swapping it in soon (maybe this cycle or next) for carfilzomib. Both are
protease inhibitors, but they have different modes of action.
Wed morning, day after out
meeting, I messaged my doctor about possibly buyng Ninlaro this week, and
swapping it in next week. This would give us a 1/3rd carfilzomib cycle
and 2/rd Ninlaro cycle. I await her thoughts on this chemo swap test.
-------------------------------------
Overview (2/8/17) (3/6/17)
Because my shortness of
breath has been slowly getting worse for a few months (and a nasty cold
for three weeks in feb 2017 exacerbated the problem) my consulting Dana
Farber multiple myeloma specialist suggested tests be run on my heart and
lungs. His concern is that one of my chemo drugs (carfilzomib) is known
to damage the heart in some people and can have toxic effects on the lungs.
As I read the results of
my recent tests (2/22/17) the 'explanation' for my shortness of breath
is in my lungs. The diffusion of gases (in the test CO, but normally oxygen
in and CO2 out) in the millions of alveoli across the alveolar-capillary
membrane is only about half of what it should be (DLCO predicted = 44%).
To me this result could be explained either by the areas of the membrane
being destroyed or compromised (reversible?), or perhaps the problem is
not in the lungs at all. It might be that my misshapen and sometimes immature
red blood cells have limited oxygen carrying capacity, or maybe for some
reason (cell clumping or high viscosity) blood flow in my capilaries
is reduced. I do have a blood cancer, my blood is not normal!
My following blood test (3/6/17)
show two signficant changes.
a) Hemoglobin popped up (12.3 => 14.1 g/dL) into the normal range
(13.8 lower limit) for the first time since on carfilzomib. Maybe relevant
here is I began taking an iron supplement pill (361% of FDA) pill
2/15/17 three weeks before this blood test.
b)
Bilirubin
(total) also showed a big jump (.9 => 1.6 mg/dL) taking it out of range
(>1.3) for first time. Bilirubin should be cleared by liver
so may indicate a liver problem. Bilirubin reslts from the breakdown of
red blood cells. Could it be related to the iron supplement pill?
-- High bilirubin levels
in adults usually means that there may be an underlying problem involving
the red blood cells, liver, or gallbladder; however, other problems also
may be found.
Heart tests (2/14/17)
BNP (B-type Natriuretic
Peptide) is a blood component test that relates to heart function.
This is the third time I have had this measured. Soon after beginning pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo the reading was 113 pg/ml, somewhat above normal. A second reading
on oct 3, 2016 was normal at 23 pg/ml as is the latest reading (2/13/17)
of 40 pg/ml.
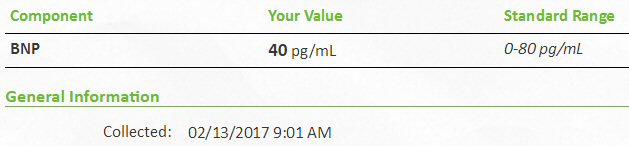
BNP peptide is normal
Heart transthoracic
echocardiogram (2/14/17)
This is my second heart
echocardiogram, my previous echocardiogram was in sept 2016. At that time
no serious problems were found with my heart and my latest heart echocardiogram
(2/14/17) shows the same, no significant change in my heart since the sept
2016 echocardiogram.
 .
.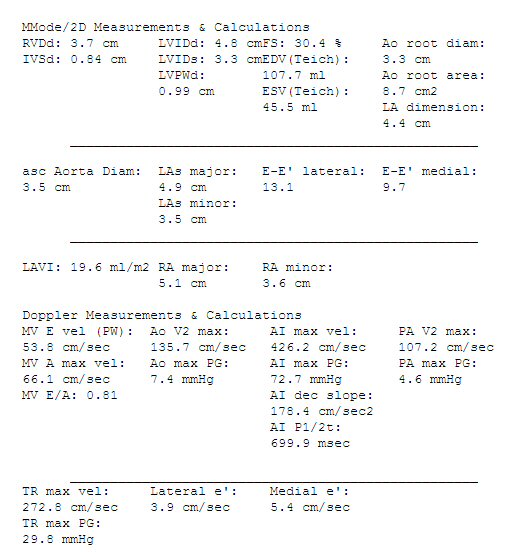
echocardiogram test 2/14/17
Echocardiogram Interpretation Summary
1. The left ventricle is normal in size and systolic function.
Estimated ejection fraction = 65%. Global longitudinal strain
(GLS) is normal (22%).
2. There is minimal thickening/calcification of the aortic
leaflets with mild aortic regurgitation.
3. Pulmonary artery systolic (peak) pressure is normal.
4. Compared to prior study of 9/2016, there is no significant
change.
-------------------------------------------------------
Right Ventricle
The right ventricle (pumps to lungs) is normal in size and function.
Left Ventricle
The left ventricle (pumps to body) is normal in size. Left ventricular
systolic function is normal. Estimated ejection fraction = 65%. Global
longitudinal strain (GLS) is normal (22%). No regional wall motion abnormalities
noted.
Atria
The left atrial size is normal. Right atrial size is normal.
Tricuspid Valve
The tricuspid valve is normal. There is trace tricuspid regurgitation.
Pulmonary artery systolic (peak) pressure is normal. (implies no deterioration
of the capillary bed in the lung?)
Pulmonic Valve
The pulmonic valve is normal in structure and function.
Mitral Valve
Mitral leaflet thickness and mobility are normal. There is trace mitral
regurgitation.
Aortic Valve
The aortic valve is trileaflet. There is minimal thickening/calcification
of the aortic leaflets. No valvular aortic stenosis (narrowing of valve
opening). Mild aortic regurgitation.
Great Vessels
The aortic root is normal size.
Pericardium/Pleura
There is no pericardial effusion. |
(source --- Wikipedia: Diagram of the human heart) |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lung Tests
(2/22/17) (4/3/17)
My moderate (to severe) shortness
of breath that developed in early 2017 while on pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo
prompted two tests of my lungs, a series of tests of lung capacity called
'pulmonary function tests' and a hires CT scan of the lungs. A related
test given at the same time is a heart echocardiogram that allows a check
of pulmonary hypertension. This is high blood pressure in the lungs, which
I would think would rise if the capillary beds in the lung were being narrowed
or obstructed.
Pulmonary function tests (2/22/17)
The most significant result
of this test is DLCO (Diffusing capacity of the lung for CO) is very low
(off the charts low). This result combined with a test that ruled out mucus
obstruction in air pathway to the lungs points to likely poor transfer
of oxygen to the blood in the million of lung air chambers (alveoli).
Below is how the results
of my pulmonary function tests are posted on MyLaheyChart. Just a list
of cryptic aberrations with no standard values (well 'Predicted'
provide reference values, but it took me a while to realized this) and
no
analysis.
Sweet, hey! Another example of no support for the patient! I was getting
over a cold when this test was done, so had some wheezing gurgling in my
lungs. What triggered this test and associated heart flow test is
moderate to severe shortness of breath I experience when doing even moderate
exercise. It's been slowly getting worst over the last three months, but
with my three week cold in feb 2017 it has increased more.
It took quite a while online
to make any sense of these pulmonary tests and numbers. Basically there
are two tests here. The first (FVC, FVC1) measures lung capacity and flow
rates, i.e. how much air you can take in an blow out in one second. 'Pred'
stands for 'predicted' using a formula based on sex, age, height and corrected
for hemoglobin (12.2 was my latest reading a couple of weeks earlier.)
Here I am 80% of predicted in capacity and 75% of predicted for a one second
exhale.
In a youtube
video
of
a doctor explaining the pulmonary function test he says an FVC below
80% of the reference value (based on population statistics of height, age,
gender and race) is abnormal. I come in just at 80%. The video goes on
to say the 'gold criteria' for obstruction is that you should be able to
exhale in one second (FEV1/FVC) 70% (or more). I come in just slightly
below at 68%, which I would think could be assigned to the gurgling in
my lungs during the test.
I question how the
capacity test was conducted. My technician was clearly experienced, and
she directed me exactly how to breath and I followed her instructions carefully.
Online I see that the the patient is instructed (reasonably) to take in
a deep breath to begin, which for me would take about two seconds, but
my instructions were to take in a quick deep breath of one second. During
the test I never felt that the lungs were at full capacity, because the
breath in time was too short.
Methacholine Challenge --- asthma test
I read about another pulmonary
test that was not included in pulmonary function test I got. It
is called the 'Methacholine Challenge' test and it typically used to diagnose
asthma. It does the opposite of the inhaled test I got. Methacholine inhibits
breathing. In asthma the airways tend to tighten (due to mucus) when you
breathe, so this test is basically an asthma test. The test involves breathing
in progressively higher levels of methacholine until FEV1 drops 20%, then
an inhaled bronchodilator (usually albuterol or levalbuterol) is given
to help reopen the airways. I don't have asthma (?)so this test would not
benefit me. I learned from the test technician that exhaled volume increased
only a tiny amount (3%) after breathing a bronodilator, indicating (to
me) that the problem is in my lungs not the airways to the lungs.
DLCO test result (2/22/17)
The second test (DLCO -- Diffusing
capacity of the lung for CO) is a test that actually measure the gas transfer
to the blood. This is far more important to me. This is test is done by
breathing in a mixture of gases which includes a low concentration (0.3%?)
of CO (carbon monoxide) and helium. The lung to blood transfer is assessed
by looking at the exhale (vs inhale). CO is used because hemoglobin has
a strong preference for carbon monoxide and will pick it up before oxygen.
A 'corrected' DLCO (I think) corrects for hemoglobin, which in my case
is below normal at 12.2 (on feb 6, but 14.1 march 6). The result is not
marked corrected, but from discussions with the technician doing the test
I suspect it is corrected. A repeat of the test after inhaling with a broncodilator
mist showed basically no change which I read rules out asthma, which is
blockage (due to mucus) in the tiny airways in the lungs to the millions
of alveoli, where the diffusion of oxygen into blood cappilaries takes
place..
The most important result
here is that DLCO is remarkably low (off the charts low) at 44% of the
predicted value (my age and height). From the plot below my DLC my of 13.98
(same units as plot) is literally off the charts! Here are the results
of Pulmonary function tests.
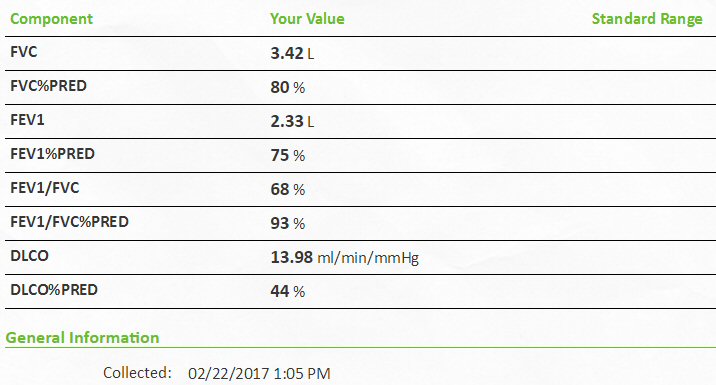 .
. 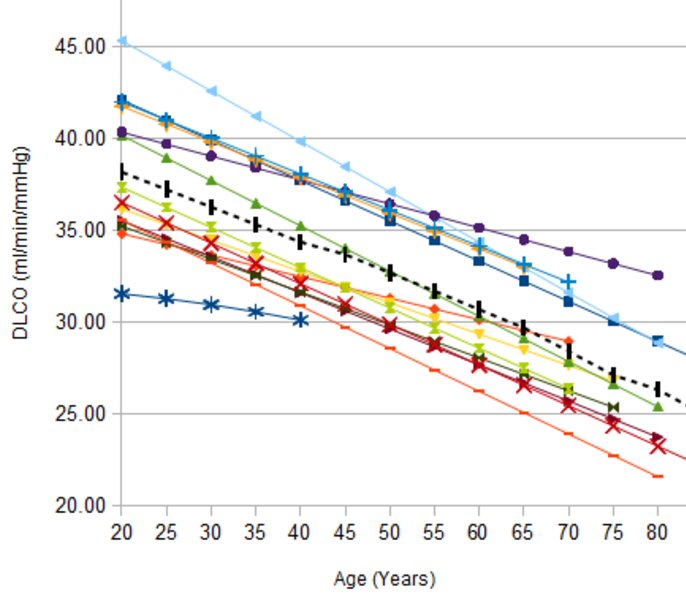
FVC --- functional vital capacity (volume)
DLCO standard chart (ml/min/mmHg)
FVV1 --- exhale capacity in one second
DLCO --- Diffusing capacity of the lung for CO (carbon monoxide)
(my 13.98 reading is so low it is off the chart!)
(source (right) -- https://www.pftforum.com/blog/whats-normal-about-dlco/)
My capacity numbers are just
at or slightly below the thresholds for a possible obstructive defect [FEV1/FVC
= 70% (my value 68%), FVC = 80% (my value 80%)]
-- An obstructive defect
is indicated by a low forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital
capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio, which is defined as less than 70% or below the
fifth percentile based on data from the Third National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey (NHANES III) in adults.
-- Physician should determine
if the disease is reversible based on the increase in FEV1 or FVC after
bronchodilator treatment (i.e., increase of more than 12% in patients five
to 18 years of age, or more than 12% and more than 200 mL in adults). Asthma
is typically reversible, whereas chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
is not.
Good reference for pulmonary function test interpretation --- http://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/0301/p359.html
'Moderate' gas exchange abnormality
What to make of these numbers?
I found (below) the following examples online. The first (left) is a normal
65 year old man. Note his DLCO is 26.14 ml/min/mmHg (84% of predicted 31.28),
whereas my DLCO is much lower at 13.98 ml/min/mmHg (44% of predicted).
If we divide my 13.98/0.44 = 31.8, pretty close to the predicted in the
65 year old example. My predicted FVC [3.42/0.80 = 4.28] also agrees quite
nicely with the 65 year old man example of 4.32. The youtube video describes
the DLCO as a measure of the surface area of the (millions) of avolea
and capillaries within the lung. (This surface area is the size of a tennis
court.) Emphezima destroys this area. DLCO can read (falsely) low not due
to a lung problem, but if the input breath is not large because air won't
get down into the avolea.
The commentary on right from
a patient with a DLCO of 43% (very close to my 44%) is that she has a 'moderate'
gas exchange abnormality. This low DLCO (44%) vs predicted I think is the
most important result of my test. I have a 'moderate' abnormality in gas
exchange which probably goes a long way to 'explaining' my shortness of
breath. I suppose this could be a lung effect (maybe due to carfilzomib)
or a blood circulation effect. I wish now that my lungs were clearer of
the cold residue when this test was done. The youtube video gives the normal
threshold for DLCO vs predicted at 80%, so I am clearly quite low.
In other words one interpretation
of this (very) low DLCO is that it is saying the lungs are being damaged
(is it reversible?) that I have lost about half of my expected surface
transfer area for gas exchange. However, this is for normal people. I have
weird blood, both weird red blood cells and maybe abnormal viscosity. The
gas exchange rate could be low because the either the number of normal
red blood cells is low (blood test often note a lot of immature red blood
cells) or maybe the viscosity is high so the flow through the capillaries
is low.
 .
. 
(left --- normal 65 year old man)
(right --- low DLCO of 43%)
(source -- http://www.fammed.usouthal.edu/Pulmonology/Self-StudyAids/PFTs/PFTCaseQuestions%26Answers.pdf)
Carfilzomib lung toxicity
Obviously my concern is
with the low DLCO predicted of 44% in the functional lung test.
** Carfilzomib literature
says if lung toxicity is occurring (without saying how this is determined)
carfilzomib should be discontinued. (check the prescribing sheet for this)
Three lung side effects of
carfilzomib are given. Two are sudden, one of being a liquid build up in
the lungs. Neither apply to me. The third is called 'Interstitial lung
disease' and basically this is scarring of the lungs (generally irreversible).
Wikipedia has a page on this.
-- "But in interstitial lung
disease, the repair process goes awry and the tissue around the air sacs
(alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for
oxygen to pass into the bloodstream."
-- (Diagnosis) Chest radiography
is usually the first test to detect interstitial lung diseases, but the
chest radiograph can be normal in up to 10% of patients, especially early
on the disease process]
Lung diagnostic test
** -- High resolution CT
of the chest is the preferred modality, and differs from routine CT of
the chest. Conventional (regular) CT chest examines 7–10 mm slices obtained
at 10 mm intervals; high resolution CT examines 1-1.5 mm slices at 10 mm
intervals using a high spatial frequency reconstruction algorithm. The
HRCT therefore provides approximately 10 times more resolution than the
conventional CT chest, allowing the HRCT to elicit details that cannot
otherwise be visualized. Radiologic appearance alone however is not
adequate and should be interpreted in the clinical context, keeping in
mind the temporal profile of the disease process.
What can be done to ease shortness of breath?
-- Pulmonary rehabilitation
(Note the answer below I think is basically for asthma suffers who have
airway restrictions)
-- Exercise is a cornerstone of this. There is someting called 'pursed
lip breathing' (also called 'diaphragmatic breathing') that is taught to
patients to ease shortness of breath. (Has its own Wikipedia page). It
consist of inhaling through nose (two seconds) and breathing out through
pursed lips (4 seconds). The purpose is to create back-pressure inside
airways to splint them open; moving air thus takes less work. I've tried
this, it might work a little. I am beginning to suspect this trick is more
for asmatics in that it helps open the passagways into the lung.
Possible further tests
* Exercise (walking only) oxygen/CO2
transfer test. (Does Lahey have this?m yes)
* Measue oxgen content of blood
--- Use my oximeter to read blood oxygen saturation levels, so climging
my hill. Resting reading are nearly always normal (95% to 100%). I four
times recently calibrated my oximeter to the oximeter used to get vitals
(each hospital trip) and they agreed exactly. A more exact test is
measuring the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (have no idea
is this is a standard, or practical test)/
* Note I found playing at
home with my oximeter that if resting and getting very low oxygen saturation
readings (91) I can raise the level 5-6 points with one minute of
rapid breathing. For about a minute nothing happens, then in a few seconds
it shoots up. Obvious some of this delay (7 to 10 seconds from power on)
is built into the procssing algorithm of the oximeter, the rest must be
due to the circulation time to the finger tip. (yup)
Check -- takes blood about one minute to circulate through
the body
-- The volume of blood in
a human body is about 5 liters. The heart pumps about 70 mL of blood on
each stroke (1.4% of the total), so at resting heart rate of 70 beats/min
it takes about one minute for blood to make the round trip to the heart.
Red blood cell
tutorial
Red bloods cells are essentially
just bags of hemoglobin wrapped in a cell membrane. They have no nucleus,
by dry weight 96% of a red blood cell is hemoglobin. They live 120 days,
so every four months all red blood cells are replaced. Red blood cells
outnumber white blood cells by 1,000:1, and platelet cells 25:1. Old red
blood cells are captured by macrophages which takes them to the spleen
where the iron atoms in the hemoglobin protein are recycled. Circulation
of a red blood cell through the body takes about one minute.
In a blood test red blood
cells count (RBC) is determined by machine, but shape and color manually
by an operator using a microscope. Red bloods technically are known as
erythrocytes.
|
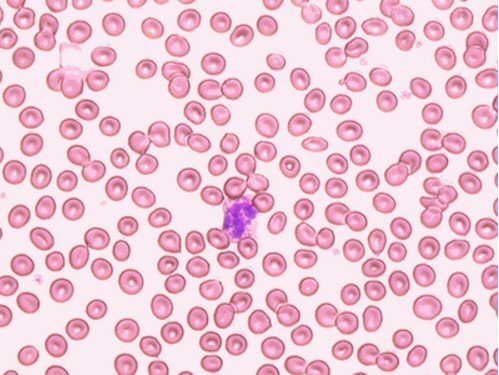
red blood cells (disk shaped) under microscope
red blood cells outnumber white blood cells (purple cell in center)
by 1,000 to 1
(souse -- http://www.uwosh.edu/med_tech/what-is-elementary-hematology/red-blood-cells)
|
My red blood cells are typically
described (RBC morphology) as having 'variation in size or shape',
sometimes as they don't look fully developed, immature. like they were
released too soon by the marrow.
Pulse Oximeter
I did a little research
on the pulse oximeter and was surprised. It know it is used by the hospital
on every visit to measure oxygen saturation. I bought one on Amazon (20
bucks) and cross checked across the hospital oximeter three times and it
agreed exactly each time. Turns out this little device has a long history,
and as a simple non-invasive way to measure oxygen saturation it has proved
to be very effective clinically. For example Wikipedia says it revolutionized
anaesthesia making it much safer, it also has proven to be very useful
in the monitoring of premature newborns who need an adequate supply of
oxygen, but too much oxygen leads to vision problems as blood vessels grow
in the eye. Visiting my lung doctor the one test he did (aside from listening
to my lungs with a stethoscope) was called 'Taking a walk', and it was
just a walk down the corridor (fast and slow) with a trailing technician
continuously monitoring oxygen level with the basic fingertip oximeter.
What a modern oximeter does
is measure the percent of hemoglobin (red blood cells) in
arterial
circulation that are oxygenated. It does this by using two LEDs of different
frequencies (visible and infrared) that alternate and a single photodiode
that shine through the finger tip, the ratio processed by a microprocessor.
Typical result is 95% to 100%, meaning this is the fraction of hemoglobin
(red blood cells are basically just bags of hemoglobin) that has picked
up an oxygen atom in the lung. Wikipedia article on COPD says supplemental
oxygen is needed if oxygen saturation is less than 88%.
Playing with my oximeter
Normally my oxygen level
is in the range of 96 to 98 (normal), and that was the result when the
'taking a walk'. However, one day at home sitting quietly with heart rate
low (60 beats/min) I measured (for the first time) very low readings of
90-91 saturation. Running a little test while watching the oximeter I began
consciously to breath more rapidly and deeply while continuing to sit quietly.
What I found was interesting.
Breathing hard increases my oxygen saturation
After about a minute of this deep
breathing, I found my oximeter oxygen saturation level rose substantially
(5 to 7 points) up into the normal region. In other words if my respiration
rate is low, which may cause my oxygen saturation level to be low, I found
I can pull my oxygen saturation level into the normal region by breathing
hard. I think the reason I have not noticed this before it that when climbing
a hill (or on the 'walk') breathlessness naturally leads to an increase
in both heart rate and more rapid and deep breathing. This is all consistent
with my very low the DLCO pulmonary test (13.98, 44%) which showed I am
taking in only half the oxygen I should be on each breath.
Hill climbing test (4/17/17)
I perfumed a more extreme
version of the 'take a walk' test that was done on my first visit with
my lung doctor. The 'take a walk' test turned out to be a short walk around
the corridors of the hospital with a technician trailing reading out blood
saturation with an oximeter connected via a wire. Clearly this was a test
to see how oxygen saturation changed with moderate levels of exercise.
With my own oximeter I saw
I could easily do a controlled and more extreme version of this test since
I live up a steep hill, 150 (to 200) yards up that takes about 2.0 minutes
to climb. Just take a reading at the bottom and a reading at the top. Walking
up this hill now at a moderate (to slow) pace leaves me breathless even
wondering if I can make it without stopping to catch my breath. Here's
the result
Baseline hill climb test -- prior to use of any inhaler
bottom of hill
96% oxygen saturation heart rate not
recorded (est 70 to 90 beat/min)
top of hill
98% oxygen saturation heart rate 130
beat/min
The result of the baseline
test is clear cut. Oxygen saturation remains in the normal region
(shows a tiny rise) with the moderate level of work required to climb the
steep hill on which I live. At the top I was breathing hard, my heart rate
was 130 beat/min. According to the table below this is consistent
with chronic bronchitis (blue bloater), not emphysema (pink puffer).
Repeat hill climb test -- after 10 days use of Spiriva HandiHaler
inhaler (5/3/17)
bottom of hill
98% oxygen saturation heart rate 69
beat/min
top of hill
98% oxygen saturation heart rate 116
beat/min
After 10 days daily use of
Spiriva HandiHaler my climb up my hill felt much easier than it has in
recent months. I didn't feel exhausted before reaching the top as I had
earlier. My heart rate at the top was a lot less (116 vs 130 beats/min).
I think the inhaler is working for me in the sense that my peak energy
output is higher.
Repeat hill climb test -- after 4 weeks use of Incruse inhaler
(6/18/17)
bottom of hill
xx% oxygen saturation heart rate xx
beat/min
top of hill
90% oxygen saturation heart rate 123
beat/min
As with the Spiriva HandiHaler my climb
up my hill after using the Incruse inhaler felt much easier than it had
before I started using any inhaler. I didn't feel exhausted before reaching
the top as I had previously. This is good. What to make of these numbers
I don't know. I didn't record the oxygen saturation at the bottom of the
hill. I don't know if the very low oxygen saturation reading of 90% at
the top of the hill is due to a shift in my body or is an issue with my
oximeter. Low oximeter readings are now fairly frequent, whereas months
ago they were very infrequent. The first order of business should be to
change the battery in the oximeter and repeat the test.
COPD -- Pink
Puffer and Blue Bloaters
In reading about COPD (Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) I find there are two classic types: Pink
Puffer (Emphysema) and Blue Bloaters (Chronic Bronchitis). One involves
the destruction of the capillary bed, which means increased pulmonary pressure
and consequent strain on the heart trying to force the blood through damaged
(and reduced) capillaries, and one does not. It is emphysema (pink puffer)
that gradually damages the pulmonary capillary bed.
A "blue bloater" is a person
where the primary underlying lung pathology is chronic bronchitis. Bronchitis
is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air
to and from your lungs. (not me) Chronic bronchitis is caused by excessive
mucus production with airway obstruction resulting from hyperplasia of
mucus-producing glands, goblet cell metaplasia, and chronic inflammation
around bronchi. Unlike emphysema, the pulmonary capillary bed is
undamaged. (In other words in a blue bloater the problem is not in
the lung, it is in the pathway to the lung.)
I don't seem to fit into
either category. A pink puffer has a reduced DLCO, which is me, but is
also described as having severe oxygen desaturation (as measured with an
oximeter) with exercise, and this is not me. I have noticed for the first
time ever some swelling in my ankles and feet. A quick test showed
my resting oxygen saturation to be 93. I kept the oximeter on and immediately
followed with a minute or two of a simple exercise (rising to the balls
of the feet). The exercise caused my oxygen saturation to rise to 99 along
with a rise in heart rate. This is exactly the opposite of what happens
to emphysema patients. (3/19/17)
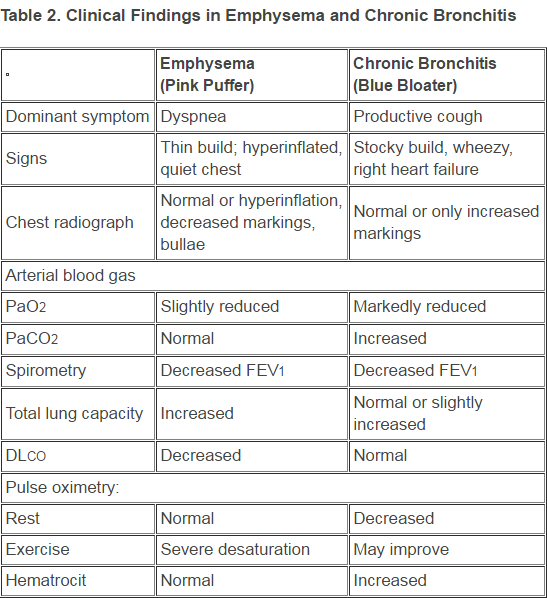
dyspnea is shortness of breath
(source -- http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/707973_5)
Lung CT scan (3/2217)
Here is the result of the
hires CT scan of my lungs. The question posed to the lung specialist was
the drug carfilzomib damaging my lungs. The most common symptoms of interstitial
lung disease are a dry cough and shortness of breath. Whle I have
shortness of breath, I do not have a dry cough. The expert reading
of the CT scan shows "no evidence of interstitial lung disease".
-- The interstitium is a
thin layer of tissue that is normally appears as a fine lace on X-rays
or imaging studies (best visualized as the appearance of a sponge).

Key results (searchable text) of expert read of 3/22/17 hi-res CT
scan of the lungs and chest with my translation of clinical jargon
no CT evidence interstitial lung disease
-- All forms of interstitial lung disease cause thickening of the interstitium,
the supporting tissues between the air sacs of the lung.
The thickening can be due to inflammation, scarring, exposure to inhaled
irritants (like asbestos) or extra fluid (edema).
Some forms of interstitial lung disease are short-lived; others are chronic
and irreversible.
no lung infiltrates
-- Pulmonary infiltrate is a substance denser than air, such as pus, blood,
or protein, which lingers within the parenchyma
of the lungs. Pulmonary infiltrates are associated with pneumonia, tuberculosis,
and nocardiosis.
no pulmnary edema
-- Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid in the lungs.
This fluid collects in the numerous air sacs in the lungs,
making it difficult to breathe.
no significant bronchial wall thickening
bronchi (with the tracea) are part of the upper air way with cartilaginous
walls
no pneumothorax or significant emphysema
-- pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space that
causes an uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall,
sometimes called a collapsed lung
no obvious suspicious hilar nodes (with caveat)
'hilar nodes' are lymph nodes in the lung high up in the broncial airways
near the branching to the right and left lung (of clinical interest)
subcentimeter axillary, mediastinal nodes
these appear to be lymph nodes in the lung below the high branching of
the airway to the right and left lung
no pleural or pericardial effusions
-- Normal pericardium is a fibroelastic sac surrounding the heart that
contains a thin layer of fluid. A pericardial effusion is considered
to be present when accumulated fluid within the sac exceeds the small amount
that is normally present.
mild vascular calcifications
-- Vascular calcification is a common complication in chronic kidney disease.
It is a leading cause of death in patients with chronic
kidney disease. (As best as i can tell, it is sort of a mineralized plaque
tumor that grows on vessels walls.)
My strange collection
of lung symptoms (3/21/17)
After 8.5 months on carfilzomib
I developed moderate (to severe) shortness of breath. A pulmonary function
lung test shows a very low gas exchange rate per breath (DLCO = 44% predicted),
a little less than half of normal. In a sense this 'explains' my shortness
of breath. Yet readings of blood oxygen, taken every time I go the hospitalalways
are
normal (95% -99% saturated). Same readings I normally get with my own oximeter,
except one day resting I got readings as low as 91/90%. Here I found if
I only increased my breathing rate for a minute, I could raise my oxygen
reading 5-6 points to well within the normal region.
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
moderate (to severe)
DLCO (diffusion lung for CO) 44% predicted
(less than half of normal gas exchange per breath)
Oxygen saturation of blood
95% to 99% (normal range) Very occasionally I will measure a very low resting
oxygen saturation
of 90/91% (with my oximeter) that I can raise into the normal region with
faster breathing for 1 min.
Pink puffer or Blue bloater
don't fit into either category.
a) Pink puffer is emphysema (smokers), inflammation of the lung with degradation
of the capillary bed.
(Pink puffers show a big drop in oxygen saturation with exercise. I don't
see this, my oxygen levels
however, do drop a little (93%) with exercise.
b) Blue bloater is asthma which is airways obstruction (due to mucus).
Capillary bed is not damaged.
(Asthma airways obstruction is in the lung. The airways that obstruct
with mucus are the
millions of tiny branch air channels that feed clusters of alveoli, which
is where the capillary
beds are that allow air oxygen to diffuxe across a thin membrane into the
blood.
FEV1/FEV
68% (one standard says FEV1/FEV < 70% "confirms the presence
of persistent airflow limitation
and thus COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)"
FEV after bronco dilator inhale 3% increase
(negligible). Indicates that obstruction is NOT in the lung airways, so
not like asthma.
Pulmonary hypertension
No -- heart electrocardiogram (2/14/17) reading, "Pulmonary artery systolic
(peak) pressure is normal"
(I would think a degraded capillary bed would be expected to lead
to high pulmonary arterial pressure)
CT lung scan (hires)
No interstitial lung disease or any other finding suggestive of pulmonary
side effect of carfilzomib.
Hill climbing test
Oxgyen saturation remains in rhe normal region (shows tiny rise) with the
moderate level of work required
to climb the steep hill on which I live. Heart rate rises to 130 beat/min.
Note one way a drug could
lower the DLCO reading is by filling the alveoli (air sacs with capillary
beds) with fluid. (I would think this might be reversible, but I go no
confirmation of this from my lung doctor.)
Raw motes
moderate to severe shortness of breath --- DLCO of 13.98 (44% predicted)
oxygen saturation --- normal (95 to 99), some drop (93) with exercise
in one test
My lung capacity numbers are just at or slightly below the thresholds
for a possible obstructive defect
[FEV1/FVC = 70%
(my value 68%), FVC = 80% (my value 80%)]
Increase of only 3% in FEV1 or FVC in bronchodilator part of pulmonary
function tests
my blood oxygen carrying capacity due to chemo is about 20% low
[hemoglobin 12.6 g/dL,
hematocrit 38.5%]
interstitial lung disease --- negative (hires CT scan)
pulmonary hypertension --- negative (heart echocardiogram)
Lung doctor meeting (4/21/17)
Since my hi-res CT scan
of my lungs was absolutely clear and pressures in my heart are normal,
my lung doctor nnow wants to check to see if I might have a blood clot
in my lungs. There is a fancy test for that involving radiation called
'lung perfusion ventilation imaging', and it is scheduled for next week
(4/27/17).
To try and live better with
my COPD that has developed in the last 3-4 months, presumably due to a
toxic effect of the chemo drug carfilzomib on my lungs (now stopped), my
doctor is prescribing an asthma type medicine, a broncodialator, a once
a day inhaler called Spiriva. This is an experiment. Since both of these
are new to me, I set out to do some research.
Pulmonary ventilation/perfusion
scan (4/28/17)
-- A pulmonary ventilation/perfusion
scan involves two nuclear scan tests to measure breathing (ventilation)
and circulation (perfusion) in all areas of the lungs. A pulmonary ventilation/perfusion
scan is actually two tests. They may be done separately or together. I
had both.
For the ventilation
scan, you first breathe in radioactive gas for 10 min. This leaves a radioactive
coating in the lungs that is then checked with a radioactive scanner that
takes three images: straight on and +/- 45 degrees. After this, is the
perfusion scan. Here a radioactive albumin (blood protein) is injected
into your vein, then the radioactive scanner again takes three images The
machine scans your lungs as blood flows through them to find the location
of the radioactive particles. I asked for a CD with the images and filled
out the form and waited for an hour or so, only to be told none of the
CD burners were working (really?). The CD is to be mailed to me.
Here's the doctor's report.
"Ventilation images show symmetric deposition of aerosol. No ventilation
defects. Perfusion images show bilateral symmetric perfusion with no segmental
or subsegmental perfusion defects." In other words no air flow obstruction
and no blood clots.
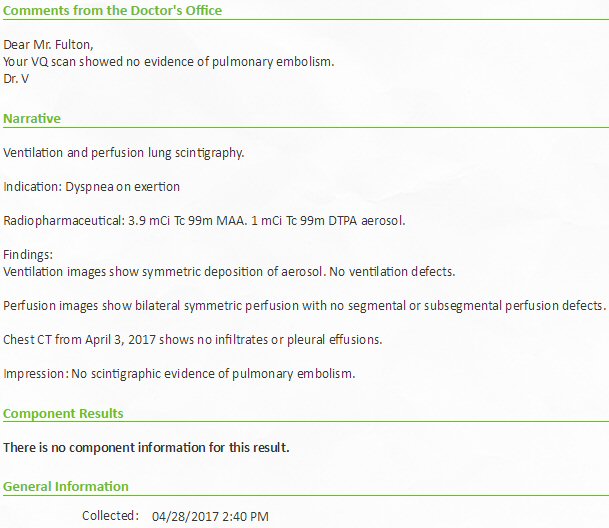
Nothing found in 4/28/17 lung perfusion tests. Air
flow uniform and symmetric, no air flow blockage and no sign of a blood
clot.
Perfusion images (4/28/17)
I waited after the scans
for a CD of the scan images, but the CD was not ready, however, it did
arrive promptly in the mail just a couple of days later. Here are my images
and a similar reference set I pulled off the internet.
My first minor mystery was
I found 16 different images on the CD, but during the test I saw the 'camera'
(radiation detector) repositioned only 6 times: three (straight on and
+/- 45 degrees) after radioactive air inhalation (vent = ventilation) and
three (straight on and +/- 45 degrees) after radioactive blood tracer injection
(perf = perfusion). What were the other ten images? Well it turns out that
even though all the lung scans were taken from the front (ant = anterior),
a rear view (post = posterior) has been calculated. This doubles the number
of images to 12. The other four are labeled right and left LAT (RLAT, LLAT)
for ventilation and perfusion. As I write this, I don't know what these
four images represent. (LAT = lateral)
Comparing my perfusion images to reference perfusion
images
The simplest
comparison is just to look at the straight on views (ant and post). Directly
below are my lung perfusion images and below them a similar set of reference
images I found online. In the two strips below the outside views line up,
but the inside views are crossed.
....
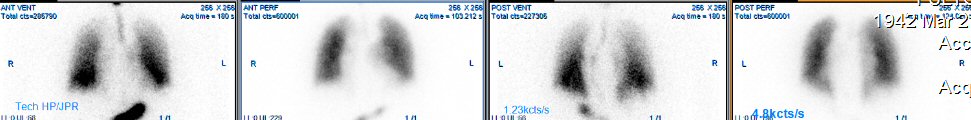
my strainght on lung perfusion scans
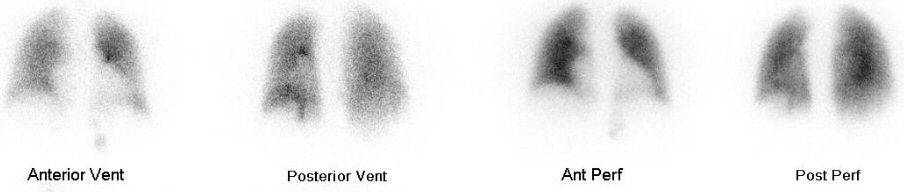
reference strainght on lung perfusion scans
(source -- https://somecasesplusmore.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/vq-scan-_normal.jpg)
As I eyeball above, my ventilation
images are a little different from the reference images. The reference
images are quite uniform across the lungs (top to bot, right to left),
whereas my ventilation images have somewhat more output in the lower part
of both lungs and somewhat less in the upper part. The blood perfusion
images match up quite well to the reference images. Since one of the purposes
of the test was to look for a blood clot (embolism) in the lungs, I don't
see any hint of that in the perfusion images, where the outlines of both
lungs are fully shown. This is the conclustion of the specialist who read
the scans. (However, my (LAT=lateral) views do show some conceentration
variations across the perfusion images.)
To complete
the story below are all my 16 images (right) and the for comparison the
12 reference images My four extra LAT images I soon found are 'lateral'
projections, so RLAT and LLAT are right and left laterial views. My lateral
(blood) perfusion views do show a concentration variation across the lungs,
a hot spot in the front of one (or both) lungs.
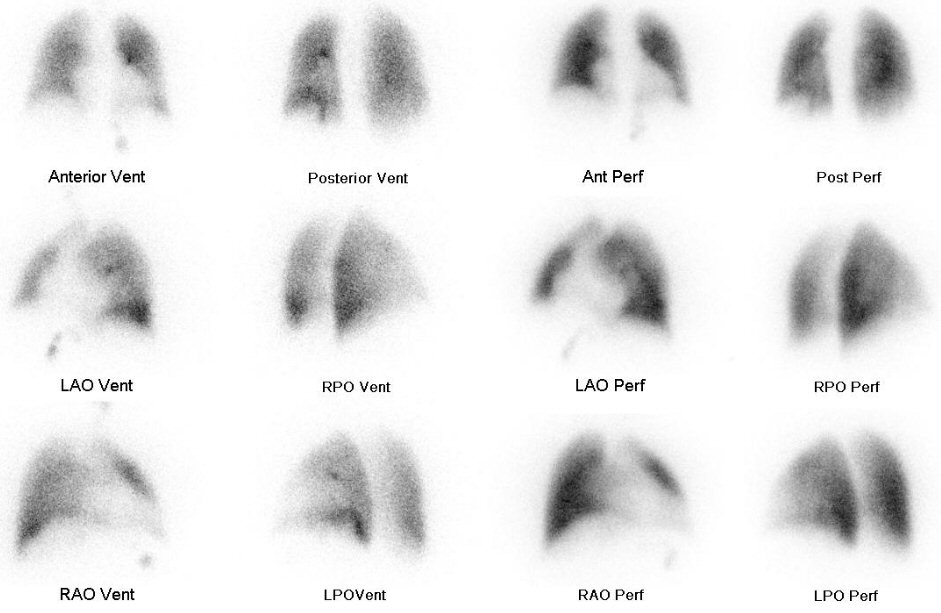 .
.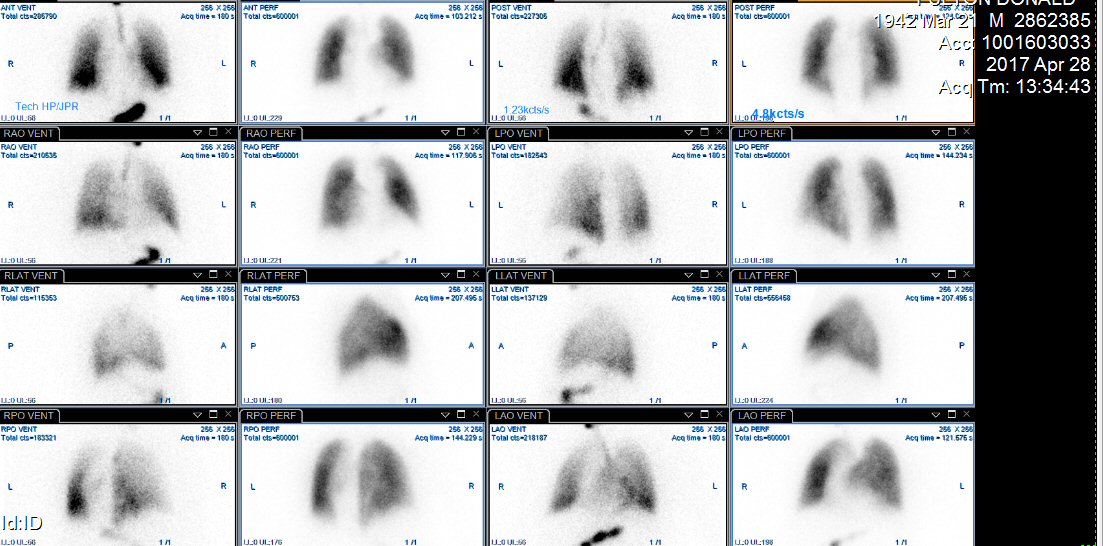
(left --- reference images from (https://somecasesplusmore.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/vq-scan-_normal.jpg)
(right --- my perfusion scans (ant = front), (post = rear), (vent
= ventilation (gas)), (perf = perfusion (blood))
(Note the sequence right and left is not the same)
Data taken 4/28/17
Here's a lung ventilation
sketch with numbers. .It looks idealized. Notice the blood coming
out of the lungs is 100% oxygen saturated, but saturation has decline to
84% after circulating around the body. My guess is the standard finger
oxygen saturation location would see about half the max oxygen saturation
drop as blood circulates around the body to the legs. (Note, this image
is from an anesthesia site so who knows how relevant it is to normal living.)
(source -- http://www.anesthesia2000.com/physics/Chemistry_Physics/19no7Boverview.gif)
Spiriva mist vs powder inhalers
I have messaged my lung
doctor's nurse to clarify whether I am supposed to buy (from Spiriva) a
mist inhaler, which the nurse spent 10 min showing me how to use, or a
powder device (also from Spiriva) that I find has been added to my medications
list on MyLaheyChart. The have the same active ingredient, but physically
they are completely different, so which one do I buy? (Turns out the mist
inhaler demo was a mistake. The drug prescribed in a Spiriva powder based
device called the Spiriva HandiHaler (see below). My part D provider is
Cigna Insurance, and while some of their plans cover the Spiriva HandiHaler,
my plan does not, so it cost me out of pocket 390 for a one month supply
(30 capsules.)
Next morning I got a reply message.
I considered this whole thing a screw up. The nurse's reply characterized
it as a "miscommunication" (blaming it on the doctor), but telling me the
device I should buy was the powder version (Spiriva HANDIHALER), not the
mist version I had been taught to use. Why? No explanation given. On the
same day (4/24/17) I went to my local CVS pharmacy and was surprised that
they had on file for me a prescription for the Spiriva HandiHaler (they
had not called me as they usually do), so avoiding the insurance approval
hassle I determined to buy it with cash sans insurance using one of my
discount card (MA card, 398, inhaler plus 30 cartridges for a 30 day supply).
The 398 he quoted agrees exactly with pricing shown on the MA drug card
site for my local CVS. The pharmacist said he could do a little better
on price and put me in with a drug insurance discount plan they have that
lowered the cost to 390, which I paid out of pocket.
Spiriva HandiHaler
powder inhaler (4/24/17)
Here I have photographed
my Spiriva powder inhaler.
 .
.
..
...
(top left) Spiriva powder inhaler closed
(top right) Spiriva powder inhaler opened showing mouthpiece
(lower) Spiriva powder inhaler with mouthpiece raised showing hole
for capsule (left).
Pressing the green button pierces the capsule with a large needle.
Using the Spiriva powder inhaler
Using it is not difficult.
I got it right the first time. Open up inhaler and put in a capsule. (Cautioned
that capusles should not be exposed to air very long, so take from bubble
pack just before putting into the inhaler.) Close it up and push the green
button (once). This forces a large needle to pierce the capsule. Breath
out all the way, put mouthpiece in mouth while holding device hor, your
head upright, and breath in deeply. "Should hear the inhaler rattling,
an indication you breathed in correctly" (I do). Hold breath for 5-10 sec,
then removed mouthpice and begin breathing normally Open the inhaler
and dump the used cartridge into the trash. When needed, the inhaler
can be cleaned by rinsing it under warm running water.
This is for one inhalation,
which is what my doctor calls for. Once a day (in the morning). There is
enough active ingredient in the 18 microgram capsule for a second inhalation,
which the manuf calls the standard dose. The nurse advised me after to
gargle with some water, apparently to flush excess powder out of the mouth
area, where she said it could cause a nasty 'thrush' fungal infection.
(Curiously I can find no estimate of the dose that would typically be inhaled.
It mut be less than 9 micrograms because the 18 microgram cartridge is
good for two inhalations.)
So while easy to use, it
is expensive, about 400 a month, and presription must be refilled monthly.
It/s been 12 hours since my first inhalation, and I feel no side effects,
a good sign.
The mist device (Spiriva Respimat)
is a combination of a plastic inhaler into which a cartridge with about
the drug is inserted. A single press of a button injects a fixed dose into
your lungs. My instructions are a single dose each morning. I find the
cartridge has about 60 doses, so it would last me about two months.
Full prescribing information for both Spiriva powder and mist devices
http://docs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/Prescribing%20Information/PIs/Spiriva/Spiriva.pdf
http://docs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/Prescribing%20Information/PIs/Spiriva%20Respimat/spirivarespimat.pdf
-- SPIRIVA® RESPIMAT®
(tiotropium bromide) inhalation spray, for oral inhalation. A cartridge
is used with SPIRIVA RESPIMAT inhaler. The RESPIMAT inhaler is a hand held,
pocket sized oral inhalation device that uses mechanical energy to generate
a slow moving aerosol cloud of medication from a metered volume of the
drug solution. When used with the SPIRIVA RESPIMAT inhaler, each cartridge
containing 4 grams of sterile aqueous solution delivers the labeled number
of metered actuations after preparation for use
-- SPIRIVA RESPIMAT, 1.25
mcg (single inhalation), is a long-term, once-daily, prescription maintenance
treatment of asthma for people 12 years and older. (The prescribing documents
says two inhalations (2.5 = 2 x 1.25 mcg) is the standard dose, but
I was advised by the nurse to use one inhalation daily.)
It looks like the manuf sells
two different forms of this inhaler that differ only in the dose. The inhaler
for COPD delivers 2.5 mcg per mist, whereas the inhaler for asthma is half
the dose (1.25 mcg per mist). (I have yet to see my prescription to find
out which I will get).
On MyLaheyChart I find the
entry below for the prescribed drug:
"tiotropium 18 mcg inhalation capsule, Commonly known as: SPIRIVA WITH
HANDIHALER"
"Instructions: Place 1 capsule (18 mcg total) into inhaler and inhale daily".
(not clear, once?)
"Prescribed quantity: 30 capsules" (without insurance discount
price of this quantity is close to 400)
Copy of my prescription (obtained
from CVS pharmacy) says
Durg:
tiotropium (Spiriva with HandiHaler) 18 mcg inhalation capsule
Qty:
30 capsule
Sig:
Place 1 capsule (18 mcg total) into inhaler and inhale daily
(does this mean ONE inhale?)
Date written: 4/21/17
Refills:
5
Proscriber: Dr. Villanueva, Andrew,
MD
41 Mall Rd. Burlington, MA 01805
781-744-8480
Diagnosis j432
(Centrilobular emphysema) -- Centrilobular primarily
the upper lobes Occurs with loss of the respiratory bronchioles in
the proximal portion
of the acinus, with sparing of distal alveoli. This pattern is most typical
for smokers.
HandiHaler prescribing document
-- Spiriva HandiHaler is
an anticholinergic indicated for the long term, once daily, maintenance
treatment of bronchospam associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and emphysem aand for reducing
COPD exacerbations.
-- Inhalation powder: SPIRIVA
capsules contain 18 mcg tiotropium bromide powder for use with HANDIHALER
device. Two inhalations of the powder contents of a single SPIRIVA capsule
(18 mcg) once daily.
-- Tiotropium is a long-acting,
antimuscarinic agent, which is often referred to as an anticholinergic.
In the airways, it exhibits pharmacological effects through inhibition
of M3-receptors at the smooth muscle leading to bronchodilation. The terminal
half-life of tiotropium in COPD patients following once daily inhalation
of 5 mcg tiotropium was approximately 25 hours.
-- In these studies, SPIRIVA
HANDIHALER, administered once-daily in the morning, provided improvement
in lung function (FEV1), with peak effect occurring within 3 hours following
the first dose. The mean peak improvement in FEV1, relative to baseline,
was 0.28 to 0.31 liters (28% to 31%), after 1 week of once-daily
treatment. Improvement of lung function was maintained for 24 hours after
a single dose and consistently maintained over the 1-year treatment period
with no evidence of tolerance.
(.30 L increase in FEV1 for my 2.31 L measurement would be about a
13% increase)
(from Spiriva HandiHaler prescribing document)
=======================================================================================================================
Incruse
Ellipta --- another once daily powder inhaler (5/4/17) (6/28/17)
(6/28/17 update)
I found in getting near
the end of the first Incruse Ellipta inhaler there is a problem in knowing
when it is empty. The package instructions say: 'Discard when the
counter reaches "0"'. But this is ambiguous! Does this mean "0" before
you slide it down to open it or after you open it? (I found
out from two telephone calls to the manuf contact tel# that the answer
is before.)
When you pick it up with
one dose remaining inside, before you open it the window counter
will read "1" (there is also a thin red bar to the left of the 1), but
after you open it in preparation for breathing, it will read "0", because
each time you slide down the slider to expose the breathing hole, the count
decrease by one. So while you are breathing in the last dose the counter
will read "0". This is confusing. The package instructions say just 'Discard
when the counter reaches "0", so when you have opened it and have not yet
breathed in with the counter showing a "0", it is not clear whether you
are going to get a dose or not! With this inhaler unlike the Spriva Handihaler,
there is no audio feedback, or in fact no feedback of any kind to the user,
that when you breath in you are breathing in the powder. The only indication
you have that you are getting a dose of the drug is the counter reading,
so the ambiguity in understanding what the counter reading means is very
important.
Here's
what the counter window means --- The window count BEFORE you open the
slider (to expose the inhale opening) indicates the remaining doses inside.
Thus the window count for the last dose will read before you open
it "1", and it will show "0" while you are breathing in.
---------------------------
The Spiriva Handihaler is
not in the formulary of my Part D provider (Cigna), but the formulary includes
three or four other drugs in the same class. GoodRx says the Incruse Ellipta
and Tudorza Pressair are similar drugs to the Spiriva and none of them
have generics, so (surprise!) this is why they are all so expensive. From
that list my lung doctor selected (Incruse, Ellipta) as an insurance covered
replacement for the Spiriva HandiHaler. It is also a powder based inhaler
taken once a day. Without insurance both drugs cost in the region of 350
to 400 per month. I expect that since by feb I am into Part D catastrophic
coverage for my super expensive chemo pills, that should apply here too.
Thus I expect my out of pocket costs for an inhaler with part D drug insurance
coverage to be about 5% of 400, or 20 per month.
Incruse Ellipta powder based inhaler for COPD
Incruse is a new drug only
approved by the FDA in 2014. It has a different active ingredient (umeclidinium)
than Spiriva. It comes with its own inhaler. The drug quantity for a daily
single inhale is 62.5 micrograms. I note its two main side effects (increased
eyeball pressure and worsening of uninary retension) are the same as Spiriva,
so the two drugs must be quite similar. Its mechanism of action is described
in its proscribing document this way:
-- Umeclidinium
is a long-acting antimuscarinic agent, which is often referred to as an
anticholinergic. It has similar affinity to the subtypes of muscarinic
receptors M1 to M5. In the airways, it exhibits pharmacological effects
through inhibition of M3 receptor at the smooth muscle leading to bronchodilation.
(Translation -- it is a bronchodilator. It relaxes the muscles that form
the airways in the lungs)
-- INCRUSE ELLIPTA is an
anticholinergic medicine. Anticholinergic medicines help the muscles around
the airways in your lungs stay relaxed to prevent symptoms such as wheezing,
cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can happen
when the muscles around the airways tighten. This makes it hard to breathe.
The instructions for use are
basically the same as for the Spiriva. Breath out deeply, then breath in
deeply through the inhaler, hold your breath for a few seconds. I haven't
had my hands on the Incruse yet, but it looks like it should be a little
easier to use than the Spiriva. With the Spiriva each day you need to open
a blister pack (a pain) to get a capsule to insert into the inhaler. With
the Incruse it looks like all 30 doses for the month are inside, a new
dose is available each time you open it, a counter displays on the front.
Breo Ellipta
Just after I had finished writing
up the Incruse Ellipta, I see an ad on TV for the Brio Ellipta inhaler.
What? This can't be a coincidence. Sure enough looking at the Brio inhaler,
it has same distinctive shape as the Incruse inhaler, they must be from
the same company. Yes, GlaxoSmithKline. So what's the difference?
Both are once daily, powder inhalers for bronchodilation. The Brio comes
in two different dosages, the lower dose marketed for COPD and asthma while
the x2 higher dose is marketed for just asthma. The Brio has two active
ingredients, both different from the Incruse, and one of the Brio active
ingredients is a corticosteroid. The Brio seems to have a lot of side effects,
perhaps because it includes a steroid.
--BREO ELLIPTA is a combination
of fluticasone furoate, an inhale corticosteroid (ICS), and vilanterol,
a long-acting beta2-adrenergic.
90 day supply of Incruse Ellipta unexpectedly arrives in the mail ---another
screw up on the inhaler (5/6/17)
Background
I found my first inhaler (Spiriva
HandiHaler) was not in the formulary of my part D (drug) provider, so I
checked a list of alternative inhalers provided by the hospital to see
if any were covered. As instructed, I called the hospital with this
information and was told by the lung support person that my doctor would
be changing my preseription to an inhaler covered by my Part D insurance
(Incruse Ellipta), and that the prescription would be sent (electronically)
to my local CVS pharmacy. When I tried to buy a 30 day supply of
Incruse inhaler at CVS, I was told my insurance would not pay for it until
after July 19, ten weeks from now. What? I said that can't be right, I
will be out of inhalant capsules in about two weeks, so I left CVS very
puzzled. When I arriced home, I found in my mail a package from Cigna Home
Delivery Pharmacy that contained three Incruse Ellipta inhalers,
a 90 days supply. The retail cost of each inhaler is about 340 dollars,
so this is about thousand dollars worth of drugs.
I did not authorize this purchase
Here's the thing I had no
idea that my prescription had been sent to Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy.
Cigna pharmacy never called me for authorization. I did not authorized
this purchase or the quantity, and I certainly did not authorize my my
credit card to be charged. Cigna has my credit card number of file, because
monthy I buy by super expensive (tier 5) chemo drugs from their seciality
pharmacy. When I do buy my chemo drugs monthly, Cigna speciality pharmacy
always
calls and verifies the drug, quantity, and asked if they can charge my
credit card.
A little googling finds
a site with 69 complaints about Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy! Here's a
poster on the site and what just happened to me happened to him in 2015.
-- "Cigna home delivery sent me $465 worth of medications I
never ordered. They charged my credit card which they had on file. I immediately
called them the day I received the shipment. I asked if I could mail it
back to them but they refused. They said the doctor sent them the prescription
so they assumed I needed it. I am now stuck with this charge for prescriptions
I never ordered."
(https://www.consumeraffairs.com/insurance/cigna_tel_drug.html)
I call Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy (5/8/17)
Cigna tells me that when
they receive a prescription, they routinely mail out the drugs
without
calling for authorization. This is their policy they tell me. They take
the (electronic) receipt of the prescription as the patient authorization.
I told them I consider this to be is an abusive billing practice perhaps
bordering on fraud. I ask them to return the money as they had already
charged my credit card. They refused. When I ask about why Cignal
always confirms my chemo drug order and confirms they can charge my credit
card, they are less than clear but seem to say they have a different policy
for super expensive tier 5 drugs.
Federal Trade Commission
Q. Am I obligated to return
or pay for merchandise I never ordered?
A. No. If you receive merchandise
that you didn’t order, you have a legal right to keep it as a free gift.
Messages to the hospital
I sent the following message
to the prescribing doctor about this unauthorized Incruse inhaler shipment"
(5/8/17)
I want to make you
aware of what I consider to be a screw up by the lung support staff. You
started me on Spiriva HandiHandiler about two weeks ago. I was handed a
sheet of paper at that time with 18 other inhalers with instructions to
see which of them are covered by my insurance. I did as instructed and
called the tel # on the sheet giving the inhalers in my insurer's formulary.
You were checked with, and I was told the inhaler prescription would be
changed to the covered Incruse Ellipta and forwarded to my local CVS pharmacy.
I said Ok. Later I verified that CVS had received the Incruse prescription.
This was last week.
Over the weekend a
package arrived in the mail (out of the blue) with a thousand dollars (retail)
worth of drugs, specifically a 90 days supply of Incruse Ellipta (three
inhalers) from Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy. I knew nothing of this order.
Neither the hospital nor the insurer called me about it. I did not authorize
the shipment, I did not authorize my credit card be charged.
The Federal Trade Commission
says if merchandise is sent to you that you never ordered, you have a legal
right to keep it as a free gift!
I can only assume that some
lung support person sent (electronically) my Incruse prescription to TWO
pharmacies: CVS and Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy. I was only told it was
going to CVS. On a call to Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy they tell me their
position is when they receive a prescription they assume receipt of the
prescription ALONE constitutes approval of the patient for shipment.
Clearly this is an aggressive
sales tactic (bordering on fraud). It has generated tons of complaints
about them to be found online. I tried to get Cigna to refund my money
since I had not ordered or in any way authorized this drug shipment. They
refused.
As a matter of principle
and procedure I think this is a pretty bad screw up, however, in practical
terms its effects are minor. The price was right (53 dollars, 5% of the
thousand dollar retail cost, since I take very expensive chemo drugs and
am in Part D catastrophic coverage). At CVS I would have bought a one month
supply to see if if the new inhaler worked for me, now I have a 90 day
supply, but other than that no problem.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
2nd followup message to the hospital the next day (5/9/17)
This is a supplement
to yesterday's message. After talking with my brother about how Cigna Home
Delivery Pharmacy came to receive my prescription for Incruse inhaler,
which they obviously did, he suggested a possibility I had not considered,
saying the point of contact between CVS pharmacy and Cigna Home Delivery
Pharmacy is likely to be my medicare part B insurer, who (surprise!) happens
to be Cigna Insurance.
I read Cigna Insurance and
Cigna Home Delivery operate as two separate companies, but clearly they
are both under the Cigna umbrella. So it might very well be (even perhaps
likely?) that when my local CVS contacted Cigna Insurance for approval,
Cigna Insurance seeing a thousand dollar purchase on the line and my credit
card on file forwarded the prescription to Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy,
who scooped the sale from under CVS's nose for themselves by immediately
hustling the drugs out the door and getting paid by charging my credit
card (all without my knowledge). This does fit all the known facts.
An inquiry to the Lahey lung
support staff could clarify matters. If they say they my new prescription
for Incruse was ONLY sent to CVS, as I was told, then I will accept it,
and I withdraw my (vague) allegation of yesterday that Lahey procedures
seem to be screwed up.
As a mere patient (an engineer)
I don't have any inside knowledge as to how the murky pharmacy/insurance
world works, so I can't figure out how Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy got
my prescription. Did it come directly from Lahey or via Lahey/CVS/Cigna
insurance? All I can do is look at the known facts and speculate.
------------------------------------------------------------
From the invoice in the
Incruse box --- Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy, PO Box 382097, Pittsburgh
PA 15250-8097, Order #:10225915300, Account #: 95027751, Ship date
5/4/17. Questions: 800-835-3784. Sold to Donald E. Fulton,
Cost: $53.23 (This is 5% of retail cost since I am now in Part D catastrophic
coverage), Payment received: $53.23. (Confirmed --- my bank checking account
shows a 53.23 charge to my debit card the next day) My debit card # is
not referenced on the invoice. Turns out that Cigna Speciality Pharmacy
(800-351-3606), where I get my super expensive chemo drugs monthly, is
probably just a division of Cigna Home Delivery Pharmacy both based South
Dakota, and as a convenience for these expensive monthly purchases they
keep my credit card # of file.
From the pharmacy label on
the Incruse box:
800-835-3784
Rx 1397229569
(important, this is the reference to this particular prescription)
Address: 4901 N. 4th Ave, Sioux SD57104
(prescribing doctor) Dr. Vxxxxx
Dispense date: 5/4/17
Refills: 3
So before I have even tried
Incruse, the alternate inhaler to Spiriva, I am sitting on a 90 day supply
of it In retail terms (sans insurance) this is more than a thousand dollars
worth of drugs. Now for me the price is right, since my out of pocket charge
for the 90 days supply is only 51 (about 17 per inhaler capsule).
This is the correct price, because due to my super expensive chemo pills
I am in Part D catastrophic coverage for 11 months of the year, hence I
pay only 5% of the retail price.
What happened here? (5/7/17)
Looking over the invoice and label
on the thousand dollars of drugs I got in the mail I have a pretty good
guess as to what happened. I think the hospital made a (minor) mistake
in forwarding my new prescription to two pharmacies: CVS and Cigna Home
Delivery Pharmacy. The told me only about CVS. Cigna is where I get
my chemo drugs, so for these monthly purchases they keep my credit card
# on file, a convenience for me.
The big screw up (if that
is what it was, but I suspect it was deliberate!) was at Cigna pharmacy.
My guess is to boost sales they take a prescription like mine with three
refills and just send out all three, billing the customer since my credit
card # is on file WITHOUT calling me to seek authorization either for the
purchase or the quantity! If Cigna had called me for authorization, as
of course they should have, I would have either denied it or changed the
quantity to one, so the hospital's error would not have mattered.
When I do some googling, I find
others complaining that Cigna home delivery pharmacy has charged their
credit cards without authorization. Another poster on the same site in
2015 writes "The pharmacy service with Cigna insurance forces you to have
90 day prescriptions written and delivered to your home regardless of whether
your physician writes 90 day prescriptions or not," and his wife works
for Cigna. (https://www.consumeraffairs.com/insurance/cigna_tel_drug.html)
Abusive billing practice
Found a 2013 posting (below)
of a patient similar to me who received an order from mail order pharmacy
that she did not authorize. The expert opinion answer is the sounds like
abusive, if not fraudulent, billing by the pharmacy. Apparently this is
a far too common abusive billing practice, even local pharmacies were doing
it at one point until Medicare ordered them to stop. In general you
have a legal right to keep for FREE anything sent to you that you did not
order or authorize. You cannot be required to return the merchandise. There
are hints in the posting that the pharmacy may rely on a patient authorization
that is obtained by the prescriber.
http://seniorsleague.org/ask-the-advisor-aprilmay-2013/
=======================================================================================================================
HandiHaler --- Now I am now totally confused. What I was shown
by the nurse is called the SPIRIVA RESPIMAT inhaler by the manuf. The prescribing
document describes the HANDIHALER as delivering a "powder" (18 mcg) not
a mist! The handihaler, which is on my drug list and presumable specified
in the prescription, is clearly a different device from the SPIRIVA RESPIMAT
inhaler that is shown in the video. GoodRx says 30 capsules are a 30 day
supply, so even though each capsule contains 18 micrograms, only a tiny
fraction of which is used for an inhalation, apparently a new capsule is
needed every day.
:
Here's a video from the manuf boehringer-ingelheim showing how to setup
and use the inhaler
https://www.spiriva.com/asthma/how-to-use
GoodRX info (4/23/17)
The GoodRx drug discount
site has some good information about this inhaler.
Spiriva Tiotropium
"Tiotropium (Spiriva) is
an expensive drug used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),
including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. This drug is more popular than
comparable drugs. There are currently no generic alternatives for Spiriva.
It is not covered by most Medicare and insurance plans, but manufacturer
and pharmacy coupons can help offset the cost. The lowest GoodRx price
for the most common version of Spiriva is around $385.02, 15% off the average
retail price of $453.83." (GoodRx)
Side effects
The three main side effects
appear to be increased pressure in the eyes, which can cause blured vision
because it raises the pressure in the eyeball, urine retention and sore
throat.
I was advised by the
nurse showing me how to use it that these types of inhalers are particle
based, so gargling is advised because accumulation of the particles in
the throat can lead to 'thrush', described as nasty.
Price and dose
From a sheet given to me
at the hospital other COPD inhalers in the same general class as Spiriva
include: Tudorza. Combivent, Incruse, Anoro, (Atrovant). GoodRx amazingly
shows these drugs are about the same price, nearly 400 for a month's supply
(smells like price fixing to me!). The active ingredient is different for
each brand.
Insurance coverage
I was handed at the hospital
a sheet titled: 'Inhaler options to review with your insurance'
with 18 inhalers (in five unlabeled classes), and advised to call
my insurance company to see what is covered and not covered, then to call
a tel # (781-744-3365) at the hospital. (This tel # is close to Dr. Villeneuva's
number)
Check of 2017 (and 2016) Cigna Insuranc Comprehensive Drug list (Formulary)
Jesus Christ --- Cigna has a bunch of formularies
Information below is from 2017 HMO plans, but Spiriva is missing
from 2017 formulary for Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure (PDP)
My plan is Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure-Xtra (note Xtra
on the end)
Yikes --- Cigna cusomer tel # printed everywhere is
totally wrong. I called it and it is another company, who told me Cigna
printed the wrong #. She read me the number, butI didn't write
it down.
Even when I log into my account the tel # is wrong. (Its the tel # I just
called).
=================================
My part D insurer, Cigna Insurance, drives me up the wall
How can one insurance company
be so incompetent? I spent literally hours trying to find out if
a prescription bronchodilotors was covered by my Part D Cigna plan.
Wrong contact tel # at Cigna
For starters Cigna's main customer
contact tel # on their online formulary documents is wrong. This
is freaking unbelievable! Not just wrong on one document , but on multiple
documents. I called the number, and it is another company who explained
to me Cigna has put down their number. They told me the correct Cigna number
(which I did not write down), and it is totally different. How can such
an error not have been corrected almost immediately? The only answer
I can come up with is they don't give a shit.
No index into the multiple formularies
The root of the problem
in checking for my new drug in the Cigna multiple formularies is finding
the right formulary. Cigna has a lot of different plans with very similar,
long, complex names. I now know (after a lot of time wasted searching)
that these plans do not use the same formulary. Cigna has multiple
formularies. What's needed is an index tying Cigna's various plans
to the formulary for that plan. If such an index exists, I can't find it
and apparently neither can google. Where it should be is in the beginning
of each formulary. All you find now at the beginning of a Cigna formulary
is the name of the plan it applies to.
For example, the exact name
of my Cigna medicare part D plan name is 'Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure-Xtra'.
Look at this name, four qualifiers after Cigna! Do all these words matter
in searching for a formulary. Turns out they do, but this is after wasting
mucho time searching. Earlier I found a formulary that says it applies
to plan: Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure (no Xtra at the end). Does this formulary
apply to my plan I wondered? I thought there was a good change it
did, the name is almost the same, it was unclear if the 'Xtra' at the end
mattered Well it turns out it does, but this became clear only
in hindsite. Why does Cigna do this? It is just needless confusion, or
is that the idea?
Formulary
Formulary (2017) for my
plan: Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure-Xtra (Note there is a separate
formulary for the 'Extra' version of Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure!)
https://www.cigna.com/iwov-resources/medicare-2017/docs/formulary-ea-pdp-b.pdf?WT.z_nav=medicare%2Fpart-d%2Fdrug-list-formulary%3BBody%3BEnglish
This formilary document says: Plan covered -- 2017 Cigna-HealthSpring
Rx Secure-Extra (PDP)
I was given at the hospital
a list of 18 COPD drugs (including Spiriva) grouped into what appear to
be four (unlabeled) categories. I searched my 2017 Cigna formulary (above)
to identify the categories and in this formulary found nine of them falling
into three categories. The results are below.
* Bronchodilators,
Anticholinergic (Spririva class)
Atrovent, Combivent, Incruse, ipratropium bromide
(Spiriva HandiHaler was included in the 2016 Cigna-HealthSpring Rx Secure-Extra
plan formulary)
---------------------------------------
Bronchodilators, Sympathomimetic
Proair, Ventolin, Anoro
Anti-inflammatories, Inhaled Corticosteroids
Advair, Breo, Flovent
==============================================================================
Pending inhaler swap to obtain insurance coverage (5/3/17)
Call to the hospital on 5/3/17 (# provided)
put me in touch with a pharmacy helper who seemed to know what drugs are
in my Part D insurer (Cigna) formulary. (Though on hindsite I don't see
how she could know what plan I have at Cigna since I didn't tell her!)
She was only interested in other drugs in the same category as Spiriva
HandiHaller (Bronchodilators, Anticholinergic) as possible swaps for it,
and there are four of them (see above).. She had identified the same three
brand names in this category as I had found, but I added the non-brand
name.
She is going to forward the
possible swaps to the lung doctor, and she tells me he will recommend a
swap, rewrite the prescription and it will be forwarded to my local CVS
pharmacy. I expect that for the second month (assuming the drug actually
works for me, which at this point is unknown, and I stay on an inhaler),
it will reduce my monthly costs about a factor of ten (400 => 40)
round numbers.
One or two inhalations?
On the same talking to a
nurse the question of one or two inhalations of Spriva Handihaller from
the 18 microgram capsule was resolved. I said this must be 'bread and butter'
medicine to lung people, and she said yes we prescribe this all the time,
and we tell everyone 'one' inhalation. Ok, I will accept this. (She claimed
two inhalations in the prescribing document are there for little old ladies,
but I don't read it this way.) My suggestion, which she said she would
feed back to the doctor, was that the label on the medicine be rewritten
to make it more clear, put in 'one' ("one inhalation" per day).
==============================================================================
Bottom line --- While the Spiriva HandiHaller bronchodilator I was
prescribed is in some of the Cigna HeathSpring formularies (those for HMOs),
it is not in my plan (even though it has 'Extra' at the end)!
Under the category: Bronchodilators, Anticholinergic were Spiriva would
normally be found, I find these: ATROVENT HFA QL(25.8/30), COMBIVENT RESPIMAT
QL(4/30), INCRUSE ELLIPTA QL(30/30)
=======================================
Yikes, yikes --- Spiriva is missing.from the 2017 formulary for my
'Extra' plan (above) (even though it is included in the HMO
versions of the Cigma 2017 formulary)
Included in the class: Bronchodilotors, Anticholinergic are Atrovent
HFA (tier 4), Combivent Respimat (tier 3), and Incruse Ellipta (tier 3)
-----------------------------
Class:
Bronchodilotors, Anticholinergic
-- Anticholinergic bronchodilators are used more to treat chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease than to treat asthma. Anticholinergics relax and enlarge
(dilate) the airways
in the lungs, making breathing easier (bronchodilators).
Tier 3 drugs are preferred brand name drugs
Spiriva HandiHaler
(tier 3) QL 30/30 (quantitiy
limits) prescribed inhaler
(quantity limits added in 2017)
Spiriva Respimat
(tier 3)
Tudorza Pressair
(tier 3)
Combivent Respimat (tier 3)
Cost sharing retail
"You must generally use network pharmacies to use your prescription drug
benefit. Benefits"
$42 / $84 / $126 (30/60/90 Days)
Preferred retail cost sharing
$47 / $94 / $141 (30/60/90 Days)
Standard retail cost sharing
Looks like good news. I think
this means my cost share for a 30 day supply is $40, whereas I paid
390. CVS pharmacist told me I may be able to get insurance to backdate
insurance approval. If not, my cost for future months would be about 1/10
of what I paid for first month.
Of course I was was not handed
a prescription at the hospital (it was to be electronically sent to my
local pharmacy), so I am blind to the details. Follows the philosphy keep
the patient ignorant! Gees....
Units are a puzzle. 'mcg',
which is what the manuf uses, stands for micrograms. But while the MA drug
discount card uses mcg as units I find Blink Health is using 'grams'. Ok,
I find each cartridge contains 4 grams of aqueous solution, so apparently
Blink Health is using the weight of the solution.
MA drug discount card
At CVS $19 for qu 1 (18 mcg) which
I think includes the inhaler (nope! this is for the HANDIHALER, which is
the powder device) but at 1.25 mcg/dose this is enough for only 14 days,
or 31 for the inhaler with two 18 mcg capsules. (From varying the quantity
it looks like the discount price is about 10 for the plastic inhaler and
10 for an 18 mcg carttridge. Bottom line it looks to be about x10 times
cheaper a one or two month test to buy the powder device rather than the
mist device. (Don't think so, from GoodRx site it looks like a new cartridge
is needed every day!)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Inhaler change --- (inhaler update 9/9/17)
Spriva Respimat -- "two puffs
daily" (mist based tiotropium bromide inhaler)
My inhaler prescription has
just been switched. Here is the history. Last spring I started with the
Spirva powder based Handihaler and used it for a month. It worked well
for me then. Because it was not covered by my part D insurance and
cost about 400/month, after one month the prescription was changed to the
bronchodilator Incruse Ellipta which was covered. The Incruse has a different
active ingredient. I was never sure if the Incruse worked as well as the
Spiriva, but in the last couple of months the Incruse inhaler clearly has
stopped working. My shortness of breath is bad, really bad, as bad as it
was before I started an inhaler.
I sent a message to my lung
doctor asking that my prescription be switched back to the powder based
Spriva Handihaler that I started on. He responded with a prescription to
the mist based Spriva Respimat that has same active ingredient as the Handihaler
(tiotropium bromide), and he specified "two puffs daily". (This I believe
is the inhaler that was first demonstrated to me by the nurse.) Two
puffs is consistent with the Spirva prescribing document which says for
a full dose and treatment of Copd:
"2 inhalations of Spriva Respimat 2.5 mcg (4 grams) once daily"
A quick check of the price
using drug discount cards is that the price will be about 390/month.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hemoglobin into
normal range (3/6/17)
Hemoglobin has been running
12-13 (10.9 to 13.1) over the last 8 months on carfilzomib, but surprisingly
three weeks after I began taking a moderately strong iron supplement pill,
hemoglobin jumped 20% (from previous month) to 14.1 into the normal range
for the first time in a year. Could be a coincidence, but the timing suggests
otherwise, that the iron pill may very well have boosted the blood's oxygen
carrying capacity from below normal (no data on that) into the normal range
(what the iron blood data now shows), so the marrow for the last three
weeks may have been receiving more iron allowing it to make more ;hemoglobin.
At this point this is just a hint that my blood's oxygen carrying capacity
may have been low helping to hold my hemoglobin down.
In recent months on carfilzomib
my red blood cell count (RBC) at 3.63 M/uL has run about 30% lower than
normal (meaning the high/low mean). My recent (3/6/17) jump of 20% in hemoglobin
to within the normal range (14.1 mar 2017 vs 12.2 feb 2017) is mirrored
by a 19% jump in RBC to (4.32 M/uL mar 2017) vs (3.63 M/uL feb 2017), and
by an 18% jump in hematocrit (percentage of blood volume occupied
by red blood cells) into the normal region (43.5% vs 36.8%). Lower edge
of normal for RBC is 4.5 M/uL and for hematocrit is 41.0%.
Iron supplement pill (2/15/17)
This jump may be related
to an iron supplement pill (65 mg, 351% of FDA) I began taking three weeks
before the 3/6/17 blood test. While sold over the counter (Stop and Shop)
the iron supplement pill bottle says it is not intended for long term use
unless under the direction of a physician. Dose check: a reputable daily
multi-vitamine pill (One-a-Day for women) has 18 mg of iron (100% FDA).
Looking for a iron lower does than 65 mg an Amazon search for 'iron supplement'
turns up 'Gentle Iron - Iron Glycinate 28 mg' from Vitamin World, which
is mini-vitamine pill with 28 mg iron plus three vitamins (C, B-12,
folic acid). Also found two pills with 18 mg iron (100% FDA) combined
with a little vitamine C (30 mg, 50% FDA) like 'EZ Milts Iron' and one
sold for children.
Iron blood tests (3/6/17)
In response to our joint
concern about my blood's oxygen carrying capacity (maybe enhanced by the
65 mg, 351% iron pill I have been taking) my doctor was able to add (after
the fact) an iron analysis of the blood sample collected the day before
(3/6/17). 70% of absorbed iron ends up in hemoglobin and 30% is stored
in tissues as Ferritin. Most of the iron blood paramaters are associated
with iron transfere in the blood from food to the the bone marrow and the
rest of the body.
The only out of range iron
parameter is Ferritin, nearly double the upper high normal. It is a measure
of iron stored not in himoglobin, but in other cells of the body.
Bottom line --- The iron
transport parameters all look good, well centwews in their ranges. So for
oxygen diffusing across the lung membranes to the capillaries it looks
like the blood has the ability to pick it up and carry it to the marrow.
However the high ferritin is other body tissues is a concern.
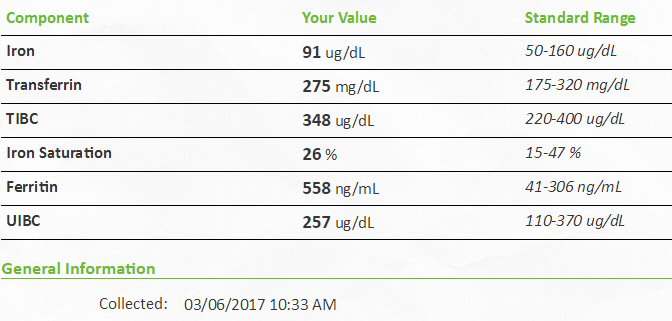
My iron tests -- only out of range parameter is Ferritin (almost
double normal high)
Ferriin is blood stored in tissues (other than hemoglobin)
Note [TIBC - UIBC = Iron], [348 - 257 = 91] ug/dL
-- TIBC (total iron-binding
capacity) measures the total amount of iron that can be bound by proteins
in the blood. Since transferrin is the primary iron-binding protein, the
TIBC test is a good indirect measurement of transferrin availability.
--Transferrin is a protein
produced in the liver to transport iron in the blood. Under normal
conditions, transferrin binding sites are typically1/3rd saturated with
Iron and 2/3rd unsaturated (UIBC) held in reserve. [yup, TIBC- Iron = UIBC]
[348 mg/dl (TIPC total) - 91 mg/dl (used by Iron) = 257 mg/dL reserve
UIBC]
-- Iron Saturation is the
ratio of iron to the ability of blood to carry it (TIBC). [ yup, Iron/TIBC
= 91/348 = 26%]
--UIBC test determines the
reserve capacity of transferrin, i.e., the portion of transferrin that
has not yet been saturated with iron
-- Serum 'iron' measures
the total amount of iron in the blood (that day), depeind on daily iron
intake from food (or pill), nearly all of which is bound to transferrin.
Reflecting on my recent tests --- health overview email to family(3/1/17)
I've reached the
point where the side effects of my powerful chemo drugs are more troublesome
than the cancer. My overall cancer numbers after seven months on my pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo are good. The percent of cancer cells in my blood protein is now
only 2% vs 50% when I was first diagnosed 2.5 years ago, a reduction of
x25. This good result is confirmed by a recent Pet scan which shows the
four bright spots in my bones I had last spring (two in the head and two
in the chest) I had prior to this chemo (and a 2nd head radiation) have
dropped to one in the chest. The secondary blood tracking signals (free
light chain) dropped nicely too, but have lately show a slight creep upward
just outside the normal range. Needs to be watched, but too early to fixate
on. (M-spike is holding steady at .11 g/dL)
The main problem
I have is a shortness of breath. This prompted Dr. L.. of Dana Farber to
suggest (order) two tests one for my heart and one for my lungs, because
he points to carfilzomib (drug given by infusion), since this drug is known
to damage these organs in some patients. The first words out of his mouth
when he called me a month ago was had I scheduled a new heart test. Well
I have recently had the heart test (echocardiogram) and the lung test (pulmonary
function test).
The heart test came out fine.
Valves and pressures Ok, no change from last sept. The posted results from
the lung test are as posted online cryptic as hell (see above), just a
bunch of obscure abbreviations and NO normal regions. What is a patient
supposed to make of raw data like this? Maybe a 'reading' of this will
show up online in a week, maybe not, who knows. Shows the level of support
the hospital gives to patients. My Lahey doctor (C...) has made no effort
to contact me about either test result either by phone or message. I don't
obsess, I know the system has built in delays. I just live with it.
Anyway I dug into lung test
and found out what it does and was able to dig up a couple of examples
of people taking the test with their numbers, which at least gives me a
clue to interpret my numbers. The test first measures how much air your
lungs can take in relative some statistical standard and here I look reasonably
OK at 80% of predicted. And when I took the tests there was still gurling
in my lungs from a three week cold, now nearly all gone.
The second part of the test
was more interesting. It measures (indirectly) how much of the oxygen you
breath in gets absorbed. It does this using a low level of CO (carbon monoxide),
which is poisonous, but has the advantage that it is not normally present
in air, so measurable, and is absorbed preferentially over oxygen. Here
the important number is called DLCO predicted, which stands for 'diffusing
capacity of the lung for CO', and came out only 44% of the statistical
standard. The closest example I could find was for a 65 year old man whose
result was 84%.
Bottom line --- it looks
like (from this one example!) I am absorbing only half the oxygen I breath
in relative to normal. This in a sense 'explains' my shortness of breath
when I exert myself. So some progress, but it is not the full story. A
3rd part of the test involved breathing in an asthma treatment drug that
opens the airways leading to the lungs. This result which was given to
me by the technician and is MISSING in the online posting is that there
was no change, showing that the poor gas exchange is not due to airway
obstruction (trachea) but is in the lungs.
So that where we stand today.
The issue to be discussed at my next doctor's meeting is whether we change
chemo based on this result. I will ask if the lung damage is going to get
worse over time if we don't change, which I suspect may be the case as
it has slowly gotten worse over the last three months and damage like this
tends to be cumulative. Is it reversible? I think probably not as the carfilzomib
is known to irrevesibly bind to the protein it targets.
I am (very) reluctant to
change chemo at this time because I view the next drug, which Laubach told
me about (daratumumab) he would swap in for carfilzomib, is a new humanized
antibody drug that I view as the last step on the chemo ladder and a wobbly
rung at that. I prefer at this point to live with the lack of energy for
a while and see what happens. If it does not get worse, I can live with
it and should be able to get to ME this summer as it doesn't affect me
when I drive. I will see next week how Dr. C... views it.
Don
====================================================================================================
Begin pom/Ninlaro/dex
chemo (4/3/17) (5/31/17) (6/20/17)
End of 3rd Ninlaro cycle (6/20/17)
At the end of my 3rd Ninlaro
cycle my cancer numbers are not looking so good. For several months my
lambda free light chain has been in the range of 3.5 to 4.5 mg/dL, but
at the end of the 3rd cycle it has broken out on the up side to 8.42 mg/dL.
A big jump, more than double its recent value and very close to the level
of disease progression used by clinical trials (10 mg/dL). This is bad.
After this big increase in free light chain, I was expecting the worst
for M-spike, but it came in a .15 g/dL, actually a small decrease and a
little lower than its been in the last four months. So my numbers
are mixed.
To the extent that free light
chain is a leading indicator. It does not bode well for numbers in the
next cycle. I have yet to meet with my oncologist to decide if pom/Ninlaro/dex
will be continued for a 4th cycle, but I am betting it will be. For one
thing the mechanics of switching chemo are tricky as drugs must be ordered
(and paid for) in advance, so they are in house. Plus to stay on chemo
I will be starting the 4th cycle before my meeting with my doctor. Some
perspective on living with these blood cancer levels (for a while) can
be obtained by looking back a year or so at my numbers before I started
pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo, which were not too different.
-------------------------------------------
Beginning of 3rd Ninlaro cycle (5/31/17)
My blood numbers have been
pretty stable for four months now (feb, mar, apr, may 2017 ). I'm hoping
I am moving into a 3rd remission. Feb and march was pom/carfilzomib/dex,
then apr and may were pom/Ninlaro/dex. Jan to march I had shortness
of breath which was getting worse and both my oncologists pointed to carfilzomib
as the likely cause. Feb to mar my numbers started to rise strongly, looked
like after six sucessful months pom/carfilzomib/dex was ceasing to work.
For both these reasons carfilzomib had to go. Carfilzomib is a proteasome
inhibitor, so we replaced it with a new (pill) proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro.
Both from the same class, but their protein targets are a little different.
To me this is a
conservative decision. Don't rush to humanized antibody yet, try to squeeze
a few more months out of this triplet chemo class. The risk I am taking,
which I won't have data on for two months with a 5th pet scan, is that
damage is occurring inside, tumors (plasmacytomas) are growing. I will
value the clinical opinion on this risk from my Dana Farber doctor, who
is a MM specialist working at world class MM research center associated
with Harvard medical school.
Not surprisingly with a 3rd
remission, the numbers aren't too deep. In the last four monthly readings
lambda free light chain is running above normal (3.5 to 4.5 mg/dL) or about
40% of its 10 mg/dL disease progression threshold, and M-spike running
.16 to .17 g/dL or about 30% of its .5 g/dL disease progression threshold.
One version of M-spike that I track (see table) is the amount of monoclonal
protein as a percentage of total protein. It is now 2.81% (may 2017).
It was 50% when I was diagnosed (!) in 2014, and it took my initial rev/dex
chemo about seven months in 2015 to bring this ratio down to the 3% to
4% range. In 2016 a lot of time was spent with the ratio in the 3% to 5%
range, so 2.81% is not too bad.
It's an open question as
to what is growing inside with these numbers and the only way to find that
out is another Pet scan, which would be my 5th. My Lahey oncologist suggests
the time for another Pet scan would be after completing four cycles of
my current pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo. I have completed now (5/31/17)
two cycles and have just begun a third cycle, so that would mean another
pet scan around the end of july.
Both mine and my oncologist
thinking now is hold course and ride this chemo as long as it works. In
practice this means until blood numbers start to strongly increase, or
a 5th pet scan shows new or growing plasmacytomas. Or maybe if my consulting
Dana Farber MM oncologist, who I meet with next week, strongly suggest
changing.
====================================================================================================================================
Begin
pom/daratumumab/dex chemo (8/1/17) (8/27/17)
Searching
for a 4th remission --- failure
Pom/daratumumab/dex chemo -- 7 and 10 week update
(9/24/17) (10/8/17)
(10/8/17)
The
most recent numbers (not yet plotted), where Pomalyst was effectively discontinued
for few weeks, shows the cancer perhaps stabilizing at a new high level:
lambda free light chain (16 - 17 mg/dL) and M-spike about .5 g/dL.
---------------
I have now
been getting daratumumab infusions weekly for about seven weeks, so there
is now seven weeks of data to evaluate if it is working. Is a 4th remission
in the offering? Unfortunately no. I've plotted up the numbers. When the
cutting edge antibody drug daratumumab (recommended by both of my oncologists)
was swapped in for the proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro, the result was a nice
two
week drop in my cancer numbers [lambda free light chain (11.3
mg/dL => 4.37 mg/dL)]. This drop was totally wiped out in the following
weeks with lambda free light chain rising in three weeks [4.37 mg/dL =>
9.89 mg/dL] and in the following two weeks to 11.2 mg/dL]. Here's the plot
of my lambda free light chain and M-spike for the six months: march to
sept 2017.

At the end
of my pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo (as it stopped working) my lambda free light
chain rose to 11.3 mg/dL, which is above its disease progression threshold
of 10 mg/dL, and M-spike rose to about .5 g/dL, which is also its disease
progression threshold. After the two week drop with daratumumab being swapped
in for Ninlaro, the early numbers seems to show that my disease may be
stabilizing out at those high numbers [lambda free light chain = 11.2 mg/dL
and M-spike = .35 g/dL, down a little from .51 g/dL].
This could
be worse with the numbers skyrocketing, because my cancer load is still
at these numbers more than ten times lower than when I was diagnosed (5.31
g/dL). So while all my tumors are not growing there can be little doubt,
based on my pet scans, that a few of my large plasmacytomas will grow at
these levels.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
End game
Health update(10/8/17)
With the failure
of daratumumab based chemo I have arrived at the end game. There are no
more good chemo options available. Worst in recent weeks my marrow is just
not making blood cells! Following daratumumab recommendations my oncologist
a few weeks ago advised me to stop taking one of my two chemo drugs (imid,
Pomalyst) hoping that platelets which had sunk to around very low 10 would
rise to 50. Looking at my numbers I thought there was little chance of
this happening. In fact what happened was platelet declined further to
super low 5, and this triggered multiple platelet infusions to keep me
from bleeding to death. I am only been kept alive by these infusions.
New marrow needle
biopsy
(10/4/17)
A 2nd marrow
needle biopsy (1st was in 2014 after I was diagnosed) was performed to
try and understand why my marrow is not making the blood cells I need.
Going in there were two possibilities. One my marrow was full of multiple
myeloma cells which had nearly squeezed out all the normal marrow. This,
however, would be inconsisten with M-spike blood data which at .5 g/dL
is about 1/10th of 5.31 g/dL I had when first diagnosed. In that case the
needle biopsy showed about 70% of the marrow space was filled with cancer
cells.
The second
option going in was that my marrow has just 'collapsed'. In effect
so damaged from three years of continuous chemo that it just can't grow
new red blood cells and/or platelet cells. And this is essentially is what
the new needle biopsy found. When doctors don't really understand stomething
they call it a 'syndrome'.
MDS
a 2nd cancer --- "myelodysplastic syndrome" (10/4/17)
The diagnosis
of the needle biopsy of my hip is I have developed (at least in my larger
bones) a 2nd cancer (hematological cancer) whose short hand is MDS. This
is a complete collapse of the marrow. In other words my body is no longer
making blood.
Myelodysplastic syndrome
Myelodysplastic
(bone marrow failure disorder) syndrome combined with "refractory cytopenia
with multi-lineage dysplasia" refractory cytopenia (low blood cell
counts) with multi-lineage dysplasia (abnormal shape)
Translation ---- marrow collapse, failure to make several
types of blood cells.
--------------
So bottom
line I view this as the end game in my fight against MM. There are no good
chemo options left and the remaining task is to adjust chemo to slow the
growth as much as possible my tumors. Also to do something about my extremely
bad shortness of breath , which is very likely due to reduced oxygen carrying
capacity of my blood since my numbers of red blood cells (8.4 g/dL) have
dropped recently to a very low lever, only 60% of the low edge of normal,
lower than in my three years of chemo.
Health
update
(10/21/17)
Summerizing
my health to friends:
On my health. The end is near. I have (at best) weeks to live.
I have developed a 2nd cancer (MDS) that has caused my body to stop making
blood. There is no treatment or cure. I have been been surviving for the
last few weeks only because I am getting red blood cell and platelet infusions
twice a week. I hope to live long enough to see the Greater Boston Stage
Company christmas production of She Loves Me.
I have extreme shortness
of breath when I have to move, but sitting I am OK. Hence I can still drive
short distances. I am taking advantage of friends and using a limo
service to pick me up for lunches, longer trips and the theater. Earlier
this week I was getting only 1-2 hours sleep, but 2 x 5 mg Ambient was
worked for last two nights though it gives me nasty dreams.
Health update
(10/14/17)
How do I feel?
Terrible. I can barley walk around my apartment without breathing hard.
I've pretty much given up cooking as I don't have the energy. I eat from
cans and defrosting. My appetite is low. I used to be able to sleep OK,
but in the last few days the nighttime is bad as my back is starting to
hurt me, and I can't find a comfortable position. I'm using a pillow to
help. Back is bothering me standing and sitting too. A new significant
degradation in quality of life.
Repeated
blood transfusions
I am being
kept alive by multiple infusions/transfusions of red blood cells and platelets.
This is the result of my new second cancer 'myelodysplastic syndrome',
which is a collapse of my blood marrow. As confirmed with a recent hip
marrow biopsy the marrow of my larger bones is not making new blood cells
(at least not red blood cells and platelets), it may be making (some) white
blood cells whose numbers have held up. In essence my blood marrow is collapsed.
My marrow is not making new blood, hence the repeated used of blood transfusions
to keep me alive. I have had two red blood cells and platelets transfusions
this week and 2-3 of each every week for the last few weeks. I now have
my blood scheduled to be tested on tue and fri with an infusion will be
done if the value is low, which is usually is. Even though normal red blood
cells are said to live four months, I find my red blood cells counts do
not hold. Platelets have a much shorter life time of ten days or so and
probably half of that lifetime is gone by the time I get them, so it makes
sense that I need platelets all the time
Two cancers
I have two cancers,
the classic multiple myeloma probably in my smaller bones which produces
clonal levels in my blood (free light chain and M-spike) that are at or
above the disease threshold. My cancer load as indicated my M-spike (.5
g/dL) is about 1/10th of the cancer load when I was first diagnosed. The
result is some tumors, likely in my ribs, are probably still growing. A
6th pet scan has been scheduled to take a look.
The second
(rare) cancer is 'myelodysplastic syndrome', which is technical jargon
for 'bone marrow failure disorder', or in simple terms 'bone marrow collapse'.
Even with all the transfusions my red blood cells levels remain very low,
undoubtedly contribution to my shortness of breath, and my platelets too
are very low, far below normal, leaving me at risk of bleeding. Most needle
sticks even in spite of pressure on the wound for 2-3 minutes result in
large bleed under the skin that takes 2-3 weeks to dissipate.
Social life
In spite of
this if I can get picked up, I still can enjoy a lunch or an evening out
at the theater, as I am all right when I am sitting down. This week I attended
with my brother and a friend the opening night of new play at the Greater
Boston Stage Company (formerly Stoneham Theater) sponsored by the Don Fulton
New Play Project (yup that's me) with dinner before hand. Three weeks ago
I was able to see the world class Boston Ballet in company class sitting
in front of the mirrors in their home studio. That was fun.
Since I am OK sitting
down, while it takes a lot of me to walk a few feet to my car which I park
as close as possible in my home parking lot. I can then sit in the car
for a few minutes and recover and then drive off safely.
Health update
(11/28/17)
Two month
after MDS has shut down my body from making red blood cells or platelets
I am still alive and can get out, but as I tell friends I am 'living on
the edge'. I live week to week. I am happy that I made it to thanksgiving
and a wonderful family dinner. Also made it to the opening on one of my
favorite shows (She Loves Me) at my local professional theater. Great show,
fantastic production, so this will provide theater entertainment through
the month of dec if I live that long.
I am being
kept alive for the last couple of months only by multiple transfusions
of red blood cells and platelets. Typically I now get 2 or 3 of both
each week, so I spend a lot of time in the hospital. Twice a week I get
up about 6:00 am and spend 5-6 hours in the hospital. A blood transfusion
takes 1.5 hr and a bag of platelets, which until recently took 30 min,
now takes 1 hr as some national panel just reduced the recommended flow
rate in half. There's also a lot of time spend with preliminaries
and waiting around for the hospital pharmacy to get the drugs ready, and
the double checking before each transfusion can start.
While my transfusion
schedule for weeks has been tues and fri, the handwriting is on the wall
with my value of 3 today that I am going to have to go three times a week
(mon, wed, fri) because it is becoming clear I cannot maintain my platelet
level when there is four days between infusions. This means not only more
time in the hospital, but worse in Boston it is going to soon begin to
snow, and I will still need to get to the hospital about every other day.
Since my energy level is super low, my problem is I won't have the energy
to clean the snow off my car, so this is going to prevent me from driving.
I will probably need to change to a taxis or car and driver. More time,
making the infusion days more tiring, probably about an extra hour three
days a week!
My shortness
of breath now is extreme. If I am picked up, I can get out no problem,
and I have been doing this as much as possible, going to the theater or
lunch and dinner with friends and family. Luckily I can still drive safely.
While walking to the car is tiring, I park the car close and I sit in the
car for a couple of minutes to regain my breath before driving.
However, just
walking around the supermarket to buy a dozen items now leaves me totally
exhausted. Luckily there is fruit and vegetable stand nearby that is physically
much smaller and hence less tiring. I am also going to again use the Stop
& Shop Peapod delivery service to stock my house with basics. Also
going to to do more ordering of take out from restraunts. A duck dinner
provides a good meal with leftovers for lunch the next day.
At home I frequently
have to lay down for 15 minutes or so after doing a little something like
filling the dishwasher. I have a spot on the couch where I can curl up
for this, and a few minutes like this not only reliably reduces my breathlessness
but it helps ease the pain in my back. For the last month or so I have
been using pain medications (morphine and Tylenol) to manage pain in my
back and side, which I speculate (but don't really know) are both connected
to a tumor (plasmacytoma) that has been growing wild in my back since I
stopped chemo. I had one day (5 grays?) of radiation this tumor in the
back, but I have felt no change at all in how the pains feels. It has not
however, gotten worse, it's the same week after week.
One good thing
is that I have been sleeping much better than couple of weeks ago. For
a week or two I was barely getting any sleep, waking up every hour. But
for the last couple of weeks I have found a procedure that (so far) reliably
works, allowing me to get a good night's sleep. One 10 mg Ambient sleeping
pill plus a pain pill (usually 500 mg Tylenol) taken just at bed time.
I can then reliably sleep either on my right or left side without my back
hurting. While I don't eat a lot, I am eating more and better that I was
2-3 weeks ago.
The social
worker at the hospital is leaning on me heavily to get trying hiring a
home worker (about $22/hr). This is different from a home health worker
who does personal things to help.
Super low platelets
(11/28/17)
In the two
month or so my platelets have been running super low. It has been running
just a little above the internal bleeding threshold of 5. A few times it
has hit 5 and today it was 3. Yikes! This is unbelievably low. The only
symptom was some bleeding into the gauss after my blood was taken (in crux
of elbow). A week or so earlier I did have blood running down my hand and
onto the floor while still in the infusion room when my blood transfusions
were finished.
Platelet mystery
Today my initial
platelet count was 3 (near zero, four days after my last platelet infusion)
and instead of just ordering an infusion of two bags, which I thought was
obvious, a nurse practitioner (standing in for my oncologist) ordered one
bag infused then a platelet test after (takes 30 min or so total). I would
get a 2nd platelet infusion only if the count was below 20. My experienced
infusion nurse was telling me it's not uncommon for a single bag of platelets
to raise the count to 60 or higher (I have seen this confirmed online.)
I was skeptical. My post infusion count was 11, so I got a 2nd platelet
infusion today.
But this brings
up a mystery. It's it just a matter of numbers? The platelet count is an
absolute count. Why isn't the post infusion count predictable? How can
it be over 60 in some people and only 11 for me (correcting for body mass)?
Is my body destroying or hiding platelets? In this case it had to happen
not over days, but in 30 minutes! Does the count (or quality) of the platelets
vary a lot from bag to bag? This seems unlikely.
--
Overall, after the initial decline in platelet count to 4,000/uL, the count
followed a saw-tooth pattern. There were transitory increases in platelet
count to as high as 60,000/uL following platelet transfusion. These increases
were immediately followed, within a few hours, by significant declines.
--
(Above was for a single hospitalized patient who received massive platelet
transfusions (72) over five days. The plot of platelet count over the five
days shows two declines of about 60,000 to maybe 10,000 occurring in about
an hour. So a rapid decline is possible. In this case the platelet crash
was triggered by a reaction to a new drug given the patient (abciximab)
and the patient has "two predisposing factor for severe thrombocytopenia".
The don't understand what happened, but speculated that the "drug could
actually induce platelet aggregation".)
-- One cause
of low platelets is an oversized spleen, because the spleen is known to
remove platelets from the blood. However, splenectomy (removing spleen)
is reserved for the most serious and refractory cases.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
First look (3 weeks) (8/27/17)
With the change
to daratumumab I thought this was my best hope going forward and was hoping
for a good deep response. Well it's only three weeks in, just a first
look,
and there are caveats, but it doesn't look like I am going to get it. Firstly
changing chemo is like turning a battleship, so I really had two off weeks
prior to beginnng the new chemo. Second problem is that due to two errors
the dose of the dex has not been right. Third issue is that the hospital
with it's keep the patient ignorant policy continues to hide the M-spike
number from me. As of today (sun) I have only the lambda free light chain
data from the blood work of last tues.
Wrong dex dose
Previously I managed
dexamethasone. I bought the pills and took them. But with this chemo the
dexamethasone has two jobs. It is partly used to minimize infusion reactions
of the daratumumab, and for this purpose some of the dexamethasone is given
as an infusion prior to the daratumumab infusion. On the day of the infusion
it was supposed to be 16 mg, but was in fact (due to an arithmetic error)
12 mg infusion followed by a single 4 mg pill at the end. (I always though
12 mg was an odd dose for the infusion, but I let is pass as I was working
on the daratumumab infusion schedule.) When I checked the Pollux clinical
trials, on which my chemo is based, I found they used 40 mg/wk of dexamethasone
and that was what I was supposed to be getting. For the additional 20 mg
I should have been taking five 4 mg dex pills the day after the
infusion. I was unaware of this. Supposedly I was told about this at the
beginning, but I have no memory of it, and certainly in the infusion room
no reminder was ever given to me to do this. The result is that for the
first three week the new chemo the dose of the dex component has been less
than half of what was planned (16 mg/wk vs 40 mg/wk). My history shows
I respond to dex, but my doctor's gueess is that this dex dose error will
matter little.
Even the available
free light chain data is somewhat hard to interpret. If we take the 3 wk
in lambda free light chain value against the last reading with the pom/Ninlaro/dex
chemo over the month, we see a drop of about 50% (11.3 => 5.84). Ok, it
is a reasonable drop, so we are getting some response to the new chemo,
and the drop takes the level below the disease progression level of the
lambda free light chain (10 mg/dL), but still the result is far above the
goal of the upper end of normal (2.63 mg/dL). If the weekly readings are
looked at, we see the lambda free light chain three weeks in is pretty
much the same as one week in (5.84 vs 5.04), and it even shows a rise from
week 2 to 3 (4.37 => 5.84).
All I can say
now is we seem to be looking at a partial response to the new pom/daratumumab/dex
chemo, and we need to give it another month. I should get visibility to
the latest M-spike (measured 8/22/17) this coming tues when I meet with
my doctor. Currently the last M-spike value that I have visibility to was
measured about a month ago prior to beginning the pom/daratumumab/dex chemo
at .26 g/dL.
===========================
I am burning through
my chemo options at a rapid pace. I am not yet three years since diagnosis,
and I have just changed chemo for the fifth time to a new cutting edge
drug, a humanized monoclonal antibody, daratumumab.
My first (weekly)
daratumumab infusion is being done over two consecutive days (tues, wed
started 8/1/17). Just half of the total first week infusion makes for a
very long, tiring day (in 7:00 am for labs, out at 2:30 pm). There are
preliminary infusions, wait an hour, then an infusion rates starts at just
50 cc (or ML)/hr, which is 10% of the bag/hr) consistent with the prescribing
information, 2nd hr 100 cc, 3rd hr 150cc, 4th+ hr 200c. (infusion
cc = mL of manuf dosing schedule)
Dose (weekly)
(16 mg) x (body weight in kg) = 16 x 193 lb/2.2 = 16 x 87.7 kg
= 1,400 mg (2 x 700 mg for first dose over two days)
I was told
by my infusion nurse the first day the multiplier for tues was (8 mg x
body weight in kg). This is right, 700 mg a half weekly dose in a 500 cc
infusion bag. The first day daratumumab infusion went as shown below (after
the preliminary prophylactic infusions and one hour wait). Dex with this
chemo is provided by the hospital, partly by infusion with a single follow
up 4 mg dexamethason pill at the end. There is a prophylactic pill (montelukcast)
that must be taken at home the night before and the morning of the infusion.
As shown below
the first week's dose delivered over two day consecutive days delivers
700 mg in 4 hours, so a total of 8 hours to deliver the first 1,400 mg.
The second week ramps up at the same rate, but has double the dose in the
bag, so full dose is delivered in a single four hour infusion. The third
week and beyond continues to increment the dose rate by 50 cc/hr but starts
at a rate of 100 cc/hr (20% of bag/hr), so the infusion time is shortened
by 45 min to 3.25 hours.
----------------------
update 8/7/17 -- having completed my 2nd week infusion
I have updated the tables below to reflect the schedule my hospital is
using. I had earlier figured the first and subsequent infusions corectly,
but found the hospital was using 'second infusion' of the manuf schedule
for the second week, so I added in the 'second dose' table for the 2nd
week. However, that actual time at the hospital is much longer than the
four hours of the infusion. I was at the hospital on the second week from
7:00 am to 3:45 pm, 8.75 hours, only four of which were the actual daratumum
infusion. In addition to the time for the preliminary infusions, the one
hour wait, there was (again) trouble setting the little tube into a vein,
so there was the added wait time while the hospital called in an IV specialist
(IV Therapy) to do it.
-------------------
First dose daretumumab infusion schedule (700 mg each
over two consecutive days, 500 cc bag)
1st hour
50cc/hr rate
450 cc remaining
dose delivered 70 mg
10% of bag
70 mg/hr
2nd hour
100cc/hr rate
350 cc remaining
dose delivered 210 mg = (70 + 140)
30% of bag 140 mg/hr
3nd hour
150cc/hr rate
200 cc remaining
dose delivered 420 mg = (70 + 140 + 210)
60% of bag 210 mg/hr
4th hour
200cc/hr rate
0 cc remaining dose
delivered 700 mg = (70 + 140 + 210 + 280)
100% of bag 280 mg/hr
Second dose daretumumab infusion schedule (1,400 mg,
500 cc bag) (2nd week)
1st hour
50cc/hr rate 450
cc remaining dose
delivered 140 mg
10% of bag 140 mg/hr
2nd hour
100cc/hr rate 350
cc remaining dose
delivered 420 mg = (140 + 280)
30% of bag 280 mg/hr
3th hour
150cc/hr rate
200 cc remaining
dose delivered 840 mg = (140 + 280 + 420)
60% of bag 420 mg/hr
4th hour
200cc/hr rate
0 cc remaining dose
delivered 1,400 mg = (140 + 280 + 420 + 560) 100%
of bag 560 mg/hr
Subsequent dose daretumumab infusion schedule (1,400
mg, 500 cc bag) (3rd week)
1st hour
100cc/hr rate 400
cc remaining dose
delivered 280 mg
20% of bag 280 mg/hr
2nd hour
150cc/hr rate 250
cc remaining dose
delivered 700 mg = (280 + 420)
50% of bag 420 mg/hr
3th hour
200cc/hr rate
50 cc remaining dose delivered
1,260 mg = (280 + 420 + 560)
90% of bag 560 mg/hr
+15 min
200cc/hr rate
0 cc remaining dose delivered
1,400 mg = (280 + 420 + 560 +140) 100% of bag
560 mg/hr
Note the dose
rate
increases
by a four (70 to 280 mg/hr) during the first two (identical) infusions
of the first week. The second week follows the same ramp up schedule as
the first week, but has double the dose in the bag, so it also increases
the dose rate by a factor of four (140 to 560 mg/hr) reaching the max dose
rate of 560 mg/hr. The 3rd and subsequent weeks start at a higher rate
(100 cc/hr or 280 mg/hr) so have only a 1:2 ramp up in dose rate (280 to
560 mg/hr). Hence it is only after the second week's infusion has been
completed that you have been exposed to the maximum dose rate and evaluation
of possible infusion related complications can be assessed.
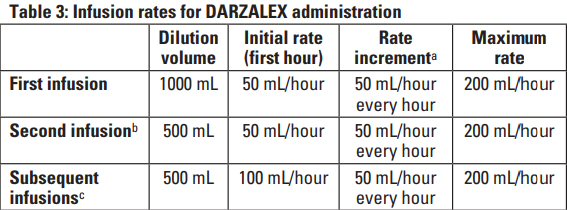
daratumumab infusion schedule from daratumumab prescribing
document
My first
dose infusion reactions
After first half
of my first weekly does, the big picture is so far so good. My only minor
reaction was cough and a little lung congestion (nothing unusual like a
little cold) that pooped up for a half hour or so and then went completely
away. A long and tiring day. Everything today was so slowwww. I was lucky
my back which had been bothering me for days was OK, and no diaherra issues.
Tomorrow it will take almost as long as it is the same dose (70 mg or half
of weekly 140 mg dose) with the same slow rate ramp up starting at 50 mL/hr.
This is consistent with daratumumab prescribing document 'second dose'
info.
The second
half of the first week dose was a piece of cake, no infusion issue. I knew
what to expect. Brought my tablet and a book, checked out news at Drudge,
played a few games, did a little reading, took a little walk and I was
done. In at 7:30 am and out at 2:15 pm when the preliminary infusions and
wait period are included. Subsequent weeks will (I am pretty sure) still
include the preliminary infusions and one hour wait period, so I expect
that they will take about 45 min less than one of the first week infusions.
In other word in at 7:00 am (for labs) and infusion 7:30 am to 1:30 pm.
(ideally)
I got a wicked
cold that started a few days after the first week: runny nose, lung congestion,
tired, low grade fever (100F) that hung on for a couple of days. It cured
up just in time for my second week's infusion with my temperature back
to normal just the night before. Was this an infusion reaction or side
effect of datatumumab? Who knows.
Infusion times
summary
Tues 7:00 am to 2:15 pm first
week only (half dose, with labs)
Wed 7:30 am to 2:15 pm first
week only (have dose, no labs)
Tues 7:00 am to 1:30 pm subsequent
weeks (full dose, with labs)
Note these
infusion time are much longer than the times the Lahey scheduling system
shows. For subsequent infusions the schedule system says plan on 3 to 5
hr. This is a joke, far too low. I have been through this process now twice
in the first week. I know how long it takes for all the preliminaries:
vital signs, labs, preliminary (non- chemo) infusions, wait an hour. On
a day with labs I am at the hospital by 7:00 am or so, but the daratumum
infusion doesn't start until near 10:00 am. Hence I don't get out the door
until 1:30 pm or so. This is a total of 6.5 hours at the hospital to get
a daratumumab infusion.
Blood type baseline
(8/1/2017)
One of the
complications with daratumumab is that it can interfere with standard tests
used for blood typing. This can be very important if you need a transfusion.
So to establish an accurate blood baseline my doctor added a bunch of blood
type tests done just prior to the first daratumumab infusion.
Type and screen
ABO group
O
Rh type
pos
Antibody
screen
neg (plus 14 specific 'antigen' tests were run, examples:
'Little c Antigen' neg; Big C Antigen pos, etc)
My blood type
[Type O, Rh pos] is the most common blood type in the country. 45% of peopla
have blood type O and 80% with type O are RH pos. [other blood
types are A, B, and AB]
======================================================================================================================================
Low platelets
--- known Ninlaro side effect
One serious side effect
of Ninlaro has arisen that could possibly force us to drop Ninlaro (or
dose decrease) is that it is driving platelets real low. My platelets droped
from 187 just before starting Ninlaro to 89 after (1st cycle) and 64 (2nd
cycle). My oncologist at our last meeting this week suggested repeating
my
labs that day since it had been about 15 days since taking my last Ninlaro
pill. The repeat labs showed platelets had recovered in just seven days
of my 'off week' to 132. This test result confirmed (she messaged me) that
Ninlaro is the cause of my low platelets, which we already suspected. I
noticed in the repeat labs after my 'week off' my hemoglobin also recovered
(13.0 => 14.1) and WBC recovered some too.
The Ninlaro manuf prescribing
info shows that low platelets (thrombocytopenia) is one of the major problems
with Ninlaro. ['Thrombo' relates to clotting of blood. 'Cytopenia
is a general term for reduction number of blood cells. Hence 'thrombocytopenia'
is a reduction in blood clotting cells (platelets).]
Ninlaro manuf on low platelets
-- Thrombocytopenia (low
platelets) has been reported with NINLARO. During treatment, monitor platelet
counts at least monthly, and consider more frequent monitoring during the
first three cycles. Manage thrombocytopenia with dose modifications and
platelet transfusions as per standard medical guidelines. Adjust dosing
as needed. Platelet nadirs occurred between days 14-21 (that is in the
3rd week of each cycle) of each 28-day cycle and typically recovered to
baseline (what the hell does this mean) by the start of the next cycle."
In the complete Ninlaro prescribing
document dose adjustments for low platelets are spelled out in considerable
detail (below). Note the platelet threshold at which chemo needs to be
scaled back is 30K/uL. My lowest reading to date has been 64 K/uL, so no
problem so far.
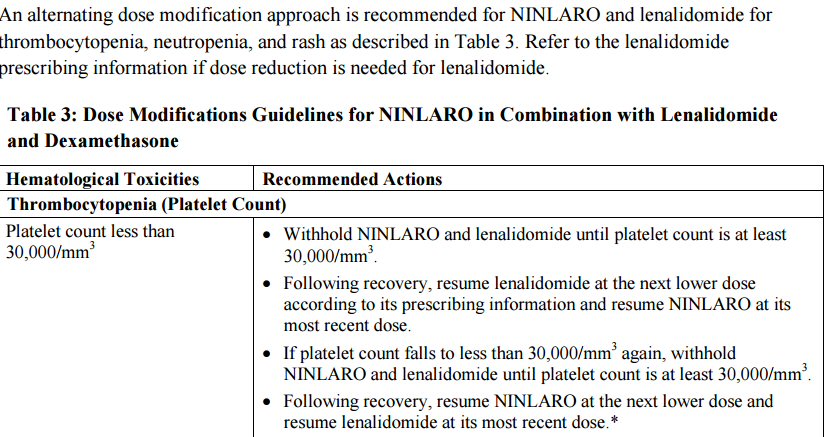
Ninlaro dose adjustments for thrombocytopenia
from Ninlaro full prescribing document
Platelets threshold
It took me a while to unscramble
the two different units used for platelets. My blood work gives platelet
units as K/uL. The lower end of the normal range is 150 K/uL. This means
150,000 platelet cells in a microliter. Turns out (this was a surprise
to me) that a liter (of water) has a volume of exactly one million cubic
mm. Hence one uL has a volume of one cubic mm. (mm^3 in the table above
is just another way of writing one cubic mm.)
Thus the threshold
for Ninlaro dose adjustments 30,000/mm^3 is 1/5th of the lower end of the
normal platelet range which is 150K/uL. [30,000/mm^3 = 30,000 platelet
cells/cubic mm = 30K/uL]
Peripheral neuropothy
Another side effect of Ninlaro
I am having is a numbness in my feet (plus a little swelling of the feet).
At this time it is basically just an annoyance. Thank goodness I don't
see any problems with my hands or typing. This side effect is not too surprising
since Ninlaro is essentially the the pill version of Velcade, and velcade
is famous for peripheral neuropothy, which is nerve damage in hands and
feet.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Searching for 3rd remission
As sort of an experiment
before moving onto a humanize monoclonal drug (daratumumab), I wanted to
try swapping out the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib for another proteasome
inhibitor Ninlaro. I consider Ninlaro, recently approved by the FDA, to
be the pill version of the well established injected drug Velcade that
to date my cancer has not seen. While both are proteasome inhibitors, they
have somewhat different targets and are formulated differently. My cancer
has evolved such that pom/carfilzomib/dex looks like it it no longer working,
but there is a chance that Ninlaro, which is boron based and has a different
target on the proteasome, may work.
The end of pom/carfilzomib/dex
chemo was indicated by three bad signs: both blood markers rising (free
light chain and M-spike) confirmed by a substantial (doubling SUV, 50%
larger) brightening of my 9th rib, posterior plasmacytoma. Surprisingly
just at the end of last pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo cycle (4/3/17) that is
also just prior to the beginning of the first pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo cycle,
the baseline lambda free light chain changed direction and dropped (kappa
free light chain dropped too). This was a surprise and what it means is
unclear.
3/6/17
lambda free light chain 4.55 mg/dL
M-spike .17 g/dL
(kappa free light chain 2.11 mg/dL)
4/3/17
lambda free light chain 3.40 mg/dL
M-spike .17 g/dL
(kappa free light chain 1.09 mg/dL)
My numbers held constant
in my first first pom/Ninlaro/dex cycle (really 3 weeks), the experiment
was a success, so we have continued onto a 2nd cycle and may hold course
with this chemo until numbers turn up (5/7/17).
4/25/17
lambda free light chain 3.48 mg/dL
M-spike .16 g/dL
(kappa free light chain 0.84 mg/dL)
5/23/17
lambda free light chain 4.03 mg/dL
M-spike .16 g/dL
(kappa free light chain 0.81 mg/dL)
What is the criteria? (4/16/17 update)
The plan was to do a one
(maybe two) month test of pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo. After a month or two the
criteria, at least in my mind, on whether this new chemo seemed to be working
was whether or not the rising pattern in my blood numbers, in particular
free light chain, reversed. The experiment was all ready to go, Ninlaro
was bought, when the last data from the previous chemo (pom/carfilzomib/dex)
came in. Perhaps good for my health, but unfortunate in terms of the experiment
with the new chemo the rising pattern in free light chain reversed [lambda
(4.55 => 3.40 mg/dL and kappa (2.11 => 1.09 (normal)] with the old chemo.
M-spike held constant at .17 g/dL. A real surprise.
This has the potential to
mess up the evaluation of the new pom/Ninlaro/dex chemo. The next monthly
blood sampling will be in a couple of weeks at the end of this first cycle
of pom/Ninlaro/dex (4/28/17). A meeting with my hematological oncologist
follows a few days later, likely before the M-spike data is available,
so the chemo decision will probably hinge on the free light chain. The
good news is that lambda free light chain at 3.40 mg/dL is still a little
high and outside the normal range (<2.63 mg/dL), so the test will be
did the new chemo drives it down into the normal range? Of course a resumption
of the earlier upward trend will be bad news indicating that the new chemo
is likely not effective.
Ninlaro side effects
Velcade is famous for damaging
nerve endings, and Ninlaro probably has a tendency to do this too, but
reduced since each generation manufs work to decrease side effects.
So far (two of three Ninlaro pills of first cycle) the only side effects
I notice is a little numbness in my feet (not serious). Here's a list of
the most common Ninlaro side effects from the manuf web site, and I note
after 5 wks on Ninlaro which I have.
-- Low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia).
Low platelet counts are common with NINLARO and can sometimes be serious.
You may need platelet transfusions if your counts are too low. Yes,
my platelets dropped from 187 to 89 (150 low normal) on the first
Ninlaro cycle
-- Stomach and intestinal
(gastrointestinal) problems. Diarrhea, constipation, nausea, and vomiting
are common with NINLARO and can sometimes be severe.
Yes?
I have occasional nausea and diarrhea, but I have had diarrhea all along.
-- Nerve problems.
Nerve problems are common with NINLARO and may also be severe.
Tingling
Numbness Yes,
some numbness in my feet began with Ninlaro
Pain
A burning feeling in your feet or hands
Weakness in your arms or legs
-- Swelling. Swelling is
common with NINLARO and can sometimes be severe. Swelling in your arms,
hands, legs, ankles, or feet, or if you gain weight from swelling.
Yes,
some moderate swelling in my feet and ankles began with Ninlaro
Liver problems.
Tell your healthcare provider if you get these signs of a liver problem:
(maybe, some hints in blood work of liver issues)
Yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
Pain in your right upper-stomach area
====================================================================================================
Carfilzomib Reference
* A phase 2 single-center study of carfilzomib 56 mg/m2 with or
without low-dose dexamethasone in relapsed multiple myeloma, Blood, Aug
2014. (42 patients) Disease progression according to criteria of 'International
Myeloma Working Group'. 77% of the patients in this study were refractory
to bortezomib (Velcade).
-- Carfilzomib, a selective
proteasome inhibitor, targets and irreversibly binds to the beta5 subunit
of the constitutive 26S proteasome and LMP7 immunoproteasome, resulting
in sustained inhibition of chymotrypsin-like activity and apoptosis of
myeloma cells.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4624439/
Pulmonary Toxicity (from carfilzomib prescribing sheet)
Acute Respiratory Distress
Syndrome (ARDS), acute respiratory failure, and acute diffuse infiltrative
pulmonary disease such as pneumonitis and interstitial lung disease have
occurred in patients receiving KYPROLIS. Some events have been fatal. In
the event of drug?induced pulmonary toxicity, discontinue KYPROLIS (carfilzomib)
-- Acute respiratory distress
syndrome (ARDS) occurs when fluid builds up in the tiny, elastic air sacs
(alveoli) in your lungs. More fluid in your lungs means less oxygen can
reach your bloodstream. This deprives your organs of the oxygen they need
to function. ARDS typically occurs in people who are already critically
ill or who have significant injuries. Severe shortness of breath — the
main symptom of ARDS — usually develops within a few hours to a few days
after the original disease or trauma. Many people who develop ARDS don't
survive.
-- Diffuse interstitial
lung disease refers to disease within both lungs that affects the interstitium
or connective tissue that forms the support structure of the lungs’ air
sacs or alveoli. When you inhale, the alveoli fill with air and pass oxygen
to your blood stream. When you exhale, carbon dioxide passes from the blood
into the alveoli and is expelled from the body. When interstitial disease
is present, the interstitium becomes inflamed and stiff, preventing the
alveoli from fully expanding. This limits both the delivery of oxygen to
the blood stream and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body. As the
disease progresses, the interstitium scars with thickening of the walls
of the alveoli, which further hampers lung function.
https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=diffuselung
-- Pneumonitis (noo-moe-NIE-tis)
is a general term that refers to inflammation of lung tissue. Although
pneumonia is technically a type of pneumonitis because the infection causes
inflammation, most doctors are referring to other causes of lung inflammation
when they use the term "pneumonitis." Factors that can cause pneumonitis
include exposure to airborne irritants at your job or from your hobbies.
In addition, some types of cancer treatments and dozens of drugs can cause
pneumonitis
Difficulty breathing — often
accompanied by a dry (nonproductive) cough — is the most common symptom
of pneumonitis. Specialized tests are necessary to make a diagnosis. Treatment
focuses on avoiding irritants and reducing inflammation.
My response so far (two cycles) to pom/carfilzomib/dex chemo(9/2/16)
After 2 cycles of carfilzomib
(with pom and dex) I have > factor of 5 reduction in the
difference
between involved and uninvolved free light chain (8 => 1.5 mg/dL), but
less than a factor of two in M-spike (.25 g/dL => .16 g/dL), but M-spike
responds on the downside with a lag, The only data on plasmacytoma so far
shows about a 50% decrease in the size of the plasmacytoma behind my left
eye. So with time and further decrease of M-spike I may meet the PR criteria
Response criteria used by clinical trials from 'International Myeloma
Working Group', 2006
(http://myeloma.org/pdfs/InternationalUniformResponseCriteria.pdf)
(PR) Partial response
Essentially for a PR there must
be a > 50% reduction in blood cancer tracking and > 50% reduction
in size of any plasmacytomas
1) > 50% reduction of M-spike (after 4 cycles in above clinical trial)
2) > 50% decrease in the difference between involved and uninvolved
FLC levels (used if M-spike not measurable)
3) > 50% reduction in the size of soft tissue plasmacytomas is also required
SD stable disease (between PR and PD)
PD (disease progression)
1) > 25% increase in of M-spike from minimum (absolute > 0.5 g/dL)
2) > 25% increase in difference between involved and uninvolved
FLC levels (absolute > 10 mg/dL) (used if M-spike not measurable)
3) development of new bone lesions or soft tissue plasmacytomas or
definite increase in the size of existing bone lesions or soft tissue plasmacytomas
VGPR (very good partial response) requires > 90% reduction in M-spike
Clinical relapse has the following criteria
1) Hypercalcemia (> 11.5 mg/d)
2) Decrease in hemoglobin of more than 2 g/dL or to less than 10 g/dL
3) Rise in serum creatinine by more than or equal to 2 mg/dL
4) Development of new soft tissue plasmacytomas or bone lesions on skeletal
survey, magnetic resonance imaging, or other imaging
5) Definite increase in the size of existing plasmacytomas or bone lesions.
A definite increase is defined as a 50% (and at least 1 cm) increase as
measured serially by the sum of the products of the cross-diameters of
the measurable lesion.
=================================================================================================================================
Castor
vs Pollux clinical trials (7/7/17)
Pairing daratumumub with a proteasome inhibitor (Castor)
on an imid (Pollux)
After four
months on pom/ninlaro/dex chemo it looks like my cancer has found a way
around it with a big jump last month in my lambda free light chain (4.03
=> 8.42 mg/dL) bringing it close to its disease progression threshold of
10 mg/dL. However, at the same time my M-spike actually declined a little
from .16 g/dL to .l5 g/dL. Before a decision to change chemo is made there
will be another blood test and a pet scan. Since free light chain is a
leading indicator I expect the next M-spike reading will show an increase.
With a likely
chemo change pending my two oncology doctors are recommending the next
step is to change to a chemo regimen that includes daratumumab. Daratumumab
is a humanized monoclonal antibody drug, very different from the small
molecule chemo drugs I have been taking. But daratumumab mated to what?
Several combinations are under study. (One clinical trial just beginning
adds daratumumab as a 4th drug to a well known chemo triad.)
The two daratumumab
studies that are most advanced, and have caused the FDA to approve the
drug, are two phase 3 clinical trials: Pollux and Castor. In the Pollux
trial daratumumab is paired with an imid (Revlimid plus dex). In the Castor
trial daratumumab is paired with a proteasome inhibitor (Velcade plus dex).
In summer of 2016 both trials reported interim one year results in the
New England Journal of Medicine. With a little searching I found these
full papers available free online in .pdf format (apparently because some
government money was involved). I have downloaded the two papers, printed
them out and have been carefully comparing them (ignoring of course the
control groups, which are irrelevant for my purposes).
Castor (aug
2016) --- http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1606038
Pollux (oct
2016) --- http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1607751
As I read the
one year interim results the advantage goes to Pollux (Revlimid), though
my doctors without giving me any reasons, are leaning toward Castor (Velcade).
Also in my view the chemo options used in the trials should be updated
to substitute the newest drugs of the same class from the same manufacturers.
This means from Celegene substitute the imid Pomalyst for Revlimid, and
from Takeda/Millennium substitute the proteasome inhibitor Ninlaro for
Velcade.
Side effects
One of my
concerns, aside from effectiveness of course, is side effects. The last
two proteasome inhibitors I have been on have damaged by body. Eight months
on carfilzomib has damaged my lungs, leading to shortness of breath, reduced
lung capacity and lack of peak energy. This has now been partially compensated
by use of a once a day inhaler. Four months on the proteasome inhibitor
Ninlaro has led to significant and sustained loss of feeling and some swelling
in both of my feet. Castor chemo includes a proteasome inhibitor (Velcade,
the predecessor of Ninlaro), whereas Pollux chemo does not include
a proteasome inhibitor. Pollux pairs daratumumab with an imid. I have taken
an imid since I began chemo more than two and half years ago (Revlimid
and Pomalyst), and I seem to tolerate it well. Daratumumab is reported
to be relatively free of side effects.
Pollux vs Castor phase 3 clinical trials --- one year
interim results (reported 2016)
The trials
are very similiar except in the pollux trial daratumumab/dex is paired
with the imid Revlimid, while in the Castor trial daratumumab/dex is paired
with decade old proteasome inhibitor Velcade. The populations are very
similar except that the Pollux patients are a little less sick than in
the Castor trial. In Pollux the percent diagnosed at Iss disease stage
3 is 19.6% vs 23.5% for Castor. Cytogenetic high risk for Pollux is 15.4%
vs 22.7% for Castor.
| |
Pollux
phase III clinical trial
Revlimid/daratumumab/dex
(data from NJM article oct 6, 2016)
|
Castor
phase III clinical trial
Velcade/daratumumab/dex
(data from NJM article aug 25, 2016)
|
|
patient initial status
|
one or more previous lines of therapy
(relapsed or refractory multiple myeloms)
|
relapsed or relapsed and refractory
multiple myeloma
|
|
ISS disease stage
|
stage 1 48.6%
stage 3 19.6%
|
stage 1 39%
stage 3 23.5%
|
|
cytogenetic profile
|
Standard risk 84.6%
High risk 15.4%
|
Standard risk 77.3%
High risk 22.7%
|
|
autologous stem cell transplant
|
62.9%
|
62.2%
|
|
median time since diagnosis
|
3.5 years
|
3.87 years
|
|
median age
|
65
|
64
|
|
daratumumab schedule
|
four week schedule
|
three week schedule
|
|
trial design and data analysis
|
Janssen Research and Development
|
Janssen Research and Development
|
| |
|
|
|
overall response
|
92.9%
|
82.9%
|
|
CR (complete response or better)
(CR is <5% plasma cells in marrow and no measurable M-spike)
|
43.1%
|
19.2%
|
VGPR (very good partial response
or better)
(VGPR > 90% reduction in M-spike)
|
75.8%
|
59.2%
|
|
12 month progression free survival
|
83.2%
|
60.7%
|
Surprisingly
the two trials used slightly different schedules for daratumumab infusions,
and I find this is consistent with the current daratumumab prescribing
document. Paired with Revlimid (Pollox) there is a 4 wk cycle and paired
with Velcade (Castor) a 3 wk cycle. But the differences are small. In the
first 24 weeks (about 6 months) the daratumumab usage for the Pollux four
wk schedule is a total of 16 doses, whereas for the Castor three wk schedule
it is a total of 14 doses.
In the four
week Pollux cycle for the first two cycles there is no off week.
Daratumumab is given once in each week for eight weeks straight, then for
cycles 3 through 6, the rate is cut in half with daratumumab given only
every other week. In the three week Castor cycle for the first three cycles
there is also no off week. Daratumumab is given once in each week
for nine weeks straight, then for cycles 4 through 8, the rate is cut by
a third with daratumumab given only every third week. After 24 weeks both
cycles are the same with daratumumab given once every 4 weeks.
Simplifying
slightly the dosing schedule for daratumumab is as follows: full strength
for two months, 1/2 strength for the next four months, and then 1/4 strength
until disease progression.
I sent the following message to my doctor (7/14/17).
My 5th pet
scan, which shows things growing wild, confirmed what the blood numbers
hinted at that I need to change chemo right away at end of this cycle (in
about a week). I am in agreement that the new chemo regimen should be built
around daratumumab that you and (my consulting oncologist) favor, however
I am NOT in agreement that it should be paired with a proteasome inhibitor
as it was in the Castor trial. I want to pair daratumumab with an imid
(Revlimid or Pomalyst) for two reasons.
One I reviewed carefully the Pollux (Revlimid) and Castor
(Velcade) phase III clinical trials from summer 2016 and pulled together
the key numbers in a table (above). While I can see that that the people
in the Pollux trial were a little less sick, nevertheless the raw numbers
across the board strongly favor Pollux. (CR 43% vs 19%, 12 mon survival
83% vs 61%)!
Two relates to my response to proteasome inhibitors. I
have been on them for a year. In 8 months carfilzomib damaged my lungs,
now 4 months on Ninlaro has damaged my feet. I want the proteasome inhibitors
GONE.
Three, I have not heard a substantive reason to favor
Castor over Pollux from either you or (my consulting oncologist).
If we can agree on pairing daratumumab with an Imid, can
we also consider the Pomalyst, which I am already taking, is just an improved
Revlimid?
Thus I want to change my chemo in the next week
from pom/Ninlaro/dex ==> pom/daratumumab/dex. My off week is next week
and we don't meet until the following tues 7/25, so if you agree, I would
like you to renew the pomalyst prescription next week so I can buy it and
begin the process of prescribing daratumumab to speed the required approvals.
Of course if there is additional data I don't have send
me a link and I will review it.
Update --- a chemo decision (7/21/17)
Well the decision
has been made. My doctor responded to my message (above) that she was "not
opposed" to what I wanted to do [pom/Ninlaro/dex ==> pom/daratumumab/dex].
She added she had several patients on it and it worked well, and she went
on to list the side effects. [ Low blood counts and a risk for infection
or needing transfusions were the biggest risks that I have noted with this
combination.] As I hoped this decision got made via messaging a few days
prior to our meeting allowing time to order the drugs get approvals so
(hopefully) I can stay on schedule. I did not want to go an extra (off)
week with no cancer drugs, even though I know the existing cancer drugs
are no longer working well.
As I write
on a sun the end of my off week, I have Pomalyst (21 of 28) for the next
cycle purchased and sitting on my shelf. Probably won't know about the
status of the infusion of daratumumab until my meeting with my doctor
on tues.
Daratumumub infusion info (from manuf)
Ok to take
a nap, eat food during infusion. Drink water prior (easier to find veins).
Drugs given prior to infusion
1) antihistamine (to prevent allergic reaction)
2) corticosteroid (probably dex) to prevent inflammation
3) acetaminophen to reduce fever
If you have
a history of breathing problems, you may also be given a bronco dilator
or inhaled corticosteroid.
After the infusion (seems to be for next day at home),
additional corticosteroids (dex?) are given to ward off delayed infusion
reactions.
1st infusion
7 hours
later
infusions 3 - 5 hours
(actual time in the infusion lab is much longer than this)
Video says daratumumab 'can' decrease WBC and Platelets
which is what my doctor mentioned with her other patents prone to infection.
Side effect list is long with all the usual suspects including 'swollen
hands and feet', back pain, etc. The default infusion schedule in the video
is every mon.
From the daratumumab prescribing document
Dose
16 mg/kg
(195 lb/2.2 lb/kg = 88.6 kg x 16 mg = 1,418 mg (total
dose)
drug is available in two size vials
400 mg in 20 mL solution, and 100 mg in 5 mL solution
(so I would need about 3.5 of the 400 mg vials)
Details of the cycle
I finally
found details of daratumumab paired with imid cycle in the the New England
Journal of Medice paper on the phase III trial. The imid was cycle was
standard 21 of 28 days (so still a week off). The daratumumab though is
for the first two cyles is given every wee, 8 weeks straigh, no week off.
Dexamethasone was as is usual 40 mg/week, but here it is coordinated with
the daratummab as follows: 20 mg is given prior to the infustion as prophylaxis
against infusion related reactions. Almost for sure this 20 mg would be
provided in the infusion room. The remaining 20 mg is taken at home the
next day, and very likely the patient is responsible for buy this.
* Potential imid dose reduction
The dose of
the imid (Revlimid in the clinical trial) was reduced (about half) if the
creatinine was less than 60 mL/min. This could be important since I tend
to be dither around this threshold, which is actually an est from the measured
creatinine concention in the blood. For example my last measured creatinine
(7/18/17) was 1.2 mg/dL (near the high end of normal) that gives an estimated
rate of 59 mL/min/BSA. Just a hair under the 60 mL/min dose reduction threshold
used in the clinical trial. I need to discuss this with my doctor.
** A check of the Pomalyst
prescribing document shows a lower threshold. Patients with a creatinine
clearance of > 45 mL/min qualified for the trial. The pharmacokinetic
of the Pomalyst were not affected by patients with "moderate" renal impairment
(30 mL/min to 60 mL/min). At levels below 30 mL/min ("severe renal impairment",
end stage renal disease) dialysis was required, and in these patients the
exposure to the drug was increased by 38%.
Infusion reactions
Any grade
46% first inifusion, 2% second infusion. Wow that's a drop off. The average
time until the first to the infusion reaction is 1.4 hours. The delay is
partly because the dose rate starts off low and is slowly increased.
CD38
'CD38 is a transmembrane
glycoprotein (48 kDa) expressed on the surface of hematopoietic cells,
including multiple myeloma and other cell types and tissues.' (A
clue to what it does is that it is a 'transmembrane glycoprotein'.)
-- Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
or hemocytoblasts are the stem cells that give rise to all the other blood
cells through the process of haematopoiesis. They are derived from mesoderm
and located in the red bone marrow, which is contained in the core of most
bones. (Translation, CD38 shows up at the beginning of the complex
process of makeng all blood cells, so interferring with it is likely to
decrease many types of blood cell, including T cells and B cells, which
explains some of the listings in the side effects.)
-- almost all
of the key molecules involved in the immune response are glycoproteins.
Since CD38
is a transmembrane molecule it must be regulating something in the cell,
but I will be damned if I can figure it out. (Partly this is because Wikipedia
cel biology stuff is very dense, written for the expert.) So I put this
question into google: 'What does transmembrane protein CD38 regulate?'
The answers seem to indicate that it has some control of CA (calcium) signling,
one of which is "smooth airway muscles cells" (lung function!). It seems
to be rather specialized.
* -- Literature
on ADP ribose (cADPR) pathway of CA2 regulation in airways, vascular, uterine,
and intestional smooth muscles. (This is the best reference so far that
I have found. It affects the smooth muscles of the (lung) airways, circulation
system and intestions. Google references a whole book about this titled:
'Cyclic ADP-Ribose and NAADP: Structures Metabolism, and Functions' edited
by Hon Cheung Lee)
Daratumumab
Daratumumab
is a large protein.
Manuf (Jassen) pisses me off
On the one
hand Jassen appears to be candid (no doubt driven by FDA regulations!)
about the side effects and risk of daratumumub with one GLARING exception.
The drug's basic mode of operation is that it helps kill multiple myeloma
cells by binding to the CD38 protein that multiple myeloma cells overexpress
(wikipedia). The manuf says it both kills the cells themselves and activates
the human immune system to kill them.
But here's
the thing. Other cells have CD38 on their surface too and to do some extent
the drug will also attack them too. Of course the manuf knows perfectly
well what these cells are but they refuse to tell the patient! What
slimeballs. Does this give you a clue about the slimy nature of drug manufacturers!
Maybe this policy is the result of action by their lawyers but it matters
little to the patient.
CD38 info (wikipedia)
CD38 is also
known as 'cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase'
ADP
I have run across
ADP before (see my photosynthesis
essay). It is part of the ATP energy distribution process widely used
by many cells. ATP has a phosphate group loosely attached. When it is hydrated,
the phosphate pops off releasing some energy (7.3 kcal/mol) available to
do some work locally in the cell. The resulting ATP molecule minus the
phosphate group is called ADP. In photosynthesis it is generated in the
light reactions and used to provide energy to the dark reactions that strip
oxygen from the carbon in CO2. (I don't know specifically, but I
presume in the human body it shows up everwhere ATP is used to move local
energy generation in microcondria to where it is actually used (like muscles,
nerves, etc.)
Daratumumab background
(8/14/17)
American
Cancer Society has some background information about 'protein' therapy
for cancer. It divides these protein 'drugs' into two groups: checkpoint
inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies. All of these drugs have a name that
ends in 'mab'. Protein therapy is the cutting edge of cancer therapy. It
is technically not chemotherapy. It is a molecule far larger than all chemotherapy
drugs. Checkpoint inhibititors work to activate/deactivate T-cells of the
immune cell. A favorite target is the protein PD-1, another is CTLA-4.
Monoclonal antibody
Daratumumab falls
into the other protein class: a monoclonal antibody. In other words a drug
that is a fully formed antibody, presumably with the usual double Y shape,
each arm of which consists of a heavy and light chain bonded together.
Some types of monoclonal antibodies, called 'conjugated monoclonal antibodies',
are used to find cancer cells and to deliver a chemo drug or radioactive
element. This is not daratumumab.
Naked monoclonal antibody
Daratumumab
falls into the class that the American Cancer Society calls a 'naked monoclonal
antibody'. "Most naked mAbs attach to antigens on cancer cells". In other
words it is the antibody itself that attacks the cancerous cell. The manuf
of daratumumab says it both directly kills cells that exhibit its target
protein (antigen) and helps identifty the cell for the immune system to
attack the cell. In the case of multiple myeloma I am not sure at this
point if the cancerous cells attacked by daratumumab is the monoclonal
anti-bodies in the blood plasma that make up the M-spike or is the cancerous
plasma cells in the bone marrow that pump them out.
A graphic on
the manuf site shows the CD38 on the surface of what is labeled "multiple
myeloma cell". Well that's sure clear! And the text uses the same language.
Daratumumab attaches itself to CD38 present in high numbers on the surface
of 'multiple myeloma cells in the body'. It mumbles that CD38 is
also present on the surface of red blood cell (bags of hemoglobin). Wikipedia
(daratumumab) uses the same language, "CD38 is overexpressed in multiple
myeloma cells." I still don't know what cells there are referring to....
Reading technical
papers it does look like CD38 targeted cells are in the cell lines of the
marrow ("B-lymphoid and myeloma cell lines") which deveop into white blood
cells.
-- Multiple
myeloma is a hematological (blood) cancer that develops in the plasma cells
found in the soft, spongy tissue at the center of your bones, called bone
marrow. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for producing
antibodies (immunoglobulins) which are critical for maintaining the body’s
immune system. Through a complex, multi-step process, healthy plasma
cells transform into malignant myeloma cells. Myeloma cells result in the
production of abnormal antibodies, or M proteins.
Above is pretty
clear. The targeted cells of daratumumab look to be the 'malignant myeloma
cells', i.e. the cancerous plasma cells of the marrow, that pump out monoclomal
anti-bodies that make up the M-spike. These 'malignant myeloma cells' are
all clones so the resulting anti-bodies are all identical.
** -- In healthy bone marrow,
B-cells, a type of white blood cell, develop into antibody-producing plasma
cells when foreign substances (antigens) enter the body. In multiple myeloma,
DNA damage to a B-cell transforms the normal plasma cell into a multiple
myeloma cell. The cancerous cell multiplies, leaving less space for normal
blood cells in the bone marrow, and produces large quantities of M protein.
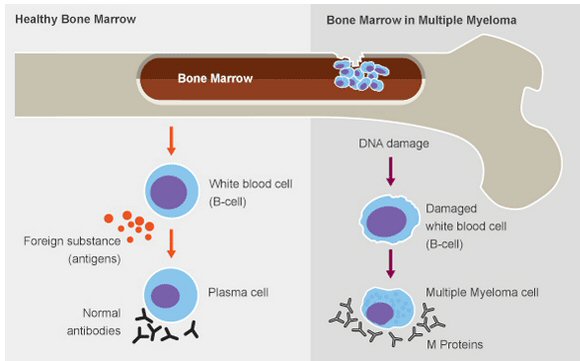
(source -- https://www.themmrf.org/multiple-myeloma/what-is-multiple-myeloma/)
Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation
DNA damage
to a B-cell transforms (what should be) a normal plasma cell into a multiple
myeloma cell. The above graphic shows that the normal developmental pathway
has a B cell (white blood cell) 'developing into' a plasma cell that produces
antibodies. But in MM the DNA of (one or multiple?) B cell gets damaged
so that it develops not into a normal plasma cell, but into a "multiple
myeloma cell", a sort of cancerous (or damaged) plasma cell that outputs
an antibody too. This cell is the target of daratumumab.
What is not
clear from this description is how all the multiple myeloma cells are generated.
One explanation would be that the DNA damaged B cell is cancerous and keeps
cloning itself. Hence each produces identical multiple myeloma cells which
in turn produce identical antibodies (M-spike). However, the text (see
ref below) appears to say that it is the mulitple myeloma cell that is
cancerous and keeps cloning itself. These are the cancer cells that fill
up the marrow of bones.
Note
the implications of this are that only ONE time does a DNA damaged B cell
need to produce a cancerous multiple myeloma cell (a damaged, cloning plasma
cell), and from then on the person has cancer.
Reference: What
is Multiple Myeloma (Multiple Myelima Research Foundation)
Huge molecule
An antibody is a
huge molecule. It consists of eight long chains, four different long chains
double bonded into a 'Y' configuration. It is far too big to be manufactured
from scratch. Daratumumab's chemical formula on wikipedia shows it has
about 20,000 atoms, and a search shows the mean number of atoms in an amino
acid is 19, so round numbers the eight chains that make up daratumumab
consists of a total of about 2,000 amino acids. The manuf gives the weight
of daratumumab as 148 kDa. A typical amino acid has a weight of 137 dalton.
[148,000/137 = 1,080 amino acids (est)] The target of daratumumab is a
transmembrane protein, CD38, that has a weight of 48 kDa. Daratumumab binds
to the CD38 protein and induces death of the cell with CD38 on its surface.
How is daratumumab made?
Since daratumumab
cannot be made from scratch it must be made starting with some living thing,
maybe a mouse or a bacteria? Nope. I think this might have been the case
with early mab drugs, but the daratumumab prescribing document describes
it as a "human monoclonal antibody" derived from a "mammalian cell line":
"chinese hamster ovary using recombinant DNA technology".
=======================================================================================
Notes on low platelets (9/30/17)
Definitions
Anemia
--- low red blood cell count 7 g/dL
(super low, no energy,, two red blood cell infusions)
8 g/dL (red blood cell infusion) to 8.5 g/dL
Thrombocytopenia ---
low platelets (<10k/uL can mean serious internal bleeding)
Neutropenia
--- low neutrophil count (low white blood
cell count)
-- For adults,
counts of less than 1,500 neutrophils per microliter of blood are considered
to be neutropenia. For children, the cell count indicating neutropenia
varies with age. Neutrophil counts less than 1,000 neutrophils per
microliter — and especially counts of less than 500 neutrophils per microliter
— are always considered to be neutropenia, where even the normal bacteria
from your mouth and digestive tract can cause serious infections.
(to date I have not had a problem with low
Lifetimes
Platelet cell lifetime
--- 10 days
Red blood cell lifttime ---
four months
-- Dangerous
internal bleeding can occur when your platelet count falls below 10,000
platelets per microliter. Though rare, severe thrombocytopenia can cause
bleeding into the brain, which can be fatal. (Mayo Clinic)
Velcade
--- if platelet count <
30k/uL withhold Velcade (for VELCADE used with Melphalan and Prednisone)
-- VELCADE
is associated with thrombocytopenia (low platelets) and neutropenia that
follow a cyclical pattern with nadirs occurring following the last dose
of each cycle and typically recovering prior to initiation of the subsequent
cycle.
Pomalyst
-------------------------
Final Diagnosis (10/1/17)
A. Iliac Crest, Left iliac crest:
Dx: MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME (bone marrow failure
disorder), REFRACTORY CYTOPENIA (low blood cell counts) WITH MULTI-LINEAGE
DYSPLASIA (abnormal shape).
NO MORPHOLOGIC OR PHENOTYPIC EVIDENCE OF MYELOMA.
------------------
-- Myelodysplastic
Syndromes is a bone marrow failure disorder
-- the mature
blood cells circulating in the blood may not function properly because
of dysplasia. The formal definition of dysplasia is the abnormal shape
and appearance, or morphology, of a cell.
-- LOW PLATELET
COUNT (THROMBOCYTOPENIA)
-- for roughly
30% of the patients diagnosed with MDS, this type of bone marrow failure
syndrome will progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
-- Refractory
cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia is a form of myelodysplastic syndrome
-- 'Refractory
cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia' (RCMD) is one of the more common
myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs). MDSs are clonal disorders of myeloid
stem cells. (This cell line develops into both white blood cells and red
blood cells.) These syndromes are characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis
( formation and development of blood cells) manifested in morphologic dysplasia
of hematopoietic precursors, 1 or more peripheral blood cytopenias, and
a propensity to progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML
=================================================================================
Case Report Surgical Pathology Report Case: SL17-24705
Authorizing Provider: Furha I Cossor, MD Collected: 10/04/2017
09:59 AM
Ordering Location: Department of Hematology Received:
10/04/2017 12:32 PM
and Oncology
Pathologist: Eric Burks, MD
Specimen: Iliac Crest, Left iliac crest
CBC and Differential
WBC
6.87 4.40 - 11.30 K/uL
RBC
2.85 Low 4.5 - 5.9 M/uL
Hemoglobin
8.8 Low 13.8 - 17.4 g/dL
Hematocrit
25.6 Low 41.0 - 51.0 %
MCV
90 80 - 96 fL
RDW
15.9 High 11.6 - 14.6 %
Platelet Count 5 Low Panic
150 - 450 K/uL
Final Diagnosis
A. Iliac Crest, Left iliac crest:
Dx: MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME (bone marrow failure disorder),
REFRACTORY CYTOPENIA (low blood cell counts) WITH MULTI-LINEAGE DYSPLASIA
(abnormal shape).
Clinical Information
75 yo M with relapsed MM and prolonged pancytopenia (deficiency
of all three cellular components of the blood red cells, white cells, and
platelets) after Daratumumab/Pomalidamide. (If only two parameters
from the full blood count are low, the term bicytopenia can be used.)
Flow Cytometry Summary
Mature granulocytes show decreased right angle light
scatter. Monocytes show aberrant HLA DR. Blasts are not increased. The
majority of lymphocytes were positive for surface antigens present on normal
T cells. The B cells present were polyclonal. The results do not demonstrate
an abnormal population of lymphocytes in the sample. (translation --- while
blood cells lymphocytes are OK.) No plasma cells seen.
-- A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell
that is part of the immune system. There are two main types of lymphocytes:
B cells and T cells. The B cells produce antibodies that are used to attack
invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins. The T cells destroy the body's
own cells that have themselves been taken over by viruses or become cancerous.
Core Biopsy
The biopsy is 40% cellular. Megakaryocytes are
decreased, hypolobated, and difficult to identify. Myeloid and erythroid
maturation are complete without left-shifted. No lymphoid infiltrate seen.
Decalcification was performed on core biopsy.
** -- A megakaryocyte (mega- + karyo- + -cyte,
"large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobulated nucleus
responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which
are necessary for normal blood clotting. Megakaryocytes normally account
for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells. (Each of these cells only
produces a few thousand platets and it is then replaced.)
-- The term
“left shift” means that a particular population of cells is “shifted” towards
more immature precursors (meaning that there are more immature precursors
present than you would normally see). Take the neutrophil series, for example.
In normal blood, the neutrophils are virtually all mature (segmented).
In a left shift, you see mature neutrophils but also immature neutrophils
(bands, metamyelocytes, myelocytes, etc.). Check out the photo of a left
shift, above: most of the cells are immature.
Aspirate Smear
The aspirate shows myeloid and erythroid maturation in
a ratio of approximately 2:1. Myeloid elements mature to completion
with but show a subpopulation which is hypogranular. Atypical monocyte
forms are mildly increased. Blasts are not increased. Erythroid
elements mature to completion with readily apparent nuclear membrane irregularities.
Iron stain shows storage iron with scattered ing sideroblasts comprising
about 20% of erythroid precursors. Megakaryocytes are decreased and
those present are small, hypolobated, and hypogranulated. Plasma
cells are not increased.
Peripheral Blood Smear
The granulocytes are variably granulated with some cells
being normal and others being hypogranular. There is an overal sense
of nuclear hyperlobulation however scattered cells pseudo-Pelger Huët
anomaly. Monocytes are unremarkable. Lymphocytes show a spectrum
of reactive appearing morphologies. Blasts are not seen. The
red cells are normochromic and normocytic with moderate anisopoikilocytosis.
Platelets are well-granulated and normal sized but reduced in number.




 .
. 
 .
. .
. 









 .
.
 .
.
 .
.  .
. 
 .
. 

 .
. .
. 

 .
. .
. 
 .
.  .
.



.jpg) .
..jpg)
 .
.





 .
.

 .
. 




 .
.
 .
.
 .
. 
 .
. 














 .
. 














 .
. 
 .
. 











 .
. 
 .
. 






 .
. 
 .
. .
.













 .
. .
. 
 .
. 

.jpg)








 .
.
 .
. 
 .
. 




 .
.
 .
. 
 .
. 

 .
.

 .
. 
 .
. 






 .
.

 .
.






